
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ghislaine Mayer | + 1292 word(s) | 1292 | 2021-09-13 04:46:25 | | | |
| 2 | Nora Tang | + 170 word(s) | 1462 | 2021-09-15 08:25:46 | | |
Video Upload Options
The apicoplast is surrounded by four membranes and is thought to be the result of secondary endosymbiosis. It is the site of quite a few metabolic pathways, such as heme, isoprenoids, and fatty acids syntheses. It is thought that the outermost membrane of the apicoplast is part of the endomembrane system.
1. Introduction
Plasmodium falciparum is a protozoan parasite that is responsible for millions of infections resulting in malaria, a devastating disease currently prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa. Malaria continues to be endemic in 87 countries with approximately 229 million cases and 2–3 million deaths [1]. Plasmodium falciparum is an obligate intracellular microbe that infects human erythrocytes. Obligate intracellular microbes use diverse mechanisms to hijack their host cellular processes. Following uptake, most intracellular microbes take over the host organelles to create distinctive and unique microenvironments. Unlike other intracellular microbes, P. falciparum has the unique challenge of residing and developing within a cell devoid of organelles.
Inside the erythrocyte, while the parasite resides within the parasitophorous vacuole, it orchestrates the drastic modification of the erythrocyte. After erythrocyte invasion, the composition of the erythrocyte membrane as well as its permeability and rigidity are radically altered [2]. All the symptoms associated with malaria are due to the invasion, intracellular development, and egress of P. falciparum merozoites into the host’s erythrocytes [3]. Once inside the erythrocyte, the parasite undergoes asexual reproduction producing 8–26 daughter merozoites that are released to invade fresh erythrocytes [4]. The life cycle of the parasite requires the trafficking of a large number of proteins to the erythrocyte, which are necessary for the complete takeover of the erythrocyte. To enable interactions with the erythrocyte, P. falciparum transports virulence proteins using de novo specialized secretion systems. The trafficking of virulence factors and their insertions into the erythrocyte membrane at the knob structures are key events in the development of the pathologies associated with severe malaria, both cerebral and placental [5]. Therefore, the pathogenesis P. falciparum is dependent on the mechanism of protein sorting and trafficking during the intraerythrocytic stage.
Protein sorting is the process by which proteins are moved to their proper destinations inside and outside the cell [6]. In eukaryotes, proteins are directed to the lumen of specific organelles, diverse intracellular membranes, the plasma membrane, or outside of the cell by the process of secretion [6]. The protein targeting process is controlled by specific sequences within the protein itself [7][8]. In order to successfully replicate inside the erythrocyte, P. falciparum needs to correctly sort and traffic its newly-made proteins to all of its organelles. In addition to trafficking proteins within its cell, the parasite ships proteins beyond its plasma membrane, into both the parasitophorous vacuole and into the host erythrocyte cytoplasm and plasma membrane [9][10]. Moreover, the parasite possesses a food vacuole, an acidic organelle where the host cell hemoglobin is digested to amino acids. The food vacuole is also the site of action of the antimalarials chloroquine and quinoline [11]. In P. faclciparum , additional organelles named mononemes and exonemes have also been described [12]. The latter seems to play a role in the parasite egress [12].
2. Protein Sorting to ER and Golgi
Akin to all eukaryotes, P. falciparum proteins that are trafficked to the various organelles contain a canonical signal peptide, a short sequence of hydrophobic amino acids located at the amino terminus. The signal peptide indicates the co-translational transport of these proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). In P. falciparum , the ER is located near the nucleus and appears as ‘‘horn-like’’ projections [8]. Except for the apicoplast-bound proteins, the parasite organellar proteins are transported to the Golgi apparatus [13]. In most eukaryotes, the Golgi apparatus is organized into biochemically well-defined compartments called cisternae termed the cis -, medial-, and trans -Golgi. In mammalian cells, these cisternae are stacked or in close apposition to each other. However, in the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae , the Golgi cisternae are unstacked [14]. Plasmodium falciparum seems to have a simplified, unstacked Golgi apparatus. N-linked glycosylation, a process that is finalized in the cis -Golgi, does not occur in P. falciparum [15]. Several ultrastructural studies involving serial sectioning and 3-D reconstruction analysis of P. falciparum -infected erythrocytes have not determined the presence of stacked Golgi cisternae in the parasite [16][17][18]. In addition, indirect immunofluorescent studies using antibodies against cis - and trans -Golgi resident proteins of P. falciparum also support the absence of stacked cisternae in P. falciparum [19][20]. Therefore, in P. falciparum , the protein sorting apparatus from the ER to Golgi appears to be reduced.
3. Protein Sorting to the Apicoplast
In the mid-1990s, a unique organelle characterized by the presence of a vestigial, non-photosynthetic plastid was discovered in P. falciparum [21][22][23]. The apicoplast in P. falciparum seems to be positioned on a small projection of the ER, but it is not clear whether it is part of the ER [13]. However, current evidence suggests that the apicoplast is separate from the cis -Golgi [13]. In addition, the apicoplast appears to be located upstream of the cis- Golgi ( Figure 1 ). The apicoplast is surrounded by four membranes and is thought to be the result of secondary endosymbiosis [24]. It is the site of quite a few metabolic pathways, such as heme, isoprenoids, and fatty acids syntheses [25]. It is thought that the outermost membrane of the apicoplast is part of the endomembrane system [24]. Most of the resident apicoplast proteins are encoded by genes located in the parasite nucleus [26][27]. These proteins are translocated across the four membranes by means of a two-part N-terminal extension that has been shown to be both necessary and sufficient for sorting to the apicoplast [24]. The first segment of the N-terminal exten sion sequence is similar to a classical signal peptide. It is responsible for the translocation into the secretory pathway. On the other hand, the second segment shares homology to chloroplast transit peptides and is needed for entering the apicoplast [28].
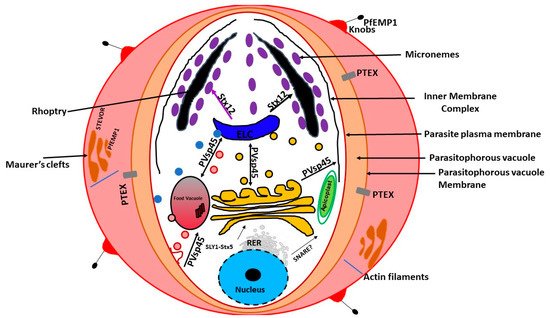
Previous experiments using green fluorescent reporter in which the apicoplast signal peptide protein was replaced by the signal peptide of a micronemal and a knob-associated protein indicated that targeting proteins to the apicoplast begins at the general secretory pathway of P. falciparum [13]. In P. falciparum, the signal peptide in apicoplast-resident proteins, was shown to facilitate translocation across the rough ER (RER) membrane through the Sec machinery releasing the protein into the ER lumen [29][30]. This is followed by the removal of the signal peptide by signal peptidase [31][32]. Once in the ER, the transit peptide directs the transport into the apicoplast [28]. This mechanism of trafficking seems to be shared by other secondary plastids [31][32][33][34][35]. Furthermore, it has been validated in Toxoplasma gondii [36][37][38][39]. On the other hand, apicoplast transmembrane proteins that are encoded by the nucleus are trafficked via the Golgi apparatus [40].
4. Vesicular Trafficking in P. falciparum
In eukaryotic cells, vesicle fusion depends on the attachment of the SNARE receptors to specific organelles [41][42][43]. Although most SNARE proteins have a C-terminal transmembrane domain that mediates their attachment to their target membranes, some lack these transmembrane domains. The latter rely on lipid modification in order to be membrane-anchored. Protein prenylation is the attachment of either a farnesyl (15-carbon) or a geranylgeranyl (20-carbon) isoprenoid group to cysteine residue of CAAX motif-containing proteins [44][45][46][47]. Protein prenylation is carried out by three groups of protein prenyltransferases: farnesyltransferase (FT), geranylgeranyl- transferase 1 (GGT1), and Rab geranylgeranyltransferase (RabGGT) [48]. The P. falciparum prenylated proteome has been characterized [49]. Interestingly, several prenylation candidates were uncovered [49]. Specifically, The SNARE protein PfYkt6p was characterized in P. falciparum and shown to be both prenylated and surprisingly geranylgeranylated [50]. Importantly, the data from this study indicate that the transport of Ykt6 in P. falciparum depends on prenylation. It is also the first evidence of protein geranylgeranyltransferase activity on SNARE proteins [50]. Taken together, prenylation might play an important role in P. falciparum vesicular trafficking. More studies are needed to uncover the role of prenylation in the endocytic and secretory pathway of P. falciparum .
References
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report: 20 Years of Global Progress and Challenges; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Miller, L.H.; Ackerman, H.C.; Su, X.; Wellems, T.E. Malaria biology and disease pathogenesis: Insights for new treatments. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 156–167.
- Yeoh, S.; O’Donnell, R.A.; Koussis, K.; Dluzewski, A.R.; Ansell, K.H.; Osborne, S.A.; Hackett, F.; Withers-Martinez, C.; Mitchell, G.H.; Bannister, L.H.; et al. Subcellular discharge of a serine protease mediates release of invasive malaria parasites from host erythrocytes. Cell 2007, 131, 1072–1083.
- Reilly, H.B.; Wang, H.; Steuter, J.A.; Marx, A.M.; Ferdig, M.T. Quantitative dissection of clone-specific growth rates in cultured malaria parasites. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 1599–1607.
- Wahlgren, M.; Goel, S.; Akhouri, R.R. Variant surface antigens of Plasmodium falciparum and their roles in severe malaria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 479–491.
- Pfeffer, S.R.; Rothman, J.E. Biosynthetic protein transport and sorting by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1987, 56, 829–852.
- Blobel, G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 1496–1500.
- von Heijne, G. Signal sequences: The limits of variation. J. Mol. Biol. 1985, 184, 99–105.
- Gubbels, M.J.; Duraisingh, M.T. Evolution of apicomplexan secretory organelles. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 1071–1081.
- Maier, A.G.; Cooke, B.M.; Cowman, A.F.; Tilley, L. Malaria parasite proteins that remodel the host erythrocyte. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 341–354.
- Banerjee, R.; Goldberg, D.E. The Plasmodium food vacuole. In Antimalarial Chemotherapy; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 43–63.
- Singh, S.; Plassmeyer, M.; Gaur, D.; Miller, L.H. Mononeme: A new secretory organelle in Plasmodium falciparum merozoites identified by localization of rhomboid-1 protease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20043–20048.
- Tonkin, C.J.; Struck, N.S.; Mullin, K.A.; Stimmler, L.M.; McFadden, G.I. Evidence for Golgi-independent transport from the early secretory pathway to the plastid in malaria parasites. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 61, 614–630.
- Glick, B.S.; Nakano, A. Membrane traffic within the Golgi apparatus. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 25, 113–132.
- Lee, M.C.; Moura, P.A.; Miller, E.A.; Fidock, D.A. Plasmodium falciparum Sec24 marks transitional ER that exports a model cargo via a diacidic motif. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 68, 1535–1546.
- Bannister, L.H.; Hopkins, J.M.; Fowler, R.E.; Krishna, S.; Mitchell, G.H. Ultrastructure of rhoptry development in Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic schizonts. Parasitol. Today 2000, 121, 273–287.
- Bannister, L.H.; Hopkins, J.M.; Margos, G.; Dluzewski, A.R.; Mitchell, G.H. Three-dimensional ultrastructure of the ring stage of Plasmodium falciparum: Evidence for export pathways. Microsc. Microanal. 2004, 10, 551–562.
- Langreth, S.G.; Jensen, J.B.; Reese, R.T.; Trager, W. Fine structure of human malaria in vitro. J. Protozool. 1978, 25, 443–452.
- Adisa, A.; Frankland, S.; Rug, M.; Jackson, K.; Maier, A.G.; Walsh, P.; Lithgow, T.; Klonis, N.; Gilson, P.R.; Cowman, A.F.; et al. Re-assessing the locations of components of the classical vesicle-mediated trafficking machinery in transfected Plasmodium falciparum. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 1127–1141.
- Van Wye, J.; Ghori, N.; Webster, P.; Mitschler, R.R.; Elmendorf, H.G.; Haldar, K. Identification and localization of rab6, separation of rab6 from ERD2 and implications for an ‘unstacked’ Golgi, in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1996, 83, 107–120.
- McFadden, G.I.; Reith, M.; Munholland, J.; Lang Unnasch, N. Plastid in human parasites. Nature 1996, 381, 482.
- Wilson, R.J.M.; Denny, P.W.; Preiser, P.R.; Rangachari, K.; Roberts, K.; Roy, A.; Whyte, A.; Strath, M.; Moore, D.J.; Moore, P.W.; et al. Complete gene map of the plastid-like DNA of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 261, 155–172.
- Köhler, S.; Delwiche, C.F.; Denny, P.W.; Tilney, L.G.; Webster, P.; Wilson, R.J.M.; Palmer, J.D.; Roos, D.S. A plastid of probable green algal origin in apicomplexan parasites. Science 1997, 275, 1485–1489.
- van Dooren, G.G.; Schwartzbach, S.D.; Osafune, T.; McFadden, G.I. Translocation of proteins across the multiple membranes of complex plastids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1541, 34–53.
- Seeber, F.; Soldati-Favre, D. Metabolic pathways in the apicoplast of Apicomplexa. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 281, 161–228.
- Deane, J.; Fraunholz, M.; Su, V.; Maier, U.-G.; Martin, W.; Durnford, D.; McFadden, G. Evidence for nucleomorph to host nucleus gene transfer: Light harvesting complex proteins from cryptomonads and chlorarachniophytes. Protist 2000, 151, 239–252.
- McFadden, G.I.; van Dooren, G.G. Evolution: Red algal genome affirms a common origin of all plastids. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, R514–R516.
- Waller, R.F.; Reed, M.B.; Cowman, A.F.; McFadden, G.I. Protein trafficking to the plastid of Plasmodium falciparum is via the secretory pathway. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 1794–1802.
- van Dooren, G.G.; Waller, R.F.; Joiner, K.A.; Roos, D.S.; McFadden, G.I. Traffic jams: Protein transport in Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitol. Today 2000, 16, 421–427.
- van Dooren, G.G.; Su, V.; D’Ombrain, M.C.; McFadden, G.I. Processing of an apicoplast leader sequence in Plasmodium falciparum and the identification of a putative leader cleavage enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 23612–23619.
- Sulli, C.; Fang, Z.; Muchhal, U.; Schwartzbach, S.D. Topology of Euglena chloroplast protein precursors within endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi to chloroplast trans- port vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 457–463.
- Wastl, J.; Maier, U.G. Transport of proteins into cryptomonads complex plastids. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23194–23198.
- Apt, K.E.; Zaslavkaia, L.; Lippmeier, J.C.; Lang, M.; Kilian, O.; Wetherbee, R.; Grossman, A.R.; Kroth, P. In vivo characterization of diatom multipartite plastid targeting signals. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 4061–4069.
- Nassoury, N.; Cappadocia, M.; Morse, D. Plastid ultrastructure defines the protein import pathway in dinoflagellates. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 2867–2874.
- Patron, N.J.; Waller, R.F.; Archibald, J.M.; Keeling, P.J. Complex protein targeting to dinoflagellate plastids. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 1015–1024.
- DeRocher, A.; Hagen, C.B.; Froehlich, J.E.; Feagin, J.E.; Parsons, M. Analysis of targeting sequences demonstrates that trafficking to the Toxoplasma gondii plastid branches of the secretory system. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 3969–3977.
- DeRocher, A.; Gilbert, B.; Feagin, J.E.; Parsons, M. Dissection of brefeldin A-sensitive and -insensitive steps in apicoplast protein targeting. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 565–574.
- Yung, S.; Unnasch, T.R.; Lang-Unnasch, N. Analysis of apicoplast targeting and transit peptide processing in Toxoplasma gondii by deletional and insertional mutagenesis. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2001, 118, 11–21.
- Harb, O.S.; Chatterjee, B.; Fraunholz, M.J.; Crawford, M.J.; Nishi, M.; Roos, D.S. Multiple functionally redundant signals mediate targeting to the apicoplast in the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Eukaryot. Cell 2004, 3, 663–674.
- Chaudhari, R.; Dey, V.; Narayan, A.; Sharma, S.; Patankar, S. Membrane and luminal proteins reach the apicoplast by different trafficking pathways in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3128.
- Pelham, H.R. SNAREs and the specificity of membrane fusion. Trends Cell Biol. 2001, 11, 99–101.
- Hong, W. SNAREs and traffic. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1744, 120–144.
- Jahn, R.; Scheller, R.H. SNAREs—Engines for membrane fusion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 7, 631–643.
- Resh, M.D. Trafficking and signaling by fatty-acylated and prenylated proteins. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 584–590.
- Michaelson, D.; Ali, W.; Chiu, V.K.; Bergo, M.; Silletti, J.; Wright, L.; Young, S.G.; Philips, M. Postprenylation CAAX processing is required for proper localization of Ras but not Rho GTPases. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 1606–1616.
- Yalovsky, S.; Rodr Guez-Concepcion, M.; Gruissem, W. Lipid modifications of proteins—Slipping in and out of membranes. Trends Plant Sci. 1999, 4, 439–445.
- Perez-Sala, D. Protein isoprenylation in biology and disease: General overview and perspectives from studies with genetically engineered animals. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 4456–4472.
- Wright, M.H.; Clough, B.; Rackham, M.D.; Rangachari, K.; Brannigan, J.A.; Grainger, M.; Moss, D.K.; Bottrill, A.R.; Heal, W.P.; Broncel, M.; et al. Validation of N-myristoyltransferase as an antimalarial drug target using an integrated chemical biology approach. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 112–121.
- Gisselberg, J.E.; Zhang, L.; Elias, J.E.; Yeh, E. The prenylated proteome of Plasmodium falciparum reveals pathogen-specific prenylation activity and drug mechanism of action. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2017, 16, S54–S64.
- Ayong, L.; DaSilva, T.T.; Mauser, J.; Allen, C.M.; Chakrabarti, D. Evidence for prenylation dependent-targeting of a Ykt6 SNARE in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2011, 175, 162–168.




