
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Leondios Kostrikis | + 1974 word(s) | 1974 | 2021-07-14 12:10:57 | | | |
| 2 | Nora Tang | + 266 word(s) | 2240 | 2021-07-19 05:17:57 | | |
Video Upload Options
The human papillomavirus is one of the most common sexually transmitted viruses, and an infection from this virus may become persistent, leading to diseases such as cervical cancer. In the past, cytology-based methods such as the Papanicolaou (Pap) test were imperative to identify the disease at a stage where it can be treated. However, since the 1980s where the etiological association of HPV and cervical cancer was identified, new tests began emerging directed towards identifying the virus. Furthermore, as the biology of HPV along with the relationships with its host are elucidated, these tests and treatments further advance. Recently in Europe, there is a movement towards the implementation of HPV testing methodologies in national screening programs to precede cytological testing. These screening strategies are recommended by the European guidelines and the World Health Organization. This review presents the current HPV testing methodologies, their application in organized population-based cervical cancer screening programs based on the most recent European guidelines, and their implementation status in countries in Europe.
1. Cervical Cytology and Reasons That Lead to HPV-Based Approaches
2. Reasoning of HPV Testing Implementation in Screening Programs
3. HPV Testing Assays and Validation
| Tests | Hybrid Capture 2 (Qiagen) | GP5+/6+ EIA a | Cobas 4800 HPV Test (Roche) | APTIMA HPV Assay (Hologic) | BD Onclarity HPV Assay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of assay | Signal amplification, hybrid capture | PCR, probe hybridization |
Real-time PCR detection | Transcription mediated amplification, probe hybridization |
Real-time PCR detection |
| Targets | DNA, Whole viral genome | L1 DNA, 150 bp |
L1 DNA 200 bp | E6/E7 mRNA | E6 and E7 DNA |
| HPV Subtypes detected |
16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 and 68 | 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, and 68 | 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66 and 68. Individual genotyping for: 16, 18 |
16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, and 68. Reflex Partial genotyping for: 16, 18–45 |
33–58; 56–59–66; 35–39–68 f. Individual genotyping for: 16, 18, 31, 45, 51, and 52 |
| Internal Controls Human genes |
NO | NO | Internal human β-globin control | Internal RNA transcript (HPV16 E6/7) control | Internal human β-globin control |
| Capacity Batch size |
88 | 96 samples in 9.5 h e |
96 | Panther system 100 and 250 test /Tigris DTS system 250 | 46 |
| VALGENT Validation |
Standard comparator tests for validation b | Standard comparator tests for validation b | YES | YES | YES |
| US FDA c Validation | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES |
| CE Mark d Validation | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Uses within a screening program | ASC-US Triage, test-of-cure |
ASC-US Triage, test-of-cure |
ASC-US Triage/co-testing/Primary testing | ASC-US Triage/co-testing | ASC-US Triage/co-testing/Primary testing |
4. Screening Algorithms Employing Primary HPV Testing
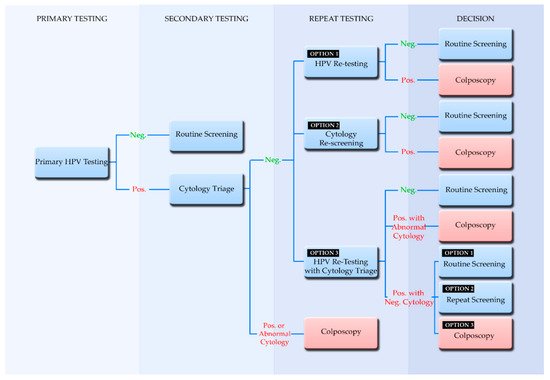
5. Participation in Screening and the Implementation of Self-Sampling
References
- Chantziantoniou, N.; Donnelly, A.D.; Mukherjee, M.; Boon, M.E.; Austin, R.M. Inception and Development of the Papanicolaou Stain Method. Acta Cytol. 2017, 61, 266–280.
- Siebers, A.G.; Klinkhamer, P.J.J.M.; Grefte, J.M.M.; Massuger, L.F.A.G.; Vedder, J.E.M.; Beijers-Broos, A.; Bulten, J.; Arbyn, M. Comparison of Liquid-Based Cytology With Conventional Cytology for Detection of Cervical Cancer Precursors: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA 2009, 302, 1757–1764.
- Gibb, R.K.; Martens, M.G. The impact of liquid-based cytology in decreasing the incidence of cervical cancer. Rev. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 4, S2–S11.
- Thakur, M.; Guttikonda, V. Modified ultrafast Papanicolaou staining technique: A comparative study. J. Cytol. 2017, 34, 149.
- Norimatsu, Y.; Yanoh, K.; Hirai, Y.; Kurokawa, T.; Kobayashi, T.K.; Fulciniti, F. A Diagnostic Approach to Endometrial Cytology by Means of Liquid-Based Preparations. Acta Cytol. 2020, 64, 195–207.
- Raifu, A.O.; El-Zein, M.; Sangwa-Lugoma, G.; Ramanakumar, A.; Walter, S.D.; Franco, E.L. Determinants of Cervical Cancer Screening Accuracy for Visual Inspection with Acetic Acid (VIA) and Lugol’s Iodine (VILI) Performed by Nurse and Physician. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170631.
- Nayar, R.; Wilbur, D.C. The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology: Definitions, Criteria, and Explanatory Notes; Nayar, R., Wilbur, D.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015.
- Goodman, A. HPV testing as a screen for cervical cancer. BMJ 2015, 350, h2372.
- Bhatla, N.; Singhal, S. Primary HPV screening for cervical cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 65, 98–108.
- Tota, J.E.; Bentley, J.; Blake, J.; Coutlée, F.; Duggan, M.A.; Ferenczy, A.; Franco, E.L.; Fung-Kee-Fung, M.; Gotlieb, W.; Mayrand, M.-H.; et al. Introduction of molecular HPV testing as the primary technology in cervical cancer screening: Acting on evidence to change the current paradigm. Prev. Med. 2017, 98, 5–14.
- Von Karsa, L.; Arbyn, M.; De Vuyst, H.; Dillner, J.; Dillner, L.; Franceschi, S.; Patnick, J.; Ronco, G.; Segnan, N.; Suonio, E.; et al. European guidelines for quality assurance in cervical cancer screening. Summary of the supplements on HPV screening and vaccination. Papillomavirus Res. 2015, 1, 22–31.
- Von Karsa, L.; Arbyn, M.; De Vuyst, H.; Dillner, J.; Dillner, L.; Franceschi, S.; Patnick, J.; Ronco, G.; Segnan, N.; Suonio, E.; et al. European Guidelines for Quality Assurance in Cervical Cancer Screening—Second Edition Supplements; EU: Luxembourg, 2015.
- Basu, P.; Mittal, S.; Bhadra Vale, D.; Chami Kharaji, Y. Secondary prevention of cervical cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 47, 73–85.
- Jin, X.W.; Lipold, L.; Foucher, J.; Sikon, A.; Brainard, J.; Belinson, J.; Schramm, S.; Nottingham, K.; Hu, B.; Rothberg, M.B. Cost-Effectiveness of Primary HPV Testing, Cytology and Co-testing as Cervical Cancer Screening for Women Above Age 30 Years. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2016, 31, 1338–1344.
- Basu, P.; Meheus, F.; Chami, Y.; Hariprasad, R.; Zhao, F.; Sankaranarayanan, R. Management algorithms for cervical cancer screening and precancer treatment for resource-limited settings. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2017, 138, 26–32.
- Georgalis, L.; de Sanjosé, S.; Esnaola, M.; Bosch, F.X.; Diaz, M. Present and future of cervical cancer prevention in Spain: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 25, 430–439.
- Malagón, T.; Kulasingam, S.; Mayrand, M.-H.; Ogilvie, G.; Smith, L.; Bouchard, C.; Gotlieb, W.; Franco, E.L. Age at last screening and remaining lifetime risk of cervical cancer in older, unvaccinated women: A modelling study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1569–1578.
- Hermansson, R.S.; Olovsson, M.; Hoxell, E.; Lindström, A.K. HPV prevalence and HPV-related dysplasia in elderly women. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189300.
- Schlichte, M.; Guidry, J. Current Cervical Carcinoma Screening Guidelines. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 918–932.
- Poljak, M.; Oštrbenk Valenčak, A.; Gimpelj Domjanič, G.; Xu, L.; Arbyn, M. Commercially available molecular tests for human papillomaviruses: A global overview. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1144–1150.
- Tsakogiannis, D.; Gartzonika, C.; Levidiotou-Stefanou, S.; Markoulatos, P. Molecular approaches for HPV genotyping and HPV-DNA physical status. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2017, 19, e1.
- Meijer, C.J.L.M.; Berkhof, J.; Castle, P.E.; Hesselink, A.T.; Franco, E.L.; Ronco, G.; Arbyn, M.; Bosch, F.X.; Cuzick, J.; Dillner, J.; et al. Guidelines for human papillomavirus DNA test requirements for primary cervical cancer screening in women 30 years and older. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 516–520.
- Gautam, A.; Gedda, M.R.; Rai, M.; Sundar, S.; Chakravarty, J. Human Papillomavirus Genome based Detection and Typing: A Holistic Molecular Approach. Curr. Mol. Med. 2019, 19, 237–246.
- Arbyn, M.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Meijer, C.J.L.M.; Berkhof, J.; Cuschieri, K.; Kocjan, B.J.; Poljak, M. Which high-risk HPV assays fulfil criteria for use in primary cervical cancer screening? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 817–826.
- Arbyn, M.; Depuydt, C.; Benoy, I.; Bogers, J.; Cuschieri, K.; Schmitt, M.; Pawlita, M.; Geraets, D.; Heard, I.; Gheit, T.; et al. VALGENT: A protocol for clinical validation of human papillomavirus assays. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 76, S14–S21.
- Bonde, J.; Ejegod, D.M.; Cuschieri, K.; Dillner, J.; Heideman, D.A.M.; Quint, W.; Pavon Ribas, M.A.; Padalko, E.; Christiansen, I.K.; Xu, L.; et al. The Valgent4 protocol: Robust analytical and clinical validation of 11 HPV assays with genotyping on cervical samples collected in SurePath medium. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 108, 64–71.
- Maver, P.J.; Poljak, M. Primary HPV-based cervical cancer screening in Europe: Implementation status, challenges, and future plans. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 579–583.
- PAHO Pan American Health Organization. Available online: (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Isidean, S.D.; Coutlée, F.; Franco, E.L. cobas ® 4800 HPV Test, a real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of human papillomavirus in cervical specimens. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 5–16.
- Haedicke, J.; Iftner, T. A review of the clinical performance of the Aptima HPV assay. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 76, S40–S48.
- Young, S.; Vaughan, L.; Yanson, K.; Eckert, K.; Li, A.; Harris, J.; Ermel, A.; Williams, J.A.; Al-Ghoul, M.; Cammarata, C.L.; et al. Analytical and Clinical Sample Performance Characteristics of the Onclarity Assay for the Detection of Human Papillomavirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020.
- Hesselink, A.T.; Heideman, D.A.M.; Berkhof, J.; Topal, F.; Pol, R.P.; Meijer, C.J.L.M.; Snijders, P.J.F. Comparison of the Clinical Performance of PapilloCheck Human Papillomavirus Detection with That of the GP5+/6+-PCR-Enzyme Immunoassay in Population-Based Cervical Screening. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 797–801.
- Ejegod, D.M.; Hansen, M.; Christiansen, I.K.; Pedersen, H.; Quint, W.; Xu, L.; Arbyn, M.; Bonde, J. Clinical validation of the Cobas 4800 HPV assay using cervical samples in SurePath medium under the VALGENT4 framework. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 128, 104336.
- Snijders, P.J.F.; van den Brule, A.J.C.; Jacobs, M.V.; Pol, R.P.; Meijer, C.J.L.M. HPV DNA Detection and Typing in Cervical Scrapes. In Human Papillomaviruses; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 101–114.
- Heideman, D.A.M.; Hesselink, A.T.; van Kemenade, F.J.; Iftner, T.; Berkhof, J.; Topal, F.; Agard, D.; Meijer, C.J.L.M.; Snijders, P.J.F. The Aptima HPV Assay Fulfills the Cross-Sectional Clinical and Reproducibility Criteria of International Guidelines for Human Papillomavirus Test Requirements for Cervical Screening. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3653–3657.
- Bonde, J.H.; Pedersen, H.; Quint, W.; Xu, L.; Arbyn, M.; Ejegod, D.M. Clinical and Analytical Performance of the BD Onclarity HPV Assay with Surepath Screening Samples from the Danish Cervical Screening Program Using the VALGENT Framework. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58.
- Lorincz, A.; Wheeler, C.M.; Cuschieri, K.; Geraets, D.; Meijer, C.J.L.M.; Quint, W. Chapter 7—Developing and Standardizing Human Papillomavirus Tests; Jenkins, D., Bosch, F.X.B.T.-H.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 111–130.
- Salazar, K.L.; Duhon, D.J.; Olsen, R.; Thrall, M. A Review of the FDA-Approved Molecular Testing Platforms for Human Papillomavirus. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2019, 8, 284–292.
- Wentzensen, N.; Schiffman, M.; Palmer, T.; Arbyn, M. Triage of HPV positive women in cervical cancer screening. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 76, S49–S55.
- D’Alessandro, P.; Arduino, B.; Borgo, M.; Saccone, G.; Venturella, R.; Di Cello, A.; Zullo, F. Loop electrosurgical excision procedure versus cryotherapy in the treatment of cervical intraepithelialneoplasia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Gynecol. Minim. Invasive Ther. 2018, 7, 145.
- Onuki, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Sakurai, M.; Ochi, H.; Minaguchi, T.; Satoh, T.; Yoshikawa, H. Posttreatment human papillomavirus testing for residual or recurrent high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: A pooled analysis. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 27, e3.
- Costa, S.; Venturoli, S.; Origoni, M.; Preti, M.; Mariani, L.; Cristoforoni, P.; Sandri, M.T. Performance of HPV DNA testing in the follow-up after treatment of high-grade cervical lesions, adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) and microinvasive carcinoma. Ecancermedicalscience 2015, 9, 528.
- Chrysostomou, A.; Stylianou, D.; Constantinidou, A.; Kostrikis, L. Cervical Cancer Screening Programs in Europe: The Transition Towards HPV Vaccination and Population-Based HPV Testing. Viruses 2018, 10, 729.
- Satake, H.; Inaba, N.; Kanno, K.; Mihara, M.; Takagi, Y.; Kondo, N.; Sagae, S. Comparison Study of Self-Sampled and Physician-Sampled Specimens for High-Risk Human Papillomavirus Test and Cytology. Acta Cytol. 2020, 64, 433–441.
- Leinonen, M.K.; Schee, K.; Jonassen, C.M.; Lie, A.K.; Nystrand, C.F.; Rangberg, A.; Furre, I.E.; Johansson, M.J.; Tropé, A.; Sjøborg, K.D.; et al. Safety and acceptability of human papillomavirus testing of self-collected specimens: A methodologic study of the impact of collection devices and HPV assays on sensitivity for cervical cancer and high-grade lesions. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 99, 22–30.
- Yeh, P.T.; Kennedy, C.E.; de Vuyst, H.; Narasimhan, M. Self-sampling for human papillomavirus (HPV) testing: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Glob. Health 2019, 4, e001351.
- Arbyn, M.; Smith, S.B.; Temin, S.; Sultana, F.; Castle, P. Detecting cervical precancer and reaching underscreened women by using HPV testing on self samples: Updated meta-analyses. BMJ 2018, 363, k4823.





