Phenolic compounds are phytochemicals such as flavonoids which consist of flavonols, flavones, flavanonols, flavanones, anthocyanidins, isoflavones, lignans, stilbenoids, curcuminoids, phenolic acids, and tannins. They have phenolic hydroxyl groups in their molecular structures. These compounds are present in most plants, are abundant in nature, and contribute to the bitterness and color of various foods. Dietary phenolic compounds, such as quercetin in onions and sesamin in sesame, exhibit antioxidant activity and help prevent cell aging and diseases. In addition, other kinds of compounds, such as tannins, have larger molecular weights, and many unexplained aspects still exist. The antioxidant activities of phenolic compounds may be beneficial for human health.
- phenolic compounds
- antioxidant
- gut microbiota
1. Introduction
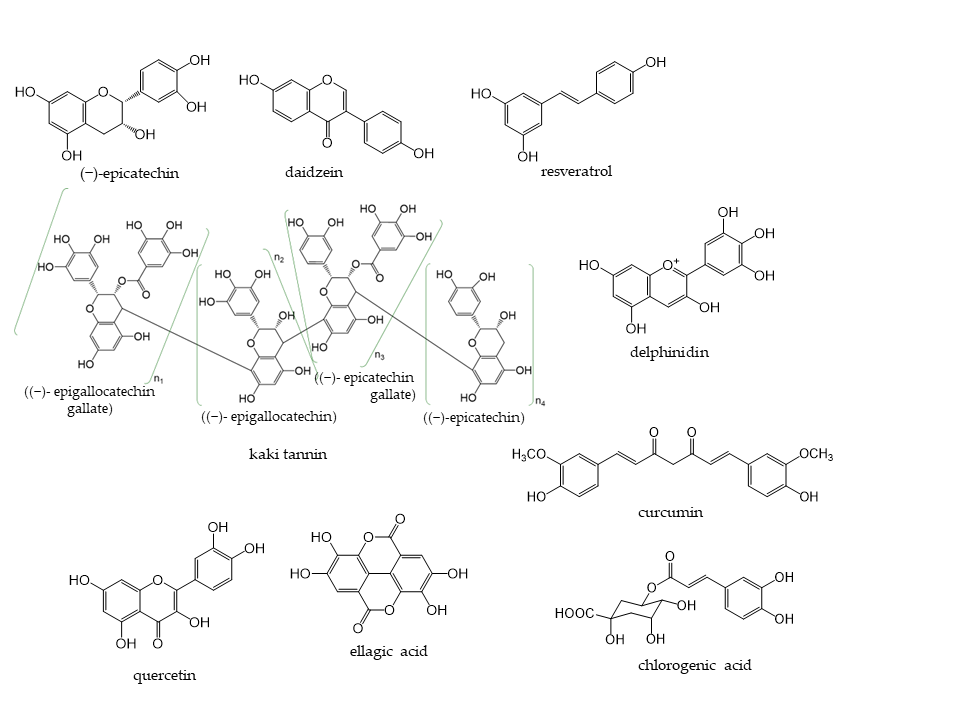
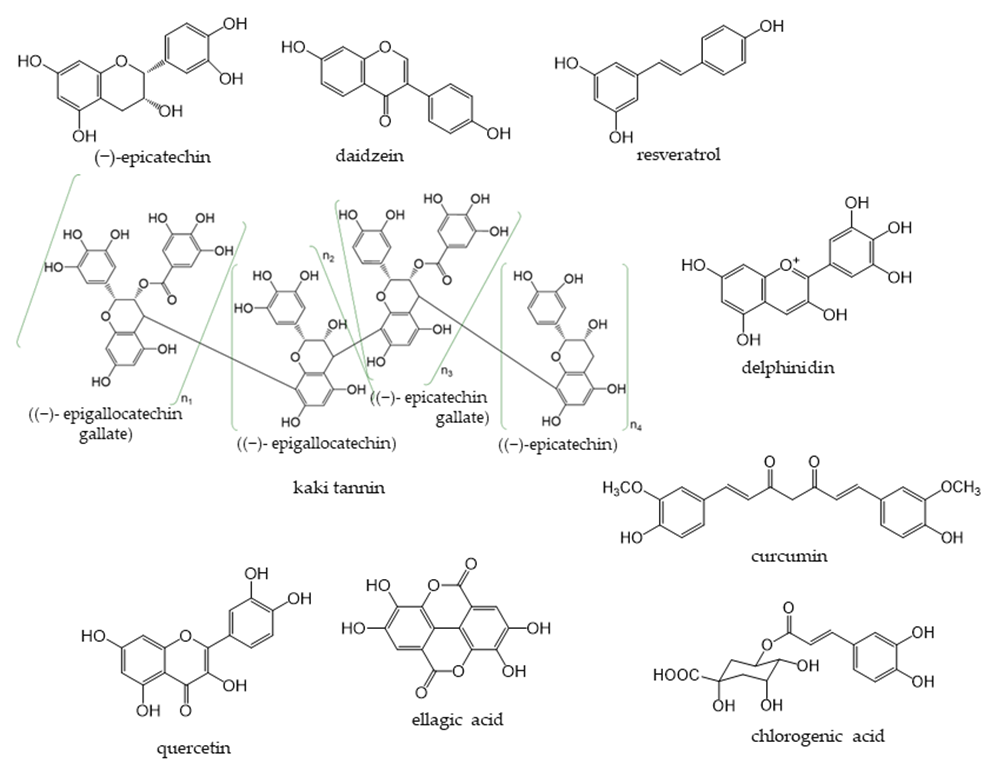
Phenolic compounds are components that contribute to the bitterness, astringency, and pigmentation of most plants. In addition to providing color to flowers, the physiological role of these compounds in plants is to confer biological protection against damage caused by ultraviolet rays, feeding by insects and herbivores, and pathogenic microorganisms. The type of phenolic compounds is dependent on its chemical structure [1] and includes well-known “catechins”, “isoflavones”, and “anthocyanins”. Phenolic compounds and their analogs have a wide variety of molecular sizes and structures (Figure 1).
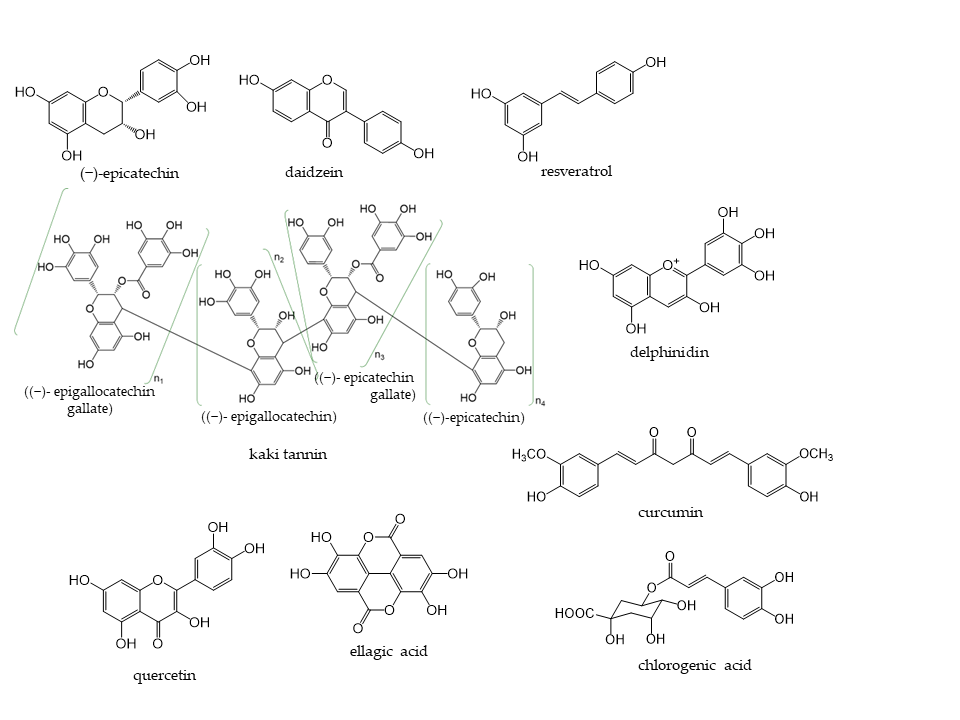 Figure 1. Representative phenolic compounds.
Figure 1. Representative phenolic compounds.
Previous studies on the antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds confirmed their role in the detoxification of excess reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the prevention of lifestyle-related diseases. The biological effects of phenolic compounds depend on the amount consumed and their digestion, absorption, and bioavailability. The majority of these compounds are not absorbed in the small intestine and reach the colon, in which glycosides are hydrolyzed and degraded by intestinal bacteria, generating various catabolites [2]. These catabolites have been found to contribute to human health.
Among health issues, lifestyle diseases and neurodegenerative diseases are of great concern. As a dietary method that contributes to health, there is a ketogenic diet that mainly consists of lipids which is useful for Alzheimer’s disease relief [3] or prevention of obesity and diabetes [4]. In addition to these kinds of diet, dietary phenolic compounds and their catabolites also have health benefits in cardiovascular diseases [5], rheumatoid arthritis [6,7], depression [8,9], and eye diseases [10].
2. Flavan-3-ols
Flavan-3-ols (flavanols) are a group of flavonoids that have a 2-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3-ol skeleton. Dietary flavan-3-ols are abundant in cocoa, tea, apples, grapes (including red wine), berries, plums, apricots, and nuts. Flavan-3-ols are complex flavonoids in which monomers, such as catechins and epicatechins, make up units to form oligomers and polymers. They are components of proanthocyanidins, and many analogs exist in nature. Catechins, major dietary monomers, are abundant in tea leaves, and many studies have investigated their antioxidant properties [20,21]. Unlike other classes of flavonoids, flavan-3-ols are not present in a glycosylated form in foods [22] and monomeric flavan-3-ols are exceptionally absorbed in the small intestine. The galloylation and polymerization of flavan-3-ols were shown to significantly delay intestinal absorption [23]. Therefore, when oligomers and polymers reach the colon, they need to be metabolized by the colonic microbiota to provide health benefits.
The mechanisms underlying the antioxidant effects of monomers have been reported [24]. The antioxidant capacity of flavan-3-ol monomers is exerted through phenolic hydroxyl groups that trap ROS and the chelation of iron ions to prevent lipid peroxidation [25,26]. By indirectly employing antioxidant pathways, flavan-3-ols regulate the synthesis of antioxidant-related enzymes and the signaling pathways of oxidative stress [27]. However, the mechanisms of action of oligomers and polymers remain unclear.
2.1. Dietary source, metabolism, and health benefits of flavan-3-ols
2.1.1. Tea
Tea is a major source of catechins. Various types of tea are available from the Camellia sinensis (L.) plant, depending on the harvesting and processing of its leaves. Green tea is unfermented tea; black tea is completely fermented tea; white tea and oolong tea are tea types with different degrees of fermentation [28]. There are five main types of catechins present in tea: (+)-catechin, (−)-epicatechin (EC), (−)-epigallocatechin (EGC), (−)-epicatechin gallate (ECG), and (−)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) (Figure 2) [29,30]. EGCG is the most abundant catechin in unfermented teas (green tea and white tea) [31]. During the fermentation of black tea, catechins are oxidized by polyphenol oxidase to complex structures, such as theaflavin dimers and thearubigin polymers [32]. Tea phenolic compounds and their metabolites possess antibacterial properties against pathogenic bacteria, such as Clostridium perfringens, C. difficile, Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Pseudomonas species, and enhance the activities of probiotics, including Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus species, thereby improving the overall balance of intestinal microbes [33,34].
Theaflavins and theasinensins are catechin dimers that are not absorbed in the small intestine to the same extent as catechin; they reach the large intestine and are metabolized by intestinal bacteria enzymes [36-38]. Four theaflavins exist in black tea: theaflavin (TF), theaflavin-3-gallate (TF3G), theaflavin-3’-gallate (TF3’G), and theaflavin-3,3’-digallate (TFDG) (Figure 2), with TFDG being the most abundant [1]. TFDG alters the composition of the intestinal flora, similar to EGCG. Theasinensins are also catechin dimers with two galloyl groups; five theasinensins in fermented tea have been identified and named theasinensins A, B, C, D, and E (Figure 2) [40]. Theasinensin A is the most abundant among the five compounds [37].
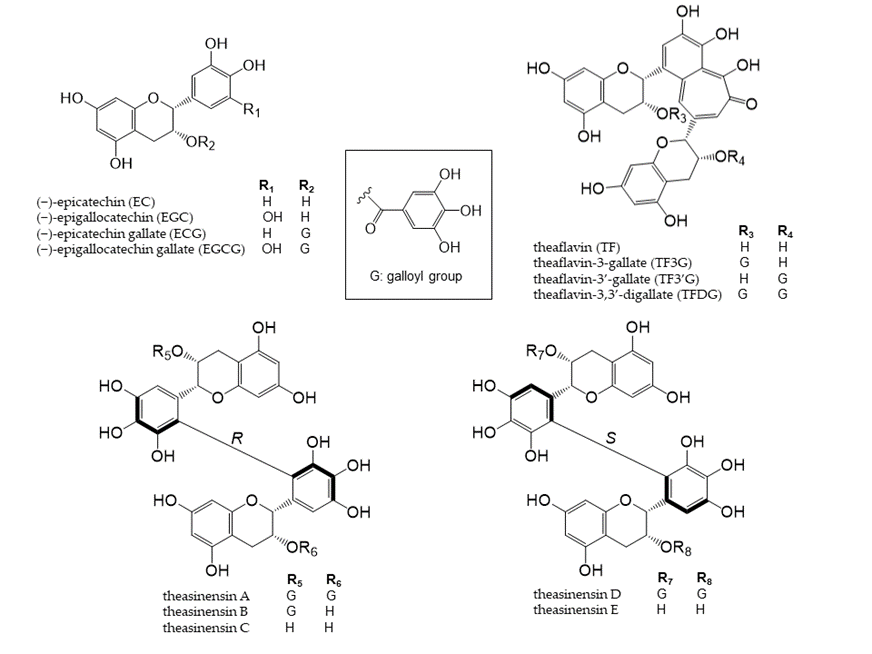
Figure 2. Chemical structures of catechins, theaflavins, and theasinensin A–E.
A well-established causal relationship has been reported between the intake of EC and the regulation of cardiovascular function [47,48]. EC is rapidly absorbed, and its metabolites are excreted in the urine 72 h after consumption [49]. Although EC does not affect the composition of the microbial flora [50], EC phase II and gut microbiota metabolites may induce complex nutrigenomic/epigenomic changes that regulate the function of brain endothelial cells [49,51]. In other words, the metabolites of EC may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases by maintaining the integrity of cerebrovascular endothelial cells, suggesting that the intake of EC contributes to improvements in cognitive ability [51].
The ingestion of tea reportedly attenuates alcoholic liver disease [52]. The administration of tea extract has been shown to activate antioxidant enzymes in the liver, change the intestinal flora, and promote liver function [53,54]. Although some types of teas promote liver function, others exert the opposite effects [52,53].
EGCG is the major catechin found in unfermented tea [28] and exhibits the highest antioxidant activity among the four catechin monomers in vitro [30]. EGCG may attenuate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) by regulating the interaction between the gut microbiota and bile acids [45].
Akkermansia muciniphila, belonging to the phylum Verrucomicrobia, has been implicated in obesity, glucose metabolism, and intestinal immunity [58]. The abundance of the genus Akkermansia has been shown to increase with the intake of phenolic compounds and exerts anti-obesity effects [59]. Furthermore, EGCG intake increased the abundance of the genus Akkermansia in mice compared to a high-fat diet [55].
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is an inflammatory disease that collectively refers to ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease, which are generally considered to have unknown (non-specific) etiologies. Catechins exhibit anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial activities, which may improve the abnormal condition of intestinal bacteria caused by IBD [60-63].
Catechins in tea are metabolized into phenyl-γ-valerolactones by the action of intestinal bacteria. Phenyl-γ-valerolactones regulate cellular proteolysis and exert neuroprotective effects [64].
2.1.2. Cocoa
Cocoa is generally produced by fermenting and roasting the seeds of Theobroma cacao and then pulverizing the cocoa cake obtained by removing the fat content. Although flavan-3-ols are relatively abundant in cocoa, its components vary depending on the type of cacao, place of origin, time of harvest, and processing of cocoa [41-43]. Cocoa flavan-3-ols, along with (+)-catechin and procyanidin B1 and B2 (Figure 3), as well as trace amounts of other flavanols [44], mostly exist as EC.
Phenolic compounds in cocoa are metabolized in both the small and large intestine to produce metabolites that affect human health [41,45,46].
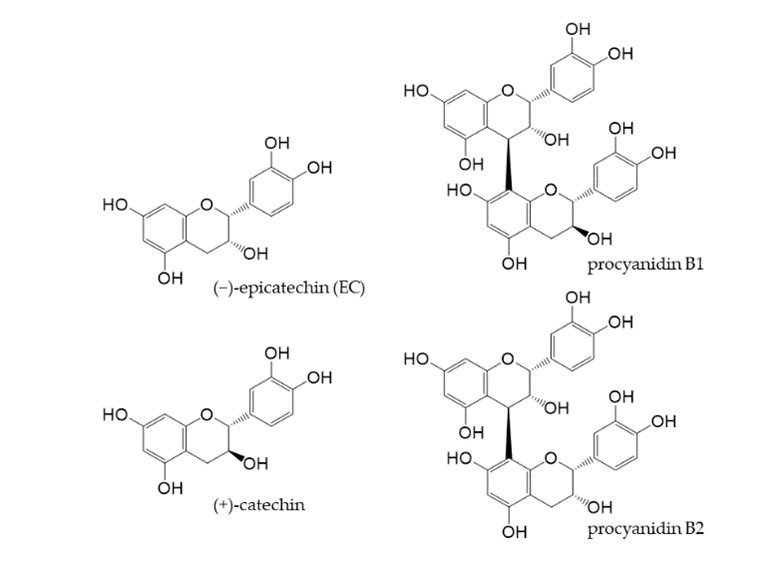
Figure 3. Chemical structures of main flavan-3-ols in cocoa powder.
Flavanols in cocoa may function as prebiotics to maintain intestinal immunomodulation by regulating the gut microbiota [74-76]. The ingestion of cocoa powder was previously suggested to change the intestinal flora of the diabetic Zucker rat model, by strengthening the intestinal barrier and ameliorating colonic inflammation, thereby attenuating diabetes [77]. Cocoa powder was also shown to down-regulate inflammation markers and suppress inflammation-related colon carcinogenesis; therefore, its consumption may be promising for the prevention of intestinal inflammation and related cancers [78]. Cocoa flavanols also exert endothelium-dependent vasodilatory effects [79], suggesting their potential to ameliorate cardiovascular diseases [80].
3. Condensed Tannins
Tannin is a general term for astringent plant components that exist widely throughout the plant kingdom and have been traditionally used to tan leather. There are two types of tannins, one of which is hydrolyzed tannins which are polymers of ellagic acids or gallic acids, and the another is condensed tannins which are polymers of catechins. They are hydrolyzed or decomposed under specific conditions and produce low molecular weight phenolic compounds. The astringent skin of chestnuts and walnuts contain hydrolyzed tannins and astringent persimmons contain condensed tannins. Red wine also contains condensed tannins, but the degree of polymerization of catechins are altered depending on the degree of fermentation and the manufacturing method.
Kaki tannins have been reported to reshape the gut microbiota in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet [90].
Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) is the most common nontuberculous mycobacterium that causes chronic pulmonary infections in immunodeficient individuals. Kaki tannins, used as a dietary supplement, reduce the symptoms of pulmonary MAC infection [17], suggesting an impact on mucosal immune inflammation, including that of the gut, through their anti-inflammatory effects and changes to the gut microbial composition. Moreover, kaki tannins may need to be digested and/or fermented into smaller molecules in vivo prior to their absorption into the body in order to exert their beneficial effects. The artificial digestion of the non-extracted residues of dried persimmons containing kaki tannins suggested that intestinal bacteria degraded the tannins into lower molecular weight fragments [19].
UC is a chronic IBD induced by the dysregulation of the immune response in the intestinal mucosa. The pathogenesis of UC was less severe in a mouse model fed kaki tannins than in a control diet group [18]. Furthermore, the gene expression of an inflammatory cytokine (IL-1β) and chemokine (CXCL1) was significantly decreased in the tannin diet group. An analysis of the composition of the fecal microbiota of mice employing 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing revealed that a treatment with DSS significantly increased the abundance of the phylum Enterobacteriaceae in the control diet group, whereas it was significantly suppressed in the kaki tannin diet group.
4. Flavonols
Flavonols, a subclass of flavonoids with a 3-hydroxyflavone skeleton, are widely present in plants [22]. Typical flavonols include myricetin (in grapes and berries), kaempferol (in tea, broccoli, and ginger), rutin (in asparagus and buckwheat), and quercetin (Figure 4). Quercetin is a representative flavonol that has been extensively examined and is present in vegetables and fruits, such as onions, broccoli, and apples. Flavonols generally exist in a glycosidic form and are deglycosylated and absorbed in the small intestine. After absorption, they are rapidly metabolized by phase II enzymes in the liver and circulate as methyl, glucuronide, and sulfate metabolites [94,95]
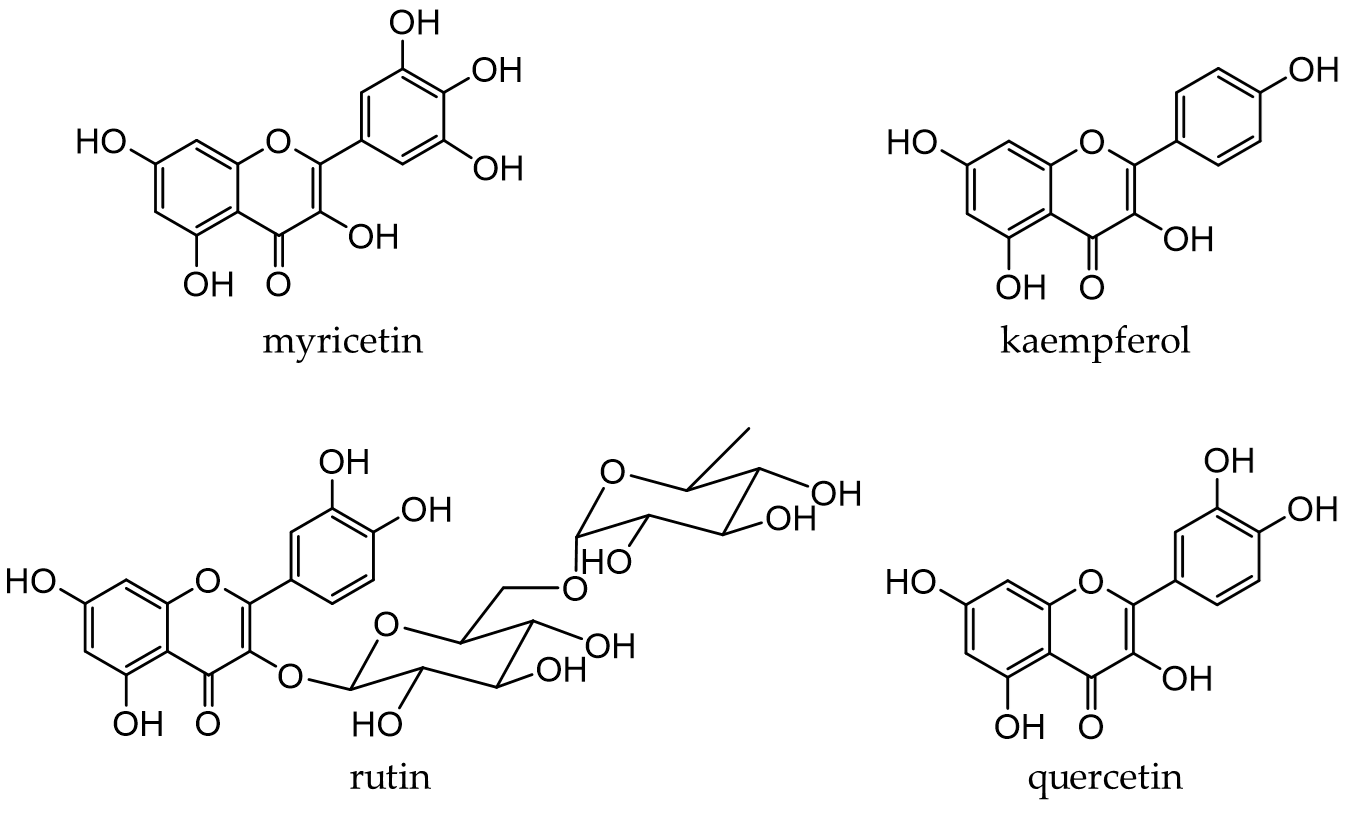
Figure 4. Chemical structures of major flavonols.
4.1. Dietary source, metabolism, and health benefits of flavonols
4.1.1. Onions
Onions (Allium cepa L.) are used as an ingredient in various dishes. They are rich in flavanols, the most abundant of which is quercetin [96,97]. Quercetin (an aglycone) is mostly present in the outer skin and quercetin 4'-glucoside and quercetin 3,4'-diglucoside in the bulbs, which are generally edible [98,99]. Figure 5 shows the quercetin catabolites produced by intestinal bacteria and phase II enzymes in the liver. Quercetin derivatives in onions increase their bioavailability through cooking processes, such as baking, frying, and grilling [100].
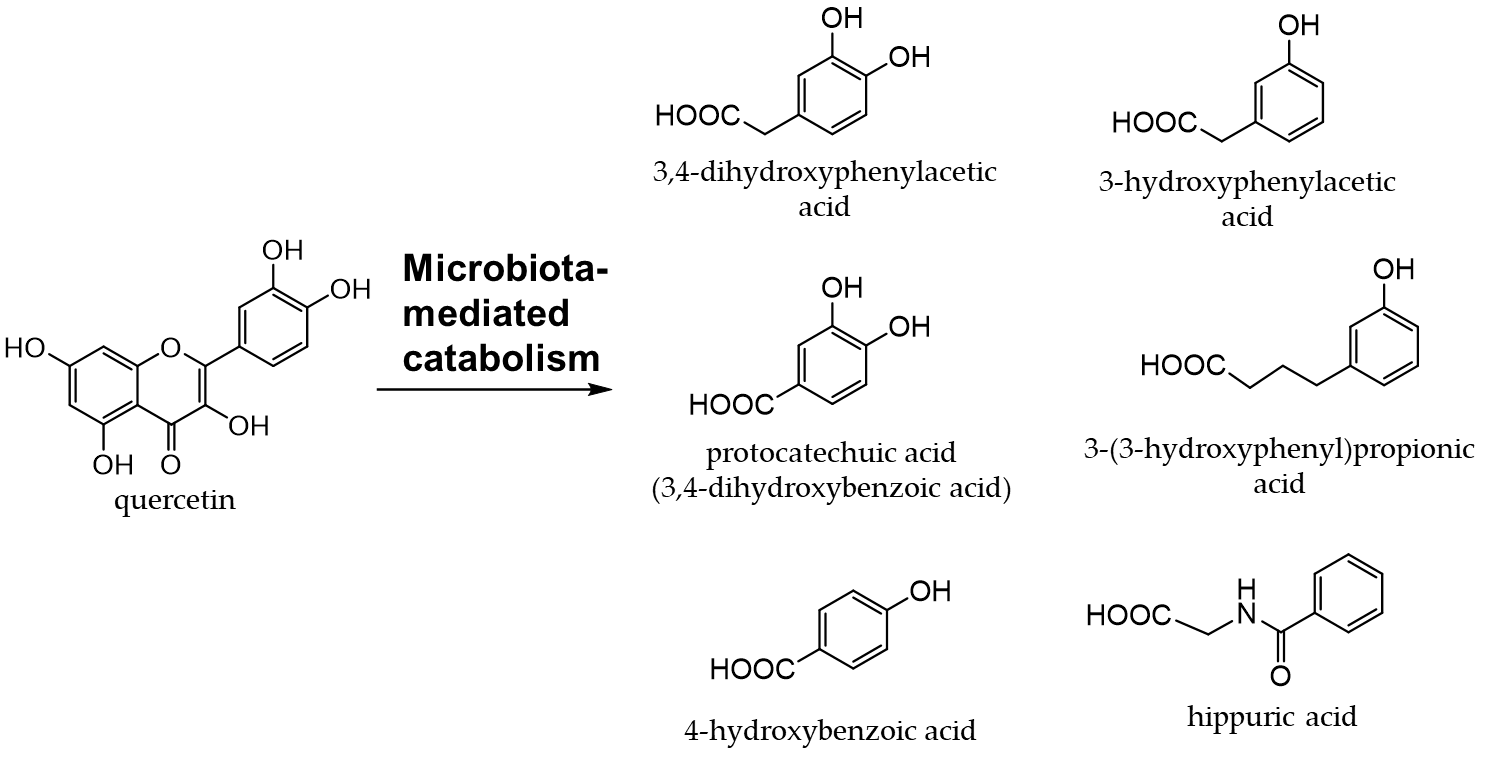
Figure 5. Quercetin catabolites by intestinal bacteria.
Quercetin exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-osteoporotic activities [95,105]. The administration of quercetin and quercetin glycosides extracted from onion skin to rats on a high-fat diet increased serum antioxidant activity and significantly increased enzyme activity derived from intestinal bacteria [106]. In other words, quercetin effectively reduced the intestinal flora abnormalities induced by the high-fat diet. However, in human clinical studies, the administration of onion peel extracts to obese patients with hypertension did not attenuate their symptoms [107]. Similarly, in clinical studies on hypertension and rheumatoid arthritis, the administration of quercetin did not exert beneficial effects [108-112].
Quercetin glycosides are catabolized to produce phenolic acids by intestinal bacteria [113]. Among the phenolic acids derived from quercetin glycosides, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid is the most effective at scavenging free radicals and inducing phase II enzymes [114]. Quercetin has been implicated in the attenuation of insulin resistance and atherosclerosis in obesity-related diseases [116-119]. It was found to promote intestinal homeostasis by changing the intestinal flora [120,121] and also plays a role in the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease [122,123].
4.1.2. Buckwheat
Buckwheat is widely grown in Asia, Europe, and the Americas. Both common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) and tartary buckwheat (F. tataricum (L.) Gilib.) are used as food sources, and the antioxidant activity of tartary buckwheat is higher than that of common buckwheat [101]. Rutin is the main flavonol in buckwheat, accounting for 90% of all phenolic compounds [102].
Rutin and quercetin contained in tartary buckwheat regulate gut microbiota and are involved in lipid metabolism [133]. Rutin had little effect on attenuating obesity but tended to decrease fat deposition in the liver [133]. Phenolic compounds extracted from tartary buckwheat bran showed dose-dependent anticancer activity against human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells [134].
5. Isoflavones
Isoflavones are flavonoids with 3-phenylchromone as the basic skeleton (Figure 6). They are abundant in plants of the legume family (Fabaceae), such as soybeans and kudzu.
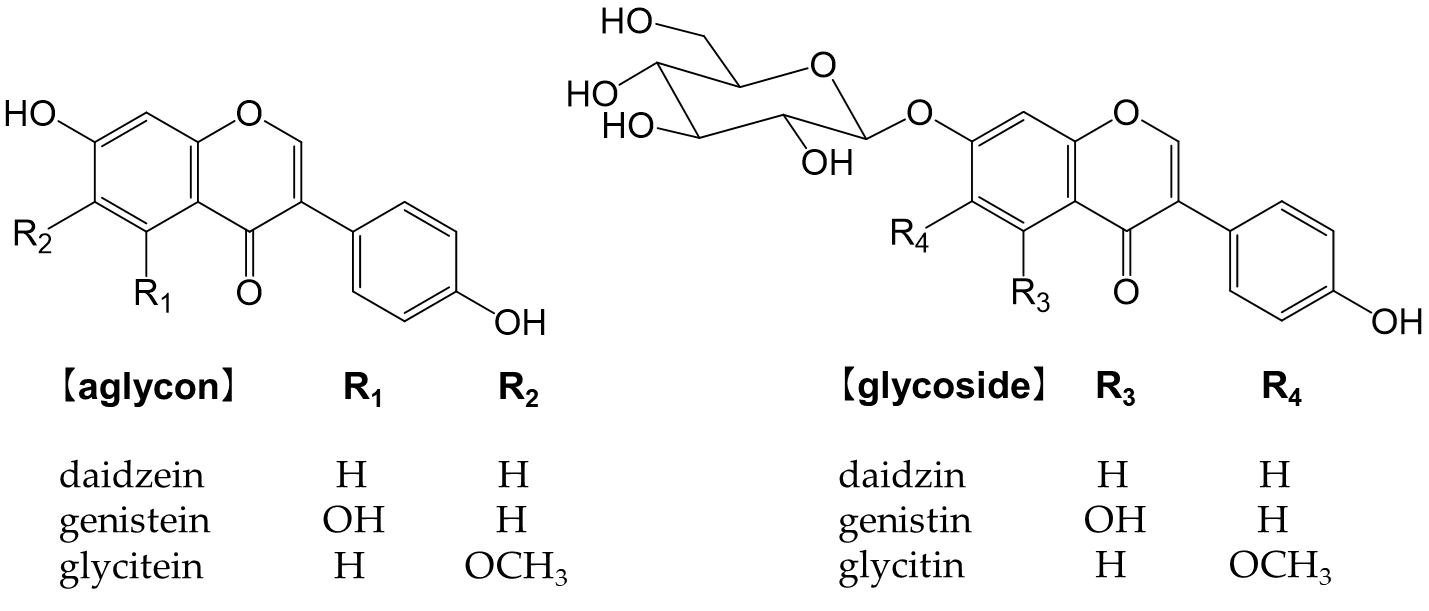
Figure 6. Chemical structure of the main isoflavones and isoflavone glycosides.
Isoflavones bind to estrogen receptors in the body and exert a number of effects because their chemical structures are similar to estrogen [147]. They may be beneficial, but also detrimental [148]. For example, while isoflavones are expected to effectively prevent osteoporosis, breast cancer, and prostate cancer, they also increase the risk of the onset and recurrence of breast cancer [148]. Glycosides are not easily absorbed in the small intestine and must be converted into aglycones, such as genistein and daidzein, to function in vivo [149,150].
Soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) are the most abundant source of isoflavones [151]. Many isoflavones, such as genistin and daidzin, are present in food (Figure 6). In the small intestine, lactase-phlorizin hydrolase and cytosolic β-glucosidase hydrolyze monoglucuronides to form aglycones [152,153]. The absorbed isoflavone aglycones are mainly metabolized to glucuronides and sulfates by endogenous phase I and phase II enzymes. Isoflavones are excreted into the intestines via the enterohepatic circulation, and unabsorbed isoflavones reach the colon and are metabolized to form the metabolite, equol, and other metabolites by intestinal bacteria [154].
Soybeans are rich in isoflavones, particularly genistin and daidzin [151]. Isoflavones are phytoestrogens, such as the female hormone 17-β-estradiol, which are less active than hormones, but exhibit estrogenic activity [156]. Therefore, the intake of isoflavones is expected to alleviate menopausal symptoms in women, increase bone formation, and reduce the incidence of cardiovascular disease. Equol is a metabolite of daidzin/daidzein formed by intestinal bacteria. It is more stable and more easily absorbed than daidzein [157] and exhibits stronger estrogenic activity than other isoflavones and isoflavone-derived metabolites [158-161]. Isoflavone aglycones and glycosides are both catabolized by enzymes of the intestinal microbiota to produce high levels of antioxidant substances, such as equol. A correlation has been reported between soybean intake and the attenuation of menopausal symptoms [162].
The intake of soy isoflavones has been suggested to reduce bone resorption, prevent some types of cancers, and improve learning [163-166]. These health effects are attributed to equol produced from soy isoflavones by the action of the intestinal microbiota.
6. Phenylpropanoids
Phenylpropanoids, also called lignoids, are compounds that have a C6-C3 skeleton, which consist with a C3 group attached to an aromatic ring. Monomers include caffeic acid, which is widely present in plants, and chlorogenic acid (an ester of caffeic acid and quinic acid), which is abundant in green coffee beans. Sesamin is a dimer, also known as lignan, and is abundant in sesame seeds. Chlorogenic acid may be ingested from food. Figure 7shows the chemical structures of the major phenylpropanoids.

Figure 7. Chemical structures of major phenylpropanoids.
6.1. Dietary source, metabolism, and health benefits of phenylpropanoids
6.1.1. Coffee
Coffee is one of the most consumed beverages in the world. It contains at least 30 types of chlorogenic acids [173]. The term “chlorogenic acids” refers to a group of phenolic compounds, of which approximately 400 have been discovered to date [174]. 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid is the main chlorogenic acid found in green coffee beans. Although the type and concentration of chlorogenic acids vary depending on the type of coffee bean, the roasting process, and extraction method, the beneficial health effects of coffee are related to its chlorogenic acid content, whether green or roasted. The high antioxidant activity of coffee is attributed to the amount of chlorogenic acid present [175].
Chlorogenic acids exhibit antioxidant activity [185-187] and anti-obesity activity in vivo [188-190]. Daily coffee consumption reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes [191]. Chlorogenic acid from coffee possesses prebiotic properties in vivo [192,193]. Therefore, the daily consumption of coffee may contribute to the prevention of obesity and lifestyle-related diseases.
6.1.2. Sesame
Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) is an edible seed and source of high-quality edible oil. Sesame oil exhibits antioxidant activity and possesses health-promoting properties because it contains vitamin E and lignans [179,180]. The major lignans in sesame are sesamin and sesamolin, which are formed by the dimerization of two phenylpropanoids [181].
The lignans in sesame have a number of health benefits, including anticancer activity, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases, and anti-inflammatory effects [199,200]. They are converted into enterolignans by intestinal bacteria and exert their effects as phytoestrogens [201]. Sesame lignans have been shown to inhibit L-tryptophan indole-lyase (TIL) produced by intestinal bacteria and suppress the production of indoxyl sulfate, a uremic toxin, catalyzed by TIL [202]. The inhibition of TIL by sesame lignans has potential as a strategy to prevent and treat chronic kidney diseases. Although sesaminol triglucoside, a sesame lignan glycoside, did not inhibit TIL, it induced significant increases in Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium spiecies and changed the intestinal microbial environment [203].
7. Stilbenoids
Stilbenoids are derivatives of stilbene, an aromatic hydrocarbon called 1,2-diphenylethene. Major stilbenoids are shown in Figure 8. Resveratrol is a type of stilbenoid that is present in many plant food materials, such as grapes, cranberries, red currants, and peanut skin, as well as in their processed products [210]. Among stilbenoids, resveratrol has been extensively studied.
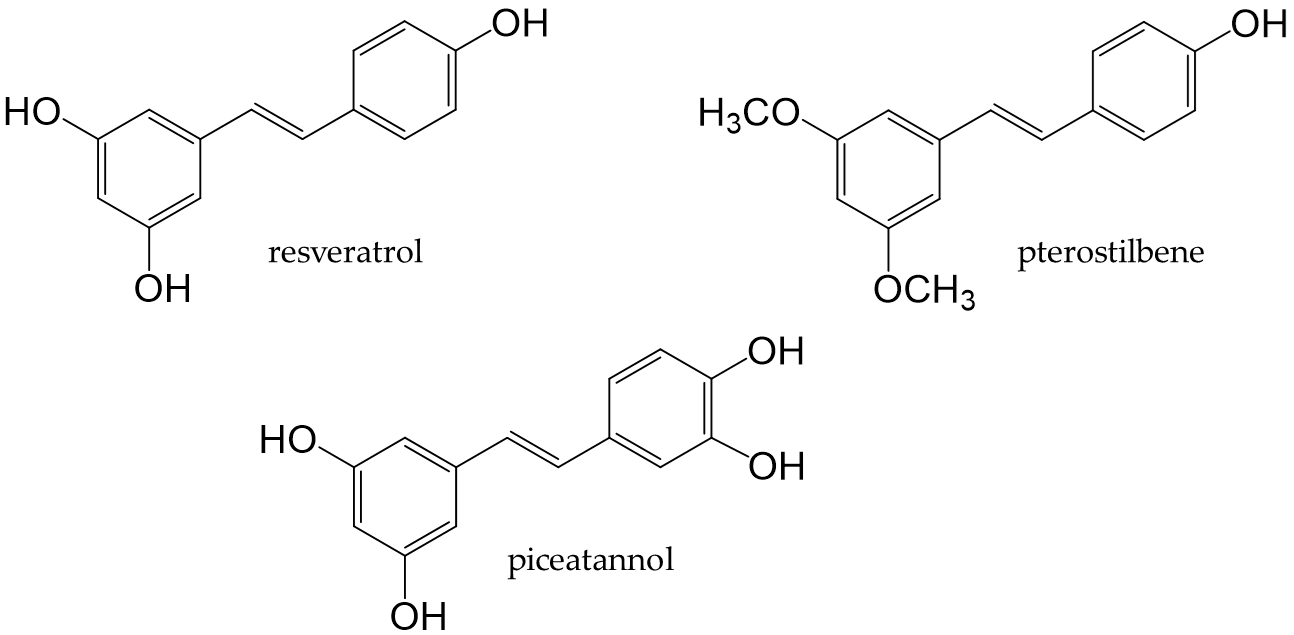
Figure 8. Chemical structures of major stilbenoids.
Resveratrol, a stilbenoid found in many plants, possesses antifungal and antibacterial properties. The food sources that contain resveratrol are grapes, wine [210], and grape seed oil [211]. Resveratrol, in its native state, is present at low amounts in humans, with only 1-8% being detected in serum. Although 75% is absorbed, it is rapidly metabolized [212,213].
Resveratrol has been shown to modulate and promote intestinal barrier function in mice, suggesting its potential to augment the intestinal flora [221,222]. Resveratrol prevented obesity and attenuated NAFLD and NASH by modulating the intestinal flora, maintaining intestinal barrier integrity, and suppressing intestinal inflammation in animal models [223-226]. Furthermore, the administration of resveratrol reportedly affected the intestinal flora and steroid metabolism in middle-aged men with metabolic syndrome [214,227-229]; however, the underlying mechanisms have not yet been elucidated. Red wine consumption reduced the risk of coronary heart disease and prevented obesity through the beneficial effects of phenolic compounds in red wine, particularly resveratrol [230,231].
8. Curcuminoids
Turmeric is a spice prepared from the underground stems of Curcuma longa L. It contains curcuminoids, such as curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxy-curcumin (Figure 9). Curcumin is the most abundant curcuminoid in turmeric [252] and contains phenolic hydroxyl groups in its chemical structure; therefore, it functions as a potent antioxidant that suppresses the production of ROS [253].
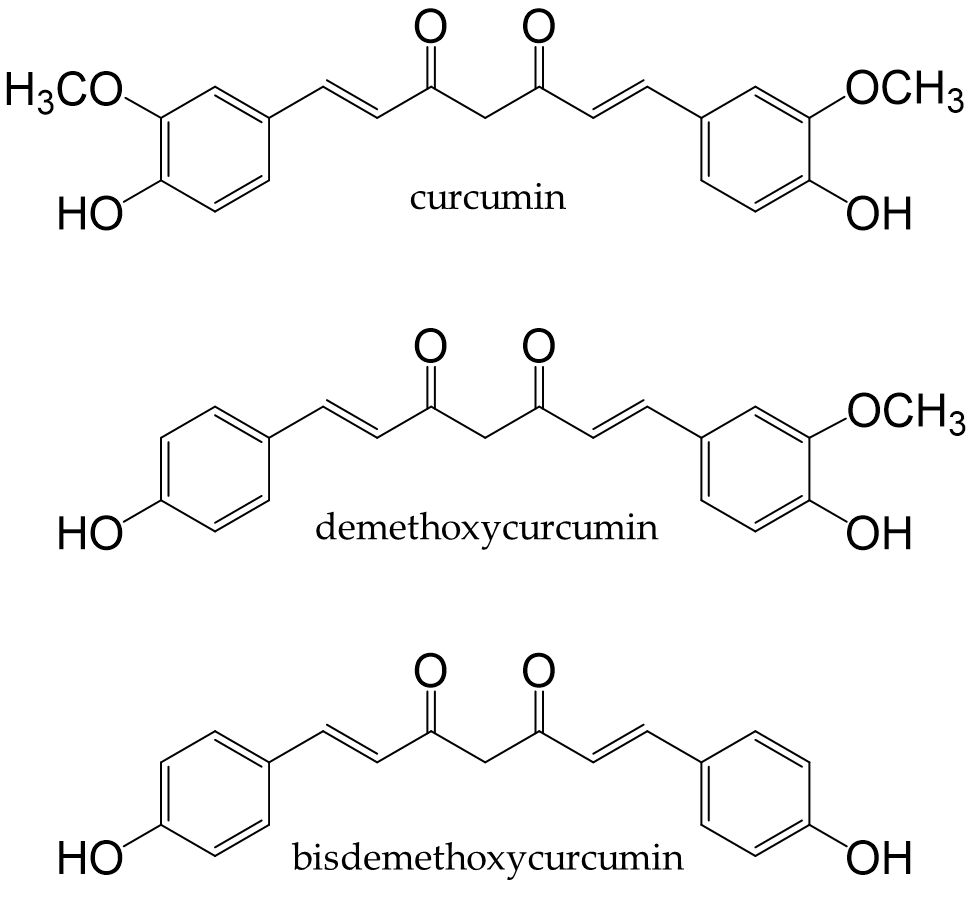
Figure 9. Chemical structures of curcuminoids.
Curcumin exhibits anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and anti-tumor activities [257-261] and interferes with cancer-associated signaling pathways by targeting proteins and modulating gene expression [262,263]. In human clinical trials, the administration of curcumin capsules to patients with colorectal cancer reduced inflammation and oxidative stress in malignant colorectal epithelial cells. It also attenuated inflammation in patients with UC and gastrointestinal disorders [264-267].
9. Conclusion
Target phenolic compounds must be absorbed to exert their effects, and this requires the cleavage of the sugar of a glycoside. The glycoside is then converted into an aglycone that is subsequently metabolized by phase I and phase II enzymes in the small intestine and liver before circulating in the body. Unabsorbed phenolic compounds undergo biotransformation by intestinal bacteria, after which they are absorbed and circulated in the body. These metabolites exert antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Although phenolic compounds have been extensively examined in animal and cell culture studies in the last decade, the number of human clinical trials has been insufficient. Research on their effects in humans requires a great deal of effort because detailed planning and massive data collection are required due to large individual differences. Dietary ingredients are safe for consumption, but do not exert immediate effects. Further research on the nutrients present in the daily diet and their beneficial effects is warranted and may provide insights into the prevention or attenuation of diseases.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/antiox12040880