Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stephen Bondy | + 2887 word(s) | 2887 | 2021-05-26 03:52:59 |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Bondy, S. Type 2 Diabetes Optimal Treatment. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/10405 (accessed on 14 January 2026).
Bondy S. Type 2 Diabetes Optimal Treatment. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/10405. Accessed January 14, 2026.
Bondy, Stephen. "Type 2 Diabetes Optimal Treatment" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/10405 (accessed January 14, 2026).
Bondy, S. (2021, June 02). Type 2 Diabetes Optimal Treatment. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/10405
Bondy, Stephen. "Type 2 Diabetes Optimal Treatment." Encyclopedia. Web. 02 June, 2021.
Copy Citation
Insulin, via a series of kinase activations and transductions, causes the glucose type 4 transporter channels to become embedded in the cellular membrane, allowing an exponential increase of glucose entry into the cell. T2D is characterized by failure of the insulin receptors to respond to insulin, thus preventing glucose uptake from the bloodstream. Later in the disease, the production of insulin by pancreatic islet cells is also curtailed. The vast preponderance of diabetes cases (95%) in the United States constitute T2D.
diabetes
insulin
inflammation
insulin resistance diet
oxidative stress
1. Introduction
1.1. History of Diabetes and of Insulin as a Medication
A brief history of the key steps in understanding and treating diabetes mellitus is given. Many important figures are not mentioned as this short description is intended to give an idea of the global nature of developments and of the very slow progress over the millennia that has recently become greatly accelerated. Diabetes mellitus is a disease that has long been known and, over the centuries, knowledge concerning its nature has grown gradually and incrementally. It was described in 1552 B.C. by Hesi-Ra, a famous physician/dentist of the Third Dynasty of Egypt. Charaka, the first known Indian medical sage, described the pathogenesis, symptomatology, and management of diabetes in a Sanskrit text on Ayurvedic medicine written in about 600 B.C. In about 150 A.D., Arateus, a Greek physician, gave a detailed and elegant description of diabetes, a feat paralleled around the same time by the Chinese doctor Chang Chung-Ching. Matthew Dobson, an English physician, in 1776 described the sweetness of diabetic urine as being due to a sugar. This idea was further developed a by a Scottish doctor, John Rollo, into the first recommendation of a low-carbohydrate diet for treating diabetes. The renowned French scientist, Claude Bernard, in the 19th century described the glycogenic action of the liver which is very pertinent to diabetes. Using animal experimentation, the crucial role of the pancreas in diabetes was discovered in the 1880s by Joseph von Mehring (1849–1908), a German doctor, and Oscar Minkowski, a Russian pathologist, working together. This led to the finding by Georg Zuelzer, a German scientist, that injection of pancreatic extracts could benefit diabetic patients. This was followed by the purification of insulin by a Canadian, Dr. Frederick Banting, and his team, with its direct administration to diabetic patients in 1921 [1]. This protein can now be manufactured synthetically and remains the primary treatment for diabetes.
2. Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in T2D
2.1. Oxidative Stress
Oversupply of nutrients, especially glucose, can result in enhanced rates of mitochondrial respiration. The consequent loss of efficiency results in excess production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [2]. The ensuing oxidative stress may be a decisive factor in furthering the pathogenesis of T2D [3]. Hyperglycemia can induce ROS generation by way of several signaling pathways [4]. In turn, oxidative stress can activate various stress-related serine/threonine kinases including JNK, ERK, and p38 MAPK leading to inhibition of insulin signaling [5]. In this mutually reinforcing manner, oxidative stress within the pancreatic beta cells can lead to apoptic events and contribute to the development of diabetes [6]. Since beta cells contain relatively low levels of antioxidant enzymes [7], there is minimal protection against oxidant events in these cells.
The Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling pathway is the primary transcriptional regulator of intracellular redox, and, in a mouse model of diabetes, induction of Nrf2 overexpression either by genetic Keap1 knockdown or by pharmacological means can enhance sensitivity to insulin and improve disease symptoms [8]. The pro-oxidant conditions associated with the high levels of glucose found in diabetes [9] are likely to be especially damaging to the retina and may in part explain diabetic retinopathy [10].
2.2. Inflammation
Immune activity and extended low-grade inflammation characterize the development of T2D. The activation of the (NOD)-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome by interleukin-1β is implicated [11]. A distinctive profile of gut microbiota associated with obesity and diabetes may lead to metabolic endotoxemia, thereby contributing to the low-level inflammation. The gut bacterial profile is unusually rich in Firmicutes species producing the potent inflammogen lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which can then be systemically distributed by way of the vascular system [12]. As a result of generalized inflammation, an increased number of active macrophages are present in the pancreatic islets, and the beta cells are adversely affected [13]. The chronic low-level inflammation associated with aging can further exacerbate inflammatory damage caused by T2D, especially within the vascular system [14].
3. Benefits of Insulin Therapy
The classical treatment of diabetes mellitus involves the administration of insulin. This is especially effective in type 1 diabetes where life expectancy after diagnosis in infancy was 1.4 years prior to the development of insulin, but is now close to normal values. Insulin can generally rapidly lower blood glucose and additionally protects against the many adverse consequences of hyperglycemia in a range of disorders unrelated to diabetes [15][16]. Despite its shortcomings, insulin has unquestionably improved and extended a great many lives, and it continues to be a major drug of choice in many cases of diabetes [1].
The difficulty of maintenance of glucose levels within a desirable range has been very problematical with insulin. However, many advances have been made to prevent the large fluxes in glucose levels that were common in diabetics following acute administration of insulin. The modes of continuously monitoring plasma glucose and the administration of precise doses of insulin in a gradual manner have been continuously improved [17][18]. Nevertheless, effective control of blood glucose content by insulin remains imperfect and still represents a challenge.
4. T2D Treatment without Use of Exogenous Insulin
In recent years, a large range of therapeutic options and lifestyle choices for the management of T2D have been recommended. These are too many to enumerate here, but some especially promising strategies are briefly described.
4.1. Behavioral and Dietary Changes
These are the most simple and effective ways to attenuate the symptoms of T2D, but they are also very challenging. Simply put, much of T2D could be effectively controlled by reversal of weight gain and restoration of normal weight. This could be furthered by dietary management. Intermittent fasting is an effective means of achieving this [19][20].
The relationship between muscle activity and levels of circulating glucose was first noted in 1887 by Chauveu and Kaufman who reported that “when a horse chews on hay, the concentration of glucose in the blood draining its masseter muscle substantially decreases” [21]. Since then, evidence has grown showing the positive role of physical activity in maintaining insulin sensitivity and in reversing insulin resistance. Regular exercise is useful in reducing levels of inflammatory indices found in T2D [22]. Furthermore, these behavioral changes have several other valuable effects on cardiovascular health. The usefulness of a diet low in carbohydrates and oriented toward more fats (“ketogenic diet”) in the treatment of T2D is becoming increasingly recognized. Its value lies not only in preventing food-induced surges in blood glucose but also in promoting increased levels of circulating ketone bodies such as d-β-hydroxybutyrate (βHB) after their production by fermentation in the intestine [23]. Such ketone bodies are able to directly protect against diabetes-related vascular disease [24]. It is important to emphasize that the concentration of ketones in persons on such as diet is far lower than the toxic concentrations seen in diabetic ketoacidosis [25]. Germ-free mice without intestinal bacteria do not develop insulin resistance or weight gain when fed a high-carbohydrate high-fat diet [26]. This reveals the importance of the specific bacterial profile of microbiome in determining disease progression.
Butyrate and propionate suppress weight gain in mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity, and acetate has been proven to reduce food intake in healthy mice [27]. The nature of the lipid components of the ketogenic diet is critical in optimizing insulin sensitivity, as monounsaturated fats from fish oil promote this, while saturated fats from animal sources have the opposite effect [28]. The quality of the carbohydrate constituent of food is also important, as diets favoring vegetables, nuts, peanut butter, and whole-grain breads have been associated with lower mortality [29].
4.2. Pharmacological Treatment of Diabetes
A recent approach to T2D is to initiate treatment with oral medications for glycemic control. A wide range of such drugs are available with a diverse range of targets [30]. Insulin therapy is generally only initiated after the failure of one of these agents or several in combination. Two main approaches to pharmacological therapy are utilized. The first of these involves the use of drugs which seem to be antiglycemic and possess a relatively well-defined mechanism of action. This includes most of the agents referenced in detail by Chaudhury et al. (2017) [30] and some newly developed precision-focused strategies, four of which are described below.
4.2.1. MicroRNA (miRNA)
miRNAs are increasingly recognized as key determinants of health or disease. Downregulation of miR-155 and miR-146a is found in T2D [14], and a role for miRNA-146 in the pathogenesis of T2D is further suggested by the report that streptozotocin-induced diabetes results in downregulation of miR-146a in rat aorta [31]. The development of insulin resistance in cardiac tissue causes reduced glucose uptake and increased fatty acid uptake and leads to accumulation of toxic fatty acids. This transition appears to be facilitated by miRNA [32]. In mice subjected to a high-fat diet, inhibition of the heart-specific microRNA, miR-208a, with an antisense oligonucleotide leads to resistance to obesity induced by a high-fat diet and re-establishes systemic insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance [33]. This may ultimately lead to a novel strategy for T2D treatment.
4.2.2. Sirtuin Activation
The sirtuins are a family of NAD(+)-dependent deacetylases that detect cellular energy availability and adjust metabolic processes. Their activation by pharmacological means can elicit multiple metabolic benefits that protect mice from diet-induced obesity, type 2 diabetes, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [34]. When activated, both SIRT1 and SIRT3 reduce inflammation, oxidative stress, and pancreatic damage, while promoting the maintenance of glucose homeostasis [35]. As well as improving disease resistance, characteristic aging processes can be delayed and longevity can be extended by activation of these signaling proteins [36]. The stimulation of several sirtuins appears to be beneficial for diabetes and can be specifically effected by rapamycin inhibition of mTOR [3] or rather less selectively by resveratrol [37].
4.2.3. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists
Synthetic glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists can improve glycemic control with a minimal risk of hypoglycemia, and they offer another possibility of treating T2D with reduced levels of insulin. Another advantage of these agents is that some of them only require administration once weekly [38].
4.2.4. Inhibitors of the Sodium-Glucose Co-Tranpsorter-2 (SGLT2)
Another valuable class of drug with a specific mechanistic focus constitutes sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors. These block the transporters responsible for roughly 90% of the resorption of glucose from the kidney tubules. Thus, excess glucose is excreted in the urine, keeping blood levels low without stimulating insulin release. Other advantages of this type of treatment include the fact that the drugs can be taken orally and that they act independently of pancreatic β-cell function [39].
4.3. Broadly Acting Materials
Another class of agents constitutes those that are likely to have broad range of action on several parameters. These include phytochemicals and modern drugs originally derived from botanical sources. In the skeletal muscle of diabetic patients, consumption of cocoa, rich in catechins, leads to activation and translocation of key transcriptional factors and increases in antioxidant enzyme (superoxide dismutase and catalase) activity [40]. Metformin, originally derived from the plant Galega officinalis (French lilac or goat’s rue), is a widely used and very effective antihyperglycemic agent [41]. It is broadly antioxidant and anti-inflammatory, has protective effects against a range of diseases including cancer and obesity, and is likely to have several modes of action [42]. Many phytochemicals that may have usefulness in T2D treatment such as berberine, curcumin, quercetin, and resveratrol, rather than acting on a single defined target, probably have many intracellular targets and involve a range of signaling pathways [43].
An advantage of the use of materials possessing a multiplicity of sites of action or the use of more than one pharmaceutical agent is a reduced risk of counteraction of a useful effect by systemic homeostatic efforts to reverse this.
4.4. Treatment of T2D with Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Agents
Classical antioxidant supplements have not proven markedly effective in arresting the progression of T2D [44][45][46]. However, vitamin C in combination with a flavanone glycoside, naringin, has been reported to ameliorate a streptozotocin-induced animal model of diabetes [47]. Lipoic acid administration has a similar effect on this animal model [48]. A clinical study involving treatment of T2D patients with a mixture of lipoate, carnosine, and thiamine reduced levels of circulating glucose [49]. T2D patients specifically possessing the haptoglobin Hp-2-2 genotype benefit from vitamin E supplementation [50]. It may be that supplementation with multiple antioxidants is able to reduce insulin requirement in T2D patients. The selective targeting of the critical Nrf2/Keap1/ARE antioxidant pathway which leads to expression of several antioxidant genes allows a wide range of protective enzymes to be induced. Specific Nrf2 activators include catechins, curcumin, sulforaphane, resveratrol, and pterostilbene [51]. Plants contain a multitude of phenolic compounds, and this may account for the finding that dietary antioxidants within food may be more useful than administration of synthetic preparations of common vitamins in ameliorating diabetes-related oxidative damage [10][52].
5. Conclusions
Some of the tactics available for the remediation of type 2 diabetes are summarized in Table 1. There is considerable overlap in these differing means of treatment, but an ever-expanding range of resources is becoming available. While each approach in isolation may have limitations, the simultaneous application of several components of the collection of resources available can be integrated. Such a combination is likely so lead to synergistic effects, thereby providing an optimal outcome.
Table 1. Approaches toward management of type 2 diabetes. SIRT, sirtuin.
| Goal of Treatment | Mechanism Involved | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Prevent hyperglycemia | Lower levels of circulating glucose | Insulin |
| Inhibition of the renal sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) | ||
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists to stimulate insulin release | ||
| Reduced rate of carbohydrate absorption | Diminished consumption of refined or simple carbohydrates | |
| Reduced hepatic gluconeogenesis, increased glucose uptake by muscle | Metformin | |
| Reduction of levels of inflammation and oxidative stress | Increased antioxidant and anti-inflammatory milieu | Activation of Nrf/KEAP/ARE pathway |
| Antioxidant vitamins (e.g., lipoate, α-tocopherol, and ascorbate) | ||
| Use of phytochemicals with a broad range of properties (e.g., curcumin, resveratrol, and catechins) | ||
| Ketogenic diet | ||
| SIRT activation | Rapamycin | |
| Moderation of fat deposition | Lower accumulation of fat | Physical activity |
| Blocking of miR-208a with an antisense oligonucleotide | ||
| Modulation of gut biome | Ketogenic diet |
T2D is a more complex multifactorial disorder than type 1 diabetes, and it involves a series of interactive pathological changes which can be bidirectional and, thus, mutually reinforcing. The initiating trigger of such an assembly of changes can be difficult to pinpoint. Figure 1 illustrates some of the interactions among relevant factors. Many risk factors for incurring T2D and associations with T2D prevalence have been identified, but this has not been translated into a true causal understanding of the disease. As a consequence, it is difficult to model this gradually developing disease with animal systems which use relatively rapidly acting drugs such as streptozocin to disable the insulin-producing beta cells of the islet cells within the pancreas. As with many other animal models of slowly progressing human disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, a successful reversal of abnormal features in laboratory animals cannot often be replicated by corresponding improvements in the clinical situation. T2D development has many unknown facets compared to the effects seen following a single-site chemical lesion in animals.
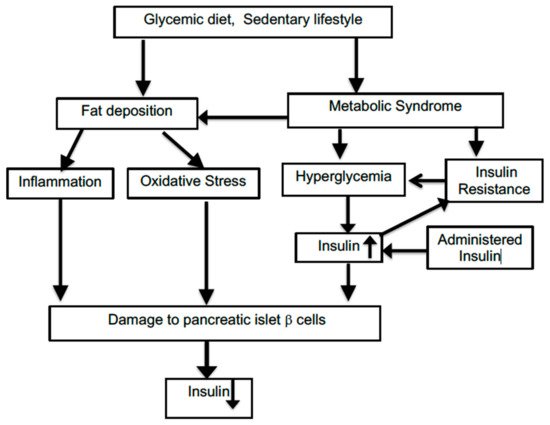
Figure 1. Connections among factors impacting on type 2 diabetes.
Obviously, initial treatment of T2D should be attempted with the least intrusive means possible. Many such measures involving lifestyle modification are available for T2D. Dietary modifications and regular exercise appear straightforward but are, in fact, very challenging. Furthermore, they do not give the impression of relying on medical expertise and may, thus, be less convincing to patients. Nevertheless, success in this area could substantially reduce the degree of reliance on antihyperglycemic agents. Another approach minimally disrupting normal metabolism may be the use of dietary supplementation with a mixture of micronutrients known to be of use in the control of blood glucose levels. This could at least reduce the insulin dose required in order to maintain glucose levels in the normal range [53]. Again, the existence of such nonprescription agents may limit the attention given by both physician and patient. This suggests that a more intense involvement of clinicians in the everyday life pattern of their patients would be helpful. Unfortunately, a means of recognizing and rewarding such a comprehensive and continuing style of medical guidance and intervention is lacking. Current medical practice emphasizes the diagnosis and treatment of a specific disease. This approach is tightly focused, and many factors that are present in the penumbra of the disorder tend to be regarded as extraneous and not crucial for therapy. Type 2 diabetes illustrates how this narrow outlook can be unsuitable and that a more holistic approach to a clinical problem considering “peripheral” factors is needed. A broader view of the setting in which the disease presents can help to establish the nature of the relevant processes preceding the frank appearance of disease. The current style of medicine in the United States accentuates the need for a rapid throughput of patients without minimal discursion into secondary issues. Remedying this perhaps by modifying the reward system of medical remuneration and applying a more integrative style of patient care could improve health outcomes substantially but would require a fresh perspective on the mode of practicing medicine.
References
- Karamanou, M.; Protogerou, A.; Tsoucalas, G.; Androutsos, G.; Poulakou-Rebelakou, E. Milestones in the history of diabetes mellitus: The main contributors. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 1–7.
- Gerber, P.A.; Rutter, G.A. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Hypoxia in Pancreatic Beta-Cell Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 26, 501–518.
- Maiese, K. New Insights for Oxidative Stress and Diabetes Mellitus. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 875961.
- Volpe, C.M.O.; Villar-Delfino, P.H.; Dos Anjos, P.M.F.; Nogueira-Machado, J.A. Cellular death, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and diabetic complications. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1–9.
- Rains, J.L.; Jain, S.K. Oxidative stress, insulin signaling, and diabetes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 567–575.
- Kaneto, H.; Matsuoka, T.-A.; Katakami, N.; Kawamori, D.; Miyatsuka, T.; Yoshiuchi, K.; Yasuda, T.; Sakamoto, K.; Yamasaki, Y.; Matsuhisa, M. Oxidative stress and the JNK pathway are involved in the development of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Curr. Mol. Med. 2007, 7, 674–686.
- Robertson, R.P.; Harmon, J.S. Diabetes, glucose toxicity, and oxidative stress: A case of double jeopardy for the pancreatic islet beta cell. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 41, 177–184.
- Uruno, A.; Furusawa, Y.; Yagishita, Y.; Fukutomi, T.; Muramatsu, H.; Negishi, T.; Sugawara, A.; Kensler, T.W.; Yamamoto, M. The Keap1-Nrf2 System Prevents Onset of Diabetes Mellitus. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2996–3010.
- Luc, K.; Schramm-Luc, A.; Guzik, T.J.; Mikolajczyk, T.P. Oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in prediabetes and diabetes. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 70, 809–824.
- Cecilia, O.-M.; Alberto, C.-G.J.; José, N.-P.; Germán, C.-M.E.; Karen, L.-C.A.; Miguel, R.-P.L.; Raúl, R.-R.R.; Daniel, R.-C.A. Oxidative Stress as the Main Target in Diabetic Retinopathy Pathophysiology. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 8562408.
- Esser, N.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Piette, J.; Scheen, A.J.; Paquot, N. Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 105, 141–150.
- Cani, P.D.; Osto, M.; Geurts, L.; Everard, A. Involvement of gut microbiota in the development of low-grade inflammation and type 2 diabetes associated with obesity. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 279–288.
- Eguchi, K.; Nagai, R. Islet inflammation in type 2 diabetes and physiology. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 14–23.
- El Assar, M.; Angulo, J.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L. Diabetes and ageing-induced vascular inflammation. J. Physiol. 2015, 594, 2125–2146.
- Berghe, G.V.D. How does blood glucose control with insulin save lives in intensive care? J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1187–1195.
- Jacobi, J.; Bircher, N.; Krinsley, J.; Agus, M.; Braithwaite, S.S.; Deutschman, C.; Freire, A.X.; Geehan, D.; Kohl, B.; Nasraway, S.A.; et al. Guidelines for the use of an insulin infusion for the management of hyperglycemia in critically ill patients. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 3251–3276.
- Cahn, A.; Miccoli, R.; Dardano, A.; Del Prato, S. New forms of insulin and insulin therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 638–652.
- Umpierrez, G.E.; Klonoff, D.C. Diabetes Technology Update: Use of Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Hospital. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1579–1589.
- Furmli, S.; Elmasry, R.; Ramos, M.; Fung, J. Therapeutic use of intermittent fasting for people with type 2 diabetes as an alternative to insulin. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr2017221854.
- Zubrzycki, A.; Cierpka-Kmiec, K.; Kmiec, Z.; Wronska, A. The role of low-calorie diets and intermittent fasting in the treatment of obesity and type-2 diabetes. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 2019, 69.
- Chauveau, A.; Kaufmann, M. Experiénces pour la determination du coefficient de l’activité nutritive et respiratoire des muscles en repos et en travail. Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci. 1887, 104, 1126–1132.
- Pedersen, B.K. Anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: Role in diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 47, 600–611.
- Soto-Mota, A.; Norwitz, N.G.; Clarke, K. Why a d-β-hydroxybutyrate monoester? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 51–59.
- Wu, X.; Miao, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, K.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Qi, J. β-hydroxybutyrate antagonizes aortic endothelial injury by promoting generation of VEGF in diabetic rats. Tissue Cell 2020, 64, 101345.
- Kalra, S.; Gupta, L.; Khandelwal, D.; Gupta, P.; Dutta, D.; Aggarwal, S. Ketogenic diet in endocrine disorders: Current perspectives. J. Postgrad. Med. 2017, 63, 242–251.
- Rabot, S.; Membrez, M.; Bruneau, A.; Gérard, P.; Harach, T.; Moser, M.; Raymond, F.; Mansourian, R.; Chou, C.J. Germ-free C57BL/6J mice are resistant to high-fat-diet-induced insulin resistance and have altered cholesterol metabolism. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 4948–4959.
- Vallianou, N.; Stratigou, T.; Tsagarakis, S. Microbiome and diabetes: Where are we now? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 146, 111–118.
- Gentile, C.L.; Weir, T.L. The gut microbiota at the intersection of diet and human health. Science 2018, 362, 776–780.
- Chambers, E.S.; Byrne, C.S.; Frost, G. Carbohydrate and human health: Is it all about quality? Lancet 2019, 393, 384–386.
- Chaudhury, A.; Duvoor, C.; Dendi, V.S.R.; Kraleti, S.; Chada, A.; Ravilla, R.; Marco, A.; Shekhawat, N.S.; Montales, M.T.; Kuriakose, K.; et al. Clinical Review of Antidiabetic Drugs: Implications for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 6.
- Emadi, S.S.; Soufi, F.G.; Khamaneh, A.M.; Alipour, M.R. MicroRNA-146a expression and its intervention in NF-?B signaling pathway in diabetic rat aorta. Endocr. Regul. 2014, 48, 103–108.
- Hathaway, Q.A.; Pinti, M.V.; Durr, A.J.; Waris, S.; Shepherd, D.L.; Hollander, J.M. Regulating microRNA expression: At the heart of diabetes mellitus and the mitochondrion. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2018, 314, H293–H310.
- Grueter, C.E.; Van Rooij, E.; Johnson, B.A.; DeLeon, S.M.; Sutherland, L.B.; Qi, X.; Gautron, L.; Elmquist, J.K.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E.N. A Cardiac MicroRNA Governs Systemic Energy Homeostasis by Regulation of MED13. Cell 2012, 149, 671–683.
- Nogueiras, R.; Habegger, K.M.; Chaudhary, N.; Finan, B.; Banks, A.S.; Dietrich, M.O.; Horvath, T.L.; Sinclair, D.A.; Pfluger, P.T.; Tschöop, M.H. Sirtuin 1 and Sirtuin 3: Physiological Modulators of Metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 1479–1514.
- Pacifici, F.; Di Cola, D.; Pastore, D.; Abete, P.; Guadagni, F.; Donadel, G.; Bellia, A.; Esposito, E.; Salimei, C.; Salimei, P.S.; et al. Proposed Tandem Effect of Physical Activity and Sirtuin 1 and 3 Activation in Regulating Glucose Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4748.
- Bonkowski, M.S.; Sinclair, M.S.B.D.A. Slowing ageing by design: The rise of NAD+ and sirtuin-activating compounds. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 679–690.
- Song, J.; Yang, B.; Jia, X.; Li, M.; Tan, W.; Ma, S.; Shi, X.; Feng, L. Distinctive Roles of Sirtuins on Diabetes, Protective or Detrimental? Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 724.
- Trujillo, J.M.; Nuffer, W. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Recent Developments and Emerging Agents. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2014, 34, 1174–1186.
- Hsia, D.S.; Grove, O.; Cefalu, W.T. An update on sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2017, 24, 73–79.
- Ramirez-Sanchez, I.; Taub, P.R.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Nogueira, L.; Coe, T.; Perkins, G.; Hogan, M.C.; Maisel, A.S.; Henry, R.R.; Ceballos, G.; et al. (−)-Epicatechin rich cocoa mediated modulation of oxidative stress regulators in skeletal muscle of heart failure and type 2 diabetes patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3982–3990.
- Zhou, T.; Xu, X.; Du, M.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J. A preclinical overview of metformin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1227–1235.
- Zhou, J.; Massey, S.; Story, D.; Li, L. Metformin: An Old Drug with New Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2863.
- Joshi, T.; Singh, A.K.; Haratipour, P.; Sah, A.N.; Pandey, A.K.; Naseri, R.; Juyal, V.; Farzaei, M.H. Targeting AMPK signaling pathway by natural products for treatment of diabetes mellitus and its complications. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 17212–17231.
- Ceriello, A.; Testa, R. Antioxidant Anti-Inflammatory Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, S232–S236.
- Abdali, D.; Samson, S.E.; Grover, A.K. How Effective Are Antioxidant Supplements in Obesity and Diabetes? Med. Princ. Pract. 2015, 24, 201–215.
- Valdes-Ramos, R.; Laura, G.-L.A.; Elina, M.-C.B.; Donají, B.-A.A. Vitamins and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 15, 54–63.
- Punithavathi, V.R.; Anuthama, R.; Prince, P.S.M. Combined treatment with naringin and vitamin C ameliorates streptozotocin-induced diabetes in male Wistar rats. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 28, 806–813.
- Ghelani, H.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Nammi, S. Chronic treatment of (R)-α-lipoic acid reduces blood glucose and lipid levels in high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin-induced metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes in Sprague-Dawley rats. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2017, 5, e00306.
- Karkabounas, S.; Papadopoulos, N.; Anastasiadou, C.; Gubili, C.; Peschos, D.; Daskalou, T.; Fikioris, N.; Simos, Y.V.; Kontargiris, E.; Gianakopoulos, X.; et al. Effects of α-Lipoic Acid, Carnosine, and Thiamine Supplementation in Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized, Double-Blind Study. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 1197–1203.
- Blum, S.; Vardi, M.; Brown, J.B.; Russell, A.; Milman, U.; Shapira, C.; Levy, N.S.; Miller-Lotan, R.; Asleh, R.; Levy, A.P. Vitamin E reduces cardiovascular disease in individuals with diabetes mellitus and the haptoglobin 2-2 genotype. Pharmacogenomics 2010, 11, 675–684.
- David, J.A.; Rifkin, W.J.; Rabbani, P.S.; Ceradini, D.J. The Nrf2/Keap1/ARE Pathway and Oxidative Stress as a Therapeutic Target in Type II Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 4826724.
- McMacken, M.; Shah, S. A plant-based diet for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 342–354.
- Prasad, K.N. Micronutrients in Prevention and Improvement of the Standard Therapy in Diabetes; Informa UK Limited: London, UK, 2019; pp. 95–129.
More
Information
Subjects:
Biology
Contributor
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
886
Revision:
1 time
(View History)
Update Date:
02 Jun 2021
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




