1.1. NF-κB Signaling
NF-κB comprises a family of five transcription factors that regulate the expression of a variety of genes involved in several biological processes. These processes include inflammation, cellular development and differentiation, cell cycle progression, cell migration and so on
[1]. The members of the NF-κB family include RelA/p65, RelB, c-Rel, NF-κB1(p50/p105) and NF- κB2(p52/p100), and they function as dimers in two separate but interconnected arms of the NF-κB pathway: the canonical pathway and the non-canonical pathway. As shown in
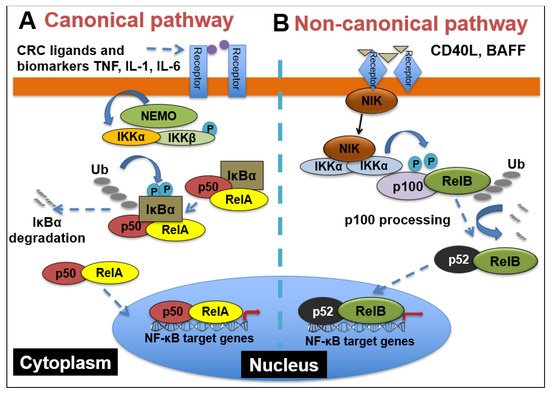
Figure 1, in the canonical pathway, which is often activated by growth factors, lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and cytokines, the inhibitor of κB kinaseβ (IKKβ) in the IKK complex is phosphorylated. Phosphorylated IKKβ triggers a signaling cascade that results in the phosphorylation of IκBα and its subsequent degradation, causing the translocation of p65 and p50 heterodimers into the nucleus
[2]. The binding of p65/p50 dimers to their cognate κB motif leads to the expression of NF-κB target genes. On the other hand, the non-canonical pathway, which is mainly involved in cell development, is activated by tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily members’ ligands, including cluster of differentiation 40 ligand (CD40L), B-cell activating factor (BAFF), receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL) and lymphotoxin-β (LT-β)
[3]. The stimulation of TNFR induces the phosphorylation of NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK), which further phosphorylates IKKα. Then, activated IKKα induces the phosphorylation of p100, triggering its proteasomal processing to p52. Following the transformation of p100 to p52, the p52/RelB dimer undergoes nuclear translocation to promote gene transcription
[4].
Figure 1. NF-κB signaling pathways. (A) Canonical NF-κB receptors TNFR, IL-1R and TLR are activated by their respective ligands, resulting in IKKβ activation. CRC biomarkers such as IL-6, IL-1 and TNFα can enhance this activity. Activated IKKβ phosphorylates IκBα, which causes its subsequent ubiquitination, separation from the p65/p50 complex and proteasomal degradation. p65/p50 heterodimers then translocate to the nucleus and can bind to their respective DNA elements and promote gene transcription. (B) In the noncanonical NF-kB signaling pathway, activation of noncanonical NF-κB receptors, including RANK and CD40, activates NIK, resulting in IKKα phosphorylation. Activated IKKα then phosphorylates p100, causing its polyubiquitination and processing to p52 via proteasomal degradation. The p52/RelB heterodimer then translocates to the nucleus to bind to its respective DNA elements.
1.2. Myriad Functions of NF-κB Signaling and Complex Interactions between Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment (TME) in CRC
As a major nexus of inflammation and cancer, NF-κB signaling has been reported to be extensively implicated in CRC progression. From the formation of polyps to the development of an invasive adenocarcinoma, NF-κB has been shown to play a role in multiple stages of malignancy development in the colon
[5]. Interestingly, the aberrant activation of NF-κB has been reported in about 50% of CRC patients, and it has also been shown to promote the development of colitis-associated cancer
[6]. As depicted in
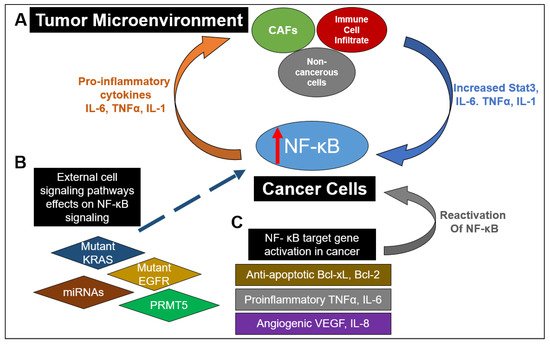
Figure 2, this constitutive activation of NF-κB drives the establishment of a pro-inflammatory tumor microenvironment in CRC, which feeds into multiple cancer hallmarks, including increased cell survival, proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis. For example, in CRC, NF-κB upregulates the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins like Bcl-2-associated athanogene-1(BAG-1), B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and B-cell lymphoma-extra-large (Bcl-xL) proteins. Similarly, enhanced NF-κB function in CRC promotes he expression of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNFα, IL-6 and IL-1β, increases the levels of angiogenic factors like HIF-1α, IL-8 and VEGF and facilitates the expression of metastatic genes, including several chemokines, cytoskeletal genes and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
[7]. Moreover, as governed by dysregulated upstream proteins, such as protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5), NF-κB has been shown to contribute to CRC cell growth, anchorage-independent growth and cell migration
[8][9][10][11]. NF-κB also hampers the effectiveness of current CRC chemotherapeutic drugs via upregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins and chemokines
[5].
Figure 2. The myriad and varied interactions between NF-κB signaling in cancer and the tumor microenvironment (TME). (A) Increased NF-κB activation in cancer cells can result in the release of proinflammatory cytokines into the TME. This results in stimulation of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), immune cell infiltrates (such as macrophages) and noncancerous cells to release IL-6 and TNFα, as well as promoting STAT3 activation. Release of these factors back into the TME further enhances NF-κB activation in cancer cells. (B) Mutations of proteins in other pathways or lack of expression of those proteins have been shown to enhance NF-κB activation. These include mutant EGFR and KRAS in the RAS-RAF signaling pathway as well as miRNAs in numerous signaling pathways. Dysregulation of key regulators in NF-κB signaling such as PRMT5 can also contribute to upregulation of NF-κB activity. (C) NF-κB downstream target genes can act to promote a proinflammatory microenvironment by promoting the release of antiapoptotic factors such as Bcl-xL and Bcl-2, proinflammatory factors TNFα and IL-6, angiogenic factors VEGF and IL8 and proinflammatory chemokines. Furthermore, release of pro-inflammatory cytokines can restimulate NF-κB activation. All these factors contribute to a continual stimulation of NF-κB signaling and an increasingly pro-inflammatory environment.
Besides these factors, NF-κB also plays a critical role in the tumor microenvironment (TME) of cancer cells (
Figure 2). Specifically in the context of CRC, IL-6 and TNFα act to mediate inflammation and cancer in the TME
[12][13][14]. IL-6 has been shown to be increased in the tumor tissue and serum of patients with CRC and is correlated with lower patient survival
[15]. TNFα has also been shown to have high serum expression in CRC patients and is linked with poor prognosis
[16]. This high expression of IL-6 and TNFα promotes invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and therapeutic resistance
[17][18]. NF-κB activation can result in activation of Stat3, which can lead to greater interactions and communication between cancer cells and the TME
[19]. Interactions between cancer cells and the TME are critical for maintenance of tumor growth
[19]. Additionally, immune cell infiltrates of tumor-associated macrophages can produce IL-6 and TNFα in CRC
[20]. Another important component of the TME are cancer stromal fibroblasts (CAFs), which in CRC, also produce IL-6, further enhancing the interaction with the TME
[18]. These data suggest the critical importance and complex nature of NF-κB signaling in relation to signaling within the TME between cancer cells and noncancerous cells in the microenvironment.
Collectively, these studies demonstrate the all-encompassing role that NF-κB plays in CRC progression and the potential it holds as a viable target for CRC treatment.