
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lilian Kato | + 8163 word(s) | 8163 | 2021-06-28 15:35:43 | | | |
| 2 | Conner Chen | Meta information modification | 8163 | 2021-07-01 03:56:27 | | |
Video Upload Options
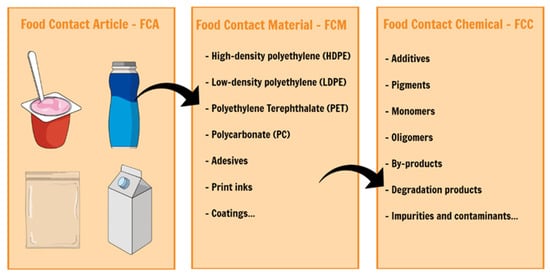
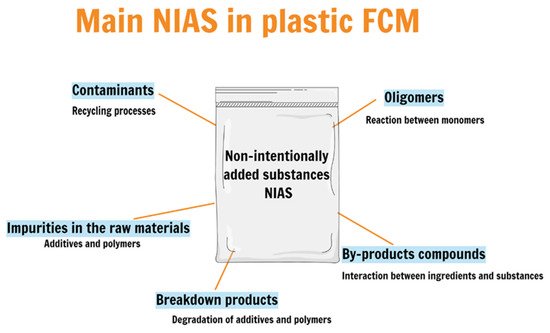
Several food contact materials (FCMs) contain non-intentionally added substances (NIAS), and most of the substances that migrate from plastic food packaging are unknown. Food packaging can contain NIAS as a result of the interactions between different substances in the packaging materials, between food content and substances (for example, additives) in FCM, from degradation processes and mainly from the impurities present in the raw materials used for FCM production. (EU) nº 10/2011 defines that “non-intentionally added substance means an impurity in the substances used or a reaction intermediate formed during the production process or a decomposition or reaction product”. Most NIAS are regularly detected when using high sensitivity analytical techniques, although the chemical structure of unknown compounds is often difficult to establish by conventional tools.
1. Migration of Substances from Packaging to the Food
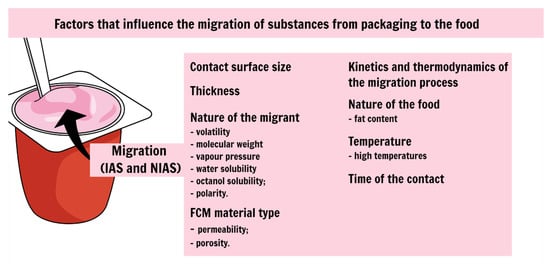
-
the contact surface size, since the more extensive the contact surface between packaging and food, the higher the migration rate [1];
-
the nature of the migrant, since the more volatile and the lower the molecular weight, the greater the migration rate (also the vapour pressure, water solubility, octanol solubility and polarity) [21];
-
FCM material type (e.g., impermeable, permeable, porous materials) [22];
2. NIAS in Plastic Food Packaging
-
Search component 1 (SC1) was a population search: “food packaging” OR “food contact article” OR “food contact material” OR “packaging, food” OR “food containers” OR “plastic packaging materials” OR “multilayer food packaging” OR “multilayer packaging materials” OR “recycled plastic packaging” OR “acrylic adhesives” OR “recycled expanded polystyrene containers” OR “polyester-polyurethane” OR “food packaging polymer” OR “biodegradable food packaging” OR “nylons” OR “polyethylenes” OR “polypropylenes” OR “polystyrenes” OR “polyurethanes” OR “polyolefins” OR “acrylic adhesives” OR “recycled expanded polystyrene containers” OR “polyester-polyurethane” OR “polyvinyls” OR “polyesters” OR “polyethylene terephthalates” OR “polyhydroxy ethyl methacrylate” OR “silicones” OR “elastomers” OR “polyvinyl chloride” OR “silicone elastomers”.
-
Search component 2 (SC2) was an intervention search: “non-intentionally added substances” OR “non-intentionally added compound” OR “NIAS” OR “breakdown products” OR “impurities” OR “side products” OR “neo-formed compounds” OR “degradation of polymers” OR “degradation of compounds” OR “degradation products” OR “non-volatile migrants” OR “volatile compounds” OR “non-volatile compounds” OR “volatile organic compound” OR “polymer additives” OR “oligomers” OR “additives” OR “plastic additives” OR “additive”.
-
Because the ScienceDirect database only allows the use of a maximum of thirteen keywords in the search string, for this base it was used the following search components:
-
SC1: (“food packaging” OR “food contact article” OR “food contact material” OR “plastic packaging materials”).
-
SC2: (“non-intentionally added substances” OR “non-intentionally added compound” OR “NIAS” OR “additives”). Table 1 presents published works that identified NIAS on different food plastic packaging, the techniques used in each work and the migration tests applied. Despite all efforts, there is much to discover and to do in this area. Below are the leading examples of possible NIAS formation, shown in Figure 3.
| Food Contact Material | NIAS | Method/Technique | Migration Tests | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyvinyl chloride PVC/polyethylene-PE multilayer film | Antioxidants derivatives: Triester analog of 1010; Plasticizers (contain glycerol): 1-oleoyl-3-linoleoyl-rac-glycerol; Slip agents (with an amide end group): Tetracosenamide, Docosanamide, Icosanamide; Others: 2-(2-hydroxyethyl-hexadecylamino)ethyl palmitate, Bis(2-ethylhexyl) 2,2′-disulfanediyldiacetate | UPLC-QTOF/MS | Stainless-steel migration cell, water, 40% ethanol or 95% ethanol | [28] |
| Multilayer plastic materials (the combination of aluminium (Al), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyamide (PA), polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) | Cyclic esters (AA-DEG and AA-DEG-IPA-DEG) | UPLC-MS-QTOF and UHPLC-MS-QqQ | Ultrapure water, ethanol 10% and 95% ethanol | [2] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Cyclic oligomers | LC-MS | 50% ethanol at 80 °C | [5] |
| Polyester resins, tin plate sheets coated with polyester–phenolic lacquers and corresponding press-twist-closures (equipped with plasticized polyvinyl chloride [PVC] sealings) | Polyester oligomers (cyclic oligomers, dimers, trimers and tetramers) | HPLC–DAD, HPLC–DAD/MS, GC-MS, GC–MSD and RP-HPLC–DAD/MS | Mashed infant food and two types of homemade carrot puree, Acetonitrile, 50% Etanol, 20% Etanol | [6] |
| Rigid thermoformed containers and films made with Recycled polyethylene terephthalate-RPET | Chromium, nickel | CP-AES | Distilled water, 5% citric acid | [8] |
| Multilayer food packaging materials | Printing unknown ink compounds | GC-MS | Tenax, isooctane and etoh 95% and etoh 50% | [9] |
| Polyurethane adhesive | 1,4,7-trioxacyclotridecane-8,13-dione; 1,6-dioxacyclododecane-7,12-dione dimer; 1,4-dioxacyclotridecane-5,13-dione; 1,4,14,19-tetraoxacyclopent acosene-5,13,20,25-tetra one and 1,4-dioxacyclotridecane-5,13-dione; by-product of the curing reaction: 1,1-(Methanediyldibenzene-4,1-diyl)bis[3-(2-hydroxyethyl)urea]; 4-(7-acetoxy-5-methoxy-8,8-dimethyl-2-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2H,6H-pyrano[3,2-g]chromen-3-yl)-1,3-phenylene diace-tate; Bis[2-(diethylamino)ethyl] 4,4′-[(2-methyl-1,3propanediyl)bis(oxycarbonylimino)] dibenzoate and Bis[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]4,4′-[1,5-p entanediylbis(oxycarbonylim ino)] dibenzoate; unknown compounds | UPLC–Q-TOF/MS | Tenax | [10] |
| Expanded polystyrene (EPS) (recycled material) | Styrene dimmers are observed, like cis-1,2-diphenylcyclobutane, 2,4-diphenyl-1-butene, trans-1,2-diphenylcyclobutane and 1-phenyltetralin. These compounds were reported as by-products during styrene polymerization or material processing | HS-SPME-GC–MS | 10% (v/v) ethanol and 3%(w/v) acetic acid | [11] |
| Polyethylene-PE, low-density polyethylene-LDPE and HIGH-density polyethylene-HDPE | Dibutyl amine, N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)alkylamines (impurity reaction or breakdown products), N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl) dodecylamine, tributylphosphine, tridodecylamine, Methyl (Ralox 35), ethyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propanoate (breakdown of Irganox 1010 or Irganox 1076), Benzenepropanoic acid, 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxy-, 1,1′-[2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediyl] ester and benzenepropanoic acid, 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxy-, 1,1′-[2-[[3-[3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl]-1-oxopropoxy]methyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediyl] ester (degradation of Irganox 1010), alkylamides N,N′-1,2-ethanediylbis-(breakdown or impurity products of the additive octadecanamide, N,N′-1,2-ethanediylbis), Irgafos 168 OXO (oxo-derivative of Irgafos 168), 11-eicosenamide (derived from oleamide) | UPLC IMS QTOF | Ethanol 95%, ethanol 50%, Tenax, ethanol 10% and acetic acid 3% | [39] |
| Empty cans with lids coated with polyester resins | Oligomers | GC–MS, HPLC-DAD/MS, UHPLC-HRMS and DART-HRMS | -- | [40] |
| Polyester coatings based on NAH | Oligomers | LC-MS/MS and LC-TOF-MS | Acetonitrile, Water, 10% Aqueous ethanol (v/v), 50% Aqueous ethanol (v/v) and diverse foodstuffs | [50] |
| Polyester can coating extracts | Linear and cyclic oligomers derived from the incomplete polymerization of polyester monomers, phthalic acids and diols | HPLC-MS, HPLC-ESI MS and HPLC-HRMS/MS | 95/5 etoh/water (v/v-%) solution for 4 h at 60 °C and 50/50 etoh/water (v/v-%) solution for 10 days at 60 °C | [51] |
| Virgin and recycled Polyethylene terephthalate-PET pellets | Cyclic and linear oligomers: TPA-EG, (TPA-EG)2 + H2O, (TPA-EG)2, (TPA-EG)3 + H20, (TPA-EG)3, (TPA-EG)4, and (TPA-EG)5, TPA2-EG-DEG + H2O, TPA2-EG-DEG, TPA3-EG2-DEG + H2O, TPA3-EG2-DEG, and TPA4-EG3-DEG, (TPA-DEG)2 and TPA4-EG2-DEG2 | UPLC-MS-QTOF | Ethanol 10% v/v) and simulant B (acetic acid 3% w/v) as aqueous simulants and ethanol 95% v/v as a fat simulant | [52] |
| Baby food squeezes with multilayer materials (Polyethylene terephthalate-PET/aluminium-Al/polyethylene-PE) | Polyester oligomers, 29 cyclic and six linear oligomers. ε-caprolactam was tentatively identified as a heterogenic polyester oligomer combined with AA, DEG, PA and NPG; BHET and diethyl 5-(2-((2,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy)acetamido)isophthalate, methoxyeugenol and Bis(2-methoxyethyl) sebacate | UHPLC-ESI-QTOF MS | Baby food: mixture of fruit purées (apple, banana, pear), fruit jelly, chocolate custard, acetic acid 3% (w/v) and ethanol 20% (v/v) | [53] |
| Polyurethane adhesives in multilayer packaging materials | Silane unknown compounds; degradation of antioxidants Irgafos and Irganox (2,6-Di-tert-butylbenzoquinone; isomer 2,5-di-tert-butylbenzoquinone; 7,9-Di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione; benzenepropanoic acid, 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxy-methyl), by-product of the polyester-based urethane 91,6-Dioxacyclododecane-7,12-dione); cyclic adipate; unknown nitrogen-compounds; unknown phenolic compounds; 1,4,7-Trioxacyclotridecane-8,13-dione | HS-SPME-GC-MS | Tenax; isooctane | [54] |
| UV-curable varnishes over polypropylene | 2-propenoic acid,1,1′-[2-[[3-[2,2-bis[[(1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl)oxy]methyl]butoxy]-1-oxopropoxy]methyl]-2-ethyl-1,3-propanediyl] ester is considered a NIAS, as it is a reaction product coming from the monomer TMPTA, 11-diethyl-7-oxo-4,6,10,12-tetraoxopentadecane-3,13-diyl diacrylate | GC-MS/Q and UHPLC-IMS/QTOF | Ethanol 95% (v/v) and Migracell® migration cells | [55] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), oriented polyamide (OPA), cast polypropylene (CPP), polyethylene (PE) and PE/ethyl vinyl alcohol PE(EVOH) | Primary aromatic amines-PAAs (1,8-diazacyclotetradecane-2,9-dione; caprolactam; 1,8,15-triazacycloheneicosane-2,9,16-trione; 1,3-bis(isocyanatomethyl)-cyclohexane, 1-cyanodecane and 1,4-bis(isocyanatomethyl)-cyclohexane; l-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-leucine; 1,4,7,18,21-pentaoxa-11,14,25,28-tetraazacyclohentriacontane (9CI); l-leucine; l-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-leucyl-; butanediamide; N4-hydroxy-N1-[(1S)-2-methyl-1-(1-pyrrolidinylcarbonyl)propyl]-2-pentyl-, (2R)-; triethylamine, naphtylethylenediamine; 1,8,15,22-tetraazacyclooctacosane-2,9,16,23-tetrone; urea; N-cyclohexyl, urea, N-cyclohexy-N′-methyl and 1-(cyclohexycarbonyl)piperazine); Dimethyl phthalate | UHPLC–Q-TOF/MSE | 3% (w/v) acetic acid | [56] |
| Polypropylene random copolymer composite films | Irgafos 168 and its two degradation products, 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol (DP1) and tris (2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphate (DP2) | GC-MS | Isooctane | [57] |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Degradation products derived from phenolic antioxidants, impurity/reaction product/breakdown product of the additives, Family 1: Family formed with the reference structure; was formed by the compounds that had a similar structure constituted by a group 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl; Family 2: With glycerol molecule (glyceryl monostearate, glyceryl palmitate and glyceryl dihexadecanoate, an ester of an acid chain bonded to a glycerol molecule); Family 3: Dihydroxy alquilamines (amine bonded to two ethanol molecules and also an alkyl hydrocarbon chain); Family 4: ceramide and dihydroceramide (a family of waxy lipid molecules which are composed of sphingosine (an 18 carbon amino alcohol with an unsaturated hydrocarbon chain) and a fatty acid); Family 5: amides bonded by ethylene (degradation products from a lubricant losing C2H4); Other compounds (amides come from the impurities or degradation products from erucamide and oleamide widely used as slip agents) | UPLC-MS-QTOF | Ethanol 95% and 10%, acetic acid 3% and Tenax | [58] |
| Hot melt adhesives (Ethylene-vinyl acetate-EVA and amorphous polyolefin APAO enriched in propene) | Degradation of Irganox 1010: 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde | UPLC-ESI-MS/QTOF | Tenax | [59] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) pellets | The degradation product of the antioxidants Irgafos 168 and Irganox 1010: 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethyl ethyl) phenol; 2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane; linear aldehydes; residual monomers: ethylene glycol (EG); thermal degradation products: toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene; phthalates (DEP, DIBP) | HS-SPME/GC-MS | -- | [60] |
| Polypropylene (PP) films | Degradation products from Irgafos 168, Tinuvin 326 and Irganox 1076 | HPLC-DAD and GC-FID–MS | Distilled water/ethanol—50/50 v/v | [61] |
| Plastic films (with and without printing ink) including PE: polyethene. PET: polyethylene terephthalate. PA: Polyamide. PP: Polypropylene. EVA: Ethylene-vinyl acetate. | 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol and 2,6-di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone. 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol is a degradation product of Irgafos 168 while 2,6-di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone is a degradation product of antioxidants such as Irganox 1010, Irgafos 168 and Irganox PS 802 | purge and trap (P&T) coupled to GC–MS | Isooctane and Tenax | [62] |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol (degradation product of Irgafos 168 and Irganox® 1010), tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6-9-diene-2,8-dione (a by-product of the antioxidant Irganox 1010) and 2,6-di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone, a degradation product of antioxidants such as Irganox 1010, Irgafos 168 and Irganox PS 802 | GC-MS | -- | [63] |
| Polypropylene food storage containers | Degradation products: 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol and tris(2,4-di-tert-buthylphenyl)phosphate, methyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate, a compound identified as product of degradation of Irganox 1076 and/or Irganox 1010; 2,6-di-tert-butylbenzoquinone (isooctane fraction) and 7,9-di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione; different compounds have been identified as metabolites of bis-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (e.g., 2-ethylhexanoic acid, 2-ethylhexanol, phthalic acid, mono-2-ethylhexyl phthalate), and consequently suggested as possible degradation products of this phthalate; by-product Benzothiazole; degradation products N,N-bis-(2-hydroxyethyl)alkyl amine | GC × GC−ToF MS | 3% (w/v) acetic acid, 10% (v/v) ethanol, and isooctane | [64] |
| Can coatings | Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP), Degradation products formed from antioxidants (1,3-di-tert-butylbenzene and 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol degradation products from antioxidants Irgafos 168 or Irganox 1076, 2,6-di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone degradation products from antioxidants Irgafos 168 and Irganox 1010, 7,9-di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione, a degradation product of Irganox 1010. | GC-MS and LC-MS/MS | -- | [65] |
| Recycled pellets obtained from post-consumer low-density polyethylene (PC-LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (PC-HPDE) | Polymer degradation products: octanal and nonanal (aldehydes); 3-decanone, 2-undecanone, 2,2,4,4,6,8,8-heptamethylnonanone and 3-dodecanone (ketones); hexane (others); Additives degradation products: 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde (aldehyde); 2,6-di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone and 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyacetophenone (ketones); methyl tetradecanoate, ethyl tetradecanoate and ethyl palmitate(esters); 7,9-di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro (4,5)deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione (others); Contaminants from external sources: methyl lactate, hexyl acetate and dimethyl butanedioate, α-methylionone, 3-(4-Isopropylphenyl)-2-methylpropionaldehyde, α-amylcinnamaldehyde, (phenylmethylene)octanal and dipropylene glycol amog others (cosmetic ingredients); alkylbenzenes (breakdown products produced by the degradation of alkylbenzene sulfonates); contamination related to food: the lactones, 5-methylfurfural, furfural and methyl hexanoate (can derive from food flavors as well as from cosmetics ingredients); furfuryl alcohol, methyl pyruvate and 2-acetyl pyridine (food flavors), methyl-2-ethylhexanoate, acetic acid, propanoic acid, pyridine and dimethyl trisulfide (rotten food products), 2,6-diisopropylnaphthalene (paper labels). | GC/MS and HS-SPME-GC/MS | -- | [66] |
| Plastic baby bibs (polyethylene vinyl acetate-PEVA, polyamide-PA and polyethylene-PE) | Azocine, octahydro-1-nitroso-(Possible NIAS from printing ink); 1,6-Dioxacyclododecane-7,12-dione (NIAS from polyurethane adhesive); 1-Propene-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid, tributyl ester (Tributyl aconitate) | GC-MS | Artificial saliva | [67] |
| Polystyrene-PS cups and multilayer films | Styrene monomer and oligomers; polyester urethane-based oligomers (PU) cyclic oligomers: α-methylstyrene; 1,1-diphenyl-ethylene; 2,4-diphenyl-1-butene; trans-1,2-diphenycyclobutane; 2,4,6-triphenyl-1-hexene; | GC-MS | 10% v/v ethanol in water and 50% v/v ethanol in water | [68] |
| Polyurethane adhesives | 1,4,7-trioxacyclotridecane-8,13-dione, a lactone | UPLC-TQMS and UPLC-QTOF-MS | Tenax and 3% acetic acid | [69] |
| Polyvinylchloride (PVC)-coated cans | 6-(4-methylphenyl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazin-3-amine and BGA (6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine) | UHPLC-HRMS | Water and 3% acetic acid | [70] |
| Monolayer film with polylactic acid (PLA), polylimonene (PL) and zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) | Tripropylene glycol diacrylate; 10-Heneicosene; α-Tocopherol acetate; N, N-Diethyldodecanamide; N-[(9Z)-9-Octadecen-1-yl]acetamide; 1-Palmitoylglycerol and Glycerol stearate | ICP-MS, GC–Q-Orbitrap-MS and LC–Q-Orbitrap-MS | 10% ethanol, 3% acetic acid | [71] |
| Flexible multilayer materials point by polyurethane (PU) layers | Polyamide oligomers; Anhydride of monomethyl succinate, 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde; Erythritol monopalmitate; PU oligomers (cyclic esters made up of phthalic acid (PA); diethylene glycol (DEG) in combination 1:1 (PA-DEG) or 2:2 (PA-DEG-PA-DEG0); adipic acid (AA) or phthalic acid (PA); and diols such as diethylene glycol (DEG), neopentyl glycol (NPG), dipropylene glycol (DPG), dihydroxyalkyl ethers (dHAE), ethylene glycol (EG), propylene glycol (PG), butylene glycol (BD) or hexanediol (HD). | UPLC MS–QTOF | Ethanol 10% v/v, acetic acid 3% w/v, and ethanol 95% v/v | [72] |
| Active packaging: Polypropylene (PP); PP + green tea; PP/poly (ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) EVOH; PP/EVOH + oregano; PP/EVOH + citral; EVOH; Polyethylene terephthalate-PET/EVOH + citral; PET/EVOH + cinnamon; PP/EVOH/PP; PP/EVOH + oregano | Degradation of active compounds; impurities from the raw materials; additives used in the manufacture of the active polymer (citral thermal reaction products; oxidation product of citral; decomposition product of adipates used as plasticizers; impurity/reaction product/breakdown product for the additives used in the manufacture of PE materials; xanthenone derivates) | UPLC-QTOF-MS | Ethanol 10%; ethanol 95% | [73] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film with an acrylic resin | Ethyl lauroyl arginate (LAE) impurities: N2-Dodecanoyl-L-arginine (LAS) | UPLC–MS(QTOF) | Ethanol 10%; ethanol 95%; sliced fresh chicken breasts | [74] |
| Multilayer materials | 1,4,7-trioxacyclotridecane-8,13-dione, and diethylene glycol (DEG) [AA-DEG]. | LC-HRMS | Ethanol 95% and Tenax | [75] |
| Silicone moulds and teats | Side reactions in the polymerization (cyclic and linear polydimethylsiloxanes; oligomeric dimethyl siloxanes) | H-NMR and GC-MS | Pizza | [76] |
| Polyurethane adhesives commonly used for food-contact laminated films | No NIAS detected. | GC–MS | Isooctane | [77] |
| Polyvinylchloride (PVC)—and polyethylene (PE)—based cling-films | 2-ethyl hexanoic acid (2-EHA), triacetin | Solid-Phase Micro-Extraction and GC/MS | PDO Italian cheeses during cold storage under light or dark | [78] |
| Oriented polypropylene (OPP) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) with printing inks | Printing unknown ink compounds | UPLC-QTOF-MS | Ethanol (95%) and Tenax | [79] |
| Polyurethanes (PURs) | Pyridine (NIAS, solvent); Dimethylacetamide (NIAS, solvent); 1,4-Dioxane (NIAS, reaction medium); Aniline NIAS, precursor, o-Toluidine NIAS, degradation product, Diaminotoluene NIAS, intermediate, o-Anisidine NIAS, intermediate, 1,4,7-trioxacyclotridecane-8,13-dione, Myristamide NIAS, contaminant, Palmitamide NIAS, contaminant, Oleamide NIAS, contaminant, Stearamide NIAS, contaminant. | GC-MS and DART-MS | -- | [80] |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Oligomers; PC-degradation products | UHPLC–ESI Q-orbitrap | -- | [81] |
| Candy wrappers based on plastic and paper materials | 2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylene-2,5-cyclohexadienone, a degradation product of BHT, Diethyl maleate, Triacetin, Propanoic acid, 2-methyl-, 3-Hydroxy-2,4,4-trimethylpentyl ester, Diethyl phthalate, Diisobutyl phthalate, 7,9-Di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6-9-diene-2,8-dione, Heneicosane, Tributyl aconitate, Docosane, Tricosane, Tetracosane, Pentacosane, Hexacosane, Heptacosane, Octocosane, Squalene, n-Nonacosane, Glycerol tricaprylate | GC-MS | -- | [82] |
| Polyester-polyurethane lacquers | Impurities or degradation products of IPDI trimer IPDI and DPMDI, two cyclic oligoesters, 2EG + 2TPA and 2NPG + 2oPA | GC-(EI)qMS, GC-(EI)Orbitrap, GC-(APCI)TOFHRMS and GC(×GC)-(EI)TOFLRMS | -- | [83] |
| Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) | Cyclic oligomers from dimer to pentamer containing TPA and BD, cyclic oligomers, linear oligomers, dehydration products | HPLC-DAD/ESI-MS | -- | [84] |
| Multilayer plastic materials (polyethylene (PE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) plus nylon) | Four cyclic oligomers of caprolactam (dimer, trimer, tetramer, and pentamer); by-products-cyclic ester oligomers made of the monomers adipic acid (AA), phthalic acid (PA), diethylene glycol (DEG), monoethylene glycol (MEG) and neopentilglycol (NPG); Nylon cyclic dimer, Caprolactam Cyclic Trimer, AA-DEG, Caprolactam Cyclic Tetramer, Caprolactam Cyclic Pentamer, PA-DEG, Cyclic ester made up of Phthalic acid and diethylene glycol in combination 1:2, AA-MEG-AA-MEG, AA-MEG-AA-DEG, AA-DEG-AA-DEG, PA-MEG-AA-DEG, PA-DEG-PA-DEG, PA-DEG-AA-NPG, AA-BD, AA-BD-AA-BD, AA-DEG + H2O, AA-DEG-PA-DEG + H2O, 3,6,9,12,15-pentaoxabicyclo(15.3.1)henicosa-1(21),17,19-triene-2,16-dione, 1,6-dioxacyclodecane-7,12-dione, 1,6-dioxacyclodecane-7,12-dione, 1,6,13,18-tetraoxacyclotetracosane-2,5,14,17-tetrone | LC-HRAMS and LC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS | 3% acetic acid in water (w/v) and 20% of ethanol in water (v/v) | [85] |
| Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) films | Calcite (CaCO3), calcium sulphate (CaSO4), polystyrene (PS) and titanium dioxide (TiO2), Ca and Ti | Raman spectroscopy and ICP-MS | -- | [86] |
| Water-based acrylic adhesive | 2-(12-(methacryloyloxy) dodecyl)malonic acid | GC-MS and UPLC-QTOF | Poly(2,6-diphenyl-p-phenylene oxide) (Tenax®) | [87] |
| High and low-density polyethylene(HDPE and LDPE) | Phthalic anhydride, phthalic acid, di-butyl phthalate (DBP) and bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) | FIA-MS, LTQ-Orbitrap | -- | [88] |
| Multilayer materials with barrier properties | Acids (nonanoic acid), Alcohols (2-nonen-1-ol), Aldehydes (5-hydroxymethylfurfural), Aldehydes (5-hydroxymethylfurfural), Alkanes (n-dodecane), Alkenes (1-undecene), Antioxidants (2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol), Aromatics (1,3-di-tert-butyl-benzene), Cyclics (n-propyl-cyclohexane), Esters (ethyl hydrogen sebacate), Ethers (1,1′-oxybis-octane), Ketones (2-undecanone), Oxidation Products (2,6-di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone) | SPME–GC–MS | -- | [89] |
| Polyester Coatings | Oligomers | HPLC-DAD/CAD, HPLC-MS and HPLC-MS/MS | Water, 3% acetic acid, 10% ethanol, 50% ethanol, and isooctane | [90] |
| Low-density polyethylen-LDPE and polyamide-PA added of NBBS, α-MSD, Irganox 1081, Irganox 1222, Santonox; LDPE 2/PA 6 2: Nonox A, Neozon D, Antioxidant 2246, Tinuvin P, TOTM | Degradation products of TOTM, including DEHP, isophthalate bis(2-ethylhexyl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate (DOIP); decomposition product of NBBS was N-ethyl-N-methylbenzenesulfonamide; The formation of the cyclic saturated isomer (1,1,3-trimethyl-3-phenyl-2H-indene) is triggered by thermal impact, and so is the rearrangement of the carbon double bond to form isomer 2,4-diphenyl-4-methyl-2(E)-pentene). Decomposition product 2,3-dimethyl-3-phenylbutan-2-yl)benzene is formed by combining two cumyl radicals during pyrolysis of the pure additive and pyrolysis of LDPE entailing α-MSD. The degradation product of Neozon D and Nonox A identified in oxidative pyrolysis of the pure analyte was 10-methyl-benz[a]acridine; degradation products of Antioxidant 2246, Santonox, Irganox 1222/1081 and Tinuvin P: o-cresol, m-cresol or p-cresol, 2-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol and 2-tert-butyl-4,6-dimethylphenol, 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde | Pyr-GC–MS and GC-EI-MS/MS | -- | [91] |
2.1. Oligomers
| Food Contact Material | NIAS | Method/Technique | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Oligomers | UHPLC–ESI Q-orbitrap | [81] |
| Polyester Coatings | Oligomers | HPLC-DAD/CAD, HPLC-MS and HPLC-MS/MS | [40] |
| Polyester coatings based on NAH | Oligomers | LC-MS/MS and LC-TOF-MS | [50] |
| Polyester can coating extracts | Linear and cyclic oligomers derived from the incomplete polymerization of polyester monomers, phthalic acids and diols | HPLC-MS, HPLC-ESI MS and HPLC-HRMS/MS | [51] |
| Empty cans with lids coated with polyester resins | Oligomers | GC–MS, HPLC-DAD/MS, UHPLC-HRMS and DART-HRMS | [40] |
| Polyester resins, tin plate sheets coated with polyester–phenolic lacquers and corresponding press-twist-closures (equipped with plasticized polyvinyl chloride (PVC) sealings) | Polyester oligomers (cyclic oligomers, dimers, trimers and tetramers) | HPLC–DAD, HPLC–DAD/MS, GC-MS, GC–MSD and RP-HPLC–DAD/MS | [6] |
| Flexible multilayer materials point by polyurethane (PU) layers | Polyamide oligomers, PU oligomers (cyclic esters made up of phthalic acid (PA) | UPLC MS–QTOF | [72] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Cyclic oligomers | LC-MS | [5] |
| Virgin and recycled Polyethylene terephthalate-PET pellets | Cyclic and linear oligomers: TPA-EG, (TPA-EG)2 + H2O, (TPA-EG)2, (TPA-EG)3 + H20, (TPA-EG)3, (TPA-EG)4, and (TPA-EG)5, TPA2-EG-DEG + H2O, TPA2-EG-DEG, TPA3-EG2-DEG + H2O, TPA3-EG2-DEG, and TPA4-EG3-DEG, (TPA-DEG)2 and TPA4-EG2-DEG2 | UPLC-MS-QTOF | [52] |
| Baby food squeezes with multilayer materials (Polyethylene terephthalate-PET/aluminium-Al/polyethylene-PE) | Polyester oligomers, 29 cyclic and six linear oligomers. ε-caprolactam was tentatively identified as a heterogenic polyester oligomer combined with AA, DEG, PA and NPG; BHET and diethyl 5-(2-((2,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy)acetamido)isophthalate, methoxyeugenol and Bis(2-methoxyethyl) sebacate | UHPLC-ESI-QTOF MS | [53] |
| Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) | Cyclic oligomers from dimer to pentamer containing TPA and BD, cyclic oligomers, linear oligomers, dehydration products | HPLC-DAD/ESI-MS | [84] |
| Multilayer plastic materials (polyethylene (PE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) plus nylon | Four cyclic oligomers of caprolactam (dimer, trimer, tetramer, and pentamer); by-products-cyclic ester oligomers made of the monomers adipic acid (AA), phthalic acid (PA), diethylene glycol (DEG), monoethylene glycol (MEG) and neopentilglycol (NPG); Nylon cyclic dimer, Caprolactam Cyclic Trimer, AA-DEG, Caprolactam Cyclic Tetramer, Caprolactam Cyclic Pentamer, PA-DEG, Cyclic ester made up of Phthalic acid and diethylene glycol in combination 1:2, AA-MEG-AA-MEG, AA-MEG-AA-DEG, AA-DEG-AA-DEG, PA-MEG-AA-DEG, PA-DEG-PA-DEG, PA-DEG-AA-NPG, AA-BD, AA-BD-AA-BD, AA-DEG + H2O, AA-DEG-PA-DEG + H2O, 3,6,9,12,15-pentaoxabicyclo(15.3.1)henicosa-1(21),17,19-triene-2,16-dione, 1,6-dioxacyclodecane-7,12-dione, 1,6-dioxacyclodecane-7,12-dione, 1,6,13,18-tetraoxacyclotetracosane-2,5,14,17-tetrone | LC-HRAMS and LC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS | [85] |
| Polystyrene-PS cups and multilayer films | Styrene monomer and oligomers; polyester urethane-based oligomers (PU) cyclic oligomers: α-methylstyrene; 1,1-diphenyl-ethylene; 2,4-diphenyl-1-butene; trans-1,2-diphenycyclobutane; 2,4,6-triphenyl-1-hexene; | GC-MS | [68] |
2.2. By-Products Compounds or Side Products
| Food Contact Material | NIAS | Method/Technique | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active packaging: Polypropylene (PP); PP + green tea; PP/poly (ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) EVOH; PP/EVOH + oregano; PP/EVOH + citral; EVOH; Polyethylene terephthalate-PET/EVOH + citral; PET/EVOH + cinnamon; PP/EVOH/PP; PP/EVOH + oregano | Degradation of active compounds; impurities from the raw materials; additives used in the manufacture of the active polymer (citral thermal reaction products; oxidation product of citral; decomposition product of adipates used as plasticizers; impurity/reaction product/breakdown product for the additives used in the manufacture of PE materials; xanthenone derivates) | UPLC-QTOF-MS | [73] |
| Polyurethane adhesives in multilayer packaging materials | By-product of the polyester-based urethane 91,6-Dioxacyclododecane-7,12-dione); cyclic adipate; unknown nitrogen-compounds; unknown phenolic compounds; 1,4,7-Trioxacyclotridecane-8,13-dione | HS-SPME-GC-MS | [54] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), oriented polyamide (OPA), cast polypropylene (CPP), polyethylene (PE) and PE/ethyl vinyl alcohol PE(EVOH) | Primary aromatic amines-PAAs (1,8-diazacyclotetradecane-2,9-dione; caprolactam; 1,8,15-triazacycloheneicosane-2,9,16-trione; 1,3-bis(isocyanatomethyl)-cyclohexane, 1-cyanodecane and 1,4-bis(isocyanatomethyl)-cyclohexane; l-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-leucine; 1,4,7,18,21-pentaoxa-11,14,25,28-tetraazacyclohentriacontane (9CI); l-leucine; l-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-leucyl-l-leucyl-; butanediamide; N4-hydroxy-N1-[(1S)-2-methyl-1-(1-pyrrolidinylcarbonyl)propyl]-2-pentyl-, (2R)-; triethylamine, naphtylethylenediamine; 1,8,15,22-tetraazacyclooctacosane-2,9,16,23-tetrone; urea; N-cyclohexyl, urea, N-cyclohexy-N′-methyl and 1-(cyclohexycarbonyl)piperazine); Dimethyl phthalate | UHPLC–Q-TOF/MSE | [56] |
| Silicone moulds and teats | Side reactions in the polymerization (cyclic and linear polydimethylsiloxanes; oligomeric dimethyl siloxanes) | H-NMR and GC-MS | [76] |
| Multilayer plastic materials (polyethylene (PE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) plus nylon | By-products-cyclic ester oligomers made of the monomers adipic acid (AA), phthalic acid (PA), diethylene glycol (DEG), monoethylene glycol (MEG) and neopentilglycol (NPG) | LC-HRAMS and LC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS | [85] |
| Polypropylene food storage containers | By-product Benzothiazole | GC × GC−ToF MS | [64] |
| UV-curable varnishes over polypropylene | 2-propenoic acid,1,1′-[2-[[3-[2,2-bis[[(1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl)oxy]methyl]butoxy]-1-oxopropoxy]methyl]-2-ethyl-1,3-propanediyl] ester is considered a NIAS, as it is a reaction product coming from the monomer TMPTA, 11-diethyl-7-oxo-4,6,10,12-tetraoxopentadecane-3,13-diyl diacrylate | GC-MS/Q and UHPLC-IMS/QTOF | [55] |
2.3. Breakdown Products or Degradation Products
| Food Contact Material | NIAS | Method/Technique | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active packaging: Polypropylene (PP); PP + green tea; PP/poly (ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) EVOH; PP/EVOH + oregano; PP/EVOH + citral; EVOH; Polyethylene terephthalate-PET/EVOH + citral; PET/EVOH + cinnamon; PP/EVOH/PP; PP/EVOH + oregano | Degradation of active compounds; impurities from the raw materials; additives used in the manufacture of the active polymer (citral thermal reaction products; oxidation product of citral; decomposition product of adipates used as plasticizers; impurity/reaction product/breakdown product for the additives used in the manufacture of PE materials; xanthenone derivates) | UPLC-QTOF-MS | [73] |
| Polyurethane adhesives in multilayer packaging materials | Silane unknown compounds; degradation of antioxidants Irgafos and Irganox (2,6-Di-tert-butylbenzoquinone; isomer 2,5-di-tert-butylbenzoquinone; 7,9-Di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione; benzenepropanoic acid, 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxy-methyl) | HS-SPME-GC-MS | [54] |
| Hot melt adhesives (Ethylene-vinyl acetate-EVA and amorphous polyolefin APAO enriched in propene) | Degradation of Irganox 1010: 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde | UPLC-ESI-MS/QTOF | [59] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate-PET pellets | The degradation product of the antioxidants Irgafos 168 and Irganox 1010: 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethyl ethyl) phenol; 2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane; linear aldehydes; residual monomers: ethylene glycol (EG); thermal degradation products: toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene; phthalates (DEP, DIBP) | HS-SPME/GC-MS | [60] |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Oligomers; PC-degradation products | UHPLC–ESI Q-orbitrap | [81] |
| Polypropylene (PP) films | Degradation products from Irgafos 168, Tinuvin 326 and Irganox 1076 | HPLC-DAD and GC-FID–MS | [61] |
| Candy wrappers based on plastic and paper materials | 2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylene-2,5-cyclohexadienone, a degradation product of BHT, Diethyl maleate, Triacetin, Propanoic acid, 2-methyl-, 3-Hydroxy-2,4,4-trimethylpentyl ester, Diethyl phthalate, Diisobutyl phthalate, 7,9-Di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6-9-diene-2,8-dione, Heneicosane, Tributyl aconitate, Docosane, Tricosane, Tetracosane, Pentacosane, Hexacosane, Heptacosane, Octocosane, Squalene, n-Nonacosane, Glycerol tricaprylate | GC-MS | [82] |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Degradation products derived from phenolic antioxidants, impurity/reaction product/breakdown product of the additives, Family 1: Family formed with the reference structure; was formed by the compounds that had a similar structure constituted by a group 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl; Family 2: With glycerol molecule (glyceryl monostearate, glyceryl palmitate and glyceryl dihexadecanoate, an ester of an acid chain bonded to a glycerol molecule); Family 3: Dihydroxy alquilamines (amine bonded to two ethanol molecules and also an alkyl hydrocarbon chain); Family 4: ceramide and dihydroceramide (a family of waxy lipid molecules which are composed of sphingosine (an 18 carbon amino alcohol with an unsaturated hydrocarbon chain) and a fatty acid); Family 5: amides bonded by ethylene (degradation products from a lubricant losing C2H4); Other compounds (amides come from the impurities or degradation products from erucamide and oleamide widely used as slip agents) | UPLC-MS-QTOF | [58] |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol (degradation product of Irgafos 168 and Irganox® 1010), tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6-9-diene-2,8-dione (a by-product of the antioxidant Irganox 1010) and 2,6-di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone, a degradation product of antioxidants such as Irganox 1010, Irgafos 168 and Irganox PS 802 | GC-MS | [63] |
| Polypropylene random copolymer composite films | Irgafos 168 and its two degradation products, 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol (DP1) and tris (2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphate (DP2) | GC-MS | [57] |
| Plastic films (with and without printing ink) including PE: polyethylene. PET: Polyethylene terephthalate. PA: Polyamide. PP: Polypropylene. EVA: Ethylene-vinyl acetate. | 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol and 2,6-di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone. 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol is a degradation product of Irgafos 168 while 2,6-di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone is a degradation product of antioxidants such as Irganox 1010, Irgafos 168 and Irganox PS 802 | purge and trap (P&T) coupled to GC–MS | [62] |
| Polypropylene food storage containers | Degradation products, 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol and tris(2,4-di-tert-buthylphenyl)phosphate, methyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate, a compound identified as product of degradation of Irganox 1076 and/or Irganox 1010, 2,6-di-tert-butylbenzoquinone (isooctane fraction) and 7,9-di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione, 2-ethylhexanoic acid, 2-ethylhexanol, phthalic acid, mono-2-ethylhexyl phthalate), and consequently suggested as possible degradation products of this phthalate, by-product Benzothiazole, degradation products N,N-bis-(2-hydroxyethyl)alkyl amine | GC × GC−ToF MS | [64] |
| Polyethylene-PE, low-density polyethylene-LDPE and HIGH-density polyethylene-HDPE | Dibutyl amine, N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)alkylamines (impurity reaction or breakdown products), N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl) dodecylamine, tributylphosphine, tridodecylamine, Methyl (Ralox 35), ethyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propanoate (breakdown of Irganox 1010 or Irganox 1076), Benzenepropanoic acid, 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxy-, 1,1′-[2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediyl] ester and benzenepropanoic acid, 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxy-, 1,1′-[2-[[3-[3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl]-1-oxopropoxy]methyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediyl] ester (degradation of Irganox 1010), alkylamides N,N′-1,2-ethanediylbis-(breakdown or impurity products of the additive octadecanamide, N,N′-1,2-ethanediylbis), Irgafos 168 OXO (oxo-derivative of Irgafos 168), 11-eicosenamide (derived from oleamide) | UPLC IMS QTOF | [39] |
| Can coatings | Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP), Degradation products formed from antioxidants (1,3-di-tert-butylbenzene and 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol degradation products from antioxidants Irgafos 168 or Irganox 1076, 2,6-di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone degradation products from antioxidants Irgafos 168 and Irganox 1010, 7,9-di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione, a degradation product of Irganox 1010. | GC-MS and LC-MS/MS | [65] |
| Low-density polyethylene-LDPE and polyamide-PA added of NBBS, α-MSD, Irganox 1081, Irganox 1222, Santonox; LDPE 2/PA 6 2: Nonox A, Neozon D, Antioxidant 2246, Tinuvin P, TOTM | Degradation products of TOTM, including DEHP, isophthalate bis(2-ethylhexyl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate (DOIP); decomposition product of NBBS was N-ethyl-N-methylbenzenesulfonamide; The formation of the cyclic saturated isomer (1,1,3-trimethyl-3-phenyl-2H-indene) is triggered by the thermal impact, and so is the rearrangement of the carbon double bond to form isomer 2,4-diphenyl-4-methyl-2(E)-pentene). Decomposition product 2,3-dimethyl-3-phenylbutan-2-yl)benzene is formed by combining two cumyl radicals during pyrolysis of the pure additive and pyrolysis of LDPE entailing α-MSD. The degradation product of Neozon D and Nonox A identified in oxidative pyrolysis of the pure analyte was 10-methyl-benz[a]acridine; degradation products of Antioxidant 2246, Santonox, Irganox 1222/1081 and Tinuvin P: o-cresol, m-cresol or p-cresol, 2-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol and 2-tert-butyl-4,6-dimethylphenol, 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde | Pyr-GC–MS and GC-EI-MS/MS | [91] |
| Recycled pellets obtained from post-consumer low-density polyethylene (PC-LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (PC-HPDE) | Polymer degradation products: octanal and nonanal (aldehydes); 3-decanone, 2-undecanone, 2,2,4,4,6,8,8-heptamethylnonanone and 3-dodecanone (ketones); hexane (others); Additives degradation products: 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde (aldehyde); 2,6-di-tert-butyl-1,4-benzoquinone and 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyacetophenone (ketones); methyl tetradecanoate, ethyl tetradecanoate and ethyl palmitate(esters); 7,9-di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro (4,5)deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione (others); Contaminants from external sources: methyl lactate, hexyl acetate, and dimethyl butanedioate, α-methylionone, 3-(4-Isopropylphenyl)-2-methylpropionaldehyde, α-amylcinnamaldehyde, (phenylmethylene)octanal and dipropylene glycol amog others (cosmetic ingredients); alkylbenzenes (breakdown products produced by the degradation of alkylbenzene sulfonates); contamination related to food: the lactones, 5-methylfurfural, furfural and methyl hexanoate (can derive from food flavors as well as from cosmetics ingredients); furfuryl alcohol, methyl pyruvate and 2-acetyl pyridine (food flavors), methyl-2-ethylhexanoate, acetic acid, propanoic acid, pyridine and dimethyl trisulfide (rotten food products), 2,6-diisopropylnaphthalene (paper labels). | GC/MS and HS-SPME-GC/MS | [66] |
2.4. Impurities in the Raw Materials
2.5. Contaminants
References
- Bhunia, K.; Sablani, S.S.; Tang, J.; Rasco, B. Migration of Chemical Compounds from Packaging Polymers during Microwave, Conventional Heat Treatment, and Storage. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 523–545.
- Ubeda, S.; Aznar, M.; Rosenmai, A.K.; Vinggaard, A.M.; Nerín, C. Migration studies and toxicity evaluation of cyclic polyesters oligomers from food packaging adhesives. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 125918.
- Mistura, L.; Sette, S.; O’Mahony, C.; Engel, K.-H.; Mehegan, J.; Leclercq, C. Modelling framework for assessment of dietary exposure to added flavouring substances within the FACET (Flavours, Additives, and Food Contact Material Exposure Task) project. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 236–241.
- Grob, K.; Biedermann, M.; Scherbaum, E.; Roth, M.; Rieger, K. Food contamination with organic materials in perspective: Packaging materials as the largest and least controlled source? A view focusing on the European situation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 529–535.
- Hoppe, M.; Fornari, R.; de Voogt, P.; Franz, R. Migration of oligomers from PET: Determination of diffusion coefficients and comparison of experimental versus modelled migration. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 1251–1260.
- Eckardt, M.; Hetzel, L.; Brenz, F.; Simat, T.J. Release and migration of cyclic polyester oligomers from bisphenol A non-intent polyester–phenol-coatings into food simulants and infant food—A comprehensive study. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2020, 37, 681–703.
- Fasano, E.; Bono-Blay, F.; Cirillo, T.; Montuori, P.; Lacorte, S. Migration of phthalates, alkylphenols, bisphenol A and di(2-ethylhexyl)adipate from food packaging. Food Control. 2012, 27, 132–138.
- Whitt, M.; Brown, W.; Danes, J.E.; Vorst, K.L. Migration of heavy metals from recycled polyethylene terephthalate during storage and microwave heating. J. Plast. Film Sheeting 2016, 32, 189–207.
- Clemente, I.; Aznar, M.; Nerín, C.; Bosetti, O. Migration from printing inks in multilayer food packaging materials by GC-MS analysis and pattern recognition with chemometrics. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2016, 33, 703–714.
- Isella, F.; Canellas, E.; Bosetti, O.; Nerin, C. Migration of non intentionally added substances from adhesives by UPLC-Q-TOF/MS and the role of EVOH to avoid migration in multilayer packaging materials. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 48, 430–437.
- Song, X.-C.; Wrona, M.; Nerin, C.; Lin, Q.-B.; Zhong, H.-N. Volatile non-intentionally added substances (NIAS) identified in recycled expanded polystyrene containers and their migration into food simulants. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 20, 100318.
- Helmroth, I.E.; Bekhuis, H.A.M.; Linssen, J.P.H.; Dekker, M. Direct measurement of additive migration from low-density polyethylene as a function of space and time. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 3185–3190.
- Lee, D.S.; Yam, K.L.; Piergiovanni, L. Food Packaging Science and Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008.
- Alberto Lopes, J.; Tsochatzis, E.D.; Karasek, L.; Hoekstra, E.J.; Emons, H. Analysis of PBT and PET cyclic oligomers in extracts of coffee capsules and food simulants by a HPLC-UV/FLD method. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128739.
- Committee, E.S.; More, S.J.; Bampidis, V.; Benford, D.; Bragard, C.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Hernández-Jerez, A.F.; Hougaard Bennekou, S.; Koutsoumanis, K.P.; Machera, K.; et al. Guidance on the use of the Threshold of Toxicological Concern approach in food safety assessment. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05708.
- Eckardt, M.; Kubicova, M.; Simat, T.J. Universal response quantification approach using a Corona Charged Aerosol Detector (CAD)—Application on linear and cyclic oligomers extractable from polycondensate plastics polyesters, polyamides and polyarylsulfones. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1572, 187–202.
- Nelson, C.P.; Patton, G.W.; Arvidson, K.; Lee, H.; Twaroski, M.L. Assessing the toxicity of polymeric food-contact substances. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1877–1897.
- Muncke, J.; Myers, J.P.; Scheringer, M.; Porta, M. Food packaging and migration of food contact materials: Will epidemiologists rise to the neotoxic challenge? J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2014, 68, 592–594.
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Kotsanopoulos, K.V. Migration Phenomenon in Food Packaging. Food–Package Interactions, Mechanisms, Types of Migrants, Testing and Relative Legislation—A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 21–36.
- Fang, X.; Vitrac, O. Predicting diffusion coefficients of chemicals in and through packaging materials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 275–312.
- Xue, M.; Chai, X.-S.; Li, X.; Chen, R. Migration of organic contaminants into dry powdered food in paper packaging materials and the influencing factors. J. Food Eng. 2019, 262, 75–82.
- Nerín, C.; Aznar, M.; Carrizo, D. Food contamination during food process. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 48, 63–68.
- Tehrany, E.A.T.; Desobry, S. Partition coefficients in food/packaging systems: A review. Food Addit. Contam. 2004, 21, 1186–1202.
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Bosnea, L. Migration of substances from food packaging materials to foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 63–76.
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Velis, C.A.; Weber, R.; Iacovidou, E.; Purnell, P. An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 179–199.
- Begley, T.H.; Biles, J.E.; Cunningham, C.; Piringer, O. Migration of a UV stabilizer from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) into food simulants. Food Addit. Contam. 2004, 21, 1007–1014.
- Ferrara, G.; Bertoldo, M.; Scoponi, M.; Ciardelli, F. Diffusion coefficient and activation energy of Irganox 1010 in poly(propylene-co-ethylene) copolymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 73, 411–416.
- Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Liu, B.; Lin, Q.; Xia, Y. Identification of chemicals in a polyvinyl chloride/polyethylene multilayer film by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and their migration into solution. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1625, 461274.
- Chung, D.; Papadakis, S.E.; Yam, K.L. Simple models for assessing migration from food-packaging films. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 611–617.
- O’Brien, A.; Cooper, L. Polymer additive migration to foods—A direct comparison of experimental data and values calculated from migration models for polypropylene. Food Addit. Contam. 2001, 18, 343–355.
- Brandsch, J.; Mercea, P.; Rüter, M.; Tosa, V.; Piringer, O. Migration modelling as a tool for quality assurance of food packaging. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19 (Suppl. S1), 29–41.
- Begley, T.; Castle, L.; Feigenbaum, A.; Franz, R.; Hinrichs, K.; Lickly, T.; Mercea, P.; Milana, M.; O’Brien, A.; Rebre, S.; et al. Evaluation of migration models that might be used in support of regulations for food-contact plastics. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 73–90.
- Galotto, M.J.; Torres, A.; Guarda, A.; Moraga, N.; Romero, J. Experimental and theoretical study of LDPE versus different concentrations of Irganox 1076 and different thickness. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 566–574.
- Bott, J.; Störmer, A.; Franz, R. A model study into the migration potential of nanoparticles from plastics nanocomposites for food contact. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2014, 2, 73–80.
- Gavriil, G.; Kanavouras, A.; Coutelieris, F.A. Food-packaging migration models: A critical discussion. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2262–2272.
- Oldring, P.K.T.; O’Mahony, C.; Dixon, J.; Vints, M.; Mehegan, J.; Dequatre, C.; Castle, L. Development of a new modelling tool (FACET) to assess exposure to chemical migrants from food packaging. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 444–465.
- Katiyar, V. Sustainable Polymers for Food Packaging; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2020.
- Genualdi, S.; Nyman, P.; Begley, T. Updated evaluation of the migration of styrene monomer and oligomers from polystyrene food contact materials to foods and food simulants. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 723–733.
- Vera, P.; Canellas, E.; Barknowitz, G.; Goshawk, J.; Nerín, C. Ion-Mobility Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry: A Novel Technique Applied to Migration of Nonintentionally Added Substances from Polyethylene Films Intended for Use as Food Packaging. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12741–12751.
- Paseiro-Cerrato, R.; MacMahon, S.; Ridge, C.D.; Noonan, G.O.; Begley, T.H. Identification of unknown compounds from polyester cans coatings that may potentially migrate into food or food simulants. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1444, 106–113.
- Groh, K.J.; Backhaus, T.; Carney-Almroth, B.; Geueke, B.; Inostroza, P.A.; Lennquist, A.; Leslie, H.A.; Maffini, M.; Slunge, D.; Trasande, L.; et al. Overview of known plastic packaging-associated chemicals and their hazards. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3253–3268.
- Geueke, B.; Wagner, C.C.; Muncke, J. Food contact substances and chemicals of concern: A comparison of inventories. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2014, 31, 1438–1450.
- Groh, K.J.; Geueke, B.; Martin, O.; Maffini, M.; Muncke, J. Overview of intentionally used food contact chemicals and their hazards. Environ. Int. 2021, 150, 106225.
- Grob, K. Work plans to get out of the deadlock for the safety assurance of migration from food contact materials? A proposal. Food Control. 2014, 46, 312–318.
- Koster, S.; Bani-Estivals, M.H.; Bonuomo, M.; Bradley, E.; Chagnon, M.C.; García, M.L.; Godts, F.; Gude, T.; Helling, R.; Paseiro-Losada, P.; et al. Guidance on Best Practices on the Risk Assessment of Non-Intentionally Added Substances (Nias) in Food Contact Materials and Articles; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2015.
- Muncke, J.; Backhaus, T.; Geueke, B.; Maffini, M.V.; Martin, O.V.; Myers, J.P.; Soto, A.M.; Trasande, L.; Trier, X.; Scheringer, M. Scientific Challenges in the Risk Assessment of Food Contact Materials. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 95001.
- Nerin, C.; Alfaro, P.; Aznar, M.; Domeño, C. The challenge of identifying non-intentionally added substances from food packaging materials: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 775, 14–24.
- Wrona, M.; Nerín, C. Analytical Approaches for Analysis of Safety of Modern Food Packaging: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 752.
- U.S. FDA CFR—Code of Federal Regulations Title 21. Available online: (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Driffield, M.; Garcia-Lopez, M.; Christy, J.; Lloyd, A.S.; Tarbin, J.A.; Hough, P.; Bradley, E.L.; Oldring, P.K.T. The determination of monomers and oligomers from polyester-based can coatings into foodstuffs over extended storage periods. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2018, 35, 1200–1213.
- Pietropaolo, E.; Albenga, R.; Gosetti, F.; Toson, V.; Koster, S.; Marin-Kuan, M.; Veyrand, J.; Patin, A.; Schilter, B.; Pistone, A.; et al. Synthesis, identification and quantification of oligomers from polyester coatings for metal packaging. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1578, 15–27.
- Ubeda, S.; Aznar, M.; Nerín, C. Determination of oligomers in virgin and recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET) samples by UPLC-MS-QTOF. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2377–2384.
- Bauer, A.; Jesús, F.; Gómez Ramos, M.J.; Lozano, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Identification of unexpected chemical contaminants in baby food coming from plastic packaging migration by high resolution accurate mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 274–288.
- Felix, J.S.; Isella, F.; Bosetti, O.; Nerin, C. Analytical tools for identification of non-intentionally added substances (NIAS) coming from polyurethane adhesives in multilayer packaging materials and their migration into food simulants. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2869–2882.
- Canellas, E.; Vera, P.; Nerín, C. Ion mobility quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the identification of non-intentionally added substances in UV varnishes applied on food contact materials. A safety by design study. Talanta 2019, 205, 120103.
- Pezo, D.; Fedeli, M.; Bosetti, O.; Nerín, C. Aromatic amines from polyurethane adhesives in food packaging: The challenge of identification and pattern recognition using Quadrupole-Time of Flight-Mass SpectrometryE. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 756, 49–59.
- Yan, Y.; Hu, C.-Y.; Wang, Z.-W.; Jiang, Z.-W. Degradation of Irgafos 168 and migration of its degradation products from PP-R composite films. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2018, 31, 679–688.
- Vera, P.; Canellas, E.; Nerín, C. Identification of non volatile migrant compounds and NIAS in polypropylene films used as food packaging characterized by UPLC-MS/QTOF. Talanta 2018, 188, 750–762.
- Vera, P.; Canellas, E.; Nerín, C. Identification of non-volatile compounds and their migration from hot melt adhesives used in food packaging materials characterized by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4747–4754.
- Kassouf, A.; Maalouly, J.; Chebib, H.; Rutledge, D.N.; Ducruet, V. Chemometric tools to highlight non-intentionally added substances (NIAS) in polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Talanta 2013, 115, 928–937.
- Riquet, A.M.; Breysse, C.; Dahbi, L.; Loriot, C.; Severin, I.; Chagnon, M.C. The consequences of physical post-treatments (microwave and electron-beam) on food/packaging interactions: A physicochemical and toxicological approach. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 59–69.
- Garcia Ibarra, V.; de Quiros, A.R.; Paseiro Losada, P.; Sendon, R. Non-target analysis of intentionally and non intentionally added substances from plastic packaging materials and their migration into food simulants. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 21, 100325.
- Garcia Ibarra, V.; de Quiros, A.R.; Paseiro Losada, P.; Sendon, R. Identification of intentionally and non-intentionally added substances in plastic packaging materials and their migration into food products. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3789–3803.
- Carrero-Carralero, C.; Escobar-Arnanz, J.; Ros, M.; Jiménez-Falcao, S.; Sanz, M.L.; Ramos, L. An untargeted evaluation of the volatile and semi-volatile compounds migrating into food simulants from polypropylene food containers by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Talanta 2019, 195, 800–806.
- Lestido Cardama, A.; Sendón, R.; Bustos, J.; Santillana, M.I.; Paseiro Losada, P.; Rodríguez Bernaldo de Quirós, A. GC-MS Screening for the Identification of Potential Migrants Present in Polymeric Coatings of Food Cans. Polymers 2019, 11, 2086.
- Horodytska, O.; Cabanes, A.; Fullana, A. Non-intentionally added substances (NIAS) in recycled plastics. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126373.
- Rajbux, C.; Pereira, J.; do Céu Selbourne, M.; Costa-Pinto, A.R.; Poças, F. Assessment of baby Bibs. GC-MS screening, migration into saliva and insight of toxicity with QSAR tools. Food Control. 2020, 109, 106951.
- Tsochatzis, E.D.; Gika, H.; Theodoridis, G. Development and validation of a fast gas chromatography mass spectrometry method for the quantification of selected non-intentionally added substances and polystyrene/polyurethane oligomers in liquid food simulants. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1130, 49–59.
- Carrizo, D.; Maccagnan, A.; Felix, J.S.; Nerin, C.; Bosetti, O. The Barrier Effect of EVOH versus 1,4,7-Triaxocyclotridecane-8,13-Dione, a Non-intentionally Added Compound from Polyurethane Adhesives in Multilayer Food Packaging. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2015, 28, 1039–1046.
- Vaclavikova, M.; Paseiro-Cerrato, R.; Vaclavik, L.; Noonan, G.O.; De Vries, J.; Begley, T.H. Target and non-target analysis of migrants from PVC-coated cans using UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS: Evaluation of long-term migration testing. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2016, 33, 352–363.
- Martinez-Bueno, M.J.; Hernando, M.D.; Ucles, S.; Rajski, L.; Cimmino, S.; Fernandez-Alba, A.R. Identification of non-intentionally added substances in food packaging nano films by gas and liquid chromatography coupled to orbitrap mass spectrometry. Talanta 2017, 172, 68–77.
- Úbeda, S.; Aznar, M.; Vera, P.; Nerín, C.; Henríquez, L.; Taborda, L.; Restrepo, C. Overall and specific migration from multilayer high barrier food contact materials—Kinetic study of cyclic polyester oligomers migration. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 1784–1794.
- Aznar, M.; Rodriguez-Lafuente, A.; Alfaro, P.; Nerin, C. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS analysis of non-volatile migrants from new active packaging materials. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 1945–1957.
- Aznar, M.; Gómez-Estaca, J.; Vélez, D.; Devesa, V.; Nerín, C. Migrants determination and bioaccessibility study of ethyl lauroyl arginate (LAE) from a LAE based antimicrobial food packaging material. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 56, 363–370.
- Aznar, M.; Domeno, C.; Nerin, C.; Bosetti, O. Set-off of non volatile compounds from printing inks in food packaging materials and the role of lacquers to avoid migration. Dye Pigment 2015, 114, 85–92.
- Helling, R.; Seifried, P.; Fritzsche, D.; Simat, T.J. Characterisation and migration properties of silicone materials during typical long-term commercial and household use applications: A combined case study. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2012, 29, 1489–1500.
- Yan, J.W.; Hu, C.; Tong, L.H.; Lei, Z.X.; Lin, Q.-B. Migration test and safety assessment of polyurethane adhesives used for food-contact laminated films. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 23, 100449.
- Panseri, S.; Chiesa, L.M.; Zecconi, A.; Soncini, G.; De Noni, I. Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) from wrapping films and wrapped PDO Italian cheeses by using HS-SPME and GC/MS. Molecules 2014, 19, 8707–8724.
- Aznar, M.; Alfaro, P.; Nerin, C.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fabric phase sorptive extraction: An innovative sample preparation approach applied to the analysis of specific migration from food packaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 936, 97–107.
- Kuki, Á.; Nagy, L.; Nagy, T.; Zsuga, M.; Kéki, S. Screening of additives and other chemicals in polyurethanes by direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry (DART-MS). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 6149–6162.
- Bignardi, C.; Cavazza, A.; Corradini, C.; Salvadeo, P. Targeted and untargeted data-dependent experiments for characterization of polycarbonate food-contact plastics by ultra high performance chromatography coupled to quadrupole orbitrap tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1372C, 133–144.
- Galmán Graíño, S.; Sendón, R.; López Hernández, J.; Rodríguez-Bernaldo de Quirós, A.; Graíño, S.G.; Sendón, R.; Hernández, J.L.; de Quirós, A.R.-B. GC-MS screening analysis for the identification of potential migrants in plastic and paper-based candy wrappers. Polymers 2018, 10, 802.
- Omer, E.; Bichon, E.; Hutinet, S.; Royer, A.-L.; Monteau, F.; Germon, H.; Hill, P.; Remaud, G.; Dervilly-Pinel, G.; Cariou, R.; et al. Toward the characterisation of non-intentionally added substances migrating from polyester-polyurethane lacquers by comprehensive gas chromatography-mass spectrometry technologies. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1601, 327–334.
- Brenz, F.; Linke, S.; Simat, T. Linear and cyclic oligomers in polybutylene terephthalate for food contact materials. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2018, 35, 583–598.
- Gómez Ramos, M.J.; Lozano, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. High-resolution mass spectrometry with data independent acquisition for the comprehensive non-targeted analysis of migrating chemicals coming from multilayer plastic packaging materials used for fruit purée and juice. Talanta 2019, 191, 180–192.
- Portesi, C.; Visentin, D.; Durbiano, F.; Abete, M.C.; Rizzi, M.; Maurino, V.; Rossi, A.M. Development of a rapid micro-Raman spectroscopy approach for detection of NIAS in LDPE pellets and extruded films for food packaging applications. Polym. Test. 2019, 80, 106098.
- Canellas, E.; Vera, P.; Nerín, C. Migration assessment and the “threshold of toxicological concern” applied to the safe design of an acrylic adhesive for food-contact laminates. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 1721–1729.
- Habchi, B.; Kassouf, A.; Padellec, Y.; Rathahao-Paris, E.; Alves, S.; Rutledge, D.N.; Maalouly, J.; Ducruet, V. An untargeted evaluation of food contact materials by flow injection analysis-mass spectrometry (FIA-MS) combined with independent components analysis (ICA). Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1022, 81–88.
- Salafranca, J.; Clemente, I.; Isella, F.; Nerín, C.; Bosetti, O. Influence of oxygen and long term storage on the profile of volatile compounds released from polymeric multilayer food contact materials sterilized by gamma irradiation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 878, 118–130.
- Paseiro-Cerrato, R.; DeJager, L.; Begley, T.H. Assessment of the Impact of Accelerated Migration Testing for Coated Food Cans Using Food Simulants. Molecules 2019, 24, 3123.
- Bartsch, N.; Girard, M.; Wilde, A.; Bruhn, T.; Kappenstein, O.; Vieth, B.; Hutzler, C.; Luch, A. Thermal Stability of Polymer Additives: Comparison of Decomposition Models Including Oxidative Pyrolysis. J. Vinyl. Addit. Technol. 2019, 25, E12–E27.
- Hoppe, M.; de Voogt, P.; Franz, R. Identification and quantification of oligomers as potential migrants in plastics food contact materials with a focus in polycondensates—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 118–130.
- EFSA; WHO. European Food Safety Authority and World Health Organization Review of the Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC) approach and development of new TTC decision tree. EFSA Support. Publ. 2016, 13, 1006E.
- EFSA Panel on Food Contact Materials, Enzymes, Flavourings and Processing Aids (CEF). Scientific Opinion on the safety assessment of the substance, furan-2, 5-dicarboxylic acid, CAS No 3238-40-2, for use in food contact materials. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3866.
- Gelbke, H.-P.; Banton, M.; Block, C.; Dawkins, G.; Leibold, E.; Pemberton, M.; Sakoda, A.; Yasukawa, A. Oligomers of styrene are not endocrine disruptors. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2018, 48, 471–499.
- Paseiro-Cerrato, R.; Noonan, G.O.; Begley, T.H. Evaluation of Long-Term Migration Testing from Can Coatings into Food Simulants: Polyester Coatings. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2377–2385.
- Campanella, G.; Ghaani, M.; Quetti, G.; Farris, S. On the origin of primary aromatic amines in food packaging materials. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 137–143.
- Wrona, M.; Nerin, C. CHAPTER 7 Risk Assessment of Plastic Packaging for Food Applications. In Food Contact Materials Analysis: Mass Spectrometry Techniques; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2019; pp. 163–191. ISBN 978-1-78801-124-2.
- Peters, R.J.B.; Groeneveld, I.; Sanchez, P.L.; Gebbink, W.; Gersen, A.; de Nijs, M.; van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Review of analytical approaches for the identification of non-intentionally added substances in paper and board food contact materials. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 44–54.
- McCombie, G.; Hötzer, K.; Daniel, J.; Biedermann, M.; Eicher, A.; Grob, K. Compliance work for polyolefins in food contact: Results of an official control campaign. Food Control. 2016, 59, 793–800.
- Karmaus, A.L.; Osborn, R.; Krishan, M. Scientific advances and challenges in safety evaluation of food packaging materials: Workshop proceedings. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 98, 80–87.




