Membrane proteins play an important role in key cellular functions, such as signal transduction, apoptosis, and metabolism. Therefore, structural and functional studies of these proteins are essential in fields such as fundamental biology, medical science, pharmacology, biotechnology, and bioengineering.
- membrane proteins
- ion channels
- nanopores
- giant lipid vesicles
- liposome
- proteoliposome
- planar bilayer lipid membrane
- artificial cell model
1. Introduction
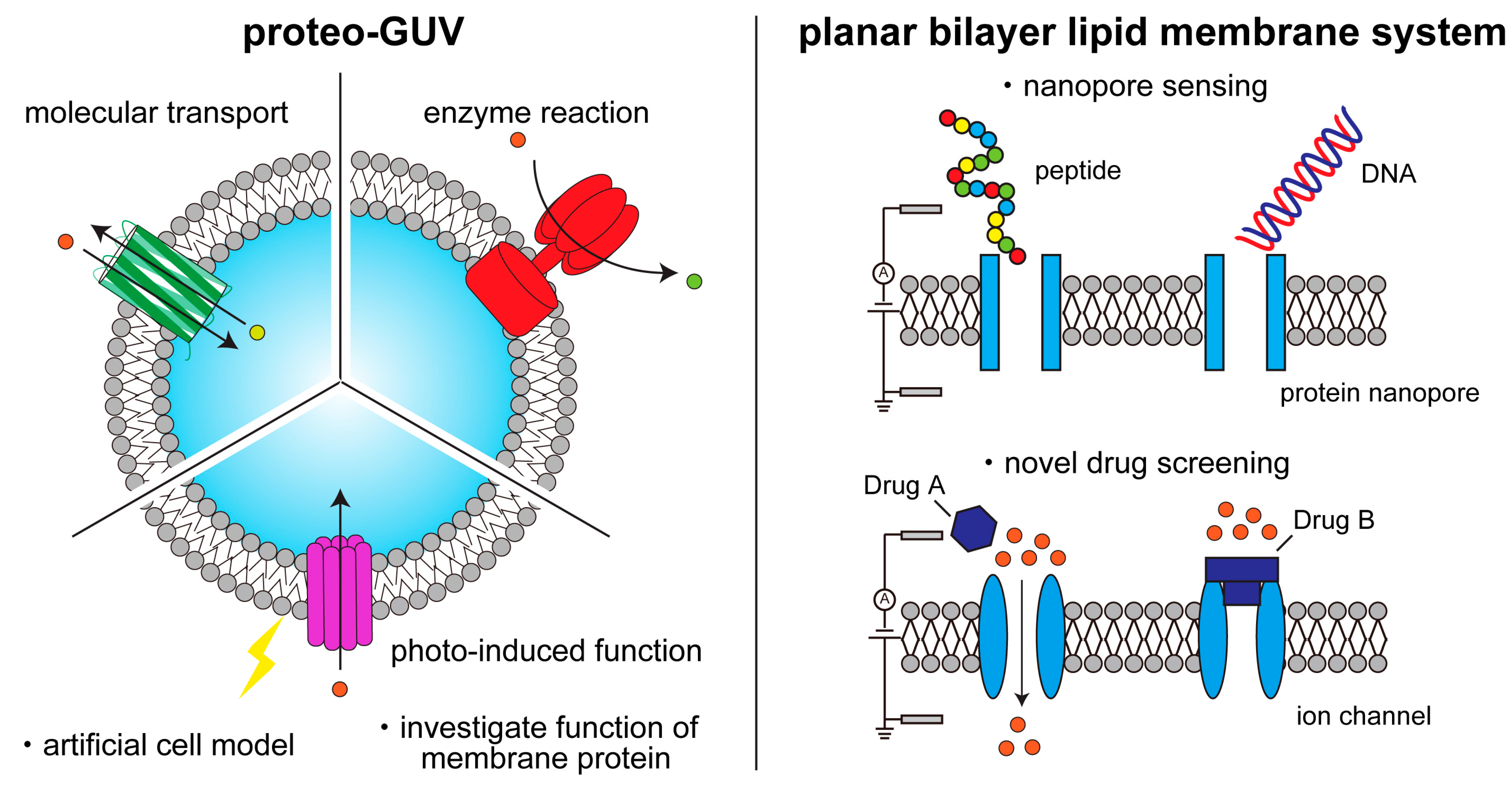
2. Formation of Cell-Sized Lipid Vesicles
3. Methodology of Reconstitution of Membrane Proteins into Cell-Sized Artificial Membrane
|
Protein |
Organism |
Type |
TM Region |
Complex |
TM Number |
Method |
Membrane Composition |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
BmrC/BmrD |
Bacillus subtilis |
ABC transporter |
α−helix |
BmrC/BmrD |
12 |
detergent mediate reconstitution |
DPhPC + DOPC/DOPE or DOPC/Sph/chol |
[74] |
|
BR |
Halophilic archaea |
proton pump |
α−helix |
− |
7 |
fusion |
EPC:EPA (9:1 [mol]) |
[74] |
|
CXCR4 |
Homo sapiens |
GPCR signaling protein |
α−helix |
homodimer |
14 (7 × 2) |
fusion |
DOPC |
[75] |
|
EmrE |
Escherichia coli |
multidrug transporter |
α−helix |
homodimer |
8 (4 × 2) |
direct reconstitution |
POPC |
[83] |
|
ETB |
Homo sapiens |
GPCR signaling protein |
α−helix |
− |
7 |
fusion |
DOPC |
[75] |
|
F1F0-ATP synthase |
Escherichia coli |
ATP production |
α−helix |
F1–F0 |
28 |
rehydration |
E. coli total lipid extract |
[84] |
|
FhuA |
Escherichia coli |
ferrichrome-iron receptor |
β−strand |
− |
22 |
fusion |
EPC:Tx-DHPE (99.5:0.5) |
[74] |
|
GL1 |
Homo sapiens |
γ-aminobutyric acid receptor |
α−helix |
− |
anchored |
rehydration |
DOPE:DOPC:DOPE-Atto647 (30:69.5:0.5) |
[85] |
|
GLUT1 |
Homo sapiens |
glucose transporter |
α−helix |
− |
12 |
fusion |
DOPC:DMPE-RhB:Biotylated PE (99.7:0.2:0.1) |
[86] |
|
IFITM3 |
Homo sapiens |
enveloped virus inhibitor |
α−helix |
− |
1 |
detergent mediate reconstitution |
POPC:cholesterol:Liss-Rho-PE (99:0.5:0.5 [mol]) |
[87] |
|
KcsA |
Streptomyces lividans |
potassium channels |
α−helix |
homotetramer |
8 (2 × 4) |
direct reconstitution |
DOPG or DOPE |
[88] |
|
KvAP |
Aeropyrum pernix |
voltage-gated potassium channels |
α−helix |
heteromer or homotetramer |
8 (2 × 4) |
rehydration |
DPhPC or EPC:EPA (9:1) |
[89] |
|
OmpF |
Escherichia coli |
porin |
β−strand |
− |
16 |
direct reconstitution |
PDMS26-b-PMOXA9 |
[90] |
|
OmpG |
Escherichia coli |
porin |
β−strand |
− |
14 |
direct reconstitution |
Outer membrane: DOPC Inner membrane: oleosin |
[76] |
|
OmpLA |
Escherichia coli |
phospholipase |
β−strand |
homodimer |
24 (12 × 2) |
direct reconstitution |
DOPC:DOPG (1:3) |
[77] |
|
PR |
SAR86 group of marine γ-proteobacteria |
proton transport |
α−helix |
− |
7 |
direct reconstitution |
POPC |
[78] |
|
RC |
Rhodobacter sphaeroides |
electron transport |
α−helix |
− |
10 |
detergent mediate reconstitution |
POPC:POPG (9:1 [mol]) |
[79] |
|
SLO |
Streptococcus pyogenes |
toxin |
α−helix |
homo 36~40 mer |
36~40 |
rehydration |
POPC, DOPC, SOPC, POPG |
[80] |
|
TmrAB |
thermus thermophilus |
ABC transporter |
α−helix |
− |
6 × 2 |
rehydration |
POPC:POPG:POPE: biotinylated-DOPE (40:30:29:1 [mol]) |
[81] |
|
TolC |
Escherichia coli |
expulsion of diverse molecules from the cell |
β−strand |
homotrimer |
12 (4 × 3) |
rehydration |
DOPC:DOPS:Atto647-DOPE (91.2:8:0.8) |
[85] |
|
t-SNARE |
Homo sapiens |
endocytosis/exocytosis |
α−helix |
Syntaxin -SNAP25 |
1 |
rehydration |
DOPC:DOPS:Atto647-DOPE (91.2:8:0.8) |
[85] |
|
VDAC1 |
Homo sapiens |
voltage dependent anion channel |
β−strand |
− |
19 |
fusion |
soybean polar extract: cholesterol (9:1) |
[82] |
4. Single-Channel Recording Using Planar Bilayer Lipid Membrane Systems
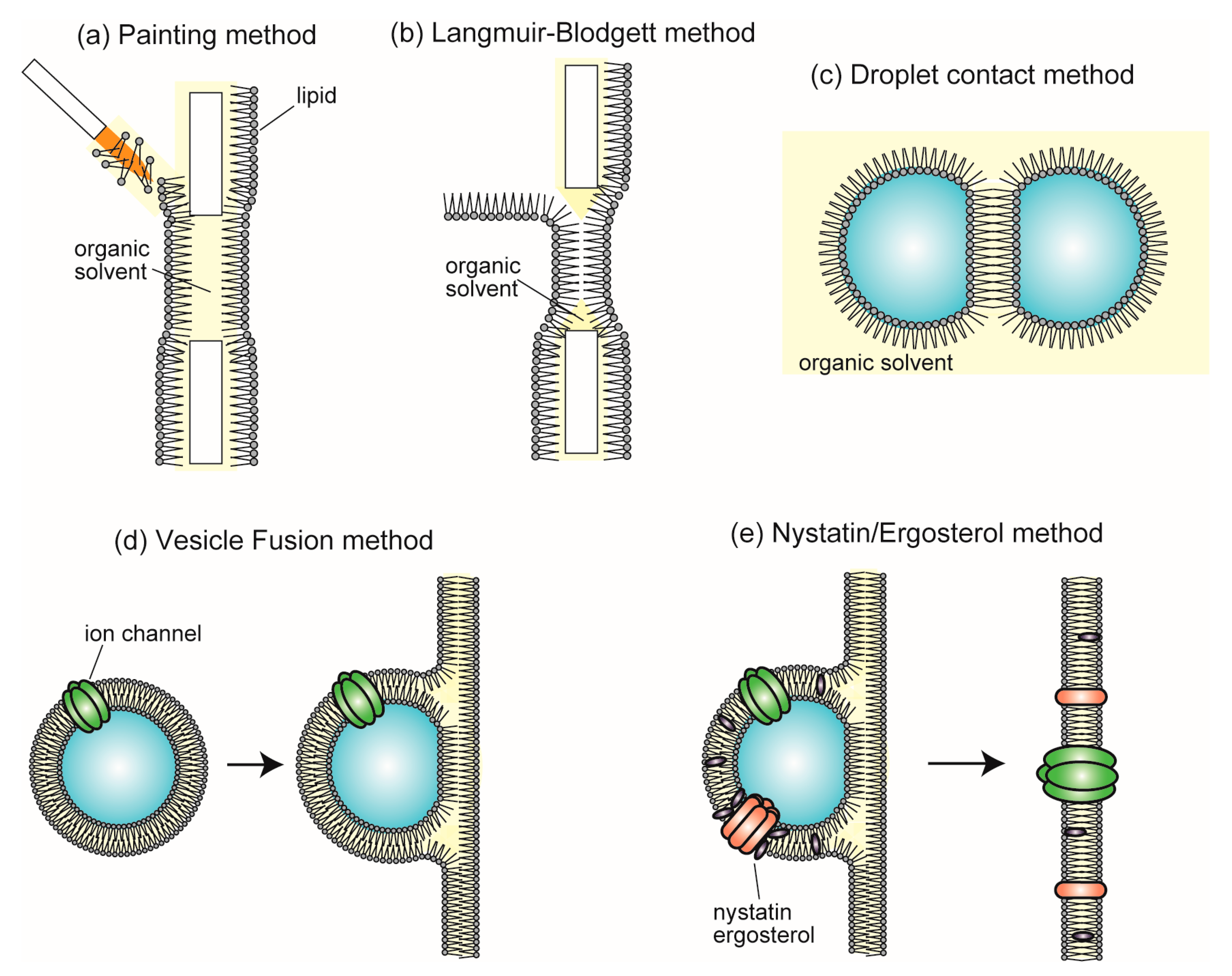
5. Lipid Vesicles Containing Some Types of Membrane Proteins for Creating Complex Artificial Cell Models
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms24087231
References
- Gilman, A.G. G proteins: Transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1987, 56, 615–649.
- Springer, T.A. Adhesion Receptors of the Immune System. Nature 1990, 346, 425–434.
- Poitelon, Y.; Kopec, A.M.; Belin, S. Myelin Fat Facts: An Overview of Lipids and Fatty Acid Metabolism. Cells 2020, 9, 812.
- Schenk, P.W.; Snaar-Jagalska, B.E. Signal Perception and Transduction: The Role of Protein Kinases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 1999, 1449, 1–24.
- Martin, T.F.J. Phosphoinositide Lipids as Signaling Molecules: Common Themes for Signal Transduction, Cytoskeletal Regulation, and Membrane Trafficking. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1998, 14, 231–264.
- Qin, J.; Guo, Y.; Xue, B.; Shi, P.; Chen, Y.; Su, Q.P.; Hao, H.; Zhao, S.; Wu, C.; Yu, L.; et al. ER-Mitochondria Contacts Promote MtDNA Nucleoids Active Transportation via Mitochondrial Dynamic Tubulation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4471.
- Li, L.; Conradson, D.M.; Bharat, V.; Kim, M.J.; Hsieh, C.H.; Minhas, P.S.; Papakyrikos, A.M.; Durairaj, A.S.; Ludlam, A.; Andreasson, K.I.; et al. A Mitochondrial Membrane-Bridging Machinery Mediates Signal Transduction of Intramitochondrial Oxidation. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1242–1258.
- Raff, M.C. Social Controls on Cell Survival and Cell Death. Nature 1992, 356, 397–400.
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Gueydan, C.; Han, J. Plasma Membrane Changes during Programmed Cell Deaths. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 9–21.
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway: Current Researches in Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742.
- Mizushima, N.; Klionsky, D.J. Protein Turnover via Autophagy: Implications for Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2007, 27, 19–40.
- Congreve, M.; de Graaf, C.; Swain, N.A.; Tate, C.G. Impact of GPCR Structures on Drug Discovery. Cell 2020, 181, 81–91.
- Davenport, A.P.; Scully, C.C.G.; de Graaf, C.; Brown, A.J.H.; Maguire, J.J. Advances in Therapeutic Peptides Targeting G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 389–413.
- Lee, Y.; Warne, T.; Nehmé, R.; Pandey, S.; Dwivedi-Agnihotri, H.; Chaturvedi, M.; Edwards, P.C.; García-Nafría, J.; Leslie, A.G.W.; Shukla, A.K.; et al. Molecular Basis of β-Arrestin Coupling to Formoterol-Bound Β1-Adrenoceptor. Nature 2020, 583, 862–866.
- Koivisto, A.P.; Belvisi, M.G.; Gaudet, R.; Szallasi, A. Advances in TRP Channel Drug Discovery: From Target Validation to Clinical Studies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 41–59.
- Rosenbaum, M.I.; Clemmensen, L.S.; Bredt, D.S.; Bettler, B.; Strømgaard, K. Targeting Receptor Complexes: A New Dimension in Drug Discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 884–901.
- He, S.; Moutaoufik, M.T.; Islam, S.; Persad, A.; Wu, A.; Aly, K.A.; Fonge, H.; Babu, M.; Cayabyab, F.S. HERG Channel and Cancer: A Mechanistic Review of Carcinogenic Processes and Therapeutic Potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1873, 188355.
- Pullman, M.E.; Penefsky, H.S.; Datta, A.; Racker, E. Partial Resolution of the Enzymes Catalyzing Oxidative Phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1960, 235, 3322–3329.
- Racker, E. Reconstitution of a Calcium Pump with Phospholipids and a Purified Ca++—Adenosine Triphosphatase from Sacroplasmic Reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 8198–8200.
- Keller, B.U.; Hedrich, R.; Vaz, W.L.C.; Criado, M. Single Channel Recordings of Reconstituted Ion Channel Proteins: An Improved Technique. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 1988, 411, 94–100.
- Ishmukhametov, R.R.; Russell, A.N.; Berry, R.M. A Modular Platform for One-Step Assembly of Multi-Component Membrane Systems by Fusion of Charged Proteoliposomes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13025.
- Berhanu, S.; Ueda, T.; Kuruma, Y. Artificial Photosynthetic Cell Producing Energy for Protein Synthesis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1325.
- Lee, K.Y.; Park, S.J.; Lee, K.A.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.; Meroz, Y.; Mahadevan, L.; Jung, K.H.; Ahn, T.K.; Parker, K.K.; et al. Photosynthetic Artificial Organelles Sustain and Control ATP-Dependent Reactions in a Protocellular System. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 530–535.
- Seddon, A.M.; Curnow, P.; Booth, P.J. Membrane Proteins, Lipids and Detergents: Not Just a Soap Opera. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2004, 1666, 105–117.
- Denisov, I.G.; Sligar, S.G. Nanodiscs in Membrane Biochemistry and Biophysics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 4669–4713.
- Dürr, U.H.N.; Gildenberg, M.; Ramamoorthy, A. The Magic of Bicelles Lights up Membrane Protein Structure. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6054–6074.
- Kim, H.J.; Howell, S.C.; Van Horn, W.D.; Jeon, Y.H.; Sanders, C.R. Recent Advances in the Application of Solution NMR Spectroscopy to Multi-Span Integral Membrane Proteins. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2009, 55, 335–360.
- Hong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, F. Membrane Protein Structure and Dynamics from NMR Spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2012, 63, 1–24.
- Binder, D.; Drepper, T.; Jaeger, K.E.; Delvigne, F.; Wiechert, W.; Kohlheyer, D.; Grünberger, A. Homogenizing Bacterial Cell Factories: Analysis and Engineering of Phenotypic Heterogeneity. Metab. Eng. 2017, 42, 145–156.
- Frank, J. Single-Particle Imaging of Macromolecules by Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2002, 31, 303–319.
- Fernandez-Leiro, R.; Scheres, S.H.W. Unravelling Biological Macromolecules with Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Nature 2016, 537, 339–346.
- Hilgemann, D.W. Cytoplasmic ATP-Dependent Regulation of Ion Transporters and Channels: Mechanisms and Messengers. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1997, 59, 193–220.
- Darszon, A.; Labarca, P.; Nishigaki, T.; Espinosa, F. Ion Channels in Sperm Physiology. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 481–510.
- Wan, Y.; Zong, C.; Li, X.; Wang, A.; Li, Y.; Yang, T.; Bao, Q.; Dubow, M.; Yang, M.; Rodrigo, L.A.; et al. New Insights for Biosensing: Lessons from Microbial Defense Systems. Chem. Rev. 2021, 122, 8126–8180.
- Misawa, N.; Osaki, T.; Takeuchi, S. Membrane Protein-Based Biosensors. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20170952.
- Misawa, N.; Fujii, S.; Kamiya, K.; Osaki, T.; Takaku, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Takeuchi, S. Construction of a Biohybrid Odorant Sensor Using Biological Olfactory Receptors Embedded into Bilayer Lipid Membrane on a Chip. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 711–716.
- Yamada, T.; Sugiura, H.; Mimura, H.; Kamiya, K.; Osaki, T.; Takeuchi, S. Highly Sensitive VOC Detectors Using Insect Olfactory Receptors Reconstituted into Lipid Bilayers. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, 2013–2026.
- Bangham, A.D.; Horne, R.W. Negative Staining of Phospholipids and Their Structural Modification by Surface-Active Agents as Observed in the Electron Microscope. J. Mol. Biol. 1964, 8, 660–668.
- Akashi, K.I.; Miyata, H.; Itoh, H.; Kinosita, K. Preparation of Giant Liposomes in Physiological Conditions and Their Characterization under an Optical Microscope. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 3242–3250.
- Horger, K.S.; Estes, D.J.; Capone, R.; Mayer, M. Films of Agarose Enable Rapid Formation of Giant Liposomes in Solutions of Physiologic Ionic Strength. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1810–1819.
- Lira, R.B.; Dimova, R.; Riske, K.A. Giant Unilamellar Vesicles Formed by Hybrid Films of Agarose and Lipids Display Altered Mechanical Properties. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 1609–1619.
- Angelova, M.I.; Dimitrov, D.S. Liposome Electroformation. Faraday Discuss. Chem. Soc. 1986, 81, 303–311.
- Dimitrov, D.S.; Angelova, M.I. Lipid Swelling and Liposome Formation Mediated by Electric Fields. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1988, 19, 323–336.
- Pautot, S.; Frisken, B.J.; Weitz, D.A. Production of Unilamellar Vesicles Using an Inverted Emulsion. Langmuir 2003, 19, 2870–2879.
- Pautot, S.; Frisken, B.J.; Weitz, D.A. Engineering Asymmetric Vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10718–10721.
- Tan, Y.C.; Hettiarachchi, K.; Siu, M.; Pan, Y.R.; Lee, A.P. Controlled Microfluidic Encapsulation of Cells, Proteins, and Microbeads in Lipid Vesicles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5656–5658.
- Hu, P.C.; Li, S.; Malmstadt, N. Microfluidic Fabrication of Asymmetric Giant Lipid Vesicles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1434–1440.
- Matosevic, S.; Paegel, B.M. Stepwise Synthesis of Giant Unilamellar Vesicles on a Microfluidic Assembly Line. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2798–2800.
- Abkarian, M.; Loiseau, E.; Massiera, G. Continuous Droplet Interface Crossing Encapsulation (CDICE) for High Throughput Monodisperse Vesicle Design. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 4610–4614.
- Karamdad, K.; Law, R.V.; Seddon, J.M.; Brooks, N.J.; Ces, O. Preparation and Mechanical Characterisation of Giant Unilamellar Vesicles by a Microfluidic Method. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 557–562.
- Karamdad, K.; Law, R.V.; Seddon, J.M.; Brooks, N.J.; Ces, O. Studying the Effects of Asymmetry on the Bending Rigidity of Lipid Membranes Formed by Microfluidics. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 5277–5280.
- Blosser, M.C.; Horst, B.G.; Keller, S.L. CDICE Method Produces Giant Lipid Vesicles under Physiological Conditions of Charged Lipids and Ionic Solutions. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 7364–7371.
- Romanov, V.; McCullough, J.; Gale, B.K.; Frost, A. A Tunable Microfluidic Device Enables Cargo Encapsulation by Cell- or Organelle-Sized Lipid Vesicles Comprising Asymmetric Lipid Bilayers. Adv. Biosyst. 2019, 3, 1900010.
- Shum, H.C.; Lee, D.; Yoon, I.; Kodger, T.; Weitz, D.A. Double Emulsion Templated Monodisperse Phospholipid Vesicles. Langmuir 2008, 24, 7651–7653.
- Arriaga, L.R.; Datta, S.S.; Kim, S.H.; Amstad, E.; Kodger, T.E.; Monroy, F.; Weitz, D.A. Ultrathin Shell Double Emulsion Templated Giant Unilamellar Lipid Vesicles with Controlled Microdomain Formation. Small 2014, 10, 950–956.
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.W.; Cho, J.C.; Weitz, D.A. Double-Emulsion Drops with Ultra-Thin Shells for Capsule Templates. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 3162–3166.
- Caschera, F.; Lee, J.W.; Ho, K.K.Y.; Liu, A.P.; Jewett, M.C. Cell-Free Compartmentalized Protein Synthesis inside Double Emulsion Templated Liposomes with In Vitro Synthesized and Assembled Ribosomes. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 5467–5469.
- Deshpande, S.; Caspi, Y.; Meijering, A.E.C.; Dekker, C. Octanol-Assisted Liposome Assembly on Chip. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10447.
- Deng, N.-N.; Yelleswarapu, M.; Huck, W.T.S. Monodisperse Uni- and Multicompartment Liposomes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7584–7591.
- Deng, N.; Huck, W.T.S. Microfluidic Formation of Monodisperse Coacervate Organelles in Liposomes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 9736–9740.
- Michelon, M.; Huang, Y.; de la Torre, L.G.; Weitz, D.A.; Cunha, R.L. Single-Step Microfluidic Production of W/O/W Double Emulsions as Templates for β-Carotene-Loaded Giant Liposomes Formation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 27–32.
- Ushiyama, R.; Koiwai, K.; Suzuki, H. Plug-and-Play Microfluidic Production of Monodisperse Giant Unilamellar Vesicles Using Droplet Transfer across Water–Oil Interface. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 355, 131281.
- Funakoshi, K.; Suzuki, H.; Takeuchi, S. Lipid Bilayer Formation by Contacting Monolayers in a Microfluidic Device for Membrane Protein Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 8169–8174.
- Kamiya, K.; Kawano, R.; Osaki, T.; Akiyoshi, K.; Takeuchi, S. Cell-Sized Asymmetric Lipid Vesicles Facilitate the Investigation of Asymmetric Membranes. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 881–889.
- Kamiya, K.; Arisaka, C.; Suzuki, M. Investigation of Fusion between Nanosized Lipid Vesicles and a Lipid Monolayer toward Formation of Giant Lipid Vesicles with Various Kinds of Biomolecules. Micromachines 2021, 12, 133.
- Kamiya, K.; Osaki, T.; Takeuchi, S. Formation of Nano-Sized Lipid Vesicles with Asymmetric Lipid Components Using a Pulsed-Jet Flow Method. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 327, 128917.
- Gotanda, M.; Kamiya, K.; Osaki, T.; Fujii, S.; Misawa, N.; Miki, N.; Takeuchi, S. Sequential Generation of Asymmetric Lipid Vesicles Using a Pulsed-Jetting Method in Rotational Wells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 261, 392–397.
- Gotanda, M.; Kamiya, K.; Osaki, T.; Miki, N.; Takeuchi, S. Automatic Generation System of Cell-Sized Liposomes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 292, 57–63.
- Kamiya, K.; Osaki, T.; Takeuchi, S. Formation of Vesicles-in-a-Vesicle with Asymmetric Lipid Components Using a Pulsed-Jet Flow Method. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 30071–30075.
- Elani, Y.; Law, R.V.; Ces, O. Vesicle-Based Artificial Cells as Chemical Microreactors with Spatially Segregated Reaction Pathways. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5305.
- Miwa, A.; Kamiya, K. Control of Enzyme Reaction Initiation inside Giant Unilamellar Vesicles by the Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Mediated Translocation of Cargo Proteins. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 3836–3846.
- Kamiya, K. Development of Artificial Cell Models Using Microfluidic Technology and Synthetic Biology. Micromachines 2020, 11, 559.
- Kamiya, K.; Takeuchi, S. Giant Liposome Formation toward the Synthesis of Well-Defined Artificial Cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5911–5923.
- Dezi, M.; Di Cicco, A.; Bassereau, P.; Lévy, D. Detergent-Mediated Incorporation of Transmembrane Proteins in Giant Unilamellar Vesicles with Controlled Physiological Contents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7276–7281.
- Fenz, S.F.; Sachse, R.; Schmidt, T.; Kubick, S. Cell-Free Synthesis of Membrane Proteins: Tailored Cell Models out of Microsomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 1382–1388.
- Suzuki, M.; Kamiya, K. Cell-Sized Asymmetric Phospholipid-Amphiphilic Protein Vesicles with Growth, Fission, and Molecule Transportation. iScience 2023, 26, 106086.
- Ohnishi, S.; Kamiya, K. Formation of Giant Lipid Vesicle Containing Dual Functions Facilitates Outer Membrane Phospholipase. ACS Synth. Biol. 2021, 10, 1837–1846.
- Eaglesfield, R.; Madsen, M.A.; Sanyal, S.; Reboud, J.; Amtmann, A. Cotranslational Recruitment of Ribosomes in Protocells Recreates a Translocon-Independent Mechanism of Proteorhodopsin Biogenesis. iScience 2021, 24, 102429.
- Altamura, E.; Milano, F.; Tangorra, R.R.; Trotta, M.; Omar, O.H.; Stano, P.; Mavelli, F. Highly Oriented Photosynthetic Reaction Centers Generate a Proton Gradient in Synthetic Protocells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3837–3842.
- Kajii, K.; Shimomura, A.; Higashide, M.T.; Oki, M.; Tsuji, G. Effects of Sugars on Giant Unilamellar Vesicle Preparation, Fusion, PCR in Liposomes, and Pore Formation. Langmuir 2022, 38, 8871–8880.
- Diederichs, T.; Tampé, R. Single Cell-like Systems Reveal Active Unidirectional and Light-Controlled Transport by Nanomachineries. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6747–6755.
- Varnier, A.; Kermarrec, F.; Blesneac, I.; Moreau, C.; Liguori, L.; Lenormand, J.L.; Picollet-D’Hahan, N. A Simple Method for the Reconstitution of Membrane Proteins into Giant Unilamellar Vesicles. J. Membr. Biol. 2010, 233, 85–92.
- Soga, H.; Fujii, S.; Yomo, T.; Kato, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Matsuura, T. In Vitro Membrane Protein Synthesis inside Cell-Sized Vesicles Reveals the Dependence of Membrane Protein Integration on Vesicle Volume. ACS Synth. Biol. 2014, 3, 372–379.
- Almendro-Vedia, V.G.; Natale, P.; Mell, M.; Bonneau, S.; Monroy, F.; Joubert, F.; López-Montero, I. Nonequilibrium Fluctuations of Lipid Membranes by the Rotating Motor Protein F1F0-ATP Synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11291–11296.
- Motta, I.; Gohlke, A.; Adrien, V.; Li, F.; Gardavot, H.; Rothman, J.E.; Pincet, F. Formation of Giant Unilamellar Proteo-Liposomes by Osmotic Shock. Langmuir 2015, 31, 7091–7099.
- Jang, H.S.; Cho, Y.K.; Granick, S. Biologically-Active Unilamellar Vesicles from Red Blood Cells. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 1393–1398.
- Guo, X.; Steinkühler, J.; Marin, M.; Li, X.; Lu, W.; Dimova, R.; Melikyan, G.B. Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Protein 3 Blocks Fusion of Diverse Enveloped Viruses by Altering Mechanical Properties of Cell Membranes. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 8155–8170.
- Yanagisawa, M.; Iwamoto, M.; Kato, A.; Yoshikawa, K.; Oiki, S. Oriented Reconstitution of a Membrane Protein in a Giant Unilamellar Vesicle: Experimental Verification with the Potassium Channel KcsA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11774–11779.
- Aimon, S.; Manzi, J.; Schmidt, D.; Larrosa, J.A.P.; Bassereau, P.; Toombes, G.E.S. Functional Reconstitution of a Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel in Giant Unilamellar Vesicles. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 25529.
- dos Santos, E.C.; Belluati, A.; Necula, D.; Scherrer, D.; Meyer, C.E.; Wehr, R.P.; Lörtscher, E.; Palivan, C.G.; Meier, W. Combinatorial Strategy for Studying Biochemical Pathways in Double Emulsion Templated Cell-Sized Compartments. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004804.
- Neher, E.; Sakmann, B. Single-Channel Currents Recorded from Membrane of Denervated Frog Muscle Fibres. Nature 1976, 260, 799–802.
- Hirano-Iwata, A.; Ishinari, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Niwano, M. Micro- and Nano-Technologies for Lipid Bilayer-Based Ion-Channel Functional Assays. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 1266–1274.
- Mueller, P.; Rudin, D.O.; Ti Tien, H.; Wescott, W.C. Reconstitution of Cell Membrane Structure In Vitro and Its Transformation into an Excitable System. Nature 1962, 194, 979–980.
- Montal, M.; Mueller, P. Formation of Bimolecular Membranes from Lipid Monolayers and a Study of Their Electrical Properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 3561–3566.
