
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dhanushka Rathnayake | + 4497 word(s) | 4497 | 2021-05-31 08:48:13 | | | |
| 2 | Vivi Li | Meta information modification | 4497 | 2021-06-24 06:14:17 | | |
Video Upload Options
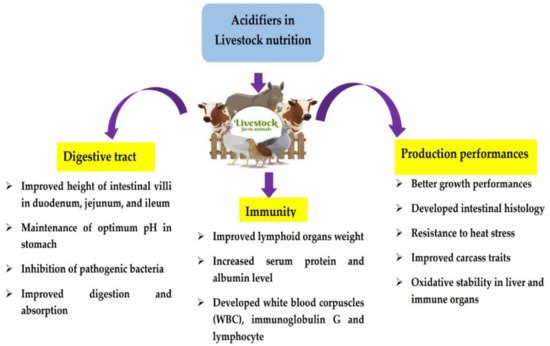
Because the application of antibiotic growth promoters (AGP) causes accelerated adverse effects on the animal diet, the scientific community has taken progressive steps to enhance sustainable animal productivity without using AGP in animal nutrition. Organic acids (OAs) are non-antibiotic feed additives and a promising feeding strategy in the swine and broiler industry. Mechanistically, OAs improve productivity through multiple and diverse pathways in: (a) reduction of pathogenic bacteria in the gastro-intestinal tract (GIT) by reducing the gut pH; (b) boosting the digestibility of nutrients by facilitating digestive enzyme secretion and increasing feed retention time in the gut system; and (c) having a positive impact and preventing meat quality deterioration without leaving any chemical residues. Recent studies have reported the effectiveness of using encapsulated OAs and synergistic mechanisms of OAs combinations in swine and broiler productivity. On the other hand, the synergistic mechanisms of OAs and the optimal combination of OAs in the animal diet are not completely understood, and further intensive scientific explorations are needed.
1. Introduction
| Acid | Chemical Name | Registration Number | Molecular Weight/GE (MJ/Kg) | Odor | pKa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Butyric | Butanoic Acid | - | 88.12/24.8 | rancid | 4.82 |
| Citric | 2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic Acid | E 330 | 192.1/10.2 | odorless | 3.13 |
| Propionic | 2-Propanoic Acid | 1a297 | 74.08/20.6 | pungent | 4.88 |
| Sorbic | 2,4-Hexandienoic Acid | E 200 | 112.1/27.85 | mildly acrid | 4.76 |
| Formic | Methanoic Acid | E 236 | 46.03/5.7 | pungent | 3.75 |
| Acetic | Ethanoic Acid | E 260 | 60.05/14.6 | pungent | 4.76 |
| Lactic | 2-Hydroxypropanoic Acid | E 260 | 90.08/15.1 | sour milk | 3.83 |
| Malic | Hydroxybutanedioic Acid | E 296 | 134.1/10.0 | apple | 3.40 |
| Fumaric | 2-Butenedioic Acid | 2b08025 | 116.1/11.5 | odorless | 3.02 |
| Benzoic | Benzenecarboxylic acid | - | - | - | 4.20 |
2. Potential Modes of Action of OAs
2.1. Effect of OAs on Mineral Utilization and Nutrient Digestibility
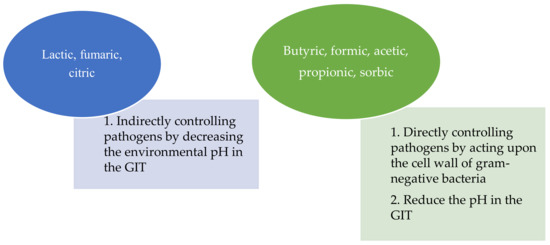
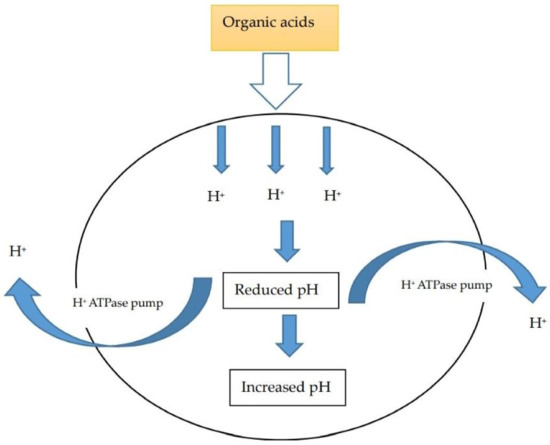
2.2. Effect of OAs on Antimicrobial Activity and Pathogenic Bacteria
3. Effect of OAs in Swine and Broiler
3.1. Supplementation of OAs on the Growth Performance of Swine and Broilers
| Dosage and Organic Acid/Acids | Growth Phase | Growth Performances | Intestinal/Fecal Microbial Counts (CFU) | Other Parameters | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BWG/FBW | ADFI | G:F | |||||
| Swine | |||||||
| 0.1% and 0.2% fumaric, citric, malic, MCFA (capric and caprylic) | Weaning | S | NS | S | E. coli; S Lactobacilli; S Clostridium; S Salmonella; S |
|
Yang et al., 2018 [54] |
| 0.1% and 0.2% fumaric, citric, malic, MCFA (capric and acrylic) | Growing | S | NS | S | Lactobacilli; S E. coli; NS |
- | Upadhya et al., 2016 [55] |
| 0.15% benzoic, fumaric, calcium formate | Weaning | S | NS | NS | E. coli; NS Lactobacilli; NS |
|
Xu et al., 2017 [56] |
| 1.1% acetic, propionic, phosphoric, citric acid | Weaning | NS | NS | NS | Lactobacilli; NS E. coli; NS Coliforms; NS |
|
Namkung et al., 2004 [57] |
| 0.4% and 0.2% fumaric, lactate, citric, propionic, benzoic acid | Weaning | NS | NS | NS | E. coli; NS | - | Walsh et al., 2007 [39] |
| 0.5% benzoic acid | Weaning | S | S | S | Lactobacilli; S | - | Wei et al., 2021 [58] |
| 0.5, 1% benzoic acid | Weaning | S | NS | NS | NE |
|
Kluge et al., 2005 [59] |
| 0.5% butanoic, fumaric, benzoic acid | Piglets | S | NS | S | Lactobacilli; NS E. coli; NS |
|
Li et al., 2008 [60] |
| 0.1% fumaric, citric, malic, MCFA (capric and caprylic) | Finishing | S | NS | S | Lactobacilli; NS E. coli; NS |
|
Upadhya et al., 2014 [61] |
| 0.85% formic, benzoic, sorbic, Ca- butyrate | Growing male pigs | NS | NS | NS | E. coli; S Lactobacilli; S |
|
Øverland et al., 2007 [62] |
| 0.5% benzoic acid | Weaning | S | S | S | E. coli; NS Lactobacilli; NS |
|
Papatsiros et al., 2011 [63] |
| 0.14% and 0.64% formic acid | Weaning | S | S | NS | Lactobacilli; S |
|
Luise et al., 2017 [9] |
| Broilers | |||||||
| 0.3% and 0.4% calcium formate, calcium propionate 0.3, 0.4% ammonium formate, ammonium propionate |
Finishing | S | NS | S | NE |
|
Saleem et al., 2020 [64] |
| 1% formic, lactic, propionic, citric acid | Finishing | S | NS | NS | NE |
|
Ali et al., 2020 [65] |
| 0.5% citric, sorbic, synthetic essential oil | Finishing | NS | NS | NS | E. coli; NS Enterococci; S Clostridium; NS Enterobacteriaceae; NS |
|
Stamilla et al., 2020 [66] |
| 0.15% formic, lactic, citric, malic, tartaric, phosphoric acids | Finishing | S | S | S | Lactobacilli; S E. coli; S |
|
Goh et al., 2020 [67] |
| 0.3% formic, acetic, propionic, ammonium formate | Finishing | S | NS | NS | NE |
|
Dai et al., 2021 [68] |
| 0.1% lactic, citric, acetic, formic, propionic, phosphoric, and sodium butyrate | Finishing | S | NS | S | Lactobacilli; S Coliforms; NS |
|
Sabour et al., 2018 [69] |
| 0.3, 0.5% formic, propionic acid | Finishing | S | NS | S | Lactobacilli; S E. coli; S |
|
Fathi et al., 2016 [70] |
| 0.06% fumaric, calcium format, calcium propionate, potassium sorbate, hydrogenated vegetable oil | Finishing | S | S | S | Lactobacilli; S Salmonella; S |
|
Hassan et al., 2010 [50] |
| 0.2, 0.4, and 0.6% butyric acid | Finishing | S | NS | S | E. coli; S |
|
Panda et al., 2009 [71] |
| 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2% citric, lactic, phosphoric acid | Finishing | S | NS | S | E. coli; S Salmonella; S |
|
Sultan et al., 2015 [72] |
| 0.6% formic acid | Finishing | S | NS | S | E. coli; S (in crop) |
|
Panda et al., 2009 [73] |
| 2% butyric, fumaric, lactic, and 3% butyric, fumaric, lactic acid | Finishing | S | NS | S | NE |
|
Adil et al., 2010 [25] |
| 0.2% propionic, 0.3% butyric acid | Finishing | S | NE | S | NE |
|
Lakshmi and Sunder., 2015 [74] |
3.2. Supplementation of OAs on Nutrient Digestibility of Swine and Broilers
| Dosage and Organic Acid/Acids | Growth Phase | Digestibility | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM | N | E | CP | |||
| Swine | ||||||
| 0.2% fumaric, citric, malic, capric, and caprylic acid | Growing | S | S | S | S | Hossain et al., 2011 [77] |
| 0.05% citric, sorbic acid | Growing | S | NS | S | NC | Cho et al., 2014 [91] |
| 2% benzoic acid | Lactating sows | S (OM) | NE | NE | S | Kluge et al., 2010 [82] |
| 0.1% and 0.2% fumaric, citric, MCFA | Finishing | S | S | S | NE | Upadhaya et al., 2014 [75] |
| 0.5% phenyllactic acid | Weaning | S | S | NE | NE | Wang et al., 2009 [92] |
| 0.3% formic, acetic, propionic, MCFA | Weaning | S (DM) NS (OM) |
NS | NS | NS | Long et al., 2018 [93] |
| 0.5% formic, propionic, lactic, citric, sorbic acid | Post-weaning | NS | NS | NS | NS | Gerritsen et al., 2010 [94] |
| 300 mEq acid/kg formic, n-butyric acid | Growing | S | S | S | S | Mroz et al., 2000 [95] |
| 0.15% citric acid | Lactating sows | NE | NE | NE | S | Liu et al., 2014a [78] |
| 0.2% fumaric, citric, malic, capric, caprylic acid | Lactating sows | S | S | S | NE | Devi et al., 2016 [96] |
| Broilers | ||||||
| 0.2% formic, propionic acid | Finishing | NS | NE | NE | S | Emami et al., 2013 [87] |
| 0.5% formic acid | Finishing | NS | NE | NE | NS | Hernández et al., 2006 [84] |
| 0.25, 0.5, and 0.75% formic acid | Finishing | NS | NE | NE | S | Ndelekwute et al., 2015 [97] |
| 5000ppm and 10,000ppm formic acid | Finishing | S | NE | NE | S | Garcia et al., 2007 [84] |
| 0.25% acetic, butyric, citric, formic acid | Finishing | S | NE | NS | S | Ndelekwute et al., 2019 [98] |
| 1, 2, and 3% citric acid | Finishing | NE | NE | S | S | Ghazalah et al., 2011 [52] |
| 0.5, 1, and 1.5% fumaric acid | Finishing | NE | NE | S | S | Ghazalah et al., 2011 [52] |
| 0.25, 0.5% formic acid | Finishing | NE | NE | NS | S | Ghazalah et al., 2011 [52] |
| 0.25, 0.5, and 0.75% acetic acid | Finishing | NE | NE | S | NS | Ghazalah et al., 2011 [52] |
3.3. Effect of OAs Supplementation on Meat Quality on Pigs and Broilers
References
- Nguyen, D.H.; Kim, I.H. Protected Organic Acids Improved Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, and Decreased Gas Emission in Broilers. Animals 2020, 10, 416.
- Tugnoli, B.; Giovagnoni, G.; Piva, A.; Grilli, E. From Acidifiers to Intestinal Health Enhancers: How Organic Acids Can Improve Growth Efficiency of Pigs. Animals 2020, 10, 134.
- Shahidi, S.; Yahyavi, M.; Zare, D.N. Influence of Dietary Organic Acids Supplementation on Reproductive Performance of Freshwater Angelfish (Pterophyllum Scalare). Global Vet. 2014, 13, 373–377.
- Kim, Y.Y.; Kil, D.Y.; Oh, H.K.; Han, I.K. Acidifier as an Alternative Material to Antibiotics in Animal Feed. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 18, 1048–1060.
- Kil, D.Y.; Piao, L.G.; Long, H.F.; Lim, J.S.; Yun, M.S.; Kong, C.S.; Ju, W.S.; Lee, H.B.; Kim, Y.Y. Effects of Organic or Inorganic Acid Supplementation on Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility and White Blood Cell Counts in Weanling Pigs. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 19, 252–261.
- Mroz, Z.; Reese, D.E.; Øverland, M.; Van Diepen, J.T.M.; Kogut, J. The effects of potassium diformate and its molecular constituents on the apparent ileal and fecal digestibility and retention of nutrients in growing-finishing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, 681–690.
- Partanen, K.H.; Mroz, Z. Organic acids for performance enhancement in pig diets. Nutr. Res. Rev. 1999, 12, 117–145.
- Spratt, C.D. Effect of Mould Inhibitor Treated High Moisture Corn on Performance of Poultry. Master’s Thesis, University of Guelph, Guelph, ON, Canada, 1985.
- Luise, D.; Motta, V.; Salvarani, C.; Chiappelli, M.; Fusco, L.; Bertocchi, M.; Mazzoni, M.; Maiorano, G.; Costa, L.N.; Van Milgen, J.; et al. Long-term administration of formic acid to weaners: Influence on intestinal microbiota, immunity parameters and growth performance. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2017, 232, 160–168.
- Ndelekwute, E.K.; Assam, E.D.; Ekere, P.C.; Ufot, U.E. Effect of organic acid treated diets on growth, apparent nutrient digestibility and faecal moisture of broiler chickens. Niger. J. Anim. Prod. 2016, 43, 218–223.
- Huang, C.; Song, P.; Fan, P.; Hou, C.; Thacker, P.; Ma, X. Dietary Sodium Butyrate Decreases Postweaning Diarrhea by Modulating Intestinal Permeability and Changing the Bacterial Communities in Weaned Piglets. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 2774–2780.
- Yang, X.; Xin, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, X. Impact of essential oils and organic acids on the growth performance, digestive functions and immunity of broiler chickens. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 388–393.
- Fascina, V.B.; Sartori, J.R.; Gonzales, E.; De Carvalho, F.B.; De Souza, I.M.G.P.; Polycarpo, G.D.V.; Stradiotti, A.C.; Pelícia, V.C. Phytogenic additives and organic acids in broiler chicken diets. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2012, 41, 2189–2197.
- Tsiloyiannis, V.K.; Kyriakis, S.C.; Vlemmas, J.; Sarris, K. The effect of organic acids on the control of porcine post-weaning diarrhea. Res. Vet. Sci. 2001, 70, 287–293.
- Dittoe, D.K.; Ricke, S.C.; Kiess, A.S. Organic Acids and Potential for Modifying the Avian Gastrointestinal Tract and Reducing Pathogens and Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 216.
- Pearlin, B.V.; Muthuvel, S.; Govidasamy, P.; Villavan, M.; Alagawany, M.; Farag, M.R.; Dhama, K.; Gopi, M. Role of acidifiers in livestock nutrition and health: A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 558–569.
- Ravindran, V.; Kornegay, E.T. Acidification of weaner pig diets: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1993, 62, 313–322.
- Nguyen, D.H.; Seok, W.J.; Kim, I.H. Organic Acids Mixture as a Dietary Additive for Pigs—A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 952.
- De Lange, C.; Pluske, J.; Gong, J.; Nyachoti, C. Strategic use of feed ingredients and feed additives to stimulate gut health and development in young pigs. Livest. Sci. 2010, 134, 124–134.
- Jongbloed, A.; Mroz, Z.; van der Weij-Jongbloed, R.; Kemme, P. The effects of microbial phytase, organic acids and their interaction in diets for growing pigs. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2000, 67, 113–122.
- Boling, S.D.; Webel, D.M.; Mavromichalis, I.; Parsons, C.M.; Baker, D.H. The effects of citric acid on phytate-phosphorus utilization in young chicks and pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2000, 78, 682–689.
- Kirchegessner, M.; Roth, F.X. Fumaric acid as a fed additive in pig nutrition. Pig News Inf. 1982, 3, 259.
- Ao, T. Exogenous Enzymes and Organic Acids in the Nutrition of Broiler Chicks: Effects on Growth Performance and In Vitro and In Vivo Digestion. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 2005.
- Afsharmanesh, M.; Pourreza, J. Effects of calcium, citric acid, ascorbic acid, vitamin D3 on the efficacy of mi-crobial phytase in broiler starters fed wheat-based diets I. Performance, bone mineralization and ileal digestibility. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2005, 4, 418–424.
- Adil, S.; Banday, T.; Bhat, G.A.; Mir, M.S.; Rehman, M. Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Organic Acids on Performance, Intestinal Histomorphology, and Serum Biochemistry of Broiler Chicken. Vet. Med. Int. 2010, 2010, 479485.
- Van Der Sluis, W. Water quality is important but often overestimated. World Poult. 2002, 18, 26–32.
- Omogbenigun, F.O.; Nyachoti, C.M.; Slominski, B.A. The effect of supplementing microbial phytase and organic acids to a corn-soybean based diet fed to early-weaned pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 81, 1806–1813.
- Skřivanová, E.; Marounek, M.; Benda, V.; Březina, P. Susceptibility of Escherichia coli, Salmonella sp and Clostridium perfringens to organic acids and monolaurin. Vet. Med. Praha 2006, 51, 81–88.
- Biagi, G.; Piva, A.; Hill, T.; Schneider, D.K.; Crenshaw, T.D. Low buffering capacity diets with added organic acids as substitute for antibiotics in diets for weaned pigs. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Digestive Physiology in Pigs, Banff, AB, Canada, 14–18 May 2003; Ball, R., Ed.; University of Alberta: Banff, AB, Canada, 2003; pp. 217–219.
- Pinheiro, V.; Mourao, J.L.; Alves, A.; Rodrigues, M.; Saavedra, M.J. Effect of Zinc bacitracin on the performance, digestibility and caecal development of growing rabbits. In Proceedings of the 8th World Rabbit Congress, Puebla, Mexico, 7–10 September 2004; pp. 942–947.
- Mroz, Z.; Koopmans, S.J.; Bannink, A.; Partanen, K.; Krasucki, W.; Overland, M.; Radcliffe, S. Carboxylic acids as bio regulators and gut growth promoters in non-ruminants. In Biology of Nutrition in Growing Animals; Mosenthin, R., Zentek, J., Zebrowska, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Edinburgh, UK, 2006; Volume 3, pp. 81–133.
- Stratford, M.; Eklund, T. Organic acids and esters. In Food Preservatives; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 48–84.
- Suiryanrayna, M.V.A.N.; Ramana, J.V. A review of the effects of dietary organic acids fed to swine. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 45.
- Dibner, J.; Buttin, P. Use of organic acids as a model to study the impact of gut microflora on nutrition and metabolism. J. Appl. Poult. Sci. 2002, 11, 453–463.
- Luckstadt, C.; Mellor, S. The use of organic acids in animal nutrition, with special focus on dietary potassium diformate under European and Austral-Asian conditions. Recent Adv. Anim. Nutr. Aust. 2011, 18, 123–130.
- Gauthier, R. Intestinal health, the key to productivity: The case of organic acids. In Proceedings of the XXVII Convention ANECA-WPDC, Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, 3–6 April 2002.
- Hirshfield, I.N.; Terzulli, S.; O’Byrne, C. Weak Organic Acids: A Panoply of Effects on Bacteria. Sci. Prog. 2003, 86, 245–270.
- Ng, W.-K.; Koh, C.-B. The utilization and mode of action of organic acids in the feeds of cultured aquatic animals. Rev. Aquac. 2016, 9, 342–368.
- Walsh, M.C.; Sholly, D.M.; Hinson, R.B.; Saddoris, K.L.; Sutton, A.L.; Radcliffe, J.S.; Odgaard, R.; Murphy, J.; Richert, B.T. Effects of water and diet acidification with and without antibiotics on weanling pig growth and microbial shedding. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, 1799–1808.
- Kathrin, B. Benzoic Acid as Feed Additive in Pig Nutrition: Effects of Diet Composition on Performance, Digestion and Ecological Aspects. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH, Zurich, Switzerland, 2009.
- Falkowski, J.F.; Aherne, F.X. Fumaric and Citric Acid as Feed Additives in Starter Pig Nutrition. J. Anim. Sci. 1984, 58, 935–938.
- Kuang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Che, L.; Xu, S.; Wu, D.; Xue, B.; et al. Effects of dietary combinations of organic acids and medium chain fatty acids as a replacement of zinc oxide on growth, digestibility and immunity of weaned pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 208, 145–157.
- Grecco, H.A.; Amorim, A.B.; Saleh, M.A.; Tse, M.L.; Telles, F.G.; Miassi, G.M.; Pimenta, G.M.; Berto, D.A. Evaluation of growth performance and gastro-intestinal parameters on the response of weaned piglets to dietary organic acids. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2018, 90, 401–414.
- Risley, C.R.; Kornegay, E.T.; Lindemann, M.D.; Wood, C.M.; Eigel, W.N. Effect of feeding organic acids on selected intestinal content measurements at varying times post weaning in pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 1992, 70, 196–206.
- Htoo, J.; Molares, J. Effects of dietary supplementation with two potassium formate sources on performance of 8- to 22-kg pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 346–349.
- Canibe, N.; Højberg, O.; Højsgaard, S.; Jensen, B.B. Feed physical form and formic acid addition to the feed affect the gastrointestinal ecology and growth performance of growing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 83, 1287–1302.
- Partanen, K.; Siljander-Rasi, H.; Alaviuhkola, T.; Suomi, K.; Fossi, M. Performance of growing-finishing pigs fed mediumor high-fibre diets supplemented with avilamycin, formic acid or formic acid-sorbate blend. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2002, 73, 139–152.
- Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Cao, G.; Feng, J.; Yue, M.; Xu, Y.; Dai, B.; Han, Q.; Guo, X. Effects of dietary supplementation with essential oils and organic acids on the growth performance, immune system, fecal volatile fatty acids, and microflora community in weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 133–143.
- Adil, S.; Banday, T.; Bhat, G.A.; Salahuddin, M.; Raquib, M.; Shanaz, S. Response of Broiler Chicken to Dietary Supplementation of Organic Acids. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2011, 12, 498–508.
- Hassan, H.M.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Youssef, A.W.; Hassan, E.R. Effect of using organic acids to substitute antibiotic growth promoters on performance and intestinal microflora of broilers. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 23, 1348–1353.
- Kamal, A.M.; Ragaa, N.M. Effect of dietary supplementation of organic acids on performance and serum biochemistry of broiler chicken. Nat. Sci. 2014, 12, 38–45.
- Ghazala, A.A.; Atta, A.M.; Elkloub, K.; Mustafa, M.E.L.; Shata, R.F.H. Effect of dietary supplementation of organic acids on performance, nutrients digestibility and health of broiler chicks. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2011, 10, 176–184.
- Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, F.; Yang, C.; Yang, X. Effects of encapsulated organic acids and essential oils on intestinal barrier, microbial count, and bacterial metabolites in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2858–2865.
- Yang, Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, I. Effects of dietary protected organic acids on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, fecal microflora, diarrhea score, and fecal gas emission in weanling pigs. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 99, 514–520.
- Upadhaya, S.D.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, I.H. Effect of protected organic acid blends on growth performance, nutrient digestibility and faecal micro flora in growing pigs. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2016, 44, 238–242.
- Xu, Y.; Liu, L.; Long, S.; Pan, L.; Piao, X. Effect of organic acids and essential oils on performance, intestinal health and digestive enzyme activities of weaned pigs. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2018, 235, 110–119.
- Namkung, H.; Gong, M.L.J.; Yu, H.; Cottrill, M.; De Lange, C.F.M. Impact of feeding blends of organic acids and herbal extracts on growth performance, gut microbiota and digestive function in newly weaned pigs. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 84, 697–704.
- Wei, X.; Bottoms, K.; Stein, H.; Blavi, L.; Bradley, C.; Bergstrom, J.; Knapp, J.; Story, R.; Maxwell, C.; Tsai, T.; et al. Dietary Organic Acids Modulate Gut Microbiota and Improve Growth Performance of Nursery Pigs. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 110.
- Kluge, H.; Broz, J.; Eder, K. Effect of benzoic acid on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, nitrogen balance, gastrointestinal microflora and parameters of microbial metabolism in piglets. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2006, 90, 316–324.
- Li, Z.; Yi, G.; Yin, J.; Sun, P.; Li, D.; Knight, C. Effects of Organic Acids on Growth Performance, Gastrointestinal pH, Intestinal Microbial Populations and Immune Responses of Weaned Pigs. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 21, 252–261.
- Upadhaya, S.; Lee, K.; Kim, I. Influence of protected organic acid blends and diets with different nutrient densities on growth performance, nutrient digestibility and faecal noxious gas emission in growing pigs. Vet. Med. 2014, 59, 491–497.
- Øverland, M.; Kjos, N.; Borg, M.; Skjerve, E.; Sørum, H. Organic acids in diets for entire male pigs: Effect on skatole level, microbiota in digesta, and growth performance. Livest. Sci. 2008, 115, 169–178.
- Papatsiros, V.G.; Tassis, P.D.; Tzika, E.D.; Papaioannou, D.S.; Petridou, E.; Alexopoulos, C.; Kyriakis, S.C. Effect of benzoic acid and combination of benzoic acid with a probiotic containing Bacillus Cereus var. toyoi in weaned pig nutrition. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 14, 117–125.
- Saleem, K.; Saima; Rahman, A.; Pasha, T.N.; Mahmud, A.; Hayat, Z. Effects of dietary organic acids on performance, cecal microbiota, and gut morphology in broilers. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 3589–3596.
- Ali, A.M.; El Agrab, H.M.; Hamoud, M.M.; Gamal, A.M.; Mousa, M.R.; Nasr, S.A.E.; El Shater, M.A.H.; Laban, S.E.; Zahran, O.K.; Ali, M.M. Effect of Acidified Drinking Water by Organic Acids on Broiler Performance and Gut Health. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2020, 8.
- Stamilla, A.; Messina, A.; Sallemi, S.; Condorelli, L.; Antoci, F.; Puleio, R.; Loria, G.R.; Cascone, G.; Lanza, M. Effects of Microencapsulated Blends of Organics Acids (OA) and Essential Oils (EO) as a Feed Additive for Broiler Chicken. A Focus on Growth Performance, Gut Morphology and Microbiology. Animals 2020, 10, 442.
- Goh, C.H.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Nobilly, F. Fecal Microbial Population and Growth in Broiler Fed Organic Acids and Palm Fat-Composed Diet. Trop. Anim. Sci. J. 2020, 43, 151–157.
- Dai, D.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, H.-J.; Wu, S.-G.; Han, Y.-M.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Qi, G.-H.; Wang, J. Organic Acids as Alternatives for Antibiotic Growth Promoters Alter the Intestinal Structure and Microbiota and Improve the Growth Performance in Broilers. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 618144.
- Sabour, S.; Tabeidian, S.A.; Sadeghi, G. Dietary organic acid and fiber sources affect performance, intestinal morphology, immune responses and gut microflora in broilers. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 5, 156–162.
- Fathi, R.; Samadi, M.S.; Qotbi, A.A.; Seidavi, A.; Marín, A.L.M. Effects of feed supplementation with increasing levels of organic acids on growth performance, carcass traits, gut microbiota and pH, plasma metabolites, and immune response of broilers. Anim. Sci. Pap. Rep. 2016, 34, 195–206.
- Panda, A.K.; Rao, S.V.R.; Raju, M.V.L.N.; Sunder, G.S. Effect of Butyric Acid on Performance, Gastrointestinal Tract Health and Carcass Characteristics in Broiler Chickens. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 22, 1026–1031.
- Sultan, A.; Ullah, T.; Khan, S.; Khan, R.U. Effect of organic acid supplementation on the performance and ileal microflora of broiler during finishing period. Pak. J. Zool. 2015, 47, 32–38.
- Panda, A.K.; Raju, M.V.L.N.; Rao, S.R.; Sunder, G.S.; Reddy, M.R. Effect of graded levels of formic acid on gut microflora count, serum biochemical parameters, performance and carcass yield of broiler chickens. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 79, 1165–1168.
- Lakshmi, K.V.; Sunder, G.S. Supplementation of Propionic Acid (PA), Butyric Acid (BA) or Antibiotic (AB) in diets and their influence on broiler performance, carcass parameters and immune response. IJSR 2015, 4, 1002–1006.
- Upadhaya, S.D.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, I.H. Protected Organic Acid Blends as an Alternative to Antibiotics in Finishing Pigs. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 1600–1607.
- Rosiński, S.; Grigorescu, G.; Lewinska, D.; Ritzén, L.G.; Viernstein, H.; Teunou, E.; Poncelet, D.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, X.; Serp, D.; et al. Characterization of microcapsules: Recommended methods based on round-robin testing. J. Microencapsul. 2002, 19, 641–659.
- Hossain, M.; Jayaraman, B.; Kim, S.; Lee, K.; Kim, I.; Nyachoti, C. Effects of a matrix-coated organic acids and medium-chain fatty acids blend on performance, and in vitro fecal noxious gas emissions in growing pigs fed in-feed antibiotic-free diets. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 98, 433–442.
- Liu, S.; Hou, W.; Cheng, S.; Shi, B.; Shan, A. Effects of dietary citric acid on performance, digestibility of calcium and phosphorus, milk composition and immunoglobulin in sows during late gestation and lactation. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2014, 191, 67–75.
- Sauer, W.; Cervantes, M.; Yanez, J.; Araiza, B.; Murdoch, G.; Morales, A.; Zijlstra, R.T. Effect of dietary inclusion of benzoic acid on mineral balance in growing pigs. Livest. Sci. 2009, 122, 162–168.
- Bühler, K.; Liesegang, A.; Bucher, B.; Wenk, C.; Broz, J. Influence of benzoic acid and phytase in low-phosphorus diets on bone characteristics in growing-finishing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 3363–3371.
- Guggenbuhl, P.; Séon, A.; Quintana, A.P.; Nunes, C.S. Effects of dietary supplementation with benzoic acid (VevoVitall®) on the zootechnical performance, the gastrointestinal microflora and the ileal digestibility of the young pig. Livest. Sci. 2007, 108, 218–221.
- Kluge, H.; Broz, J.; Eder, K. Effects of dietary benzoic acid on urinary pH and nutrient digestibility in lactating sows. Livest. Sci. 2010, 134, 119–121.
- Hernandez, F.; García, V.; Madrid, J.; Orengo, J.; Catalá, P.; Megías, M.D. Effect of formic acid on performance, digestibility, intestinal histomorphology and plasma metabolite levels of broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2006, 47, 50–56.
- García, V.; Catalá-Gregori, P.; Hernandez, F.; Megías, M.D.; Madrid, J. Effect of Formic Acid and Plant Extracts on Growth, Nutrient Digestibility, Intestine Mucosa Morphology, and Meat Yield of Broilers. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2007, 16, 555–562.
- Ao, T.; Cantor, A.H.; Pescatore, A.J.; Ford, M.J.; Pierce, J.L.; Dawson, K.A. Effect of enzyme supplementation and acidification of diets on nutrient digestibility and growth performance of broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 111–117.
- Lohakare, J.D.; Ryu, M.H.; Hahn, T.-W.; Lee, J.K.; Chae, B.J. Effects of Supplemental Ascorbic Acid on the Performance and Immunity of Commercial Broilers. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2005, 14, 10–19.
- Emami, N.K.; Naeini, S.Z.; Ruiz-Feria, C. Growth performance, digestibility, immune response and intestinal morphology of male broilers fed phosphorus deficient diets supplemented with microbial phytase and organic acids. Livest. Sci. 2013, 157, 506–513.
- Smulikowska, S.; Czerwiński, J.; Mieczkowska, A.; Jankowiak, J. The effect of fat-coated organic acid salts and a feed enzyme on growth performance, nutrient utilization, microflora activity, and morphology of the small intestine in broiler chickens. J. Anim. Feed. Sci. 2009, 18, 478–489.
- Stefanello, C.; Rosa, D.P.; Dalmoro, Y.K.; Segatto, A.L.; Vieira, M.S.; Moraes, M.L.; Santin, E. Protected Blend of Organic Acids and Essential Oils Improves Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, and Intestinal Health of Broiler Chickens Undergoing an Intestinal Challenge. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 6, 491.
- Centeno, C.; Arija, I.; Viveros, A.; Brenes, A. Effects of citric acid and microbial phytase on amino acid digestibility in broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2007, 48, 469–479.
- Cho, J.H.; Song, M.H.; Kim, I.H. Effect of microencapsulated blends of organic acids and essential oils supplementation on growth performance and nutrient digestibility in finishing pigs. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Pecu. 2014, 27, 264–272.
- Wang, J.P.; Yoo, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, H.D.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, S.O.; Seong, S.I. Effects of phenyllactic acid on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, microbial shedding, and blood profile in pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, 3235–3243.
- Long, S.; Xu, Y.; Pan, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Han, Y.; Yun, C.; Piao, X. Mixed organic acids as antibiotic substitutes improve performance, serum immunity, intestinal morphology and microbiota for weaned piglets. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2018, 235, 23–32.
- Gerritsen, R.; van Dijk, A.; Rethy, K.; Bikker, P. The effect of blends of organic acids on apparent faecal digestibility in piglets. Livest. Sci. 2010, 134, 246–248.
- Mroz, Z.; Jongbloed, A.W.; Partanen, K.H.; Vreman, K.; Kemme, P.A.; Kogut, J. The effects of calcium benzoate in diets with or without organic acids on dietary buffering capacity, apparent digestibility, retention of nutrients, and manure characteristics in swine. J. Anim. Sci. 2000, 78, 2622–2632.
- Devi, S.M.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, I.H. Analysis of the effect of dietary protected organic acid blend on lactating sows and their piglets. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2016, 45, 39–47.
- Ndelekwute, E.; Afolabi, K.; Uzegbu, H.; Essien, E. Effect of dietary formic acid as replacement of streptomycin on growth and nutrient digestibility in broiler. Bangladesh J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 44, 69–74.
- Ndelekwute, E.K.; Unah, U.L.; Udoh, U.H. Effect of dietary organic acids on nutrient digestibility, faecal moisture, digesta pH and viscosity of broiler chickens. MOJ Anat. Physiol. 2019, 6, 40–43.
- Lei, X.J.; Lee, S.I.; Lee, K.Y.; Nguyen, D.H.; Kim, I.H. Effects of a blend of organic acids and medium-chain fatty acids with and without Enterococcus faecium on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, blood parameters, and meat quality in finishing pigs. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 98, 852–859.
- Jansons, I.; Jemeljanovs, A.; Konosonoka, I.H.; Sterna, V.; Lujane, B. The influence of organic acid additive, phytoadditive and complex of organic acid additive phytoadditive on pig productivity, meat quality. Agron. Res. 2011, 9, 389–394.
- Brzóska, F.; Sliwiński, B.; Michalik-Rutkowska, O. Effect of Dietary Acidifier on Growth, Mortality, Post-Slaughter Parameters and Meat Composition of Broiler Chickens/Wpływ zakwaszacza diety na masę ciała, śmiertelność, wydajność rzeźną i skład mięsa kurcząt rzeźnych. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2013, 13, 85–96.
- Jha, A.K.; Azad, H.; Ali, S.N.; Alam, P.; Sheikh, N.; Ali, H.; Ansari, K. Evaluation of Growth and Carcass Characteristics of Broiler Chickens (Cobb 500) Feed on Different Level of Organic Acids Inclusion in Diet at Parwanipur. Nepal. Vet. J. 2019, 36, 137–147.
- Galli, G.M.; Aniecevski, E.; Petrolli, T.G.; da Rosa, G.; Boiago, M.M.; Simões, C.A.; Wagner, R.; Copetti, P.M.; Morsch, V.M.; Araujo, D.N.; et al. Growth performance and meat quality of broilers fed with microencapsulated organic acids. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 271, 114706.
- Mir, N.A.; Rafiq, A.; Kumar, F.; Singh, V.; Shukla, V. Determinants of Broiler Chicken Meat Quality and Factors Affecting Them: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2997–3009.
- Karunanayaka, D.S.; Jayasena, D.D.; Jo, C. Prevalence of pale, soft, and exudative (PSE) condition in chicken meat used for commercial meat processing and its effect on roasted chicken breast. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 27.
- Sugiharto, S.; Yudiarti, T.; Isroli, I.; Widiastuti, E.; Wahyuni, H.I.; Sartono, T.A.; Nurwantoro, N.; Al-Baarri, A.N. Effect of dietary supplementation of formic acid, butyric acid or their combination on carcass and meat characteristics of broiler chickens. J. Indones. Trop. Anim. Agric. 2019, 44, 286–294.
- El-Senousey, H.K.; Fouad, A.M.; Yao, J.H.; Zhang, Z.G.; Shen, Q.W. Dietary Alpha Lipoic Acid Improves Body Composition, Meat Quality and Decreases Collagen Content in Muscle of Broiler Chickens. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 26, 394–400.
- Menconi, A.; Kuttappan, V.A.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Urbano, T.; Matté, F.; Layton, S.; Kallapura, G.; Latorre, J.; Morales, B.E.; Prado, O.; et al. Evaluation of a commercially available organic acid product on body weight loss, carcass yield, and meat quality during preslaughter feed withdrawal in broiler chickens: A poultry welfare and economic perspective. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 448–455.
- Attia, F.M. Effect of organic acids supplementation on nutrients digestibility, gut microbiota and immune response of broiler chicks. Egypt Poult. Sci. J. 2018, 38, 223–239.
- Akbar, M.A.; Tewatia, B.S.; Kumar, S. Effect of dietary supplementation of salts of organic acids on gut morphology and meat quality of broilers. Indian J. Anim. Res. 2018, 52, 1727–1731.




