| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yun Jiang | + 850 word(s) | 850 | 2019-09-29 07:33:59 | | | |
| 2 | Yun Jiang | Meta information modification | 850 | 2021-07-21 01:09:50 | | | | |
| 3 | Yun Jiang | -1 word(s) | 849 | 2021-07-21 01:27:10 | | | | |
| 4 | Yun Jiang | -1 word(s) | 849 | 2021-07-21 01:28:46 | | | | |
| 5 | Yun Jiang | + 14 word(s) | 863 | 2021-07-23 10:27:00 | | | | |
| 6 | Yun Jiang | Meta information modification | 863 | 2021-07-26 18:45:19 | | | | |
| 7 | Yun Jiang | Meta information modification | 863 | 2021-07-26 18:48:13 | | | | |
| 8 | Yun Jiang | Meta information modification | 863 | 2021-07-26 18:52:26 | | | | |
| 9 | Yun Jiang | Meta information modification | 863 | 2021-07-26 20:26:24 | | | | |
| 10 | Yun Jiang | Meta information modification | 863 | 2021-07-27 01:33:54 | | | | |
| 11 | Yun Jiang | Meta information modification | 863 | 2021-07-27 16:04:09 | | | | |
| 12 | Yun Jiang | + 49 word(s) | 912 | 2021-08-10 19:42:04 | | | | |
| 13 | Yun Jiang | -2 word(s) | 910 | 2021-08-27 20:10:48 | | | | |
| 14 | Yun Jiang | -57 word(s) | 853 | 2021-09-07 03:37:14 | | | | |
| 15 | Yun Jiang | + 56 word(s) | 909 | 2021-09-10 22:19:37 | | | | |
| 16 | Yun Jiang | -1 word(s) | 908 | 2021-09-11 00:46:22 | | | | |
| 17 | Yun Jiang | -3 word(s) | 905 | 2021-09-13 20:15:28 | | | | |
| 18 | Yun Jiang | -509 word(s) | 396 | 2022-01-04 04:15:37 | | |
Video Upload Options
The tin-iodate battery is a rechargeable battery for large scale energy storage.
A tin-iodate rechargeable battery is a redox flow battery that was first disclosed in 2021 with high energy density and high power density [1]. The energy density tested with a static battery achieved 150Wh/L at the current density of 100mA/cm2, six times higher than 25Wh/L of the all-vanadium redox flow battery, benefiting from the high solubility of iodic acid in water (13 M) and stannous ions in hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid solution (5 M).
Electrochemistry
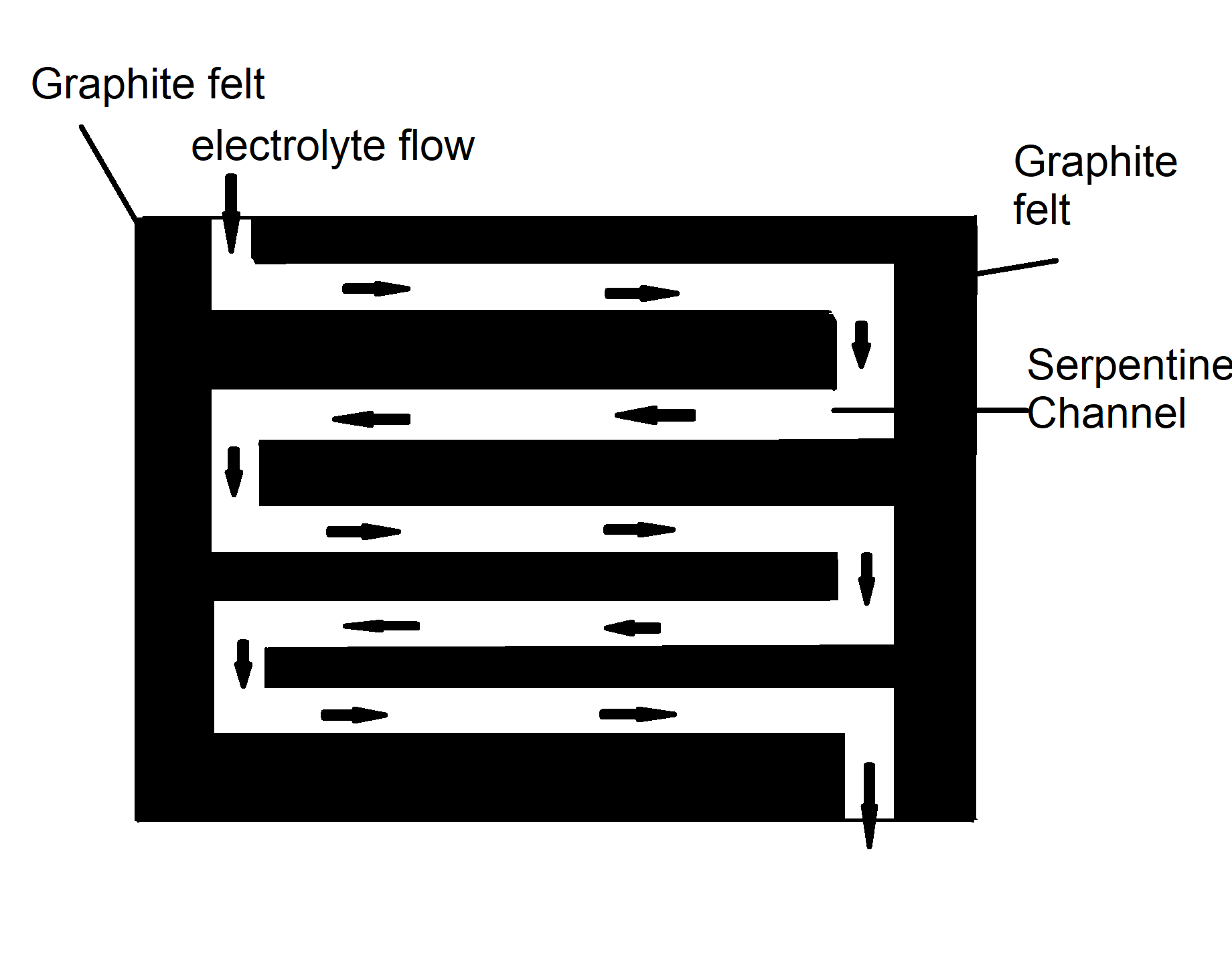
The tin-iodate flow battery comprises a tin anode, a carbon cathode, a proton exchange membrane (PEM), and acidic aqueous electrolytes. The tin-iodate battery is constructed based on the following redox reactions:
Anode: 3Sn - 6e- ↔ 3Sn2+ E0= -0.13 V
3Sn2+- 6e- ↔ 3Sn4+ E0= 0.15 V
Cathode: 2IO3- + 12H+ + 10e- ↔ I2 + 6H2O E0= 1.20 V
I2 + 2e-↔ 2I- E0= 0.54 V
Overall: 3Sn + 12H+ +2IO3- ↔ 3Sn4+ +2I- +6H2O E= 1.33/0.39 V
The protons in the anolyte penetrate the selectively permeable membrane to enter the catholyte and participate in the electrochemical reaction during the discharging process.
Practically, only part of electrochemical reactions needs to be used:
Anode: 5Sn - 10e- ↔ 5Sn2+ E0= -0.13 V
Cathode:2IO3- + 12H+ + 10e- ↔ I2 + 6H2O E0= 1.20 V
Overall: 5Sn + 12H+ +2IO3- ↔ 5Sn2+ +I2- + 6H2O E= 1.33 V
The standard electrode potential is 1.33 V for the tin-iodate couple. However, the actual open-circuit voltage of the battery can achieve 1.55 V due to the high proton and iodate concentrations in the acidic aqueous electrolytes.
The theoretical energy density is calculated as 319 Wh/L. Practically half can be achieved. The energy density is limited by the concentrations of the acids.

The tin anode may react with the pure high concentration hydrochloric acid anolyte, but the reaction can be prohibited with the increase of stannous concentration in the anolyte, therefore some 20% stannous chloride should be added to the hydrochloric acid anolyte to prevent the reaction at the beginning. Carbon fiber or graphite felt can be used for the cathode material.
Carbon, tin, and iodine are low toxic and the aqueous solution is non-flammable, ensuring the system's safety and environmental friendliness. The costs of graphite, tin and iodic acid are low as well. All the performance characteristics make the tin-iodate battery perfect for large-scale energy storage.