Glucansucrase (GS) belongs to the GH70 family, which not only can synthesize exopolysaccharides (EPSs) with different physicochemical properties through glucosyl transglycosylation (by hydrolyzing sucrose) but can also produce oligosaccharides.
- lactic acid bacteria
- glucansucrase
- exopolysaccharides
1. Introduction
Polysaccharide polymers are one of the most valuable natural substances, and they play an important role in the fields of medical devices, food chemicals, and ecological and environmental protection [1]. Among them, the production of microbial exopolysaccharide (EPS) has the characteristics of being unaffected by environmental factors and easier downstream processing compared with plants, algae, fungi, and petroleum-based EPSs, which makes it shine in the field of production [2]. Bacterial enzymes involved in the production of EPS from sucrose, termed glucansucrases (GSs), are extracellular enzymes that can be assisted by branched sucrases (BRSs). GSs belong to the glycoside hydrolase GH70, which are very efficient transglycosylases and do not require expensive nucleotide-activated sugars (NDP- sugars) [3−5].
GSs are additionally named glucosyltransferases (GTFs), which catalyze the synthesis of EPSs and oligosaccharides using the glucose unit from the sucrose donor. GSs are applied in the fields of feed, food, medicine, and other engineering fields because of their outstanding physicochemical properties [6,7]. Bacterial GSs are mainly produced by lactic acid bacteria (LAB), a group of Gram-positive bacteria like Leuconostoc, Streptococcus, Lactobacillus, and Weissella species [8−10]. According to the glycosidic linkages present in the polymer, these enzymes are classified as (i) the synthesis of dextran by dextransucrases, consisting mainly of α-1,6 linkage and some α-1,2, α-1,3 and α-1,6 branches, (ii) the synthesis of mutan α-1,3, by mutansucrases (iii) forming alternan via alternansucrase, composed of alternating α-1,6 and α-1,3 glucosidic linkages, and (iv) reuteransucrase synthesizing reuteran containing α-1,4 and α-1,6 linkages [5]. These enzymes additionally catalyze the formation of oligosaccharide and glycoconjugate products in the presence of sucrose and nonsucrose receptor substrates [9,11,12].
EPSs and oligosaccharides are being extensively studied for their prospects toward probiotics by stimulating the growth of probiotic strains or beneficial endogenous strains from the gastrointestinal tract [13−15]. Although these investigations have touched on a few imperative issues, such as the approximate structure of GS, uncovering the relationship between the structure and activity of GS and its component of activity are still issues to be unraveled.
2. Structure of the GS
Sequence similarity analysis showed that GSs belonged to the GH70 family of glycoside hydrolases, with an average molecular weight of about 160 kDa and an optimum temperature and pH of 30 °C and 5.0–6.0, respectively [16,17]. GSs have been found from Lactobacillus kunkeei H3 and H25 have a mass of 300 kDa [18]. Due to the relatively large molecular weight of enzymes, and structural analysis being very difficult, only the crystal structures of four GSs have been resolved. However, with the advent of the cryoelectron microscopy technology revolution, it is possible to resolve protein structure using a high resolution, which will help to promote the 3D structure exploration and characterization of GS.
Amino acid sequence analysis showed that the GSs from LAB share a frequent structure and are composed of four different domains: (i) a sign peptide, followed by using (ii) an extraordinarily variable stretch, (iii) a quite conserved catalytic or sucrose-binding domain and (iv) a C-terminal glucan binding domain composed of a series of tandem repeats [16,19]. Currently, crystallographic analysis of the 3D structure of Lactobacillus GSs showed that they contain a common domain organization. A truncated enzyme was used for crystallization [5]. With the elucidation of the 3D structure of GTF180-∆N, the hypothesis of the ring arrangement was confirmed [20,21]. Different from the previous prediction of the primary structure of the enzyme, the three-dimensional structure of the truncated GSs formed five domains (domain A, domain B, domain C, domain IV, and domain V) and are arranged as C-A-B-IV-V lines (Figure 1). Except for domain C, these four domains are composed of two discontinuous polypeptide chains at the N-terminal and C-terminal ends. Among them, A, B, and C are catalytic cores, while IV and V are unique to GH70 GS [5]. The active site of the GSs is located at the interface of domain A and domain B [22], providing residues for the active site gap and their possible role in determining the ligation specificity of the product is discussed.
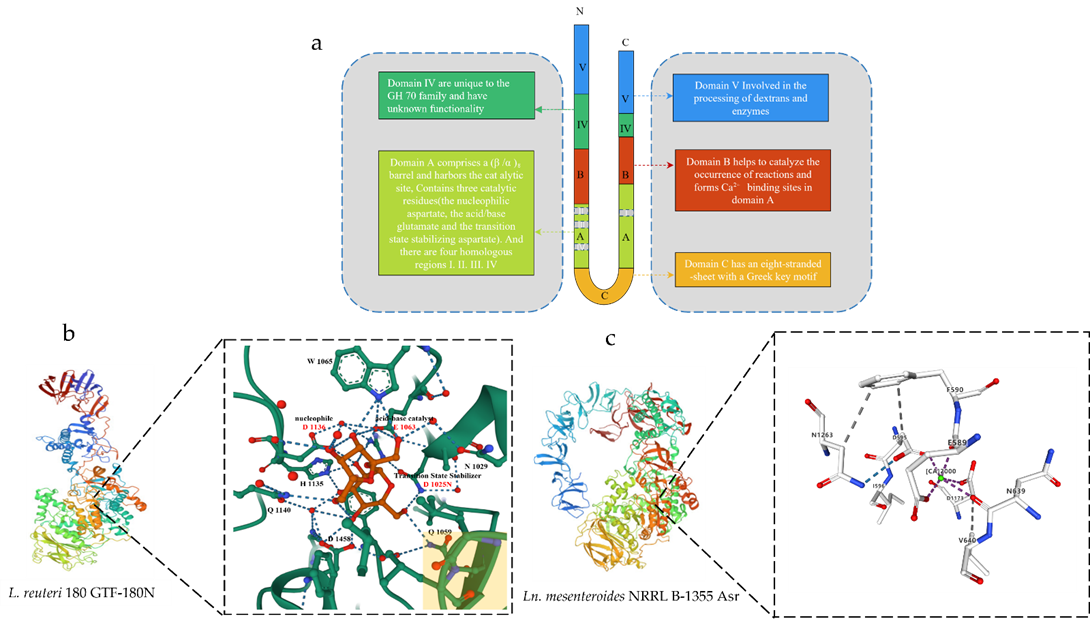
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the 3D structure of GS. (a) Schematic representation of the U-shape fold formed by the various domains of GS. (b) Schematic diagram of the 3D structure of Ln. reuteri GTF-180N (PDB: 3HZ3) and sucrose binding site. Sucrose molecules are shown in red, residues in domain A are shown in green carbon, and residues in domain B are shown in yellow at the bottom right. (c) Schematic diagram of the 3D structure of Ln. mesenteroides NRRL B-1355 Asr (PDB: 6HVG) and Ca2+ binding sites. The green circles represent Ca2+.
Domain A consists of (β/α)8 barrels and contains a catalytic site with the catalytic residue at the bottom of the domain. A crystal structure analysis of the GTF180-N mutant D1025N bound to sucrose [23,24] confirmed that these three residues constitute the catalytic site of GS. Domain B can form a Ca2+ binding site in domain A, which are used to form the binding site of substrate and receptor [5]. Domain C is located at the U-shaped bottom end of GS. It is the only domain in GH70 GS enzymes that is formed by a continuous polypeptide segment, but its function is still unclear. IV and V are additional domains; the structure of domain IV is different from that of any other known protein and only occurs in GH70 enzymes (Figure 1) [5,24].
Domain V is adjacent to domain IV. It contains several repeats and has been shown to be involved in glucan binding [13] and is a glucan-binding domain that is involved, to a certain extent, in glucan extension and enzymatic processing, providing a high-affinity anchoring platform for the synthesis of high-molecular-weight dextran [25,26]. There may well be subtle interactions between the V domain and the catalytic domain. It can help capture the polymer chain and keep it near the active site to facilitate the extension or branching of the sugar chain. Partial or total truncation of domain V affects the binding capacity of glucan and also changes the size of the synthesized polymer. Structural analysis of domain V revealed the presence of a consensus β-solenoid fold with multiple copies [27]. In the crystal structure, it has a variety of conformations, mainly divided into two types, one is the extension to the active catalytic center, and the other is the extension to the outside of the conformation in Leuconostoc mesenteroides NRRL B-1355-alternating α-1,3/1,6-glucosyltransferase (Asr). Its domain V was found to extend to the catalytic core in Ln. reuteri GTF-180N. Its domain V was found to extend out of the conformation (Figure 1) [5,27].
The exact role of domain IV is unclear. It is speculated that domain IV acts as a hinge to promote the growth of glucan chains by directing the glucan chains bound to domain V towards or away from the catalytic site. The N-terminus of GS contains a signal peptide (36 to 40 amino acids) for its secretion [5,28]. The amino acid fragment between the signal peptide and the GS core region is highly variable in content and dimension (200 to 700 amino acids) [28]. The function of the N-terminal domain remains unknown.
3. Catalytic Mechanism of GS
Both the catalytic mechanism and structure of GH70 are closely related to the GH13 and GH77 families [24]. The newly discovered GH70 subfamily GtfB, GtfC, and GtfD are inactive against sucrose but can catalyze starch and maltodextrin to α-glucan [24]. The common characteristic of GH family enzymes is that they also use a catalytic (β/α)8 barrel domain to break down the α-glycosidic bonds between glucose and other glucose or fructose [29,30]. Robyt found there are two active sites; according to the GS catalytic reaction, one is composed of covalent β-glucose-enzyme intermediates under oxygen-carbon ion-like transformation conditions [5,31]. The β-glucose-enzyme intermediate is catalyzed through the a-retaining double displacement reaction, which involves three important residues: a nucleophile, an acid-base catalyst, and a transition state stabilizer (Figure 2). Aspartic acid, which first acts as a nucleophile, attacks the ectopic C1 carbon of the sucrose–glucose unit. Glutamate acts as an acid-base catalyst to transfer protons to fructose and release fructose. The transition state stabilizes the stable residue dimension and transitions to a covalent β-glucose-enzyme. Finally, the covalent β-glucosyl-enzyme is formed from the transition state stabilizer (Figure 2). The other is composed of chain and enzyme intermediates [30]. The C1 position in the later intermediate attacks the C6 position of the glucosyl group to form a glycosidic bond, thereby increasing the length [31]. Although the determinants of the size distribution of GS products have been broadly studied before, many are still unknown [26, 32−36]. The N-terminal variable region and C-terminal glucan-binding domain have been indicated as playing a role in product size distribution [26].
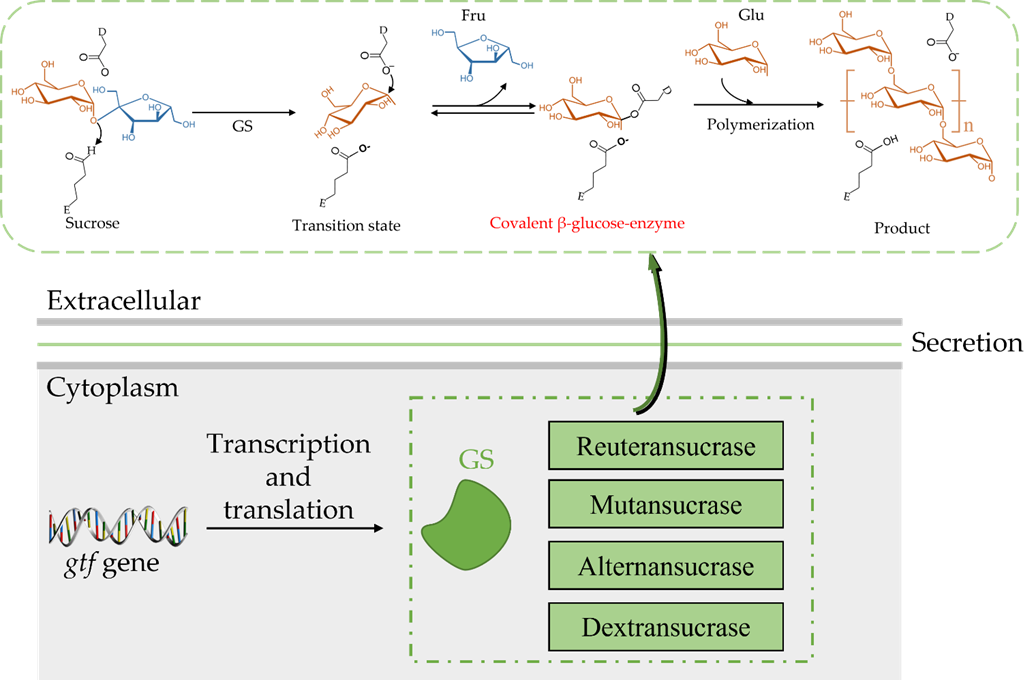
Figure 2. General reaction mechanism for GH70 glucansucrases; D is the nucleophilic asparte residue; E is the general acid/base residue [27].
The catalytic mechanism of GS allows for the hydrolysis of sucrose to obtain a glucosyl-enzyme intermediate, and this mechanism is based on a detailed structural analysis of Bacillus circulans 251 CGTase [37]. Due to the different receptors, GS appears to synthesize different products: (i) through hydrolysis, water acts as a receptor and hydrolyses to glucose; (ii) through transglycosylation, the glucosyl moiety is converted to an accepting sugar after the fructose is discharged [27]. When substrate-only sucrose exists, GS hydrolyses sucrose to dextran; furthermore, due to the different amino acid sequences of the GS active center, the glycosidic bond composition and branching structure of the produced glucan is also different. Most of the synthesized glucans are composed of one or two types of glycosidic bonds, in which the composition ratio, branching degree, and branch length are also random, which depends on the amino acid sequences of the GS active center [38,39].
4. Isolation and Purification of GS
GS is an extracellular enzyme for which its structure and catalytic mechanism have not been clarified. In order to understand the structure and function of GS, it is necessary to isolate and purify GS [17]. Various GS purification methods, including salting-out and solvents [40], phase partition [41−43], polyethylene glycol fractioning [41,43,44], chromatography column [45−47], ultrafiltration [48], and combined processes such as sugaring and gel permeation chromatography [49,50].
Salting out, normally as ammonium sulfate precipitation, is when the ionic strength in a solution and the solubility of different proteins are different; high concentrations of salt ions compete with proteins for water molecules in protein solutions, therefore destroying the hydrated membrane on the surface of the protein, reducing its solubility, and allowing it to precipitate out of the solution. Due to different protein solubility, different concentrations of salt solution can be used to precipitate different proteins. Normally, people use ammonium sulfate precipitation as the first step for purification because of its high solubility. Robyt [51] thought ammonium sulfate would hurt the enzyme activity of GS as the concentration rose, especially to more than 80%.
At present, a variety of techniques have been successfully used for the isolation and purification of Ln. mesenteroides GS, and ultrafiltration and gel filtration chromatography are considered to be the best way to purify GS due to the resulting high recovery of enzyme activity. Miao [52] used freeze-drying ion-exchange chromatography and gel filtration methods to purify the enzyme. The crude enzyme solution was concentrated by freeze-drying and loaded into a DEAE-Sepharose FF 16/10 anion exchange column. Further purification was performed using Sepharose CL-6B gel filtration chromatography. The GS was purified 8.6-fold, and its specific activity was 1.3 IU/mg. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is an uncharged linear macromolecular polymer, and its strong dehydration ability can destroy the hydration layer on the surface of protein molecules and cause protein precipitation. This method is cheap and easy to perform but it is easily affected by centrifugation temperature and pH, so it is usually used in combination with other methods. Song [16] precipitated the crude GS with 10% (v/v) PEG 2000 and then loaded it into a HiTrap Q FF anion exchange column and Sepharose CL-6B column. The purified fractions were dialyzed, concentrated, and collected, resulting in a specific activity of 1.4 U/mg protein, with 13.2-fold purification. Nigam et al. [53] compared the phase separation and purification effect of polyethylene glycol PEG 6000 and PEG 400 on dextransucrase, and the results showed that the tertiary phase separation effect of PEG 6000 was better; the final recovery rate was 84%, and the specific activity of the enzyme after purification.
The yield from GS separation by traditional separation technology is low, and its catalytic properties have not been thoroughly analyzed. In recent years, the cloning and expression of GS by means of genetic engineering is expected to overcome the shortcomings of low enzyme yield and expand the industrial application of the enzyme [54,55]. Kim et al. [56]. constructed Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) carrying the Ln. lactis EG001 GS gene. The crude enzyme was mixed with Ni-NTA agarose, and the mixture was loaded onto a chromatography column. The proteins were eluted, and the specific activity of the purified enzyme showed an increase of over 2.3-fold with respect to the crude enzyme. Amari [54] et al. constructed engineered bacteria that could express the dextransucrase gene of W. confusa C39-2. The recombinant enzyme was purified using an affinity chromatography protocol, and the activity was 4-fold higher. At present, GS derived from a variety of LAB has been isolated and purified, and its structure and properties have been continuously analyzed (Table 1).
Table 1. Information on GS from different strains and their related properties in recent years was analyzed and collated using the CAZy database.
|
Enzyme |
MASS |
Organism |
Genebank |
Length |
Reference |
|
Gtf1624 |
183 kDa |
Latilactobacillus curvatus TMW 1.624 |
CCK33643.1 |
1697 aa |
[57] |
|
DSR-F |
170 kDa |
Ln. citreum B/110-1-2 |
ACY92456.2 |
1527 aa |
[58] |
|
LcDS |
165 kDa |
Ln. citreum HJ-P4 |
BAF96719.1 |
1477 aa |
[59] |
|
DexT |
167 kDa |
Ln citreum KM20 |
ACA83218.1 |
1495 aa |
[60] |
|
DSR-A |
145 kDa |
Ln. citreum NRRL B-1299 |
CDX67012.1 |
1290 aa |
[61] |
|
DSR-B |
168 kDa |
Ln. citreum NRRL B-1299 |
AAB95453.1 |
1508 aa |
[62] |
|
DSR-E |
313 kDa |
Ln. citreum NRRL B-1299 |
CDX66820.1 |
2836 aa |
[63] |
|
DSR-DP |
- |
Ln. citreum NRRL B-1299 |
CDX66641.1 |
1278 aa |
[63] |
|
DSR-M |
144 kDa |
Ln. citreum NRRL B-1299 |
CDX66895.1 |
1293 aa |
[61] |
|
DexYG |
170 kDa |
Ln. mesenteroides 0326 |
ABC75033.1 |
1527 aa |
[64] |
|
DsrBCB4 |
168 kDa |
Ln. mesenteroides B-1299CB4 |
ABF85832.1 |
1505 aa |
[65] |
|
DsrC |
165 kDa |
Ln. mesenteroides B-1355 |
CAB76565.1 |
1477 aa |
[66] |
|
Dsrb74 |
169 kDa |
Ln. mesenteroides B-742CB |
AAG38021.1 |
1508 aa |
[67] |
|
DsrP |
161 kDa |
Ln. mesenteroides IBT-PQ |
AAS79426.1 |
1454 aa |
[68] |
|
DsrN |
169 kDa |
Ln. mesenteroides KIBGE-IB-22 |
AFP53921.1 |
1527 aa |
[69] |
|
DsrX |
169 kDa |
Ln. mesenteroides L0309 |
AAQ98615.2 |
1522 aa |
[70] |
|
DsrD |
169 kDa |
Ln. mesenteroides LCC4 |
AAG61158.1 |
1527 aa |
[50] |
|
DSR-S |
169 kDa |
Ln. mesenteroides NRRL B-512F |
AAD10952.1 |
1527 aa |
[71] |
|
DSR-T |
110 kDa |
Ln. mesenteroides NRRL B-512F |
BAA90527.1 |
1016 aa |
[72] |
|
Gtf1971 |
178 kDa |
Ligilactobacillus animalis TMW 1.971 |
CCK33644.1 |
1585 aa |
[57] |
|
Gtf106A |
199 kDa |
L. reuteri TMW 1.106 |
ABP88726.1 |
1782 aa |
[57] |
|
GTF-S |
151 kDa |
Streptococcus downei MFE 28 |
AAA26898.1 |
1365 aa |
[73] |
|
GTF-U |
176 kDa |
Streptococcus sobrinus |
BAA14241.1 |
1592 aa |
[74] |
|
GTF-B |
166 kDa |
Streptococcus mutans GS 5 |
AAA88588.1 |
1476 aa |
[75] |
|
GTF-D |
163 kDa |
S. mutans GS 5 |
AAA26895.1 |
1462 aa |
[76] |
|
DsrK39 |
158 kDa |
Weissella cibaria LBAE-K39 |
ADB43097.3 |
1445 aa |
[77] |
|
WcCab3-DSR |
154 kDa |
Weissella confusa Cab3 |
AKE50934.1 |
1401 aa |
[78] |
|
DSR-C39-2 |
155 kDa |
W. confusa LBAE C39-2 |
CCF30682.1 |
1412 aa |
[54] |
|
DSR |
156 kDa |
W. confusa VTT E-90392 |
AHU88292.1 |
1418 aa |
[79] |
|
LcALT |
229 kDa |
Ln. citreum ABK-1 |
AIM52834.1 |
2057 aa |
[80] |
|
GtfB-SK2 |
- |
Ln. citreum SK24.002 |
- |
- |
[81] |
|
ASR |
229 kDa |
Ln. mesenteroides NRRL B-1355 |
CAB65910.2 |
2057 aa |
[82] |
|
GtfO |
197 kDa |
L. reuteri ATCC 55730 |
AAY86923.1 |
1781 aa |
[83] |
|
Gtf-SK3 |
- |
L. reuteri SK24.003 |
- |
- |
[84] |
|
GtfML1 |
- |
L. reuteri ML1 |
- |
- |
[34] |
|
DSRI |
- |
Ln. mesenteroides NRRL B-1118 |
- |
- |
[85] |
|
GtfB |
- |
S. mutans GS5 |
- |
- |
[86] |
|
GtfC |
- |
S. mutans GS5 |
- |
- |
[87] |
|
GTF-Kg15 |
174 kDa |
Latilactobacillus sakei KG15 |
AAU08011.1 |
1595 aa |
[34] |
|
GTF-33 |
172 kDa |
Lentilactobacillus parabuchneri 33 |
AAU08006.1 |
1561 aa |
[34] |
|
- |
164 kDa |
Leuconostoc lactis EG001 |
ACT20911.1 |
1500 aa |
[56] |
|
GTF-Kg3 |
161 kDa |
Limosilactobacillus fermentum KG3 |
AAU08008.1 |
1463 aa |
[34] |
|
GtfB |
179 kDa |
L. f ermentum NCC2970 |
AOR73699.1 |
1593 aa |
[88] |
|
GtfB |
179 kDa |
L. reuteri 121 |
AAU08014.2 |
1619 aa |
[89] |
|
GtfML1 |
196 kDa |
L. reuteri ML1 |
AAU08004.1 |
1772 aa |
[34] |
|
GtfML4 |
180 kDa |
L. reuteri ML1 |
AAU08003.2 |
1620 aa |
[90] |
|
GtfB |
196 kDa |
L. reuteri NCC2613 |
ASA47879.1 |
1662 aa |
[91] |
|
GtfC |
163 kDa |
S. mutans |
BAA26114.1 |
1455 aa |
[89] |
|
DsrwC |
162 kDa |
W. cibaria CMU |
ACK38203.1 |
1472 aa |
[92] |
|
GtfD |
87 kDa |
Azotobacter chroococcum NCIMB 8003 |
AJE22990.1 |
780 aa |
[93] |
|
GtfC |
99 kDa |
Exiguobacterium sibiricum 255-15 |
ACB62096.1 |
893 aa |
[94] |
5. Physiological and Biochemical Properties of GS
Many factors can affect the catalytic activity of GS, including pH, temperature, and some organic solvents and metal ions. According to Kralj [34], the maximum GS activity from L. reuteri was gained at a pH of 4.0–5.5, which is comparable with most papers. Miao [52] found that GS from L. reuteri SK24.003 retained high activity at a low pH, showing better acid-resistance. However, a pH value that is too high or too low is still not conducive to the synthesis of GS. Previous studies have shown that GS has the highest purity and the most stable activity at pH 7 [95], while a low pH can significantly reduce enzyme synthesis. The analysis of the GS produced by Ln. mesenteroides DRP2-19 and isolated from sauerkraut showed that the optimum pH for GS was 5.56, and the synthesis of GS was severely affected at pH <4.5 or >7, which corroborated the previous point [96]. Because of the different sources and structures of GSs, the optimum reaction temperature for each GS is different. Generally, the optimum range is from 30–40℃ in culture. When the temperature exceeds 45℃, the enzyme activity begins to decrease, and when it exceeds 50℃, the enzyme loss is more obvious. Most double-charged ions (Mg2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, Co2+, Ca2+, Fe2+, and Zn2+) activated enzyme activity, suggesting it was a metal-activated enzyme [52]. GS has a calcium ion activation site, which can increase enzyme activity. It is concluded that calcium ion can enhance the activity of dextransucrase. The stability of the entire edifice is enhanced by calcium coordination, which likely reinforces the interaction between the two domains [97]. Qader et al. [98] found that when the concentration of CaCl2 was 0.005%, the enzyme activity increased to 108.26 DSU/mL/h, which was 2.03 times higher than that of the control group. When the content of CaCl2 was higher than 0.005%, enzyme activity decreased gradually. Some reports found that when Ca2+ is within a certain concentration range, Ca2+ will preferentially bind to the activation site on the enzyme, and the activation effect is stronger than the inhibitory effect. Furthermore, Hg+, Zn2+, Cu2+, Pb2+, and Fe3+ had a strong inhibitory effect on enzyme activity, which was the same as in previous reports; when copper ions were present, there was no transferase activity [99]. The activity and stability of GS in the presence of organic solvents were related to the solvent concentration and its nature. Chemical inhibitors indicate that the function of amino acid residues is located at the GS-active site [16]. Most chemical inhibitors had an inhibition effect on GS, like sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), ethylene diamine, tetraacetic acid (EDTA), and β-Mercaptoethanol (β-ME) [25,100]. Other chemical reagents, including butanol, n-hexane, chloroform, calcium ammonium nitrate (CAN), and ethyl acetate, also inhibited the activity of GS with increasing concentrations, whereas glycerol, formaldehyde, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) enhanced the activity of GS to a certain extent [101].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/fermentation8110629
