纳米颗粒 (NP) 已被广泛用作治疗产品的靶向运载工具;然而,与无机和有机纳米材料相比,蛋白质纳米材料具有更好的生物相容性,可以自组装成高度有序的笼状结构,更有利于在靶向药物递送方面的应用。
一、简介
近几十年来,用于药物递送的纳米载体的开发引起了许多研究人员的极大兴趣,因为它们克服了传统药物递送方法的局限性 [
1 ]。纳米粒子 (NP) 在物理、光学、化学和治疗特性方面具有独特的特性。传统的药物递送载体,如非纳米药物和无机纳米粒子,面临着高毒性和低递送效率的问题,这使得天然衍生的纳米载体成为可行的替代品。蛋白质纳米笼 [
2],如病毒、病毒样颗粒、铁蛋白等,都是由蛋白质亚基自组装形成笼状结构,由数量不等的亚基组成大小不一的蛋白笼,笼径大小不一从几纳米到几十纳米不等(
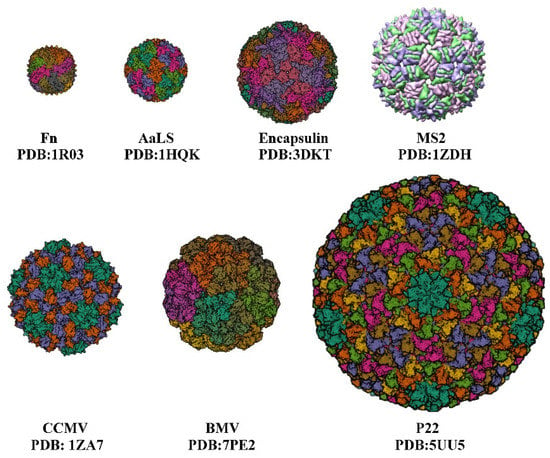
图1), which are suitable for the encapsulation and application of various drugs, respectively. Virus-like particles (VLPs) are a class of multimeric proteins derived from viral capsids that self-assemble into protein cage NPs with hollow interiors. The creation and structure of VLPs are identical to those of wild-type viruses, but since they lack the viral genome, they are not harmful. The virus’s shell is a symmetrical supramolecular complex composed of proteins. Each icosahedral virus contains 12 pentameric substructures that are located according to their triangulation number (T). When the subunits remain the same size, increasing the number of subunits will increase the T number and the size of the capsid [
3]. 在蛋白质 NPs 中,VLPs 是最有优势的。
就生物相容性、细胞吸收效率和在 PBS 缓冲液、细胞培养基和小鼠血清中的稳定性而言 [
4、5、6 ]
, VLP优于传统的有机或无机 NP。主要位于肿瘤组织中的靶向肽修饰 VLP 可以防止 DOX 扩散到多个器官,从而减少治疗副作用 [
7 ]。VLP 还可以降低封装有毒货物的细胞毒性 [
8 ]。
图 1.几个不同大小的蛋白质笼。Fn,铁蛋白笼;AaLS,
Aquifex aeolicus;封装蛋白笼;MS2;CCMV,豇豆褪绿斑驳病毒;BMV,溴花叶病毒;P22,噬菌体。
2. Strategies for Drugs Encapsulation in Various Protein Cage Nanoparticles
Due to their good biocompatibility, protein cage NPs are commonly used to encapsulate drugs and enzymes. Protein cage NP encapsulation generally uses the following methods:
(1) Diffusion. It is only possible to load a limited amount of small molecule cargoes (<5 Å) or metal ions smaller than the pores of the protein cage NPs. Additionally, some protein cage NPs allow drugs to enter the interior of the protein cage NPs by thermally responding to cargo pores. (2) Electrostatic adsorption. It facilitates the selective adsorption of oppositely charged drugs by charged protein cage NPs. (3) Covalent modification. Enhanced encapsulation efficiency of drugs can be achieved by chemical modification or specific short peptide modification. (4) Disassembly/reassembly. Reversible disassembly or reorganization of protein cage NPs by adjusting pH or salt concentration. (5) Fusion expression. The fusion and expression of encapsulated drugs on protein cages, by combining drugs with scaffold proteins and encapsulating them in cages, can increase the local concentration of the reaction.
2.1. Diffusion
Passive diffusion allows drugs to be loaded into Human H ferritin (HFn) through protein pores. The drugs are packaged into the cage-like structure only after passing through the pores. Although there are fewer drugs loaded into the HFn nanocages, the packaging efficiency is low, and they are limited to some small molecule drugs (with size <5 Å) or some metal ions. Thus, a natural temperature-sensitive thermal-response channel on HFn shell has been discovered, facilitating drug entry into protein cages [
6]. A ferritin cage with a 4-fold channel was formed by artificially removing the E-helix formed by the C-terminal channel. To ensure the stability of the protein cage NPs, Nicked-HF partially forms a quadruple channel, and the drug is actively encapsulated into the cage-like structure via this channel [
18]. Similarly, the natural encapsulins have pores of 3–4 Å in diameter, which are only suitable for some metal ions to pass through. With the pores modified to 11 Å, Tb
3+ is able to diffuse into the cage and the transport rate is increased 7-fold, making it easier for encapsulins to transport drugs [
19].
2.2. Electrostatic Adsorption
The use of electrostatic charge-mediated interactions facilitated the selective encapsulation of negatively/positively charged drugs by positively/negatively charged protein cage NPs.
Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase (PhoA) can be encapsulated by the positively charged protein capsid MS2, and the negatively charged acidic peptide can be fused to PhoA, which can further improve the encapsulation efficiency [
20]. Negatively charged siRNA can interact electrostatically with the arginine-binding domain of the CCMV [
14].
Archaeoglobus fulgidus ferritin (AfFtn) has negatively charged proteins inside, which can encapsulate positively charged gold nanoparticles [
21].
2.3. Covalent Modification
用于封装药物的两种主要共价修饰类型是使用天然和非天然氨基酸残基的共价修饰 [
24 ],以及蛋白质介导的共价修饰 [
25 ]。
2.3.1. 天然和非天然氨基酸残基的共价修饰
典型氨基酸的侧链具有反应性,这意味着它们能够形成生物相容的共价键 [
24 ]]. These amino acids include cysteine, lysine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and tyrosine. Cysteine covalent crosslinking relies on the free sulfhydryl group on the cysteine, is chemically loaded onto protein cage NPs by thiol-maleimide Michael-type addition, and can occur at any desired location on the protein surface, e.g., inside or outside the protein cage NPs. There are more established synthetic protocols for maleimide-linked drugs, which are relatively easy to obtain, so cysteine covalent links are commonly used. Aldoxorubicin (AlDox) is a commonly used anticancer prodrug that encapsulates the drug through cysteine residues-maleimide Michael-type addition to 123-site Cys located on the outer surface of encapsulin protein cage NPs, and the activity of AlDox is not reduced by a covalent modification to the protein cage [
12 ]。
从超嗜热菌 Aquifex aeolicus 中分离出的
AaLS经过基因改造,在 108 位含有半胱氨酸,该半胱氨酸已用于封装药物,例如 AlDox 和硼替佐米 [
11 ]。Gd (III)-DOTA-Mal 复合物也成功连接到 AaLS 蛋白笼第 108 位的半胱氨酸残基 [
26 ]。硒代半胱氨酸 (Sec) 在空气中被氧化成硒代半胱氨酸二聚体 (Sec2)。使用具有一个半胱氨酸的 AaLS 突变体,Sec 被封装在 AaLS 每个亚基的序列位置 122,Sec2 有效地形成与 AaLS 的 Sec 硫化物连接偶联,而不改变衣壳的原始结构 [
27]. 使用谷胱甘肽或二硫苏糖醇等还原剂,封装的 Sec 可以从 AaLS–ICSec 中定量释放 [
27 ]。直径为 20 nm 的基于铁蛋白的纳米载体利用内部突变的半胱氨酸残基来包裹 SOD [
28 ]。
2.3.2. 蛋白质介导的封装策略
Spytag (ST)/Spycatcher (SC) 共价连接策略:蛋白笼 NP 的结构不受蛋白笼 NP 外部 ST 融合表达的影响,SC 可以靶向识别 ST 并创建共价异肽键 [
31 ]]. After modifying SC on the drug, the drug can be encapsulated onto protein cage NPs; protein cage NPs have the same formation process and structure as wild viruses, but they are not infectious and can be used for vaccine production. Seasonal influenza A virus (IAV) often undergoes gene mutations or gene recombination, resulting in the need for frequent updates of IAV and the use of P22 VLPs as a vector for constructing vaccines, which have different globular head structural domains of hemagglutinin (HA) proteins, allowing for rapid updates of IAV. Expression of SP at the C-terminus of the CP of P22 VLPs allows ST to be expressed outside of VLPs and ST/SC to bind covalently, resulting in a P22-HA
head that activates antigen-specific immune responses in mice, and exhibiting enhanced immunogenicity and potential for antigen delivery [
29,
32]. AaLS also uses the irreversible covalent isopeptide bond formed by ST/SC to modify the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) to the outside of the protein cage, and each AaLS nanoparticle successfully attaches to an average of approximately 30 TRAIL and EGFRAfb molecules [
25].
分选酶介导的连接策略:分选酶催化 C 端含有 LPETG 氨基酸序列的蛋白质的苏氨酸与 N 端含有聚甘氨酸序列的蛋白质的甘氨酸之间形成肽键 [
33 ]。在 P22 VLP 外壳蛋白的 C 端融合表达 LPETG 序列,在药物的 N 端用多聚甘氨酸修饰,同样允许将不同的药物稳定加载到蛋白笼 NP 上,并在外部修饰蛋白质笼 NPs 的一侧,促进一些大蛋白质或蛋白质结构域的封装 [
33 ]。
2.4. 拆卸/重新组装
某些蛋白质笼具有在特定情况下调节笼状结构的分解和重组的能力。例如,铁蛋白可以从植物、动物和微生物中收集,是一种储存铁的细胞内球形蛋白质。为了将药物装载到铁蛋白笼的空腔中,蛋白质可以自动形成带有空腔的笼状结构,蛋白质笼的分解和重组可以通过 pH 值和尿素浓度来调节 [
36 ]。此外,pH 值可以控制豇豆褪绿斑驳病毒 (CCMV) 的衣壳结构。
蛋白质笼的 pH 调节药物封装策略
铁蛋白笼可在pH为2.5的磷酸盐缓冲液中解离,然后加入阿霉素。将蛋白壳放回原处,用NaOH将pH值升至7.4后,药物成功包封在蛋白笼中;但是,如果将溶液的pH值直接从2.5提高到7.4,药物和蛋白质就会发生聚集,对蛋白质产生不可逆的影响。随后增强了 pH 调节铁蛋白笼的药物包封,发现阿霉素在 pH 3-4 时更易溶解和稳定。
蛋白质笼的尿素调节药物封装策略
铁蛋白笼的 PH 调节药物包封技术得到改进;然而,最近的一项研究表明,酸性 pH 值分解会在铁蛋白笼表面产生无法修复的孔洞,导致更多人选择较温和的尿素来控制铁蛋白笼的分解和重组 [
38 ]。HFn 在 8 M 尿素中完全解离,然后添加附着在铁蛋白上的药物。梯度去除尿素,然后将组件放回原处,形成一个包裹药物的铁蛋白笼 [
39 ]。
2.5. 融合表达
利用蛋白质纳米笼装载肽类药物,从而以纯生物学方式包封药物,可以成功避免包封过程中使用化学试剂造成的活性损失。将多肽或酶等蛋白质药物装载到蛋白质纳米笼内部,也可以保护药物不发生变性和降解,提高药物的稳定性和有效性。
P22 VLPs are guided by scaffolding protein (SP) to assemble 420 coat protein (CP) into cage-like structures, and there are two commonly used methods for expressing drug fusions on the P22 protein cage [
40]. 1. Using an SP fusion technique that does not interfere with the self-assembly of the SP-guided CP, one capable of encasing the target protein within the P22 capsid, and fusing the target gene to the N-terminal end of a shortened SP [
41]. It can be used, for instance, to encapsulate certain peptide medications and enzymes. Such encapsulation can enhance the local concentration of the drug protein within a specified range, and the local concentration of the drug protein can reach more than 300 mg/mL while still maintaining the original action of the drug [
42]. 2. 使用CP融合技术,每个VLP可以容纳特定数量的药物,这些药物与P22 VLPs(420种药物)的CP有遗传联系。例如,P22 CP 的 N 端融合表达肽药物,但肽药物被包裹在蛋白笼内,组蛋白蛋白酶 b 附着在药物上。组织蛋白酶 B(Cathepsin B,CTB)在肿瘤细胞中高表达,可调节肿瘤部位肽类药物的释放[
47 ]。
铁蛋白双腔纳米笼 (DCNC) 由双腔短铁蛋白 (sFt) 构建体组成,该构建体在 N 末端融合,应该是多价凝块靶向肽 (CLT),以及一个大蛋白C 末端的微纤溶酶 (μPn)。CLT 靶向凝块中的纤维蛋白-纤连蛋白复合物,μPn 可有效溶解血栓中的凝块,并可将 DCNC 靶向肿瘤部位以改善肿瘤内药物递送
[ 48、49
]。
AaLS 纳米笼也已用于递送肽药物。periostin 肽 (PP) 与 AaLS 亚基的 C 末端融合允许药物在 AaLS 纳米笼表面表达,并且检测到 AaLS-PP 的促血管生成活性高于游离 PP。因此,AaLS 可以成为转运多肽类药物的良好载体 [
50 ]。
3. 蛋白笼纳米粒子的应用
3.1. 抗肿瘤
Dox 用 HFn 封装,这最大限度地减少了健康器官中的药物泄漏,并表明 HFn-Dox 在小鼠肿瘤中的 Dox 浓度高于游离 Dox 给药 [ 39 ]。这表明这种蛋白笼 NPs 药物递送方法具有良好的安全性。乳腺癌的主要治疗方法一直是细胞毒性化疗,使用蛋白笼 NP 载体递送可以成功地防止细胞毒性药物对正常组织的损伤 [ 29 ]]. 乳腺癌细胞通常过度表达生长因子 EGFR 和 HER2 的表面受体。乳腺癌细胞被携带药物的 P22 VLPs 吸引,然后可以通过将荧光标签融合到 EGFRAfb 和 HER2Afb 并将它们共价结合到 P22 VLPs 建议的 SP 来诊断疾病。细胞毒性蛋白小单线态氧发生器,一种成功靶向乳腺癌细胞并导致其死亡的封装蛋白笼,被加载到T. maritima封装蛋白的表面,并与转基因抗体蛋白 DARPin9.29 融合。此外,该团队还发现,一种 18.4 kDa 的蛋白质可以直接融合到包囊蛋白的表面,而不会改变其稳定性或结构 [ 53 ]]. 这一发现使得在封装蛋白表面表达一些大蛋白变得更加容易,并开辟了更多的应用可能性。通过共价键将 TNF 相关凋亡诱导配体 (TRAIL) 加载到 AaLS 上,并将它们与癌细胞中过表达的促凋亡死亡受体结合,是一种有效的癌症蛋白质治疗策略 [ 25 ]。
3.2. siRNA递送
由于精氨酸结构域促进与带负电荷的生物分子的静电相互作用,因此带负电荷的 siRNA 可以包含在 CCMV 中。可以构建在 37 °C 下稳定的蛋白笼 NP,用于使用 DTSSP 交联剂在颗粒表面偶联赖氨酸 [
14 ] 进行体外 siRNA 递送。Forkhead box transcription factor (FOXA1) 被用作 CCMV siRNA 递送的治疗靶点,细胞穿透肽 (CPPs) L17E 共价偶联到载有 siRNA 的 CCMV 表面,有效沉默 FOXA1,靶点乳腺癌细胞中的 mcf-7 基因 [
56 ]。
3.3. 肽和蛋白质递送
癌症、心血管和代谢疾病都可以用肽药物有效治疗。然而,肽药物的溶解度、稳定性和膜渗透性使得它们不太适合作为递送肽药物的载体。在这些载体中,蛋白质纳米笼非常适合肽类药物的递送,因为它们可以成功地将肽类药物精确靶向并释放到焦点位点。举例来说,P22 VLP 的肽药物融合到 P22 CP 的 N 末端,两种不同的肽,NuBCP-9 肽和 KLAK 肽,通过 CTB 可切割接头连接。这两种肽通过不同的机制发挥作用,可能具有协同杀伤肿瘤细胞的作用。在肽和 CP 之间以及两个肽之间,放置了 CTB 可切割接头。
3.4. 成像
临床诊断中最常用的技术之一是磁共振成像 (MRI)。造影剂 (CA) 用于在分辨率不足时增加 MR 图像的分辨率,并且经常使用 T1 加权和 T2 加权 (CA) [
60 ]。
最广泛使用的 T1 CA 是顺磁性钆 (Gd(III)),但研究表明 Gd 具有潜在的细胞毒性,使用基于 Gd 的造影剂可能导致全身性肾毒性,需要与螯合剂络合 [
26 ]。由于蛋白笼NP独特的球形空心形态、可生物降解、诱变简单、化学偶联变化等特点,可以将造影剂固定在蛋白笼NP上,降低造影剂的释放速率。带有 Gd 标记的重组人重链铁蛋白旨在靶向 T1 造影剂 (HFn-Gd) [
4 ]。P22“wiffleball”的空腔封装了 DTPA-Gd 复合物,其分辨率高于游离 DTPA-Gd,并且具有 1900 Gd
3+包含在每个 P22 VLP [
61 ] 中。钆四氮杂环十二烷四乙酸 (GdDOTA) 通过与病毒衣壳表面的赖氨酸残基反应附着到 CCMV [
62 ]。在使用 ST/SC 改变其表面的肿瘤靶向肽以生成共价杂肽连接后,Gd(III)-DOTA 复合物化学附着到 AaLS 的表面以创建靶向 T1 造影剂。利用具有慢铁释放速率、高铁负载能力和热稳定性的黄素蛋白 (AfFtnAA) 纳米笼封装基于超顺磁性氧化铁和金属铁氧体 NP 的磁性纳米结构 (MNS),以在 MR 成像中产生更高的对比度 [
63 ]。
4。结论
纳米材料药物递送系统的研究最近引起了更多关注,这有助于创建蛋白质笼纳米材料。蛋白质笼纳米材料为开发复杂的蛋白质纳米材料药物递送系统提供了新的机会,因为它们具有良好的生物相容性、无毒性和理想的内腔形状,即使在蛋白质笼 NPs 的表面,也可以用于药物递送。大量研究还表明,蛋白笼 NPs 可以有效保护蛋白酶活性,并且与游离酶相比,封装在蛋白笼 NPs 中的酶可以在高浓度下保持酶活性,药物蛋白浓度偶尔达到 300 mg/mL [
42,
65 ]。
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122609