Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Marine products are among the most promising sources of biologically active molecules. Aplysinopsins, tryptophan-derived marine natural products, were isolated from different natural marine sources including sponges, stony corals (hard corals) especially genus scleractinian, as well as sea anemone, in addition to one nudibranch. Aplysinopsins were reported to be isolated from different marine organisms related to various geographic areas such as Pacific, Indonesia, Caribbean, and Mediterranean regions.
- aplysinopsin
- sources
- synthesis
- bioactivity
1. Different Sources and Chemical Structures of Aplysinopsins
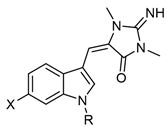
The chemical backbone of the natural aplysinopsins include a simple configuration of monomeric aplysinopsin-type structures and their brominated derivatives at the A ring, variation in the structure of the C ring, the presence and configuration of the C-8-C-1′ double bond, the oxidation state of the 2-aminoimidazoline fragment and N-alkylated at the B ring (Figure 1), in addition to the aplysinopsin dimers form.
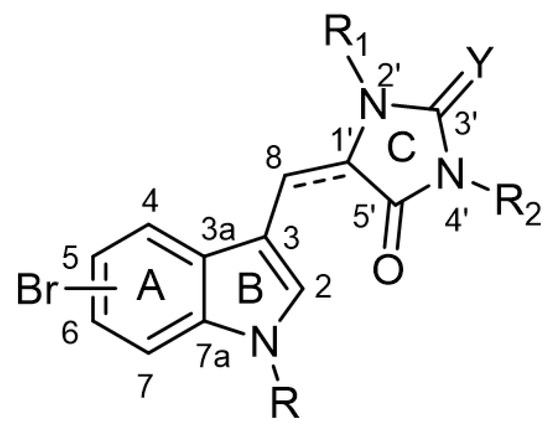
Figure 1. The chemical configuration of monomeric aplysinopsin-type structures shows detailed segmentation of the rings, carbon numbering, and type of bonds.
Aplysinopsin, (E)-5-((1H-indol-3-yl)methylene)-2-imino-1,3-dimethylimidazo-li-din-4-one (1), was first isolated from the sponge genus Thorecta of the Australian Great Barrier Reef by Kazlauskas et al. [1]. Sequentially, aplysinopsin and its derivatives have been reported in many other marine organisms from various geographic areas (Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4) [2].
Table 1. Monomeric aplysinopsin-type structures and their brominated derivatives.
 |
||||||
| Aplysinopsin Derivatives | X1 | X2 | R1 | R2 | Y | Source [Ref.] |
| Aplysinopsin (1) | H | H | Me | Me | NH | Thorecta sp. sponge Great Barrier Reef Australia [1], Verongia spengelli sponge Florida Keys [3], Dercitus sp. sponge Caribbean [4], Smenospongia aurea sponge Caribbean [5], Astroides calycularis anthozoan Mediterranean [6], Tubastraea aurea Japan scleractinian coral [7], Tubastraea sp. scleractinian coral Philippines [8], Radianthus kuekenthali sea anemone Japan [9], Aplysina sp. sponge Japan [10], Tubastraea faulkneri scleractinian coral Australia [11], Tubastraea sp. scleractinian Japane [12], Smenospongia sp. sponge Indo-Pacific reefs [13], and Verongula rigida sponge Florida Keys [14]. |
| Isoaplysinopsin (2) | H | H | H | Me | NMe | Aplysina sp. sponge Japan [10] and Smenospongia aurea sponge Jamaica [15]. |
| 2′-de-N-methylaplysinopsin (3) | H | H | H | Me | H | Dercitus sp. sponge Caribbean [4], Tubastrea coccinea coral Hawaii [16], Phestilla melanobrachia mollusk [16], Dendrophyllia sp. scleractinian coral Philippines [8], Smenospongia aurea sponge Jamaica [15], Verongula rigida sponge Florida Keys [14]. |
| Methylaplysinopsin (4) |
H | H | Me | Me | NMe | Aplysinopsis reticulata sponge Australia [2] and Smenospongia aurea sponge Jamaica [15]. |
| 4′-Demethyl-3′-N-methylaplysinopsin (5) | H | H | Me | H | NMe | Dendrophyllia sp. scleractinian coral Philippines [8] and Smenospongia aurea sponge Jamaica [15]. |
| N-3′-ethyl-aplysinopsin (6) | H | H | Me | Et | NMe | Smenospongia aurea sponge Jamaica [15]. |
| 3′-Deimino-2′,4′-bis(demethyl)-3′-oxo-aplysinopsin (7) | H | H | H | H | O | Leptopsammia pruvoti scleractinian coral France [8]. |
| 3′-Deimino-3′oxoaplysinopsin (8) |
H | H | Me | Me | O | Thorecta sp. sponge Great Barrier Reef Australia [1] and Tubastraea sp. scleractinian coral Philippines [8]. |
| 6-Bromo-2′-de-N-methylaplysinopsin (9) |
Br | H | Me | H | NH | Dercitus sp. sponge Caribbean [4], Tubastrea coccinea coral Hawaii [16], Phestilla melanobrachia mollusk [16], Dendrophyllia sp. scleractinian coral Philippines [8], Tubastraea faulkneri scleractinian coral Australia [11], Smenospongia aurea sponge Jamaica [15], Hyrtios erecta sponge Japan [17]. |
| 6-Bromoaplysinopsin (10) | Br | H | Me | Me | NH | Tubastrea coccinea coral Hawaii [16], Smenospongia aurea sponge Caribbean [5], Astroides calycularis anthozoan Mediterranean [6], Radianthus kuekenthali sea anemone Japan [9], Tubastraea faulkneri scleractinian coral Australia [11], Smenospongia aurea sponge Jamaica [15], Smenospongia aurea sponge Florida Keys [14]. |
| 6-Bromo-4′-de-N-methylaplysinopsin (11) | Br | H | H | Me | NH | Smenospongia aurea sponge Caribbean [5]. |
| 6-Bromo-4′-demethyl- 3′-N-methyl-aplysinopsin (12) |
Br | H | H | Me | NMe | Dendrophyllia sp. scleractinian coral Philippines [8]. |
| 5,6-Dibromo-2′-demethylaplysinopsin (13) | Br | Br | Me | H | NH | Hyrtios erecta sponge Japan [17]. |
| 6-Bromo-3′-deimino-2′,4′-bis(demethyl)-3′- Oxoaplysinopsin (14) |
Br | H | H | H | O | Smenospongia aurea sponge Caribbean [18] and Leptopsammia pruvoti scleractinian coral France [8]. |
| 6-Bromo-3′-deimino-3′-oxoaplysinopsin (15) |
Br | H | Me | Me | O | Astroides calycularis anthozoan Mediterranean [6] and Tubastraea sp. scleractinian coral Philippines [8]. |
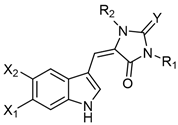
Table 2. Aplysinopsins substituted at the nitrogen atom.
Table 3. Aplysinopsins with a single C-8-C-1′ bond.
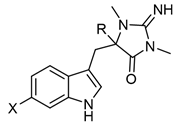 |
|||
| Aplysinopsin Derivatives | R | X | Sources [Ref.] |
| 1′,8-Dihydroaplysinopsin (19) | H | H | Tubastrea coccinea coral Hawaii [16], Radianthus kuekenthali sea anemone Japan [9], and Thorectandra sp. sponge Indo-Pacific reefs [13]. |
| 6-Bromo-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (20) | Br | H | |
| 6-Bromo-1-hydroxy-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (21) | Br | OH | Thorectandra sp. sponge Indo-Pacific reefs [13]. |
| 6-Bromo-1-methoxy-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (22) | Br | OCH3 | |
| 6-Bromo-1-ethoxy-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (23) | Br | OCH2CH3 | |
Table 4. Aplysinopsin dimers.
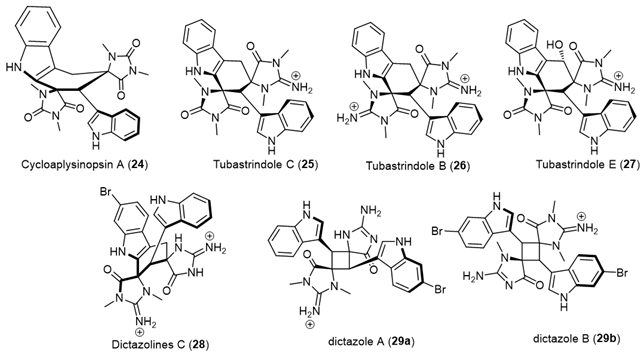 |
|
| Aplysinopsin Dimers | Sources [Ref.] |
| Cycloaplysinopsin (24) | Scleractinian corals of the family Dendrophylliidae from Comoro islands and hard coral Tubastraea sp., from the Great Hanish in the Archipelago of the Hanish Islands, Yemen, tropical Indo-Pacific (Comoros, Philippines) scleractinian corals of the family Dendrophylliidae [19][20]. |
| Tubastrindoles A–C (25) | Stony Coral, Tubastraea sp. scleractinian Japane [12]. |
| Tubastrindole B (26) | Australian Marine Sponge, a specimen of the sponge Ianthella cf. flabelliformis [21]. |
| Tubastrindoles D–H (27) | Stony Coral, Tubastraea aurea Odomari area, Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan [22]. |
| Dictazolines A and B | Marine Sponge Smenospongia cerebriformis, Hospital Point on Solarte Isle, Boca del Toro, on the northwest coast of Panama [23]. |
| Dictazolines C–E (28) and Dictazoles A and B (29) |
Marine Sponge Smenospongia cerebriformis, Panamanian sponge [24]. |
2. Biological Activity
Aplysinopsins possess an array of biological activities (Table 5).
Table 5. Biological activities of aplysinopsins.
| Aplysinopsin Derivatives | Activity [Ref.] |
|---|---|
| Aplysinopsin (1) | - CNS permeable scaffold for dual inhibition of cholinesterase and BACE-1 inhibition [25][26]. - Possess monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitory activity (IC50 of 5.6 nM) [27]. - Antiplasmodial activity (IC50: 0.43 µg/mL) [28]. - Antineoplastic activity (IC50 values against L-1210 and KB cells, respectively, 2.3 and 6.4 µg/mL [3][10]. - Inhibit the growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis [13]. - An inhibitor of development of fertilized sea urchin eggs at 2.5 µg/mL [7]. - Induce symbiosis between sea anemone and anemonefish [9]. |
| Isoaplysinopsin (2) | - Showed cytotoxic against murine lymphoma L-1210 (IC50 11.5 µg/mL) and human epidermoid carcinoma KJ3 (31% inhibition at 20 µg/mL) cells [10]. |
| Methylaplysinopsin (4) | - Antidepressant activity by enhancing serotonin activity in the central nervous system [29][30]. - Inhibition of monoamine oxidase (MAO) [30]. - Showed cytotoxicity (IC50 values against L-1210 and KB cells of 3.5 and 6.7 µg/mL, respectively) [10]. |
| N-3′-ethyl-aplysinopsin (6) | - Serotonin receptors modulator with Ki value 1.7 µM to the 5-HT2A and 3.5 µM to 5-HT2C serotonin subtypes [15]. |
| 6-Bromo-2′-de-N-methylaplysinopsin (9) | - Serotonin receptors modulator (showed significant selectivity to the 5-HT2C serotonin subtype over the 5-HT2A subtype) [15]. - Antiplasmodial. - Inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (nNOS). |
| 6-Bromoaplysinopsin (10) | - Serotonin receptors modulator (showed highest affinity to 5-HT2C with a Ki value similar to that of serotonin 0.33 µM) [15]. |
| 5,6-Dibromo-2′-demethylaplysinopsin (13) | - Inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) [17]. |
| 6-Bromo-3′-deimino-3′-oxoaply-sinopsin (15) | - Antiplasmodial activity [20]. |
| 1′,8-Dihydroaplysinopsin (19) | - Induce symbiosis between sea anemone and anemonefish [9]. |
| 6-Bromo-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (20) 6-Bromo-1-hydroxy-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (21) 6-Bromo-1-methoxy-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (22) 6-Bromo-1-ethoxy-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (23) |
- Inhibit the growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis [13]. |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/md21050268
References
- Kazlauskas, R.; Murphy, P.T.; Quinn, R.J.; Wells, R.J. Aplysinopsin, a new tryptophan derivative from a sponge. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 18, 61–64.
- Bialonska, D.; Zjawiony, J.K. Aplysinopsins—Marine Indole Alkaloids: Chemistry, Bioactivity and Ecological Significance. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 166.
- Kh, H.; Fj, S. Aplysinopsin: Antineoplastic Tryptophan Derivative from the Marine Sponge Verongia Spengelii. Lloydia 1977, 40, 479–481.
- Djura, P.; Faulkner, D.J. Metabolites of the marine sponge Dercitus species. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 735–737.
- Tymiak, A.A.; Rinehart, K.L.; Bakus, G.J. Constituents of morphologically similar sponges: Aplysina and Smenospongia Species. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 1039–1047.
- Fattorusso, E.; Lanzotti, V.; Magno, S.; Novellino, E. Tryptophan Derivatives from a Mediterranean Anthozoan, Astroides calycularis. J. Nat. Prod. 1985, 48, 924–927.
- Fusetani, N.; Asano, M.; Matsunaga, S.; Hashimoto, K. Bioactive marine metabolites—XV. Isolation of aplysinopsin from the Scleractinian coral Tubastrea aurea as an inhibitor of development of fertilized sea urchin eggs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1986, 85, 845–846.
- Guella, G.; Mancini, I.; Zibrowius, H.; Pietra, F. Novel Aplysinopsin-Type Alkaloids from Scleractinian Corals of the Family Dendrophylliidae of the Mediterranean and the Philippines. Configurational-assignment criteria, stereospecific synthesis, and photoisomerization. Helvetica Chim. Acta 1988, 71, 773–782.
- Murata, M.; Miyagawa-Kohshima, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Naya, Y. Characterization of Compounds That Induce Symbiosis Between Sea Anemone and Anemone Fish. Science 1986, 234, 585–587.
- Kondo, K.; Nishi, J.; Ishibashi, M.; Kobayashi, J. Two New Tryptophan-Derived Alkaloids from the Okinawan Marine Sponge Aplysina sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1008–1011.
- Koh, E.G.; Sweatman, H. Chemical warfare among scleractinians: Bioactive natural products from Tubastraea faulkneri Wells kill larvae of potential competitors. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 251, 141–160.
- Iwagawa, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Okamura, H.; Nakatani, M.; Doe, M.; Takemura, K. Three novel bis(indole) alkaloids from a stony coral, Tubastraea sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 2533–2535.
- Segraves, N.L.; Crews, P. Investigation of Brominated Tryptophan Alkaloids from Two Thorectidae Sponges: Thorectandra and Smenospongia. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1484–1488.
- Kochanowska, A.J.; Rao, K.V.; Childress, S.; El-Alfy, A.; Matsumoto, R.R.; Kelly, M.; Stewart, G.S.; Sufka, K.J.; Hamann, M.T. Secondary Metabolites from Three Florida Sponges with Antidepressant Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 186–189.
- Hu, J.-F.; Schetz, J.A.; Kelly, M.; Peng, J.-N.; Ang, K.K.H.; Flotow, H.; Leong, C.Y.; Ng, S.B.; Buss, A.D.; Wilkins, S.P.; et al. New Antiinfective and Human 5-HT2 Receptor Binding Natural and Semisynthetic Compounds from the Jamaican Sponge Smenospongia aurea. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 476–480.
- Okuda, R.K.; Klein, D.; Kinnel, R.B.; Li, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Marine natural products: The past twenty years and beyond. Pure Appl. Chem. 1982, 54, 1907–1914.
- Aoki, S.; Ye, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Takashima, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Kitagawa, I.; Kobayashi, M. Novel Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase (nNOS) Selective Inhibitor, Aplysinopsin-Type Indole Alkaloid, from Marine Sponge Hyrtios erecta. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 1372–1374.
- Djura, P.; Stierle, D.B.; Sullivan, B.; Faulkner, D.J.; Arnold, E.V.; Clardy, J. Some metabolites of the marine sponges Smenospongia aurea and Smenospongia (Ident.Polyfibrospongia) echina. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 1435–1441.
- Mancini, I.; Guella, G.; Zibrowius, H.; Pietra, F. On the origin of quasi-racemic aplysinopsin cycloadducts, (bis)indole alkaloids isolated from scleractinian corals of the family Dendrophylliidae. Involvement of enantiodefective Diels–Alderases or asymmetric induction in artifact processes involving adventitious catalysts? Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 8757–8762.
- Meyer, M.; Delberghe, F.; Liron, F.; Guillaume, M.; Valentin, A.; Guyot, M. An antiplasmodial new (bis)indole alkaloid from the hard coral Tubastraea sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 178–182.
- Balansa, W.; Islam, R.; Gilbert, D.F.; Fontaine, F.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H.; Piggott, A.M.; Lynch, J.W.; Capon, R.J. Australian marine sponge alkaloids as a new class of glycine-gated chloride channel receptor modulator. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4420–4425.
- Iwagawa, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Yokogawa, Y.; Okamura, H.; Nakatani, M.; Doe, M.; Morimoto, Y.; Takemura, K. Aplysinopsin Dimers from a Stony Coral. Tubastraea aurea. Heterocycles 2008, 75, 2023.
- Dai, J.; Jiménez, J.I.; Kelly, M.; Barnes, S.; Lorenzo, P.; Williams, P. Dictazolines A and B, Bisspiroimidazolidinones from the Marine Sponge Smenospongia cerebriformis. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1287–1290.
- Dai, J.; Jiménez, J.I.; Kelly, M.; Williams, P.G. Dictazoles: Potential Vinyl Cyclobutane Biosynthetic Precursors to the Dictazolines. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 2399–2402.
- Nuthakki, V.K.; Yadav Bheemanaboina, R.R.; Bharate, S.B. Identification of aplysinopsin as a blood-brain barrier permeable scaffold for anti-cholinesterase and anti-BACE-1 activity. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 107, 104568.
- Nuthakki, V.K.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.; Bharate, S.B. Identification of embelin, a 3-undecyl-1,4-benzoquinone from Embelia ribes as a multitargeted anti-Alzheimer agent. Drug Dev. Res. 2019, 80, 655–665.
- Lewellyn, K.; Bialonska, D.; Loria, M.J.; White, S.W.; Sufka, K.J.; Zjawiony, J.K. In vitro structure–activity relationships of aplysinopsin analogs and their in vivo evaluation in the chick anxiety–depression model. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 7083–7090.
- Passemar, C.; Saléry, M.; Soh, P.N.; Linas, M.-D.; Ahond, A.; Poupat, C.; Benoit-Vical, F. Indole and aminoimidazole moieties appear as key structural units in antiplasmodial molecules. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1118–1125.
- Wells, R.J.; Murphy, P.T. 5-(Indol-3-Ylmethylene)-1,3-Dimethyl-2-Methylamino-4-Imidazolidinone. U.S. Patent US4195179A, 25 March 1980.
- Baird-Lambert, J.; Davis, P.A.; Taylor, K.M. Methylaplysinopsin: A natural product of marine origin with effects on serotonergic neurotransmission. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1982, 9, 203–212.
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!