
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Asfar Azmi | + 1618 word(s) | 1618 | 2021-06-08 11:35:56 | | | |
| 2 | Lindsay Dong | Meta information modification | 1618 | 2021-06-29 10:18:00 | | |
Video Upload Options
Pancreatic cancer is a highly aggressive and lethal malignancy mostly due to its late-stage presentation. This malignancy is difficult to diagnose, monitor, and treat, hence the development of novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers and better therapeutic strategies are urgently needed. Several groundbreaking discoveries over the past decade on cancer-associated exosomes demonstrated an association between exosomal miRNA and the development, progression, and therapy-resistance of pancreatic cancer.
1. Introduction
Due to the variations in tissue types within the pancreas, it gives rise to tumors of multiple origins broadly categorized into exocrine and endocrine tumors [1]. Among them, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is responsible for the highest morbidity not only in exocrine tissue-derived malignancy but also among all pancreatic cancer types [2]. PDAC can be localized, locally advanced invasive, or metastasized to distant organs, [2] most commonly the liver [3][4]. Alterations in other tumor suppressor genes include CDKN2A [5], TP53 [6], and DPC4/SMAD4 [7].
Surgical removal of the tumor mass is considered as the only curative treatment of PDAC [8][9], but most cases are being diagnosed at more advanced stages [8][10] and only 15–20% of patients are eligible for surgery [8][9]. Despite the success of surgery, a large number of patients experience disease recurrence either locally or distantly within a year, keeping the five-year survival rate as low as 20% [11]. A number of pathological factors, such as resection margin status as well as lymph node and perineural invasions, are associated with such recurrence [12][13][14][15]. The carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9) is frequently elevated in 75–85% of PDAC patients [16], but it lacks sensitivity (80%) and specificity (73%) as a biomarker of PDAC [8][10][17].
One of the major players in tumor microenvironment-associated intercellular communication is exosomes. The cargo of exosomes contains lipids, proteins, metabolites, and genetic material, including DNA, mRNA, microRNAs (miRNAs), and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) [18][19][20]. Mounting evidence has revealed that exosomal miRNAs are intensely connected with various cancers, including pancreatic cancer [21]. In this current review, we discuss recent advancements in diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutics for pancreatic cancer utilizing novel findings of exosomal miRNAs.
2. Exosomal miRNAs and Pancreatic Cancer
Differential expression of miRNAs is observed in normal pancreatic ductal cells and pancreatic cancer cells. The elevation of about twenty circulatory miRNAs has been demonstrated in pancreatic cancer patients. The miRNA panel detected in plasma served as promising biomarkers for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer [22][23][24][25][26][27][28][29]. For being one of the most important cargos of exosomes [30], exosomal miRNAs went through excessive profiling in different cancers, including pancreatic cancer [31][32][33][34][35][36].
In pancreatic cancer cells, Sun et al. showed that IL-26 level was regulated by the exosomes loaded with miR-3607-3p secreted by natural killer (NK) cells, which suppressed disease progression in vivo [37]. It has been demonstrated that activated pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) continuously release miR-21-enriched exosomes that are endocytosed by pancreatic cancer cells. The abundant miR-21 inside cancer cells activates RAS/ERK signaling and induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) [38]. This allows cancer cells to repair their DNA and repopulate with residual tumor cells [39]. The exosomal miRNA-mediated regulations of pancreatic cancer are summarized in Figure 1.
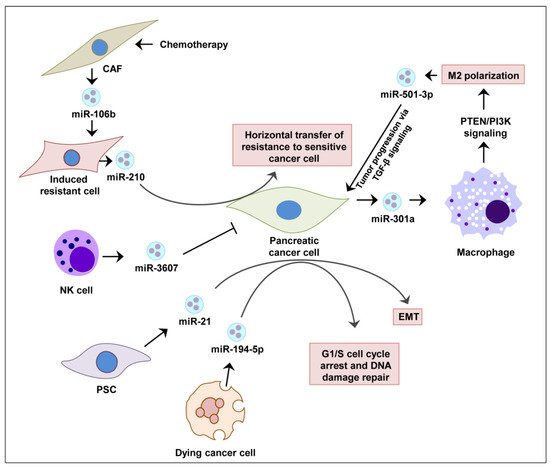
3. Exosomal miRNAs as a Prognostic Biomarker in PDAC
The exosomal miRNA-mediated cell-to-cell signaling in the tumor microenvironment plays a significant role in the progression of cancer [40][41]. In the primary tumor exosomes, selective miRNAs are enriched, exceeding the levels of normal cells that affect specific signaling pathways associated with cancer progression [42][33][35][43]. In a mechanistic study of pancreatic cancer, it has been demonstrated that enriched miR-21 and miR-221 take part in the crosstalk among pancreatic cancer cells, pancreatic stellate cells, and cancer-associated fibroblasts [44]. It is speculated that such crosstalk was governed by the release of exosomal miRNAs from cancer cells to neighboring cells.
Pancreatic cancer cells were shown to release exosomes enriched with miR-301a under hypoxic conditions. Mechanistically, miR-301a was found to contribute to the polarization of M2 macrophages via PTEN/PI3K signaling and the metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells [45] In the tumor microenvironment of pancreatic cancer, M2 macrophages can release exosomes enriched in miR-501-3p. MiR-501-3p suppresses TGFBR3, a tumor suppressor gene, and promotes pancreatic cancer development and progression via the activation of the TGF-β signaling pathway [46] as well as IL10 and arginase secretion [45].
In contrast to a cancer-promoting role of exosomal miRNAs, a recent pancreatic cancer study found that exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC) contain elevated levels of miR-126-3p, which subsequently downregulate ADAM9 and suppress cancer progression [47]. Moreover, exosomal miR-145-5p derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells was reported to reduce the progression of pancreatic cancer [48]. A study also demonstrated that potential miRNA biomarkers derived from portal vein blood exosomes (miR-4525, miR-451a, and miR-21) can be utilized for the evaluation of pancreatic cancer recurrence and overall survival [49]. In vitro and in vivo studies conducted by Shang et al. demonstrated that exosomal-derived miR-27a from pancreatic cancer cells promotes angiogenesis of human microvascular endothelial cells via BTG2 [50].
miRNAs can be utilized to assess therapy response. For example, plasma miR-221 levels are elevated in pancreatic cancer patients after just three weeks of lapatinib and capecitabine treatment. Exosomes from lapatinib- and capecitabine-treated pancreatic cancer patients likely contain elevated levels of miR-221. Therefore, exosomal miR-221 may serve as a potential biomarker to predict therapy response against these two drugs during the treatment period.
Recent studies have constructed the foundation of exosomal miRNA biomarker research for the assessment of proliferation, migration, and invasion in pancreatic cancer. However, the exchange mechanism of exosomes between cancer cells and stromal cells and how they regulate recipient cells remains to be defined. Sufficient longitudinal studies are essential for the proper identification of exosomal miRNA as prognostic biomarkers in PDAC.
4. Exosomal miRNAs in the Treatment of PDAC
A recent in vivo study has demonstrated the ability of exosomes to cross the blood–brain barrier and deliver siRNAs into the brain [51]. Evidence also showed the absorption of therapeutic exosomal content by target cells in a mouse model when introduced intravenously. Additionally, toxic side effects have not been observed in vivo even after repeated injection of exosomes derived from mesenchymal or epithelial cells [52]. The tolerability of exosomes collected from mesenchymal stem cells was demonstrated by Kordelas et al.
A growing body of research findings suggests that exosomes can be used for treating pancreatic cancer in the clinic for disease stabilization or reduction of aggressiveness [53]. The use of exosomes has been drawing intense attention because of their capability to transfer diverse biomolecules, including miRNAs, that may modulate the tumor microenvironment in an interactive fashion [53].
The initiation of pancreatic cancer is a multi-step process that starts with the mutations of certain genes, such as KRAS, TP53, and CDKN2A [54]. More than 90% of cases show activating KRAS mutations in pancreatic cancer [55] that are being considered attractive targets by any means, including through exosomal regulation. In 2017, engineered exosomes loaded with siRNAs were first introduced in a mouse model for PDAC. After subsequent verification of their safety and efficacy in organoid and patient-derived tumor xenograft models, it can be expected that engineered exosomes can be used as vehicles to deliver miRNAs as therapeutic agents for the targeted treatment of PDAC.
Thus far, the use of engineered exosomes in pancreatic cancer is still in its infancy. There are ample studies that identified a number of miRNAs for targeting pancreatic cancer [56][57]. Xia et al. demonstrated that miR-7 can block pancreatic cancer via suppression of cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Using such a strategy, it can be expected that the delivery of exosomal miR-7 will have more pronounced effect in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
5. Future Perspective
In future studies, the molecular and cellular processes by which miRNAs as exosomal cargoes exert their effects on the growth and invasive properties of cancer cells should also be examined under hypoxic experimental conditions. As discussed earlier, some cancer-relevant miRNAs are exclusively upregulated in hypoxic cancer cells. While most studies are being performed under normoxic conditions, the experimental results and may not be readily applicable to in vivo cancer models or humans. Another under-studied area is the feedback loop of exosomal-miRNA-based regulation besides unidirectional signaling, which also requires further attention. So far exosome-based treatment is limited to in vitro and in vivo experiments for pancreatic cancer. Besides preclinical, clinical investigations are essential to identify universal exosomal miRNA signatures for the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of pancreatic cancer. In summary, extensive research on exosomal miRNAs in pancreatic cancer is needed to overcome current obstacles and guide current progress ahead toward a novel biomarker discovery and a new therapeutic avenue.
References
- Lanfredini, S.; Thapa, A.; O’Neill, E. RAS in pancreatic cancer. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 961–972.
- Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Williams, A.; Ding, W. The role of exosomal microRNAs in pancreatic cancer. Stem Cell Investig. 2020, 7.
- Gao, X.; Wan, Z.; Wei, M.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Qin, W.; Yang, G.; Liu, L. Chronic myelogenous leukemia cells remodel the bone marrow niche via exosome-mediated transfer of miR-320. Theranostics 2019, 9, 5642–5656.
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826.
- Waddell, N.; Pajic, M.; Patch, A.M.; Chang, D.K.; Kassahn, K.S.; Bailey, P.; Johns, A.L.; Miller, D.; Nones, K.; Quek, K.; et al. Whole genomes redefine the mutational landscape of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 518, 495–501.
- Hingorani, S.R.; Wang, L.; Multani, A.S.; Combs, C.; Deramaudt, T.B.; Hruban, R.H.; Rustgi, A.K.; Chang, S.; Tuveson, D.A. Trp53R172H and KrasG12D cooperate to promote chromosomal instability and widely metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 469–483.
- Martinez-Useros, J.; Garcia-Foncillas, J. Can Molecular Biomarkers Change the Paradigm of Pancreatic Cancer Prognosis? BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4873089.
- Ryan, D.P.; Hong, T.S.; Bardeesy, N. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1039–1049.
- Vincent, A.; Herman, J.; Schulick, R.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2011, 378, 607–620.
- Bond-Smith, G.; Banga, N.; Hammond, T.M.; Imber, C.J. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. BMJ 2012, 344, e2476.
- Garrido-Laguna, I.; Hidalgo, M. Pancreatic cancer: From state-of-the-art treatments to promising novel therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 319–334.
- Sohn, T.A.; Yeo, C.J.; Cameron, J.L.; Koniaris, L.; Kaushal, S.; Abrams, R.A.; Sauter, P.K.; Coleman, J.; Hruban, R.H.; Lillemoe, K.D. Resected adenocarcinoma of the pancreas-616 patients: Results, outcomes, and prognostic indicators. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2000, 4, 567–579.
- Winter, J.M.; Cameron, J.L.; Campbell, K.A.; Arnold, M.A.; Chang, D.C.; Coleman, J.; Hodgin, M.B.; Sauter, P.K.; Hruban, R.H.; Riall, T.S. 1423 Pancreaticoduodenectomies for Pancreatic Cancer: A Single-Institution Experience. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2006, 10, 1199–1211.
- van Roest, M.H.G.; Gouw, A.S.H.; Peeters, P.M.J.G.; Porte, R.J.; Slooff, M.J.H.; Fidler, V.; de Jong, K.P. Results of pancreaticoduodenectomy in patients with periampullary adenocarcinoma: Perineural growth more important prognostic factor than tumor localization. Ann. Surg. 2008, 248, 97–103.
- Kuhlmann, K.; De Castro, S.; Wesseling, J.; Kate, F.T.; Offerhaus, G.; Busch, O.; Van Gulik, T.; Obertop, H.; Gouma, D. Surgical treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Actual survival and prognostic factors in 343 patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 549–558.
- Ballehaninna, U.K.; Chamberlain, R.S. The clinical utility of serum CA 19-9 in the diagnosis, prognosis and management of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: An evidence based appraisal. J. Gastrointest Oncol. 2012, 3, 105–119.
- Winter, J.M.; Yeo, C.J.; Brody, J.R. Diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 107, 15–22.
- Wu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Lv, D.; Zhu, X.; Tang, H. Exosome-mediated communication in the tumor microenvironment contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 53.
- Hannafon, B.N.; Ding, W.-Q. Intercellular Communication by Exosome-Derived microRNAs in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14240–14269.
- Chen, K.; Wang, Q.; Kornmann, M.; Tian, X.; Yang, Y. The Role of Exosomes in Pancreatic Cancer from Bench to Clinical Application: An Updated Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 644358.
- Li, L.-M.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.-H.; Hu, H.-B.; Liu, S.-M. Clinical significance of exosomal miRNAs and proteins in three human cancers with high mortality in China. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 11–22.
- Cote, G.A.; Gore, A.J.; McElyea, S.D.; Heathers, L.E.; Xu, H.; Sherman, S.; Korc, M. A Pilot Study to Develop a Diagnostic Test for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Based on Differential Expression of Select miRNA in Plasma and Bile. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 1942–1952.
- Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Du, Y.; Yao, W.; Shen, L.; Wang, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhuang, R.; Ning, G.; Zhang, C.; et al. Serum MicroRNA Expression Profile as a Biomarker in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 610–618.
- Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Takeshita, H.; Morimura, R.; Hirajima, S.; Tsujiura, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Miyamae, M.; Nagata, H.; Konishi, H.; et al. Circulating miR-18a: A sensitive cancer screening biomarker in human cancer. In Vivo 2014, 28, 293–297.
- Morimura, R.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Takeshita, H.; Tsujiura, M.; Nagata, H.; Konishi, H.; Shiozaki, A.; Ikoma, H.; Okamoto, K.; et al. Novel diagnostic value of circulating miR-18a in plasma of patients with pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1733–1740.
- Liffers, S.-T.; Munding, J.B.; Vogt, M.; Kuhlmann, J.D.; Verdoodt, B.; Nambiar, S.; Maghnouj, A.; Mirmohammadsadegh, A.; Hahn, S.A.; Tannapfel, A. MicroRNA-148a is down-regulated in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas and regulates cell survival by targeting CDC25B. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 1472–1479.
- Munding, J.; Adai, A.T.; Maghnouj, A.; Urbanik, A.; Zöllner, H.; Liffers, S.T.; Chromik, A.M.; Uhl, W.; Szafranska-Schwarzbach, A.E.; Tannapfel, A.; et al. Global microRNA expression profiling of microdissected tissues identifies miR-135b as a novel biomarker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, E86–E95.
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.-Y.; Zhang, S.-H.; Yu, D.-H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.-H.; Shi, M.; Ni, C.-R.; Zhu, M.-H. Upregulation of miR-194 contributes to tumor growth and progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1157–1164.
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shi, M.; Ni, C.; Zhu, M. Diagnostic and biological significance of microRNA-192 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 276–284.
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659.
- Barceló, M.; Castells, M.; Bassas, L.; Vigués, F.; Larriba, S. Semen miRNAs Contained in Exosomes as Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13772.
- Zhang, X.; Sai, B.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, G.; Tang, J.; Xiang, J. Hypoxic BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs promote metastasis of lung cancer cells via STAT3-induced EMT. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 40.
- Hannafon, B.N.; Trigoso, Y.D.; Calloway, C.L.; Zhao, Y.D.; Lum, D.H.; Welm, A.L.; Zhao, Z.J.; Blick, K.E.; Dooley, W.C.; Ding, W.Q. Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 90.
- Xu, Y.-F.; Hannafon, B.N.; Khatri, U.; Gin, A.; Ding, W.-Q. The origin of exosomal miR-1246 in human cancer cells. RNA Biol. 2019, 16, 770–784.
- Xu, Y.-F.; Hannafon, B.N.; Zhao, Y.D.; Postier, R.G.; Ding, W.-Q. Plasma exosome miR-196a and miR-1246 are potential indicators of localized pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 77028–77040.
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Geng, C.; Zhou, H.; Gao, W.; Chen, W. Serum exosomal microRNAs as novel biomarkers for multiple myeloma. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 409–417.
- Sun, H.; Shi, K.; Qi, K.; Kong, H.; Zhang, J.; Dai, S.; Ye, W.; Deng, T.; He, Q.; Zhou, M. Natural killer cell-derived exosomal miR-3607-3p inhibits pancreatic cancer progression by targeting IL-26. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2819.
- Ma, Q.; Wu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, Z.; Liu, T. Upregulation of exosomal microRNA-21 in pancreatic stellate cells promotes pancreatic cancer cell migration and enhances Ras/ERK pathway activity. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 1025–1033.
- Jiang, M.; Chen, Y.; Dai, J.; Gu, D.; Mei, Z.; Liu, F.; Huang, Q.; Tian, L. Dying tumor cell-derived exosomal miR-194-5p potentiates survival and repopulation of tumor repopulating cells upon radiotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 1–15.
- Thind, A.; Wilson, C. Exosomal miRNAs as cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 31292.
- Pitt, J.M.; Kroemer, G.; Zitvogel, L. Extracellular vesicles: Masters of intercellular communication and potential clinical interventions. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1139–1143.
- Hannafon, B.N.; Carpenter, K.J.; Berry, W.L.; Janknecht, R.; Dooley, W.C.; Ding, W.-Q. Exosome-mediated microRNA signaling from breast cancer cells is altered by the anti-angiogenesis agent docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 1–13.
- Pigati, L.; Yaddanapudi, S.C.S.; Iyengar, R.; Kim, D.-J.; Hearn, S.A.; Danforth, D.; Hastings, M.; Duelli, D.M. Selective Release of MicroRNA Species from Normal and Malignant Mammary Epithelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13515.
- Ali, S.; Suresh, R.; Banerjee, S.; Bao, B.; Xu, Z.; Wilson, J.; Philip, P.A.; Apte, M.; Sarkar, F.H. Contribution of microRNAs in understanding the pancreatic tumor microenvironment involving cancer associated stellate and fibroblast cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1251–1264.
- Wang, X.; Luo, G.; Zhang, K.; Cao, J.; Huang, C.; Jiang, T.; Liu, B.; Su, L.; Qiu, Z. Hypoxic Tumor-Derived Exosomal miR-301a Mediates M2 Macrophage Polarization via PTEN/PI3Kgamma to Promote Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4586–4598.
- Yin, Z.; Ma, T.; Huang, B.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, J.; Zou, Y.; Chen, S. Macrophage-derived exosomal microRNA-501-3p promotes progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through the TGFBR3-mediated TGF-beta signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 310.
- Wu, D.-M.; Wen, X.; Han, X.-R.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.-J.; Shen, M.; Fan, S.-H.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Shan, Q.; Li, M.-Q.; et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNA-126-3p Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Development by Targeting ADAM9. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 229–245.
- Ding, Y.; Cao, F.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Cui, Q.; Mei, W.; Li, F. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells deliver exogenous miR-145-5p to inhibit pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression. Cancer Lett. 2019, 442, 351–361.
- Kawamura, S.; Iinuma, H.; Wada, K.; Takahashi, K.; Minezaki, S.; Kainuma, M.; Shibuya, M.; Miura, F.; Sano, K. Exosome-encapsulated microRNA-4525, microRNA-451a and microRNA-21 in portal vein blood is a high-sensitive liquid biomarker for the selection of high-risk pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. J. Hepato Biliary Pancreat Sci. 2019, 26, 63–72.
- Shang, D.; Xie, C.; Hu, J.; Tan, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Z. Pancreatic cancer cell–derived exosomal microRNA-27a promotes angiogenesis of human microvascular endothelial cells in pancreatic cancer via BTG2. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 588–604.
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J.A. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345.
- Mendt, M.; Kamerkar, S.; Sugimoto, H.; McAndrews, K.M.; Wu, C.-C.; Gagea, M.; Yang, S.; Blanko, E.V.R.; Peng, Q.; Ma, X.; et al. Generation and testing of clinical-grade exosomes for pancreatic cancer. JCI Insight 2018, 3.
- Gabriel, A.N.A.; Wang, F.; Jiao, Q.; Yvette, U.; Yang, X.; Al-Ameri, S.A.; Du, L.; Wang, Y.-S.; Wang, C. The involvement of exosomes in the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 132.
- Kamisawa, T.; Wood, L.D.; Itoi, T.; Takaori, K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 73–85.
- Cheng, H.; Fan, K.; Luo, G.; Fan, Z.; Yang, C.; Huang, Q.; Jin, K.; Xu, J.; Yu, X.; Liu, C. KrasG12D mutation contributes to regulatory T cell conversion through activation of the MEK/ERK pathway in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 446, 103–111.
- Mittal, A.; Chitkara, D.; Behrman, S.W.; Mahato, R.I. Efficacy of gemcitabine conjugated and miRNA-205 complexed micelles for treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 7077–7087.
- Xu, B.; Liu, J.; Xiang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhong, P.; Xie, F.; Mou, T.; Lai, L. Expression of miRNA-143 in Pancreatic Cancer and Its Clinical Significance. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2018, 33, 373–379.




