Quercetin is a dietary flavonoid present in vegetables, fruits, and beverages, such as onions, apples, broccoli, berries, citrus fruits, tea, and red wine. Flavonoids have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, acting in the prevention of several diseases.
- quercetin
- metabolism
- inflammatory
1. Introduction
Flavonoids are dietary phytochemicals, from the polyphenol class, found in a variety of fruits, vegetables, and beverages, including citrus fruits, strawberries, raspberries, apples, grapes, cocoa, legumes, grains, coffee, green tea, and red wine [1]. According to their chemical characteristics, flavonoids are classified into subgroups, such as flavonols, flavones, isoflavones, flavanones, flavanols, and anthocyanidins [2]. In general, flavonoid subgroups have nutritional properties and therapeutic potential on different pathologies, such as cancer, cardiovascular, neurological, inflammatory, and metabolic diseases [2][3][4]. Due to their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, antimicrobial, antitumor, and antiviral properties, flavonoids can exert significant beneficial effect, modulating various biological processes [5]. Flavonoids exhibit the ability to scavenge ROS, activate antioxidant enzymes and inhibit enzymes related to the production of free radicals, as well as downregulate the expression and synthesis of factors related to oxidative stress, such as iNOS and nitric oxide (NO) [6][7]. Thus, the main mechanisms of action by which flavonoids exert their effect are related to their ability to inhibit ROS production and reduce the synthesis of inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α, IL-6, interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), COX-2, and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) [4][8].
2. Flavonoid Quercetin
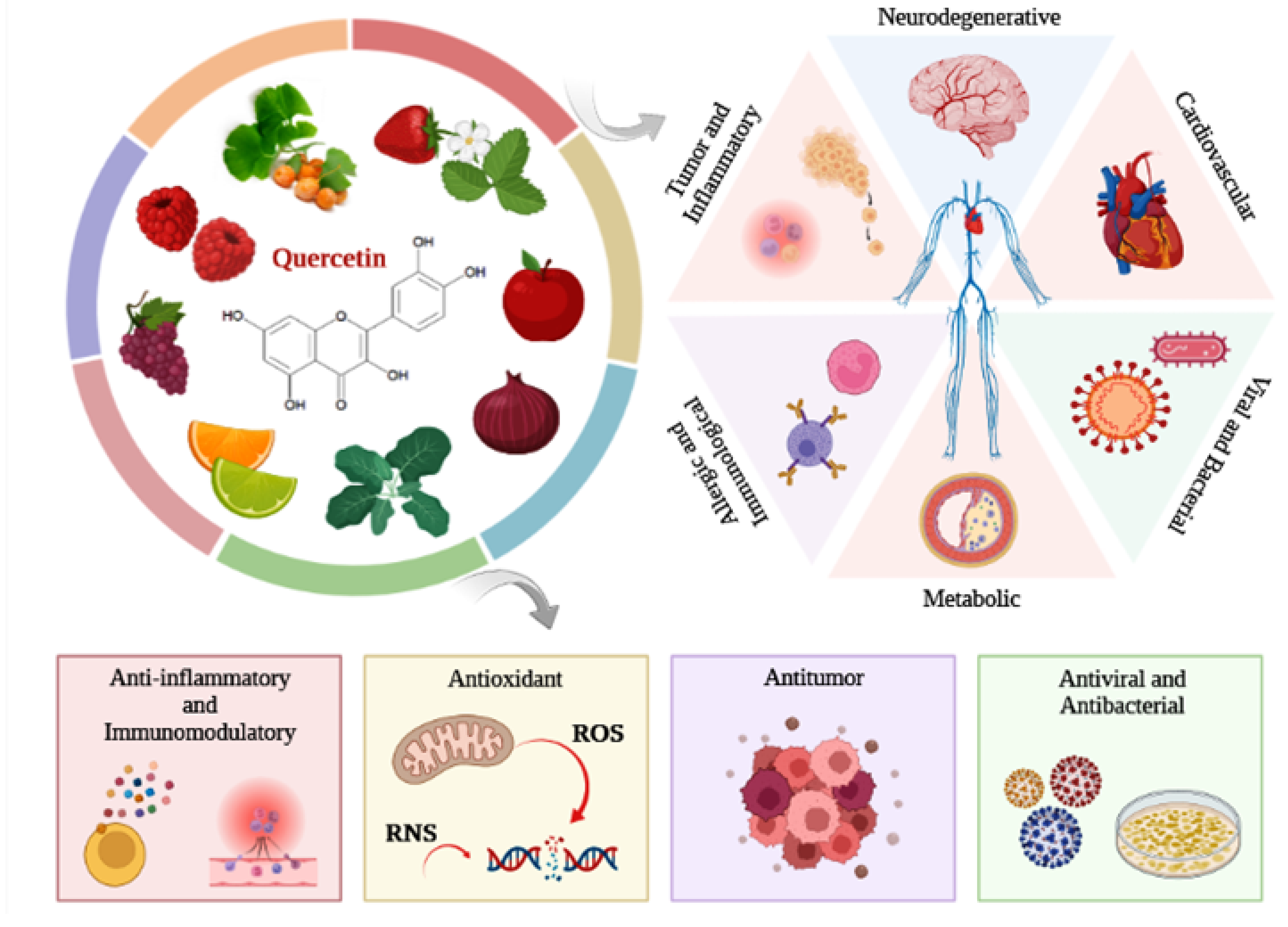
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/antiox12010149
References
- Cassidy, A.; Minihane, A.M. The role of metabolism (and the microbiome) in defining the clinical efficacy of dietary flavonoids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 10–22.
- Birt, D.F.; Jeffery, E. Flavonoids. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 576–577.
- Crasci, L.; Basile, L.; Panico, A.; Puglia, C.; Bonina, F.P.; Basile, P.M.; Rizza, L.; Guccione, S. Correlating In Vitro Target-Oriented Screening and Docking: Inhibition of Matrix Metalloproteinases Activities by Flavonoids. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 901–911.
- Hwang, S.L.; Yen, G.C. Neuroprotective effects of the citrus flavanones against H2O2-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 859–864.
- Li, X.; Chen, B.; Xie, H.; He, Y.; Zhong, D.; Chen, D. Antioxidant Structure(-)Activity Relationship Analysis of Five Dihydrochalcones. Molecules 2018, 23, 1162.
- Dias, M.C.; Pinto, D.; Silva, A.M.S. Plant Flavonoids: Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 5377.
- Shen, P.; Lin, W.; Deng, X.; Ba, X.; Han, L.; Chen, Z.; Qin, K.; Huang, Y.; Tu, S. Potential Implications of Quercetin in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 689044.
- Chen, B.H.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, I.H.; Lee, J.C.; Won, M.H.; Lee, C.H.; Hwang, I.K.; Kim, J.D.; et al. Pretreated quercetin protects gerbil hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons from transient cerebral ischemic injury by increasing the expression of antioxidant enzymes. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 220–227.
- Deepika; Maurya, P.K. Health Benefits of Quercetin in Age-Related Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 2498.
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, C.; Yang, J.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 167.
- Andres, S.; Pevny, S.; Ziegenhagen, R.; Bakhiya, N.; Schäfer, B.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Lampen, A. Safety Aspects of the Use of Quercetin as a Dietary Supplement. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700447.
- Grewal, A.K.; Singh, T.G.; Sharma, D.; Sharma, V.; Singh, M.; Rahman, M.H.; Najda, A.; Walasek-Janusz, M.; Kamel, M.; Albadrani, G.M.; et al. Mechanistic insights and perspectives involved in neuroprotective action of quercetin. Biomed. Pharm. 2021, 140, 111729.
- Shabbir, U.; Rubab, M.; Daliri, E.B.; Chelliah, R.; Javed, A.; Oh, D.H. Curcumin, Quercetin, Catechins and Metabolic Diseases: The Role of Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 206.
- Suganthy, N.; Devi, K.P.; Nabavi, S.F.; Braidy, N.; Nabavi, S.M. Bioactive effects of quercetin in the central nervous system: Focusing on the mechanisms of actions. Biomed. Pharm. 2016, 84, 892–908.
- Guo, Y.; Bruno, R.S. Endogenous and exogenous mediators of quercetin bioavailability. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 201–210.
- Kawabata, K.; Mukai, R.; Ishisaka, A. Quercetin and related polyphenols: New insights and implications for their bioactivity and bioavailability. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1399–1417.
- Murota, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Uehara, M. Flavonoid metabolism: The interaction of metabolites and gut microbiota. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 600–610.
- Ghosh, A.; Sarkar, S.; Mandal, A.K.; Das, N. Neuroprotective role of nanoencapsulated quercetin in combating ischemia-reperfusion induced neuronal damage in young and aged rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57735.
- Huang, C.; Fu, C.; Qi, Z.P.; Guo, W.L.; You, D.; Li, R.; Zhu, Z. Localised delivery of quercetin by thermo-sensitive PLGA-PEG-PLGA hydrogels for the treatment of brachial plexus avulsion. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 1010–1021.
- Sadalage, P.S.; Patil, R.V.; Havaldar, D.V.; Gavade, S.S.; Santos, A.C.; Pawar, K.D. Optimally biosynthesized, PEGylated gold nanoparticles functionalized with quercetin and camptothecin enhance potential anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and anti-angiogenic activities. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 84.
- Testa, G.; Gamba, P.; Badilli, U.; Gargiulo, S.; Maina, M.; Guina, T.; Calfapietra, S.; Biasi, F.; Cavalli, R.; Poli, G.; et al. Loading into nanoparticles improves quercetin’s efficacy in preventing neuroinflammation induced by oxysterols. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96795.
- Thipkaew, C.; Wattanathorn, J.; Muchimapura, S. Electrospun Nanofibers Loaded with Quercetin Promote the Recovery of Focal Entrapment Neuropathy in a Rat Model of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2017493.
- Alizadeh, S.R.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.A. Quercetin derivatives: Drug design, development, and biological activities, a review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 229, 114068.
- Mendoza, E.E.; Burd, R. Quercetin as a systemic chemopreventative agent: Structural and functional mechanisms. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 1216–1221.
- Wang, Y.; Tao, B.; Wan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Li, C. Drug delivery based pharmacological enhancement and current insights of quercetin with therapeutic potential against oral diseases. Biomed. Pharm. 2020, 128, 110372.
- Yi, H.; Peng, H.; Wu, X.; Xu, X.; Kuang, T.; Zhang, J.; Du, L.; Fan, G. The Therapeutic Effects and Mechanisms of Quercetin on Metabolic Diseases: Pharmacological Data and Clinical Evidence. Oxi. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 6678662.
- Barreca, D.; Bellocco, E.; D’Onofrio, G.; Nabavi, S.F.; Daglia, M.; Rastrelli, L.; Nabavi, S.M. Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin: From Chemistry to Medicine. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2016, 15, 964–975.
- Güran, M.; Şanlıtürk, G.; Kerküklü, N.R.; Altundağ, E.M.; Süha Yalçın, A. Combined effects of quercetin and curcumin on anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial parameters in vitro. Eur. J. Pharm. 2019, 859, 172486.
- Han, X.; Xu, T.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yue, L.; Hu, G.; Sun, L. Quercetin hinders microglial activation to alleviate neurotoxicity via the interplay between NLRP3 inflammasome and mitophagy. Redox. Biol. 2021, 44, 102010.
- Luo, X.; Bao, X.; Weng, X.; Bai, X.; Feng, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, S.; Jia, H.; Yu, B. The protective effect of quercetin on macrophage pyroptosis via TLR2/Myd88/NF-κB and ROS/AMPK pathway. Life Sci. 2022, 291, 120064.
- Tang, J.; Diao, P.; Shu, X.; Li, L.; Xiong, L. Quercetin and Quercitrin Attenuates the Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells: In Vitro Assessment and a Theoretical Model. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7039802.
- Wang, C.P.; Shi, Y.W.; Tang, M.; Zhang, X.C.; Gu, Y.; Liang, X.M.; Wang, Z.W.; Ding, F. Isoquercetin Ameliorates Cerebral Impairment in Focal Ischemia Through Anti-Oxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptotic Effects in Primary Culture of Rat Hippocampal Neurons and Hippocampal CA1 Region of Rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2126–2142.
- Song, J.; Du, G.; Wu, H.; Gao, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, B.; Cui, S. Protective effects of quercetin on traumatic brain injury induced inflammation and oxidative stress in cortex through activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2021, 39, 73–84.
- Yang, T.; Kong, B.; Gu, J.W.; Kuang, Y.Q.; Cheng, L.; Yang, W.T.; Xia, X.; Shu, H.F. Anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidative roles of quercetin after traumatic brain injury. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 797–804.
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, C.; Wen, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Mao, L.; et al. Quercetin induces mitochondrial biogenesis in experimental traumatic brain injury via the PGC-1α signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 3558–3566.
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, C.; Wen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, M.; Mao, L.; Fan, Y. Protective Effects of Quercetin on Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164237.
- Qu, X.; Qi, D.; Dong, F.; Wang, B.; Guo, R.; Luo, M.; Yao, R. Quercetin improves hypoxia-ischemia induced cognitive deficits via promoting remyelination in neonatal rat. Brain Res. 2014, 1553, 31–40.
- Wang, Y.Y.; Chang, C.Y.; Lin, S.Y.; Wang, J.D.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, W.Y.; Kuan, Y.H.; Liao, S.L.; Wang, W.Y.; Chen, C.J. Quercetin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion and oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation neurotoxicity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 83, 108436.
- Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, H.T.; Cai, Y.Q.; Han, Y.J.; Yao, F.; Yuan, Z.H.; Wu, B.Y. Anti-inflammatory Effect of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Transplantation and Quercetin Treatment in a Rat Model of Experimental Cerebral Ischemia. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 1023–1034.
- Khan, A.; Ali, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, M.S.; Alam, S.I.; Ikram, M.; Muhammad, T.; Saeed, K.; Badshah, H.; Kim, M.O. Neuroprotective Effect of Quercetin Against the Detrimental Effects of LPS in the Adult Mouse Brain. Front. Pharm. 2018, 9, 1383.
- Josiah, S.S.; Famusiwa, C.D.; Crown, O.O.; Lawal, A.O.; Olaleye, M.T.; Akindahunsi, A.A.; Akinmoladun, A.C. Neuroprotective effects of catechin and quercetin in experimental Parkinsonism through modulation of dopamine metabolism and expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, NF-κB, IκKB, and p53 genes in male Wistar rats. Neurotoxicology 2022, 90, 158–171.
- Zhang, Q.; Song, W.; Zhao, B.; Xie, J.; Sun, Q.; Shi, X.; Yan, B.; Tian, G.; Liang, X. Quercetin Attenuates Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy by Correcting Mitochondrial Abnormality via Activation of AMPK/PGC-1α Pathway in vivo and in vitro. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 636172.
- Espinosa-Juárez, J.V.; Jaramillo-Morales, O.A.; Déciga-Campos, M.; Moreno-Rocha, L.A.; López-Muñoz, F.J. Sigma-1 receptor antagonist (BD-1063) potentiates the antinociceptive effect of quercetin in neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury. Drug. Dev. Res. 2021, 82, 267–277.
- Komirishetty, P.; Areti, A.; Gogoi, R.; Sistla, R.; Kumar, A. Combination strategy of PARP inhibitor with antioxidant prevent bioenergetic deficits and inflammatory changes in CCI-induced neuropathy. Neuropharmacology 2017, 113, 137–147.
- Muto, N.; Matsuoka, Y.; Arakawa, K.; Kurita, M.; Omiya, H.; Taniguchi, A.; Kaku, R.; Morimatsu, H. Quercetin Attenuates Neuropathic Pain in Rats with Spared Nerve Injury. Acta Med. Okayama 2018, 72, 457–465.
- Ye, G.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Chen, Y.; Kong, L.; Yuan, L.; Ma, T. Quercetin Alleviates Neuropathic Pain in the Rat CCI Model by Mediating AMPK/MAPK Pathway. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 1289–1301.
