
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dalia Barsyte-Lovejoy | + 3355 word(s) | 3355 | 2021-08-02 05:40:10 | | | |
| 2 | Bruce Ren | -21 word(s) | 3334 | 2021-08-10 03:46:11 | | |
Video Upload Options
PRMT7 is a member of the protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) family, which methylates a diverse set of substrates. Arginine methylation as a posttranslational modification regulates protein–protein and protein–nucleic acid interactions, and as such, has been implicated in various biological functions. PRMT7 is a unique, evolutionarily conserved PRMT family member that catalyzes the mono-methylation of arginine. The structural features, functional aspects, and compounds that inhibit PRMT7 are discussed here. Several studies have identified physiological substrates of PRMT7 and investigated the substrate methylation outcomes which link PRMT7 activity to the stress response and RNA biology. PRMT7-driven substrate methylation further leads to the biological outcomes of gene expression regulation, cell stemness, stress response, and cancer-associated phenotypes such as cell migration. Furthermore, organismal level phenotypes of PRMT7 deficiency have uncovered roles in muscle cell physiology, B cell biology, immunity, and brain function.
1. Introduction
2. Structural Features of PRMT7
2.1. Domain Architecture and Evolution
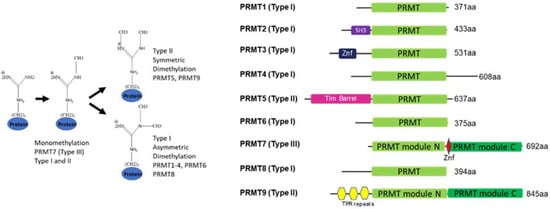

2.2. Structure
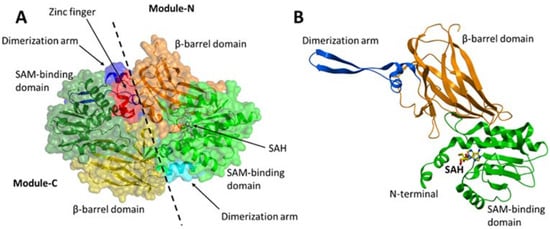
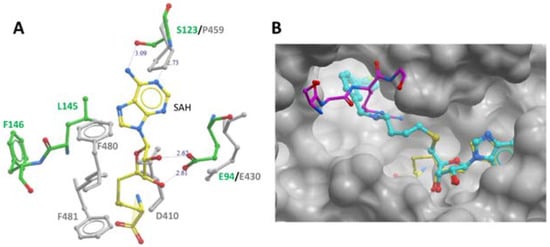
3. Enzyme Function of PRMT7
3.1. Regulation, Enzymatic Properties, and Crosstalk with Other PRMTs
3.2. PRMT7 Substrates
| Substrate | R Methylation Sites | Function, Disease Relevance, Reference |
|---|---|---|
| DVL3 | 271, 342, 614 | DVL3 localization, wnt signaling, cancer [30] |
| EIF2S1 (EIF2 alpha) | 55 | Translation arrest, stress granule regulation, [31] |
| G3BP2 | 432, 438, 452, 468 | Wnt signaling, cancer, [32] |
| GLI2 | 225/227 | Cell senescence, [33] |
| Histone H4, H2A | H4R3, H2AR3 | Gene expression, [23][24][25][26][27] |
| HNRNPA1 | 194, 206, 218, 225 | Splicing, [28] |
| HSP70 | 469 | Stress response, [13] |
| NALCN | 1653 | Neuronal excitability, [34] |
| MAVS | 52 | Viral infection, [35] |
| MRPS23 | 21 | Oxidative phosphorylation, cell invasion, cancer [36] |
| P38MAPK | 70 | Myoblast differentiation, [37] |
| PRMT7 | 531 | Cell migration, cancer [16] |
3.3. Inhibitor Compounds for PRMT7
4. Cellular Roles of PRMT7
4.1. The Role of PRMT7 in Gene Expression and Genome Maintenance
4.2. Regulation of Pluripotency, Cell Differentiation, and Senescence
4.3. PRMT7 and Stress Response
References
- Guccione, E.; Richard, S. The regulation, functions and clinical relevance of arginine methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 642–657.
- Lorton, B.M.; Shechter, D. Cellular consequences of arginine methylation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2933–2956.
- Bedford, M.T.; Clarke, S.G. Protein arginine methylation in mammals: Who, what, and why. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 1–13.
- Bedford, M.T.; Richard, S. Arginine methylation an emerging regulator of protein function. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 263–272.
- Hwang, J.W.; Cho, Y.; Bae, G.U.; Kim, S.N.; Kim, Y.K. Protein arginine methyltransferases: Promising targets for cancer therapy. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 788–808.
- Debler, E.W.; Jain, K.; Warmack, R.A.; Feng, Y.; Clarke, S.G.; Blobel, G.; Stavropoulos, P. A glutamate/aspartate switch controls product specificity in a protein arginine methyltransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2068–2073.
- Zurita-Lopez, C.I.; Sandberg, T.; Kelly, R.; Clarke, S.G. Human protein arginine methyltransferase 7 (PRMT7) is a type III enzyme forming omega-NG-monomethylated arginine residues. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 7859–7870.
- Feng, Y.; Hadjikyriacou, A.; Clarke, S.G. Substrate specificity of human protein arginine methyltransferase 7 (PRMT7): The importance of acidic residues in the double E loop. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32604–32616.
- Fisk, J.C.; Sayegh, J.; Zurita-Lopez, C.; Menon, S.; Presnyak, V.; Clarke, S.G.; Read, L.K. A type III protein arginine methyltransferase from the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma brucei. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 11590–11600.
- Tewary, S.K.; Zheng, Y.G.; Ho, M.C. Protein arginine methyltransferases: Insights into the enzyme structure and mechanism at the atomic level. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2917–2932.
- Cura, V.; Troffer-Charlier, N.; Wurtz, J.M.; Bonnefond, L.; Cavarelli, J. Structural insight into arginine methylation by the mouse protein arginine methyltransferase 7: A zinc finger freezes the mimic of the dimeric state into a single active site. Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 2014, 70, 2401–2412.
- Hasegawa, M.; Toma-Fukai, S.; Kim, J.D.; Fukamizu, A.; Shimizu, T. Protein arginine methyltransferase 7 has a novel homodimer-like structure formed by tandem repeats. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1942–1948.
- Szewczyk, M.M.; Ishikawa, Y.; Organ, S.; Sakai, N.; Li, F.; Halabelian, L.; Ackloo, S.; Couzens, A.L.; Eram, M.; Dilworth, D.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of PRMT7 links arginine monomethylation to the cellular stress response. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2396.
- Boriack-Sjodin, P.A.; Jin, L.; Jacques, S.L.; Drew, A.; Sneeringer, C.; Scott, M.P.; Moyer, M.P.; Ribich, S.; Moradei, O.; Copeland, R.A. Structural Insights into Ternary Complex Formation of Human CARM1 with Various Substrates. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 763–771.
- Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Caceres, T.B.; Liu, L.; Peng, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zuo, X.; et al. Structural determinants for the strict monomethylation activity by trypanosoma brucei protein arginine methyltransferase 7. Structure 2014, 22, 756–768.
- Geng, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, C.; Yan, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, G.; et al. Automethylation of protein arginine methyltransferase 7 and its impact on breast cancer progression. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 2287–2300.
- Li, A.S.M.; Li, F.; Eram, M.S.; Bolotokova, A.; Dela Sena, C.C.; Vedadi, M. Chemical probes for protein arginine methyltransferases. Methods 2020, 175, 30–43.
- Tarighat, S.S.; Santhanam, R.; Frankhouser, D.; Radomska, H.S.; Lai, H.; Anghelina, M.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Alinari, L.; Walker, A.; et al. The dual epigenetic role of PRMT5 in acute myeloid leukemia: Gene activation and repression via histone arginine methylation. Leukemia 2016, 30, 789–799.
- Jain, K.; Jin, C.Y.; Clarke, S.G. Epigenetic control via allosteric regulation of mammalian protein arginine methyltransferases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10101–10106.
- Jain, K.; Clarke, S.G. PRMT7 as a unique member of the protein arginine methyltransferase family: A review. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 665, 36–45.
- Gonsalvez, G.B.; Tian, L.; Ospina, J.K.; Boisvert, F.M.; Lamond, A.I.; Matera, A.G. Two distinct arginine methyltransferases are required for biogenesis of Sm-class ribonucleoproteins. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 733–740.
- Lee, J.H.; Cook, J.R.; Yang, Z.H.; Mirochnitchenko, O.; Gunderson, S.I.; Felix, A.M.; Herth, N.; Hoffmann, R.; Pestka, S. PRMT7, a new protein arginine methyltransferase that synthesizes symmetric dimethylarginine. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 3656–3664.
- Blanc, R.S.; Vogel, G.; Chen, T.; Crist, C.; Richard, S. PRMT7 Preserves Satellite Cell Regenerative Capacity. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 1528–1539.
- Dhar, S.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kan, P.Y.; Voigt, P.; Ma, L.; Shi, X.; Reinberg, D.; Lee, M.G. Trans-tail regulation of MLL4-catalyzed H3K4 methylation by H4R3 symmetric dimethylation is mediated by a tandem PHD of MLL4. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 2749–2762.
- Karkhanis, V.; Wang, L.; Tae, S.; Hu, Y.J.; Imbalzano, A.N.; Sif, S. Protein arginine methyltransferase 7 regulates cellular response to DNA damage by methylating promoter histones H2A and H4 of the polymerase delta catalytic subunit gene, POLD1. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29801–29814.
- Ying, Z.; Mei, M.; Zhang, P.; Liu, C.; He, H.; Gao, F.; Bao, S. Histone Arginine Methylation by PRMT7 Controls Germinal Center Formation via Regulating Bcl6 Transcription. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 1538–1547.
- Migliori, V.; Muller, J.; Phalke, S.; Low, D.; Bezzi, M.; Mok, W.C.; Sahu, S.K.; Gunaratne, J.; Capasso, P.; Bassi, C.; et al. Symmetric dimethylation of H3R2 is a newly identified histone mark that supports euchromatin maintenance. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 136–144.
- Li, W.J.; He, Y.H.; Yang, J.J.; Hu, G.S.; Lin, Y.A.; Ran, T.; Peng, B.L.; Xie, B.L.; Huang, M.F.; Gao, X.; et al. Profiling PRMT methylome reveals roles of hnRNPA1 arginine methylation in RNA splicing and cell growth. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1946.
- Zhang, F.; Kerbl-Knapp, J.; Rodriguez Colman, M.; Macher, T.; Vujić, N.; Fasching, S.; Jany-Luig, E.; Korbelius, M.; Kuentzel, K.; Mack, M.; et al. Global analysis of protein arginine methylation. Cell Rep. Methods 2021, 1, 100016.
- Bikkavilli, R.K.; Avasarala, S.; Vanscoyk, M.; Sechler, M.; Kelley, N.; Malbon, C.C.; Winn, R.A. Dishevelled3 is a novel arginine methyl transferase substrate. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 805.
- Haghandish, N.; Baldwin, R.M.; Morettin, A.; Dawit, H.T.; Adhikary, H.; Masson, J.Y.; Mazroui, R.; Trinkle-Mulcahy, L.; Cote, J. PRMT7 methylates eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2alpha and regulates its role in stress granule formation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2019, 30, 778–793.
- Bikkavilli, R.K.; Malbon, C.C. Wnt3a-stimulated LRP6 phosphorylation is dependent upon arginine methylation of G3BP2. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 2446–2456.
- Vuong, T.A.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, B.G.; Leem, Y.E.; Cho, H.; Kang, J.S. PRMT7 methylates and suppresses GLI2 binding to SUFU thereby promoting its activation. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 15–28.
- Lee, S.Y.; Vuong, T.A.; Wen, X.; Jeong, H.J.; So, H.K.; Kwon, I.; Kang, J.S.; Cho, H. Methylation determines the extracellular calcium sensitivity of the leak channel NALCN in hippocampal dentate granule cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–14.
- Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Cai, X.; Zha, H.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, X.; Rong, F.; Tang, J.; Zhu, C.; Liu, X.; et al. Arginine monomethylation by PRMT7 controls MAVS-mediated antiviral innate immunity. Mol. Cell 2021. Online ahead of print.
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Ding, H.; Liu, X.; Cao, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Lin, C.; Zhang, N.; Wang, G.; et al. Arginine and lysine methylation of MRPS23 promotes breast cancer metastasis through regulating OXPHOS. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3548–3563.
- Jeong, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Vuong, T.A.; Choi, K.S.; Choi, D.; Koo, S.H.; Cho, S.C.; Cho, H.; Kang, J.S. Prmt7 Deficiency Causes Reduced Skeletal Muscle Oxidative Metabolism and Age-Related Obesity. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1868–1882.
- Ferreira, T.R.; Dowle, A.A.; Parry, E.; Alves-Ferreira, E.V.C.; Hogg, K.; Kolokousi, F.; Larson, T.R.; Plevin, M.J.; Cruz, A.K.; Walrad, P.B. PRMT7 regulates RNA-binding capacity and protein stability in Leishmania parasites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 5511–5526.
- Feng, Y.; Maity, R.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Hadjikyriacou, A.; Li, Z.; Zurita-Lopez, C.; Al-Hadid, Q.; Clark, A.T.; Bedford, M.T.; Masson, J.Y.; et al. Mammalian protein arginine methyltransferase 7 (PRMT7) specifically targets RXR sites in lysine- and arginine-rich regions. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 37010–37025.
- Wu, Q.; Schapira, M.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; Barsyte-Lovejoy, D. Protein arginine methylation: From enigmatic functions to therapeutic targeting. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 7, 509–530.
- Smil, D.; Eram, M.S.; Li, F.; Kennedy, S.; Szewczyk, M.M.; Brown, P.J.; Barsyte-Lovejoy, D.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; Vedadi, M.; Schapira, M. Discovery of a Dual PRMT5-PRMT7 Inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 408–412.
- Jelinic, P.; Stehle, J.C.; Shaw, P. The testis-specific factor CTCFL cooperates with the protein methyltransferase PRMT7 in H19 imprinting control region methylation. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e355.
- Buhr, N.; Carapito, C.; Schaeffer, C.; Kieffer, E.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Viville, S. Nuclear proteome analysis of undifferentiated mouse embryonic stem and germ cells. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 2381–2390.
- Wang, B.; Pfeiffer, M.J.; Drexler, H.C.; Fuellen, G.; Boiani, M. Proteomic Analysis of Mouse Oocytes Identifies PRMT7 as a Reprogramming Factor that Replaces SOX2 in the Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 2407–2421.
- Lee, S.H.; Chen, T.Y.; Dhar, S.S.; Gu, B.; Chen, K.; Kim, Y.Z.; Li, W.; Lee, M.G. A feedback loop comprising PRMT7 and miR-24-2 interplays with Oct4, Nanog, Klf4 and c-Myc to regulate stemness. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 10603–10618.
- Chen, T.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Dhar, S.S.; Lee, M.G. Protein arginine methyltransferase 7-mediated microRNA-221 repression maintains Oct4, Nanog, and Sox2 levels in mouse embryonic stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 3925–3936.
- Morita, K.; Hatanaka, Y.; Ihashi, S.; Asano, M.; Miyamoto, K.; Matsumoto, K. Symmetrically dimethylated histone H3R2 promotes global transcription during minor zygotic genome activation in mouse pronuclei. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10146.
- Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Li, K.; Li, L.; Yin, P.; Tong, G. The role of protein arginine methyltransferase 7 in human developmentally arrested embryos cultured in vitro. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2021, 53, 925–932.
- Abe, Y.; Tanaka, N. Fine-Tuning of GLI Activity through Arginine Methylation: Its Mechanisms and Function. Cells 2020, 9, 1973.
- Leem, Y.E.; Bae, J.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Kang, J.S. PRMT7 deficiency enhances adipogenesis through modulation of C/EBP-beta. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 517, 484–490.
- Gros, L.; Delaporte, C.; Frey, S.; Decesse, J.; de Saint-Vincent, B.R.; Cavarec, L.; Dubart, A.; Gudkov, A.V.; Jacquemin-Sablon, A. Identification of new drug sensitivity genes using genetic suppressor elements: Protein arginine N-methyltransferase mediates cell sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 164–171.
- Gros, L.; Renodon-Corniere, A.; de Saint Vincent, B.R.; Feder, M.; Bujnicki, J.M.; Jacquemin-Sablon, A. Characterization of prmt7alpha and beta isozymes from Chinese hamster cells sensitive and resistant to topoisomerase II inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 1646–1656.
- Bleibel, W.K.; Duan, S.; Huang, R.S.; Kistner, E.O.; Shukla, S.J.; Wu, X.; Badner, J.A.; Dolan, M.E. Identification of genomic regions contributing to etoposide-induced cytotoxicity. Hum. Genet. 2009, 125, 173–180.
- Verbiest, V.; Montaudon, D.; Tautu, M.T.; Moukarzel, J.; Portail, J.P.; Markovits, J.; Robert, J.; Ichas, F.; Pourquier, P. Protein arginine (N)-methyl transferase 7 (PRMT7) as a potential target for the sensitization of tumor cells to camptothecins. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1483–1489.
- Wek, R.C.; Cavener, D.R. Translational control and the unfolded protein response. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 2357–2371.
- Jung, G.A.; Shin, B.S.; Jang, Y.S.; Sohn, J.B.; Woo, S.R.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, G.; Lee, K.M.; Min, B.H.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Methylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 induced by basic fibroblast growth factor via mitogen-activated protein kinase. Exp. Mol. Med. 2011, 43, 550–560.
- Gao, W.W.; Xiao, R.Q.; Peng, B.L.; Xu, H.T.; Shen, H.F.; Huang, M.F.; Shi, T.T.; Yi, J.; Zhang, W.J.; Wu, X.N.; et al. Arginine methylation of HSP70 regulates retinoid acid-mediated RARbeta2 gene activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3327–E3336.
- Mayer, M.P.; Bukau, B. Hsp70 chaperones: Cellular functions and molecular mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 670–684.
- Gerstberger, S.; Hafner, M.; Tuschl, T. A census of human RNA-binding proteins. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 829–845.
- Hadjikyriacou, A.; Clarke, S.G. Caenorhabditis elegans PRMT-7 and PRMT-9 Are Evolutionarily Conserved Protein Arginine Methyltransferases with Distinct Substrate Specificities. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 2612–2626.




