Friends of Science (FoS) is a non-profit advocacy organization based in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. The organization rejects the established scientific conclusion that humans are largely responsible for the currently observed global warming. Rather, they propose that "the Sun is the main direct and indirect driver of climate change," not human activity. They argued against the Kyoto Protocol. The society was founded in 2002 and launched its website in October of that year. They are largely funded by the fossil fuel industry. Madhav Khandekar, Chris de Freitas, Tim Patterson and Sallie Baliunas act or acted as advisers to the Friends of Science with their work cited in Friends' publications. Douglas Leahey has been president since December, 2009.
- fossil fuel
- climate
- sallie
1. History
In the late 1990s the Calgary-based Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists, a group modeled on the American Association of Petroleum Geologists, invited Chris de Freitas,[1] from The University of Auckland,[2] a critic of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC),[3] as guest speaker. Following these talks in which de Frietas was "very critical of what was being said about the role of carbon dioxide in global warming, ...[w]e all left the luncheon speeches all shaking our heads that this silliness was going on." After the Canadian government signed the Kyoto Protocol, Eric Loughead, former editor of the Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin and his fellow members of the Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists responded by creating the Friends of Science Society, who held its first meeting in the curling lounge of the Glencoe Club in Calgary in 2002.[4]
The first board of directors in 2002 included oil industry geologist and member of the Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists, Arthur M. Patterson,[5][6] as President; Gordon C. Wells, as Vice-President; Charles Simpson as Secretary and H. Graham Donoghue as Treasurer.[7] Founding members of the Friends of Science, Arthur M. Patterson, Albert Jacobs,[8] and David Barss (Hons. Geol. published the Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists (CSPG) position on global climate change science in January 2003 in which they cite an article by Chris de Freitas entitled "Are Observed Changes in the Concentration of Carbon Dioxide in the Atmosphere Really Dangerous?"[9][10][11]
In 2002, as faculty member of the University of Calgary, political scientist Barry Cooper, set up the Science Education Fund which could accept donations through the Calgary Foundation. The 57-year-old charity, Calgary Foundation administers charitable giving in the Calgary area and had "a policy of guarding donors' identities." Albert Jacobs, a geologist and retired oil explorations manager, who attended the first meeting held in the curling lounge of Calgary's Glencoe Club back in 2002, described how donations from industry donors were passed on to the Science Education Fund set up by Barry Cooper, which in turn supported the activities of the Friends of Science.[12][13]
In 2004 Talisman Energy, a Calgary-based, global oil and gas exploration and production company, one of Canada's largest independent oil and gas companies, donated $175,000 [14] to fund a University of Calgary-based "public relations project designed to cast doubt on scientific evidence linking human activity to global warming." Journalist Mike De Souza published the list of significant donations to the Friends of Science which had been received by the press, in an article published in the Vancouver Sun in 2011. Sydney Kahanoff, a Calgary oil and gas executive and philanthropist donated $50,000 through his Kahanoff Foundation, a charity he established in 1979. Murphy Oil matched one of its employees $1,050 donations. Douglas Leahey defended the donations to the Friends of Science from the then CEO of Talisman Energy, James Buckee,[15][16] who shared the Friends' views on climate change.[17]
On their original web page, dated 2002, the Friends recommended several key documents explaining their standpoint, including testimonies by George C. Marshall Institute [18][19][20] former board members, Richard S. Lindzen and Sallie Baliunas. Richard S. Lindzen's testimony[21] before the Senate Environment and Public Works Committee on 2 May 2001. Lindzen, a former member of the UN's Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change became one of the most well-known climate ”skeptic” scientists. A prolific writer, he has been criticizing the IPCC since the early 1990s.[22][23][24] Noted deniers Sallie Baliunas was also a paid consultant of the George C. Marshall Institute.[25]
The Friends' short recommended reading list also included the anti-Kyoto testimony[26] provided by Harvard-Smithsonian astrophysicist, Sallie Baliunas, well-known denier, to the Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works. Baliunas claimed that, "[p]roposals like the Kyoto agreement to sharply cut greenhouse gas emissions are estimated in most economic studies to have enormous economic, social and environmental costs. The cost estimates for the U.S. alone amount to $100 billion to $400 billion per year. Those costs would fall disproportionately on America's and the world's elderly and poor."[27] MacRae, an engineer, investment banker and environmentalist warned of economic fall-out and inaccurate science of the Kyoto accord.[28] The Friends recommended Wildavaky's 1995 publication in which he claimed that "an all-powerful environmental community" overstated risks in everyday life.[29]
In 2008 Canwest News Service confirmed that Morten Paulsen, senior vice president and general manager of Fleishman-Hillard Canada, was hired by the Friends of Science in 2006 on "a one-year contract to manage communications" and during that time was also a registered lobbyist for the Friends as well as two oil and gas industry companies. Paulsen, who had ties with the Reform and Canadian Alliance parties, volunteered for the Conservative party’s 2006 federal election campaign while working for the Friends of Science as paid communications consulted. The Friends of Science launched radio ads, directed by Paulsen, "targeting key markets in vote-rich Ontario" during the 2006 federal election. The ads attacking the Liberal government's spending on climate change, attracted 300,000 visits to the Friends of Science webpage.[30][31]
2. Position
Friends of Science publishes a list of "ten myths of climate change," each of which they disagree with:[32]
- Global temperatures are rising at a rapid, unprecedented rate.
- The "hockey stick" graph proves that the earth has experienced a steady, very gradual temperature decrease for 1000 years, then recently began a sudden increase.[33][34]
- Human produced carbon dioxide has increased over the last 100 years, adding to the greenhouse effect, thus warming the earth.
- CO2 is the most common greenhouse gas.
- Computer models verify that CO2 increases will cause significant global warming.
- The UN proved that man–made CO2 causes global warming.
- CO2 is a pollutant.
- Global warming will cause more storms and other weather extremes.
- Receding glaciers and the calving of ice shelves are proof of global warming.
- The earth’s poles are warming; polar ice caps are breaking up and melting and the sea level rising
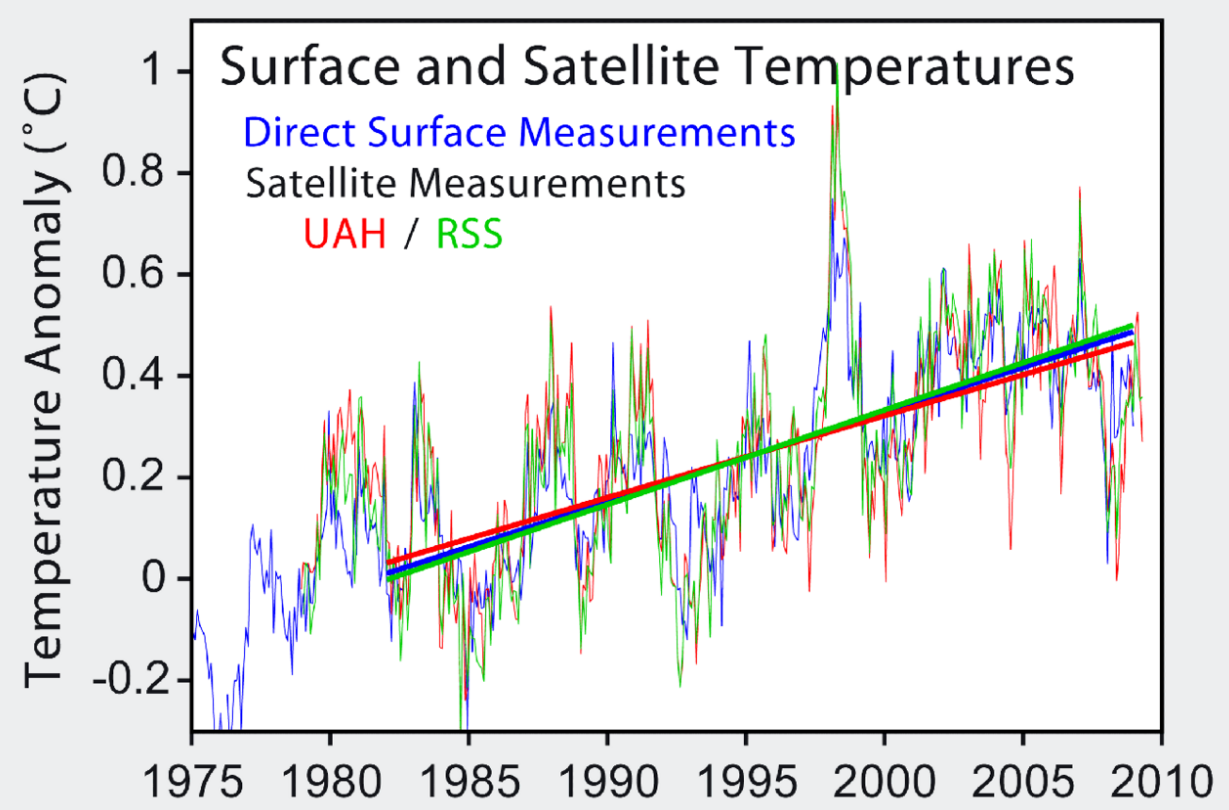
Friends of Science states that the satellite and balloon temperature records indicate no significant global warming has taken place over the last three decades.
Friends of Science states:[35]
- Accurate satellite, balloon and mountain top observations made over the last three decades have not shown any significant change in the long term rate of increase in global temperatures. Average ground station readings do show a mild warming of 0.6 to 0.8 C over the last 100 years, which is well within the natural variations recorded in the last millennium. The ground station network suffers from an uneven distribution across the globe; the stations are preferentially located in growing urban and industrial areas ("heat islands"), which show substantially higher readings than adjacent rural areas ("land use effects").
3. Activism and Education
In April 2005, Friends of Science released a 23-minute on-line video directed by Mike Visser, entitled "Climate Catastrophe Cancelled: What You're Not Being Told About the Science of Climate Change" that contrasts the views of politicians and scientists on the question of climate change.[36] The video featured consultant Tim Ball, Sallie L. Baliunas, geologist Tim Patterson of Carleton University, Ross McKitrick and political scientist Barry F. Cooper of the University of Calgary, all of whom are known for their rejection of the mainstream scientific view on global warming. A second edition was released 13 September 2007.
Madhav Khandekar,[37][38] Chris de Freitas, Tim Patterson, Sallie Baliunas and Douglas Leahey were among the 60 "accredited experts in climate and related scientific disciplines," signatories along with prominent members of The Heartland Institute,[39] to the letter sent to Prime Minister Stephen Harper calling on him to walk away from the Kyoto agreement,[40] which he eventually did. On 31 December 2011, Canada became the first signatory to announce its withdrawal from the Kyoto Protocol.[41]
The Friends of Science endorsed the Heartland Institute's 2008 Manhattan Declaration on Climate Change.[42] Some of the Friends, such as Madhav Khandekar, Chris de Freitas, Tim Patterson, Sallie Baliunas and Douglas Leahey, Tom Harris,[43] were present at the conference which took place in New York City at the Heartland Institute's 2008 International Conference on Climate Change in March 2008. Other Friends, like Timothy F. Ball, who were endorsers are climate science specialists or scientists in closely related fields.[44] Arthur M. Patterson was another Friend and endorser.
The Friends of Science are proponents of the Manhattan Declaration statements agreeing that "global Warming is not a global crisis" and arguing that "there is no convincing evidence that CO2 emissions from modern industrial activity has in the past, is now, or will in the future cause catastrophic climate change." The Manhattan Declaration calls for an end to "all taxes, regulations, and other interventions intended to reduce emissions of CO2."[42]
In 2013 in his opinion piece in the Financial Post Tom Harris described the climate symposium, "Earth climate: past, present, future" at the Geological Association of Canada, the Mineralogical Association of Canada (GAC-MAC) annual joint conference where Friends of Science presenters included Calgary geophysicist, independent oil and energy professional, Norm Kalmanovitch, a long-time member of Friends of Science.[38] Kalmanovitch argued that the greenhouse effect from greenhouse gas emissions has never existed to any measurable extent.[38] In a letter to the editor of the Calgary Herald dated 16 April 2015, Kalmanovitch claimed that in 1970, "the world was in the grips of a global cooling scare brought on by the 1942 reversion from global warming to global cooling, ending the 250-year recovery from the Little Ice Age and threatening its return. In 1975, the threat ended with the reversion to global warming, but returned with the reversion to global cooling in 2002 that is in place today." Kalmanovitch based his arguments on those of Jim Peden.[45]
In June 2014, the organization put up a billboard in Calgary stating that the sun is "the main driver of climate change." This provoked criticism from, among others, Greenpeace, whose request for their own advertisement to appear on an Alberta billboard had been denied by the same company that displayed Friends of Science's ad.[46]
4. Funding
In October 2005 Barry Cooper set up the Science Education Fund at the University of Calgary which was able to access funds from the Calgary Foundation.[47] Critics remark that Cooper established the Science Education Fund to "obscure the political and financial interests behind the donations, not only providing anonymity to donors but also a tax break for their contributions to science education."[48] Friends of Science has been "criticized for its close financial ties to the Alberta patch."[48] In 2010, in the section on "Donations" published in the Friends of Science's newsletter in 2010, Chuck Simpson, the Past Director of Friends of Science called for fund raising to help this "small group of volunteers" with administrative costs. One of their claimed problems is that they were unable to "attract money from corporations",[49][50] although their antagonists claim the Friends of Science are funded by the petroleum industry[49] and close links to the oil and gas industry.[51] In April 2007, The Friends of Science newsletter claimed their "efforts to bring balance to the climate change debate are being restricted because of our lack of funding. We have mostly relied upon the good nature of our members, with some contributions from Charitable Foundations. There has also been some funding from 'big oil', but they seldom smile on us. They appear to believe that marketing is more important than historical climate information."[52]
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Organization:Friends_of_Science
References
- Chris de Freitas is the brother of Tim de Freitas, an active member of the Calgary branch of the Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists.
- Chris de Freitas' Geography 101 workbook used for teaching the basics of climate at the University of Auckland, omits references to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and its landmark 2007 reports.
- Barton, Chris (16 July 2011). "The climate dissenter holds his ground". The New Zealand Herald. http://www.nzherald.co.nz/nz/news/article.cfm?c_id=1&objectid=10738739. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- Roe, Jon. "Science, education, funds: A look into the Friends of Science connection to the University of Calgary". Calgary, Alberta: The Gauntlet. http://www.thegauntlet.ca/story/science-education-funds.
- "Arthur Patterson". Calgary, Alberta: Glenbow Museum. 1999. http://www.glenbow.org/collections/search/findingAids/archhtm/extras/elbow/patterson_arthur.pdf. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- After graduating with a Bachelor Science degree in Geology, Friends of Science founding member and first president, Arthur M. Patterson, had a successful career in the oil industry. In retirement he ran a small independent oil company. His father was a well-known lawyer in Calgary and the present neighbourhood of Patterson Heights gets its name from his family. His grandfather was a lawyer and parliamentarian.
- "Friends of Science". website Developed and maintained by MichellComputing, Calgary Canada. Archived from the original on 16 October 2002. https://web.archive.org/web/20021016082106/http://www.friendsofscience.org/. Retrieved 2011-12-04.
- Jacobs was a Senior Manager of Frontier Exploration at Canterra Energy (1981 – 1986), District Manager at Aquitaine Company of Canada (1971 – 1981), Senior Staff Geologist at Tenneco Oil & Minerals (1960 – 1971) and District geologist at Petrofina Group (1955 – 1960).
- Chris de Freitas (June 2002). "Are Observed Changes in the Concentration of Carbon Dioxide in the Atmosphere Really Dangerous?". Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology.
- The article was described as "an exhaustive review of global climate science by Chris de Freitas of the University of Auckland" (Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, June 2002; also posted on the CSPG website).
- "Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists (CSPG) Position on Global Climate Change Science". Calgary, Alberta. January 2003. Archived from the original on August 19, 2003. https://web.archive.org/web/20030819031444/http://www.cspg.org/CSPG_Climate_Change_Backgrounder.pdf.
- Charles Montgomery (2006-08-12). "Mr. Cool: Nurturing doubt about climate change is big business". The Globe and Mail. Archived from the original on 2007-04-02. https://web.archive.org/web/20070402110349/http://www.charlesmontgomery.ca/mrcool.html. Retrieved 2007-05-01.
- "Elections Canada to probe anti-Kyoto Protocol group", Victoria Times-Colonist, February 18, 2008, archived from the original on November 8, 2012, https://web.archive.org/web/20121108112401/http://www.canada.com/victoriatimescolonist/news/story.html?id=3c955256-f327-465a-8135-778088f6131a .
- According to Canwest News Service reporter, Mike De Souza's article published in the Vancouver Sun in 2011, the letter from University of Calgary account administrator, Chantal-Lee Watt, accompanying $175,000 Talisman cheque, dated 4 November 2004, was part of documents released by the University of Calgary under the orders of Franklin J. Work, the office of Alberta's information and privacy commissioner.
- The Calgary Herald described James Buckee's retirement from Talisman in May 2007 as the end of an oilpatch era with Buckee as one of its most colourful characters.
- "Jim Buckee retires at Talisman:An oilpatch era ended Wednesday with the retirement of one of its most colourful characters". Calgary, Alberta: The Calgary Herald. 31 May 2007. http://www.canada.com/story.html?id=fdc3b6fd-ca3e-454d-9894-f9894a0ef4dd. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- De Souza, Mike (4 September 2011). "Talisman Energy kick-started U of C climate skeptic fund". Postmedia News. http://www2.canada.com/vancouversun/news/archives/story.html?id=15b2e521-9f14-43e6-87ac-0a21a2a79e3d&p=2.
- Hamilton, Clive (2010). Requiem for a Species: Why We Resist the Truth about Climate Change. Earthscan. p. 103. ISBN 978-1-84971-081-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=EuE0RmNLlp4C.
- Naomi Oreskes and Erik M. Conway (2010). Merchants of Doubt, Bloomsbury Press, pp. 8-9.
- Clive Hamilton, Naomi Oreskes and Erik M. Conway claim the George C. Marshall Institute, founded by three prominent physicists -- Frederick Seitz, Robert Jastrow, and William Nierenberg in 1984, led the conservative backlash against global warming research and focused on attacking climate change science by creating confusion.
- Lindzen, Richard S. (2 May 2001). "Testimony of Richard S. Lindzen before the Senate Environment and Public Works Committee". http://housemajority.org/coms/cli/Kramm_UAF_Lindzen_2001.pdf.
- Richard S. Lindzen was a meteorologist, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Member, Annapolis Center Science and Economic Advisory Council. Contributing Expert, Cato Institute. Contributing Expert, George C. Marshall Institute. Member, National Academy of Sciences.
- Ross Gelbspan reported in 1995 that Lindzen "charges oil and coal interests $2,500 a day for his consulting services; his 1991 trip to testify before a Senate committee was paid for by Western Fuels, and a speech he wrote, entitled 'Global Warming: the Origin and Nature of Alleged Scientific Consensus,' was underwritten by OPEC ("The Heat is On: The warming of the world's climate sparks a blaze of denial," Harper's magazine, December 1995)."
- Gelbspan, Ross (December 1995). "The heat is on: The warming of the world's climate sparks a blaze of denial". Harper’s Magazine. http://www.harpers.org/archive/1995/12/0007823. Retrieved 2007-08-02.
- Sanchez, Irene (2005-11-13). "Warming study draws fire". The Harvard Crimson. http://www.thecrimson.com/article.aspx?ref=348723. Retrieved 2009-05-30.
- https://web.archive.org/web/20030225010718/http://www.sepp.org/NewSEPP/Testimony-baliunas.htm
- Sallie Baliunas (13 March 2002). "Separating Climate Fact From Fiction: Testimony by Sallie Baliunas provided to the Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works, chaired by Sen. James M. Jeffords". Archived from the original on February 25, 2003. https://web.archive.org/web/20030225010718/http://www.sepp.org/NewSEPP/Testimony-baliunas.htm. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- MacRae, Allan M.R. (1 September 2002). "Kyoto Hot Air Can't Replace Fossil Fuels". Calgary, Alberta: Calgary Herald. Archived from the original on April 4, 2003. https://web.archive.org/web/20030404154737/http://www.vision.net.au/~daly/guests/macrae.htm. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- Wildavsky, Aaron (April 1995). But Is It True?: A Citizen's Guide to Environmental Health and Safety Issues. Harvard University Press. pp. 704. ISBN 0674089227. https://archive.org/details/butisittruecitiz00wild/page/704.
- "President's Message". Friends of Science Membership Quarterly Newsletter. July 2005. p. 1. http://sourcewatch.org/images/2/22/FOS_2005_Q2_Newsletter_7.pdf.
- De Souza, Mike (22 February 2008). "Anti-Kyoto campaigner volunteer member of Tory election team". Canwest News Service. http://www.canada.com/topics/news/story.html?id=595cc20a-7e54-4882-b3db-23e75f19a9a4&k. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- http://www.friendsofscience.org/index.php?id=3
- Soon, Willie; Sallie Baliunas (January 31, 2003). "Proxy climatic and environmental changes of the past 1000 years". Climate Research (Inter-Research Science Center) 23: 89–110. doi:10.3354/cr023089. Bibcode: 2003ClRes..23...89S. http://www.int-res.com/articles/cr2003/23/c023p089.pdf.
- In 1999, Mann, Bradley and Hughes published a study which used a new statistical approach to find patterns of climate change in both time and global distribution. covering a 1,000 years summarized in a graph which showed relatively little change until a sharp rise in the 20th century, earning it the nickname of the hockey stick graph. Baliunas disputed that man-made chemicals (halocarbon refrigerants such as CFCs) were causing ozone depletion. Baliunas and Soon prepared a literature review which used data from previous papers to argue that the Medieval Warm Period had been warmer than the 20th century, and that recent warming was not unusual and sent it Climate Research editor Chris de Freitas, an opponent of action to curb carbon dioxide emissions, who published the article. Their abstract concluded that "Across the world, many records reveal that the 20th century is probably not the warmest or a uniquely extreme climatic period of the last millennium". The paper acknowledged funding support from the American Petroleum Institute, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and NASA.
- "Myths/Facts: Common Misconceptions About Global Warming". http://www.friendsofscience.org/index.php?ide=4. Retrieved 2007-03-05.
- "Climate Catastrophe Cancelled: What You're Not Being Told About the Science of Climate Change". https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KnipKZAhgW4&list=PL76D04BD1D7D39C1D. Retrieved 2007-03-05.
- Madhav Khandekar, retired as research scientist with Environment Canada in 1997, argued that there were uncertainties in IPCC science and called for an open debate on the issue in the Canadian Meteorological and Ocean Society (CMOS) Bulletin.
- Tom Harris (6 July 2011). "Climate isn't up for debate". Financial Post. http://opinion.financialpost.com/2011/06/07/climate-isnt-up-for-debate.
- "Open Kyoto Debate". Chicago, Illinois: The Heartland Institute. 6 April 2007. http://heartland.org/policy-documents/open-kyoto-debate. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- "Open Kyoto to debate". The National Post. 6 April 2006. https://nationalpost.com/story.html?id=3711460e-bd5a-475d-a6be-4db87559d605. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- "Canada and Kyoto: A history of the country's involvement and its greenhouse gas emissions". CBC News. 13 December 2011. http://www.cbc.ca/news/interactives/canada-kyoto/. Retrieved 20 December 2011.
- "endorsers of The Manhattan Declaration on Climate Change". Climate Science International. March 2008. http://www.climatescienceinternational.org/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=48:a-list&catid=14:text. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- Tom Harris is Executive Director of the International Climate Science Coalition (ICSC).
- "Endorsers of The Manhattan Declaration on Climate Change 2". Climate Science International. March 2008. http://www.climatescienceinternational.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=66. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- "Letter to the Editor: Read Naomi Klein Letter, April 15", Calgary Herald (Calgary, Alberta), 16 April 2015, https://calgaryherald.com/opinion/letters/letters-for-thursday-april-16, retrieved 16 April 2015
- Canadian Press (8 June 2014). "Greenpeace claims double standard on Alberta billboards". Cbc.ca. http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/calgary/greenpeace-claims-double-standard-on-alberta-billboards-1.2669070. Retrieved 12 June 2014.
- Roe, Jon (2007-11-01). "Science, education, funds — A look into the Friends of Science connection to the University of Calgary". Gauntlet. http://www.archive.thegauntlet.ca/story/science-education-funds. Retrieved 2011-12-04.
- Greenberg, Josh; Graham Knight; Elizabeth Westersund (2011). "Spinning climate change: Corporate and NGO public relations strategies in Canada and the United States". The International Communication Gazette 73 (1–2): 65–82. doi:10.1177/1748048510386742. https://dx.doi.org/10.1177%2F1748048510386742
- "President's Message". Calgary, Alberta: Friends of Science. March 2010. http://www.friendsofscience.org/assets/files/documents/2010_March_Newsletter.pdf. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- According to an interview with Albert Jacobs and The Globe and Mailfreelancer Charles Montgomery, in 2006, the Friends of Science' first fundraiser in 2002 with guest speaker, Tim Ball, who makes speeches around the country trying to convince people climate change isn't happening, did not raise enough money. Tim Ball, retired University of Manitoba climatologist, International Climate Science Coalition (ICSC) Science Advisory Board member. Ball became the public face of Friends of Science.
- "The Denial Machine: a Canadian Broadcasting Corporation documentary about climate scepticism and funding". CBC News. 15 November 2006. http://www.cbc.ca/fifth/denialmachine. Retrieved 3 May 2007.
- "Friends of Science Newsletter, April 2007". http://www.friendsofscience.org/documents/2007%20April%20Newsletter.pdf.
