Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Mitochondria are key players in energy production, critical activity for the smooth functioning of energy-demanding organs such as the muscles, brain, and heart. Therefore, dysregulation or alterations in mitochondrial bioenergetics primarily perturb these organs. Within the cell, mitochondria are the major site of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production through the activity of different enzymes since it is one of the organelles with the major availability of oxygen.
- calcium
- ROS
- mitochondria
1. Introduction
Mitochondria are crucial to maintaining the regulation and performance of different important cellular activities, in particular, with their critical role in energy production for the smooth functioning of energy-demanding organs such as muscles, the brain, and the heart [1]. As a consequence, any dysregulation or alteration in mitochondrial bioenergetics primarily perturbs these organs. Within several cell types and particularly in cardiac myocytes, mitochondria are the major site of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production through the activity of different enzymes (including NADPH oxidase and uncoupled nitric oxide synthase) [2] since they are organelles with great oxygen availability [3].
ROS can act as signaling molecules in a number of different pathways by modulating calcium (Ca2+) signaling. Intracellular calcium (Ca2+) is the most common second messengers of living cells. This versatility allows it to control diverse processes mediated by rapid Ca2+ fluxes, such as contractility, secretion, proliferation, apoptosis, protein folding, and energy metabolism [1,4]. Calcium and ROS mutually influence each other, ROS regulate cellular calcium signaling, whereas calcium signaling is crucial for ROS production [5]. These interplays have been studied in depth in the cardiovascular system.
2. ROS
Redox (reduction–oxidation) homeostasis is the dynamic equilibrium of electron transfer reactions, and is related to the concept of free radicals, fundamental to redox signaling and biological function [14]. Free radicals can be oxidants and they are unstable molecular entities with an unpaired electron on the outer layer [14]. As a result of this unpaired electron the free radical undergoes electron transfer reactions, being a reductase when it donates the electron, or an oxidase when it takes an electron from another molecule. The most abundant form of free radicals in the cell originates from diatomic oxygen (O2) [15], and they are known as ‘reactive oxygen species’ (ROS).
The term “ROS” does not refer to a specific species, however it is a wide-range term and comprehends different oxygen species with different reactivities and half-lives. The term ROS might refer to both free radicals such as superoxide anion (O2•−) and hydroxyl radical (•OH), and non-radical oxidants, such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) [16]. Since these molecules are highly reactive, they can react with lipids, proteins, DNA and even other ROS [17].
It is worth noting that the sites of ROS production and Ca2+ storage coincide in the cells, at the interface between the plasma membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and between this last one and mitochondria.
The major redox signaling agents are the superoxide anion radical (O2•−) and the hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Superoxide is produced mainly through the electron transfer chains (ETC) in mitochondria, but also in other organelles such as the ER and the plasma membrane, by NADPH oxidases (NOX), that catalyze the transfer of an electron from NADPH to O2 [18]. In mitochondria, the superoxide radicals (O2•−) are generated by electrons that escape from complex I and III and that reduce O2 [19]. When O2•− reacts with another superoxide radical, generates the hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which can be reduced to water or partially reduced to hydroxyl radical (•OH), reactions catalyzed by the enzyme superoxide dismutase [20].
Together with O2•−, H2O2 is generated in healthy cells at a controlled steady-state level [21] and is physiologically produced by NOXs in the plasma membranes, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, peroxisomes in response to external stimuli [14]. H2O2 is not a hazardous molecule itself, however it can undergo Fenton reactions through which there is the generation of hydroxyl radical (HO2), consequent to the reaction of H2O2 with the reduced metal ions (Fe2+ or Cu+). HO2 is the most aggressive form of ROS and is the initiator of lipid peroxidation, in fact, can diffuse in lipids, and can produce a carbon-centered radical of polyunsaturated lipids [22].
Like calcium (Ca2+) [23], H2O2 is also a crucial redox signaling agent [14] and the pivotal molecule in homeostatic metabolism, according to the third principle of the Redox Code [24]. In physiological conditions, H2O2 can oxidize target proteins through reversible reactions—as occur in the reversible oxidation of specific cysteine residues of proteins [25,26,27]—regulating protein activity, localization, and interactions, contributing to organizing cellular processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and autophagy [20,28,29].
The Alpha and Omega of Mitochondrial ROS
Within the cell, the mitochondria are the major site of ROS production, through the activity of different enzymes (complex I and III; oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (OGDH); pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH); complex II (site IIF) [30]), however, the ETC is the site with the highest production of ROS [31], in particular complexes I and III of the respiratory chain [20,32,33]. In particular, complex I and to a lesser extent complex II release O2•−/H2O2 toward the mitochondrial matrix, whereas release from complex III is toward the cristae lumen and the intermembrane space [34,35]. This single electron might reduce oxygen and generate superoxide anion (O2•−), which is then converted to H2O2−. H2O2 is generated in the mitochondrial matrix by the action of SOD2 (manganese superoxide dismutase) matrix and in the intermembrane space by SOD1 (Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase) [3,35,36]. The generated H2O2 is highly permeable and can be reduced by peroxidases such as glutathione peroxidases (GPx), peroxiredoxins 3 and 5 [37], and catalase (CAT) [38].
Independently of ETC, other mitochondrial enzymes are responsible for ROS production. ROS can be produced in the outer mitochondrial membrane by enzymes such as monoamine oxidase (MAO) and cytochrome b5 reductase (Cb5R) [39], and in the mitochondrial matrix by enzymes of the Krebs cycle such as pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (αKGDH), which produce both superoxide and hydrogen peroxide [40,41], and in the inner mitochondrial membrane by glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and various cytochrome P450 monooxygenases [39]. Interestingly, the activity of the latter enzymes in ROS production is dependent on mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨ) [42,43]. Mitochondria produce more ROS at high membrane potential [44]. The closure of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, the inhibition of complex I and III with rotenone and antimycin A, respectively, and the inhibition of ATP synthase, can all lead to an increase ΔΨ and to an increased ROS production [45,46,47]. However, in pathological conditions, an opposite situation might be also observed, for example, in a neuronal cell model carrying a loss of function SPART variant (c.892dupA), cause of Troyer syndrome where a reduced ΔΨ and decreased respiratory activity with a concurrent increase in ROS production have been reported [48].
3. Calcium
The crucial role of mitochondria for normal cell physiology is evident in the natural history of various disorders. Indeed, the presence of calcium in mitochondria acts as a double-edged sword: whereas cellular homeostasis is maintained by optimal Ca2+ levels, an excess of this ion is reportedly found in many diseases, including neurodegenerative and muscular diseases, such as Huntington’s disease (HD) [49] and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) [50].
Mitochondrial calcium influx is driven by differences in electric changes across the inner mitochondrial membrane and resulting from the proton pumping of the respiratory chain.
The diffusion of Ca2+ within the cell is tightly controlled by the elaborate mechanism of cytosolic Ca2+ chelation. Under basal conditions, cytosolic calcium concentrations are maintained low and controlled (100 nM) by continuous extrusion to the extracellular environment or uptake by intracellular stores, thus creating a gradient of rapidly increasing Ca2+ upon opening of ion pumps and specialized channels [51]. This finely regulated balance allow the genesis of localized Ca2+ signals that coordinate the function of target proteins/organs with great spatio-temporal precision [4].
3.1. Influx and Efflux of Ca2+ in Mitochondria
A variety of targets and Ca2+ transport systems are present on the mitochondrial membrane that modulate several mitochondrial functions. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) represents the primary intracellular Ca2+ store and the release of Ca2+ occurs through the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP3Rs) and ryanodine receptors (RyRs), located in its membranes.
The close proximity and juxtaposition of the ER to mitochondria grants a direct and selective transmission of physiological and pathological Ca2+ signals [52]). The membrane contact sites between the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria are called mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs) [53].
The Ca2+ transfer between ER and mitochondria through the MAMs depends on a tripartite protein complex that includes IP3R, localized on the ER membrane, voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1) residing on the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM), and the cytosolic glucose-regulated chaperone protein 75 (GRP75) that forms a tether between the two organelles [54].
When the cytosolic Ca2+ level is high, the cation is passively transported through the OMM. The presence and function of VDAC1, which enables the transport of all energy metabolites (pyruvate, malate, succinate, NADH, ATP, ADP, and phosphate) from the cytosol to the mitochondria, provides high membrane permeability.
In contrast, the transit of Ca2+ across the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) is driven by the negative membrane potential and the MCU channel protein [55].
The key components of the MCU channel protein complex include MCU, EMRE, MICU1, and MICU2 (MEMMS) [56]. MCU is the main protein of the holo-complex responsible for the transfer of Ca2+ into the mitochondrial matrix. The transmembrane domain of each of the four subunits of MCU (TMD) forms a tetrameric conformation and shapes a pore in the inner mitochondrial membrane effective for Ca2+ transfer [57,58,59]. In fact, the TMD contains a ‘DIME’ motif, with conserved amino acids required for MCU-mediated Ca2+ uptake: the two residues of aspartic acid and glutamic acid form two parallel side-chain carboxylate rings that act as Ca2+ selectivity filter [55,60].
MICU1 forms a large interaction surface area with MCU to seal the intermembrane pore space entrance, while MICU2 binds to MICU1 from the side without contacting MCU [61]. According to literature data, it has been found that MICU1 and MICU2 form a plug to occlude the MCU channel under conditions of low Ca2+ concentrations. In the presence of high Ca2+ concentrations, these two regulators undergo conformational changes through their EF-handed motif, which result in pore opening and Ca2+ permeation into the mitochondria [60]. The conserved aspartate ring of MCU mediates MICU1 binding and regulation in the mitochondrial calcium uniporter complex [60]. EMRE interacts with MICU1 in the intermembrane space and MCU oligomers in the inner membrane. Thus, EMRE appears to operate as a bridge between the channel properties of MCU and Ca2+ sensing activity of MICU1/MICU2 [59].
In addition to the Ca2+ uptake mechanism, mitochondria present Ca2+ release systems, mediated by Na+/Ca2+ (NCLX, Na+/Ca2+/Li+ exchanger) and H+/Ca2+ (mHCX, mitochondrial H+/Ca2+ exchanger) exchangers, which export Ca2+ outside the mitochondria. In this way, the organelle limits the accumulation of Ca2+ within the matrix and regulates its homeostasis [62].
3.2. Key Ca2+ Targets and Roles in the Regulation of Mitochondrial Bioenergetics
The controlled uptake of Ca2+ in mitochondria regulates the rate of energy production and metabolism, shapes the amplitude and spatio-temporal patterns of intracellular Ca2+ signals, and is crucial for programmed cell death [5]. Calcium in mitochondria is critical for the regulation of four dehydrogenases (glycerol phosphate, pyruvate, α-ketoglutarate, and isocitrate dehydrogenase), F0-F1 ATP synthase and two isoforms of the mitochondrial aspartate/glutamate transporter, aralar1 and citrin [56,63]. Of these protein complexes, the two transporters and the glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase have Ca2+-binding domains facing the intermembrane space and are affected by changes in the cytoplasmic concentration of calcium ions [56].
In addition, when Ca2+ activates the complex F1-F0-ATP synthase, by replacing its natural cofactor (Mg2+), the increased steric bulk within the catalytic sites of F1 triggers conformational changes that reverse the function of the complex, and thus ATP synthase hydrolyzes ATP [64].
The other three dehydrogenases are rate-limiting enzymes in feeding electrons at complex I of the ETC [65]. In vertebrates, the mechanisms of activation of these enzymes are all dependent on the accumulation of Ca2+ in the mitochondrial matrix [66]. Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) depends on de-phosphorylation of the catalytic subunit by a Ca2+-dependent phosphatase [67], while α-ketoglutarate and isocitrate dehydrogenases are activated directly by Ca2+ binding [68]. As a result of high mitochondrial Ca2+ levels, PDH, α-ketoglutarate, and isocitrate dehydrogenases are activated and stimulate the synthesis of ATP by the mitochondria.
These enzymes are very responsive to changes in Ca2+ in the matrix, but the increase in this ion is not the only mechanism that induces their activation; in particular, PDH is also regulated by other allosteric modulators such as pyruvate, ATP, NADH, and matrix pH [66].
Recently, Foskett and collaborators proposed a new regulatory mechanism for cellular bioenergetics, showing that a constitutive reduced Ca2+ release through IP3R is crucial for the maintenance of optimal cellular bioenergetics under normal basal conditions because it provides sufficient reducing equivalents to support oxidative phosphorylation [69,70]. In fact, inhibition of IP3R-dependent Ca2+ release and, consequently, of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake, causes an overall impairment of cellular bioenergetics. If Ca2+ transfer to the mitochondria is absent, an increase in pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphorylation is observed, resulting in its inactivation and decreased TCA (tricarboxylic acid) cycle activity. The slowdown of the TCA cycle reduces NADH and FADH2 production, affecting the activity of the ETC and causing less ATP production. This reduction is detected by the cellular energy sensor AMPK, which, in the presence of a higher AMP/ATP ratio, determines the activation of autophagic processes [70].
Similarly, Filadi et al. described for the first time a new role for TOM70 in modulating ER–mitochondria communication and cellular bioenergetics in mammalian cells [71]. TOM70 is a subunit of the translocase of the outer membrane (TOM) complex and, with the translocase of the inner membrane (TIM), is responsible for the post-translational import of mitochondrial proteins encoded by the nucleus. TOM70 forms clusters along the OMM frequently associated with ER–mitochondria contact sites. Here, it interacts with IP3R isoform 3 and GRP75 (chaperone 75 kDa glucose-regulated protein), stabilizing the functional IP3R-3/GRP75/VDAC1 complex and promoting Ca2+ shuttling. This, in turn, promotes and sustains the Krebs cycle and mitochondrial respiration. In fact, the downregulation of TOM70 reduces Ca2+ uptake and alters mitochondrial function by reducing ETC activity and ATP synthesis, thereby activating autophagy [71,72].
Regardless of its link to the juxtaposition of ER and mitochondria, the mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake process itself plays a crucial role. In 2012, Mallilankaraman and coauthors identified a regulator of the MCU complex (MCUR1), an integral membrane protein required for mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake, which was found to be important for maintaining a normal cell metabolism. Knockdown of MCUR1 did not alter MCU localization, but prevented Ca2+ uptake by mitochondria. Ablation of MCUR1 also disrupted oxidative phosphorylation, reduced cellular ATP production and oxygen consumption, and finally activated AMP kinase [73].
4. The Interplay between Ca2+ and ROS
The capacity of mitochondria to accumulate Ca2+ is critical for maintaining proper tissue homeostasis. However, Ca2+ accumulation in mitochondria leads to decreased ATP production and prolonged opening of the mPTP (permeability transition pore), a high-conductance channel, whose opening allows the release of proapoptotic mitochondrial components [74].
mPTP opening depends not only on Ca2+ concentration, but also on other factors including high phosphate concentrations, low adenine nucleotide concentrations and oxidative stress. In fact, Madesh and Hajnoczky showed that O2•− is able to induce mPTP opening in a Ca2+-dependent manner [75]. The opening of the channel triggers the mitochondrial permeability transition (mPT), which is characterized by a drastic increase in mitochondrial membrane permeability, causing the entry of any molecule with a weight less than 1.5 kDa. This event in turn causes the immediate collapse of the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨ m), membrane depolarization, and ATP depletion. The initial uncoupling effect is followed by the reduction in respiratory activity caused by the loss of pyridine nucleotides and cytochrome c [76]. Swelling of the mitochondrial matrix causes disruption of the outer membrane. Subsequent inhibition of electron flow could explain the increase in ROS formation generated by PTP opening; since the last event is promoted by ROS, a vicious cycle of damage amplification is triggered (Figure 1) [77].
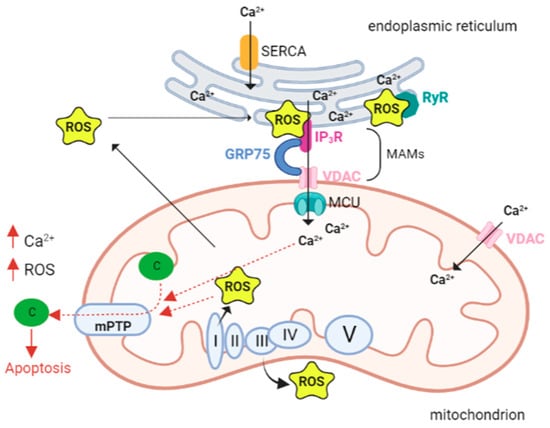
Figure 1. Calcium and ROS interplay in mitochondria. The close proximity and juxtaposition of the ER to mitochondria facilitate a straight and selective transport of calcium (Ca2+). The mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs) are the site of contact between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondria. Here calcium release channels accumulate, and these channels include the IP3R localized on the ER membrane, the voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1) on the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM), and the cytosolic glucose-regulated chaperone protein 75 (GRP75) that forms a tether between the two organelles. Increased levels of mitochondrial calcium stimulate the activity of the electron transport chain leading to a higher release of reactive oxygen species (ROS). As a vicious circle ROS can hit Ca2+ channels localized in the ER membranes and cause a further leak of Ca2+ from the ER that leads to increased ROS production in the mitochondria. A pick in the levels of both Ca2+ and ROS opens the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP), allowing the release of cytochrome c that leads to the activation of apoptosis. Abbreviations: ROS reactive oxygen species; Ca2+ calcium ion, IP3R IP3 receptor; GRP75 glucose-regulated chaperone protein 75; VDAC voltage-dependent anion channel; MCU mitochondrial calcium uniporter; c cytochrome c; SERCA sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase; RyR ryanodine receptors; mPTP—mitochondrial permeability transition pore; I, II, III, VI, V respiratory complex I–V. Created with BioRender.com.
In addition, the continuous release of ROS from mitochondria allows mitochondrial ROS peaks to be maintained during apoptosis. This mechanism may be necessary for signaling to adjacent mitochondria, resulting in global activation of cell death by apoptosis [78].
Proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids can be altered by the accumulation of ROS in mitochondria, which result in covalent modifications and profoundly alter their structure and function [77].
One of the most susceptible targets is cardiolipin, a highly abundant phospholipid in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It has been proposed that oxidation of cardiolipin contributes to complex I impairment [79] and cytochrome c release [80]. Oxidative alterations of mitochondrial lipids and proteins can result in true dysfunction due to alterations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in the long term. Among the DNA products generated by ROS attack, 8-oxo-deoxyguanosine is the most prevalent [81].
Ben-Kasus Nissim and coworkers have shown that NCLX knockdown increases the mitochondrial Ca2+ levels and leads to an stimulates l ROS production in mitochondria [82]. Furthermore, the consequences of specific redox alterations of different isoforms of VDAC are only beginning to be investigated, and it is unclear whether these play a role in VDAC function or might have a role in the pathophysiology of disorders [83].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/antiox12020353
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
