
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xin Chen | + 953 word(s) | 953 | 2021-06-01 09:57:49 | | | |
| 2 | Vicky Zhou | Meta information modification | 953 | 2021-06-09 03:28:27 | | |
Video Upload Options
Neuroprotective natural products, for exmaple, the cholinesterase inhibitor galantamine, have effects on neurovegetative diseases. Rivastigmine is also a semi-synthetic derivative of a natural product called physostigmine. Mixtures or extracts of natural products might have advantages compared to individual natural compounds, as they have multiple simultaneous target approaches, which could be a novel treatment option for Alzheimer’s disease (AD), considering the complexity of its pathophysiology. Mounting evidence has suggested that herbs or herbal formulations, together with mixtures obtained from other natural sources, may provide cognitive benefits to AD patients. Consequently, various natural sources and their extracts are extensively employed in animal models and AD patients.
1. Introduction
Neuroprotective Effects from Natural Products
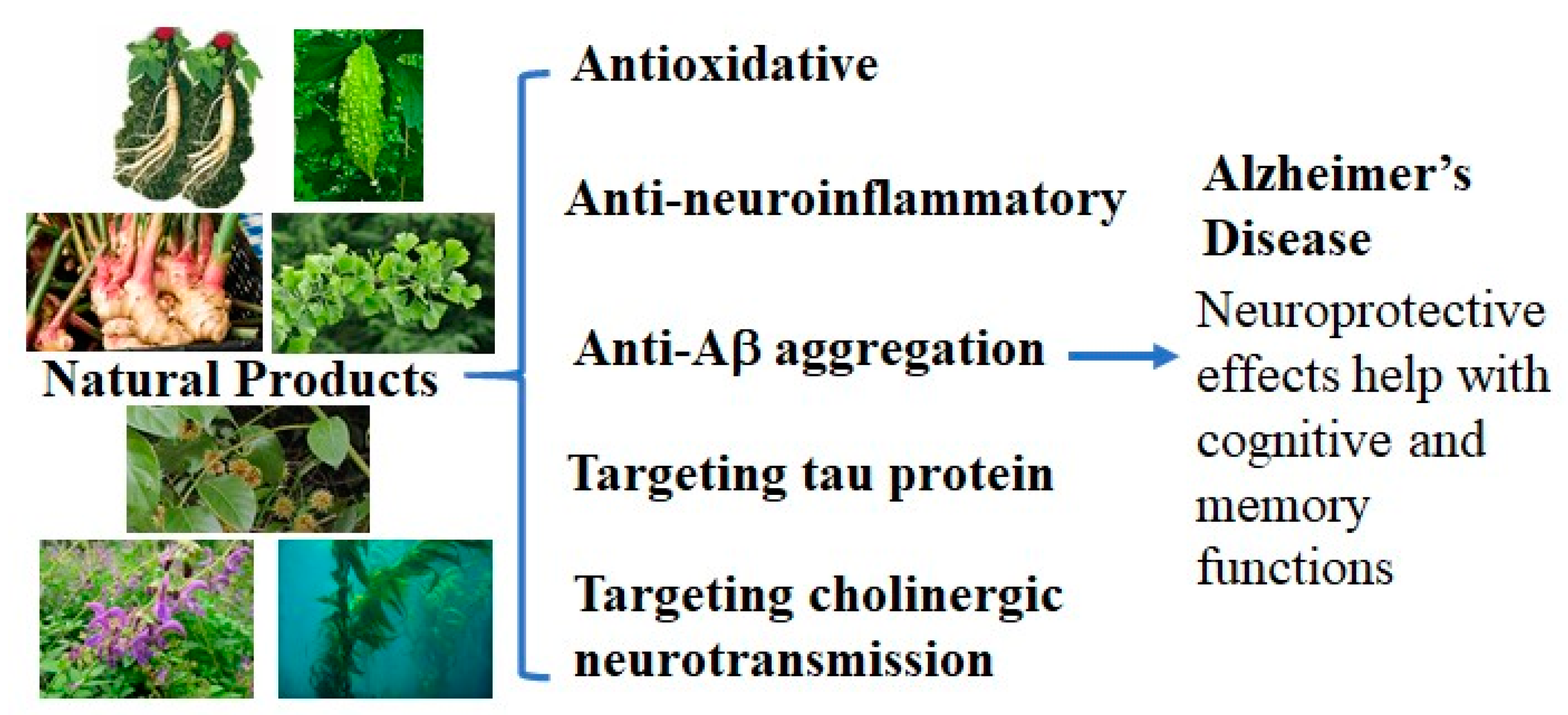 Figure 1. Neuroprotective effects from natural products for AD.
Figure 1. Neuroprotective effects from natural products for AD.2. Neuroprotective Natural Products for AD
Neuroprotective Natural Products from Medicinal Plants for AD
3. Conclusions
References
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356.
- Yiannopoulou, K.G.; Papageorgiou, S.G. Current and Future Treatments in Alzheimer Disease: An Update. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2020, 12, 1179573520907397.
- Longo, F.M.; Massa, S.M. Neuroprotective strategies in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 117–127.
- Niikura, T.; Tajima, H.; Kita, Y. Neuronal cell death in Alzheimer′s disease and a neuroprotective factor, humanin. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2006, 4, 139–147.
- Ding, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Viola, K.L.; Chow, F.E.; Zhang, Y.; Lippa, C.; Klein, W.L.; Gong, Y. Amyloid Beta Oligomers Target to Extracellular and Intracellular Neuronal Synaptic Proteins in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1140.
- Du, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Fu, M.; Li, J.; Pang, Y.; Lei, P.; Wang, Y.T.; Song, W.; et al. MKP-1 reduces Abeta generation and alleviates cognitive impairments in Alzheimer’s disease models. Signal. Transduct Target. 2019, 4, 58.
- Quiroz-Baez, R.; Ferrera, P.; Rosendo-Gutierrez, R.; Moran, J.; Bermudez-Rattoni, F.; Arias, C. Caspase-12 activation is involved in amyloid-beta protein-induced synaptic toxicity. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 26, 467–476.
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.W.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhou, F.; Wang, W.; Xian, B.; Zhang, X.; Masliah, E.; Chen, Q.; et al. Appoptosin is a novel pro-apoptotic protein and mediates cell death in neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 15565–15576.
- Iqbal, K.; Liu, F.; Gong, C.X.; Grundke-Iqbal, I. Tau in Alzheimer disease and related tauopathies. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2010, 7, 656–664.
- Ferreira-Vieira, T.H.; Guimaraes, I.M.; Silva, F.R.; Ribeiro, F.M. Alzheimer′s disease: Targeting the Cholinergic System. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 101–115.
- Black, I.B. Trophic regulation of synaptic plasticity. J. Neurobiol. 1999, 41, 108–118.
- Tonnies, E.; Trushina, E. Oxidative Stress, Synaptic Dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 1105–1121.
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; El Khoury, J.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405.
- Wang, R.; Reddy, P.H. Role of Glutamate and NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 1041–1048.
- Olila, D.; Olwa, O.; Opuda-Asibo, J. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of extracts of Zanthoxylum chalybeum and Warburgia ugandensis, Ugandan medicinal plants. Afr. Health Sci. 2001, 1, 66–72.
- Venkatesan, R.; Ji, E.; Kim, S.Y. Phytochemicals that regulate neurodegenerative disease by targeting neurotrophins: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 814068.
- Ma, X.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J. Resveratrol improves cognition and reduces oxidative stress in rats with vascular dementia. Neural Regen Res. 2013, 8, 2050–2059.
- Zhao, H.F.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.J.; Li, X.M.; Liu, T.T. Resveratrol decreases the insoluble Abeta1-42 level in hippocampus and protects the integrity of the blood-brain barrier in AD rats. Neuroscience 2015, 310, 641–649.
- He, X.; Li, Z.; Rizak, J.D.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z.; He, R.; Su, M.; Qin, D.; Wang, J.; Hu, X. Resveratrol Attenuates Formaldehyde Induced Hyperphosphorylation of Tau Protein and Cytotoxicity in N2a Cells. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 598.
- Schmatz, R.; Mazzanti, C.M.; Spanevello, R.; Stefanello, N.; Gutierres, J.; Correa, M.; da Rosa, M.M.; Rubin, M.A.; Chitolina Schetinger, M.R.; Morsch, V.M. Resveratrol prevents memory deficits and the increase in acetylcholinesterase activity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharm. 2009, 610, 42–48.
- Rahvar, M.; Nikseresht, M.; Shafiee, S.M.; Naghibalhossaini, F.; Rasti, M.; Panjehshahin, M.R.; Owji, A.A. Effect of oral resveratrol on the BDNF gene expression in the hippocampus of the rat brain. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 761–765.
- Kaufmann, D.; Kaur Dogra, A.; Tahrani, A.; Herrmann, F.; Wink, M. Extracts from Traditional Chinese Medicinal Plants Inhibit Acetylcholinesterase, a Known Alzheimer’s Disease Target. Molecules 2016, 21, 1161.
- Howes, M.J.; Perry, N.S.; Houghton, P.J. Plants with traditional uses and activities, relevant to the management of Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive disorders. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 1–18.
- Ansari, N.; Khodagholi, F. Natural products as promising drug candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Molecular mechanism aspect. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 414–429.
- D’Onofrio, G.; Sancarlo, D.; Ruan, Q.; Yu, Z.; Panza, F.; Daniele, A.; Greco, A.; Seripa, D. Phytochemicals in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 1487–1498.




