The learning crisis is the reality that while the majority of children around the world attend school, a large proportion of them are not learning. A World Bank study found that "53 percent of children in low- and middle-income countries cannot read and understand a simple story by the end of primary school." While schooling has increased rapidly over the last few decades, learning has not followed suit. Many education systems leave lots of children behind in learning as they progress in schooling. For example, in India, over half of Grade 5 students have not mastered Grade 2 literacy. In Nigeria, only about 1 in 10 women who completed Grade 6 can read a single sentence in their native language. Across seven low- and middle-income countries that participated in PISA for Development, only 12 percent of children who were tested met minimum proficiency levels for math, and just 23 percent for reading. While the skills of Brazilian 15-year-olds have improved in recent decades, at the current rate of improvement, students will not meet the average score of wealthy countries in math for 75 years. For reading, it will take more than 260 years. It is highly likely that the learning crisis will be further exacerbated with the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic and the vast disruptions that this pandemic caused for education across the globe.
- children
- middle-income countries
- schooling
1. Background
1.1. Education as a Human Right
In 1948, the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), in which Article 26 guaranteed the right to an education.[1] Article 26 also set out the ambitious goal of universal primary education. In full, Article 26 of the UDHR states:
1. Everyone has the right to education. Education shall be free, at least in the elementary and fundamental stages. Elementary education shall be compulsory. Technical and professional education shall be made generally available and higher education shall be equally accessible to all on the basis of merit.
2. Education shall be directed to the full development of the human personality and to the strengthening of respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms. It shall promote understanding, tolerance and friendship among all nations, racial or religious groups, and shall further the activities of the United Nations for the maintenance of peace.
3. Parents have a prior right to choose the kind of education that shall be given to their children.[1]
In 1950, the average adult in developing countries had just two years of schooling.[2]
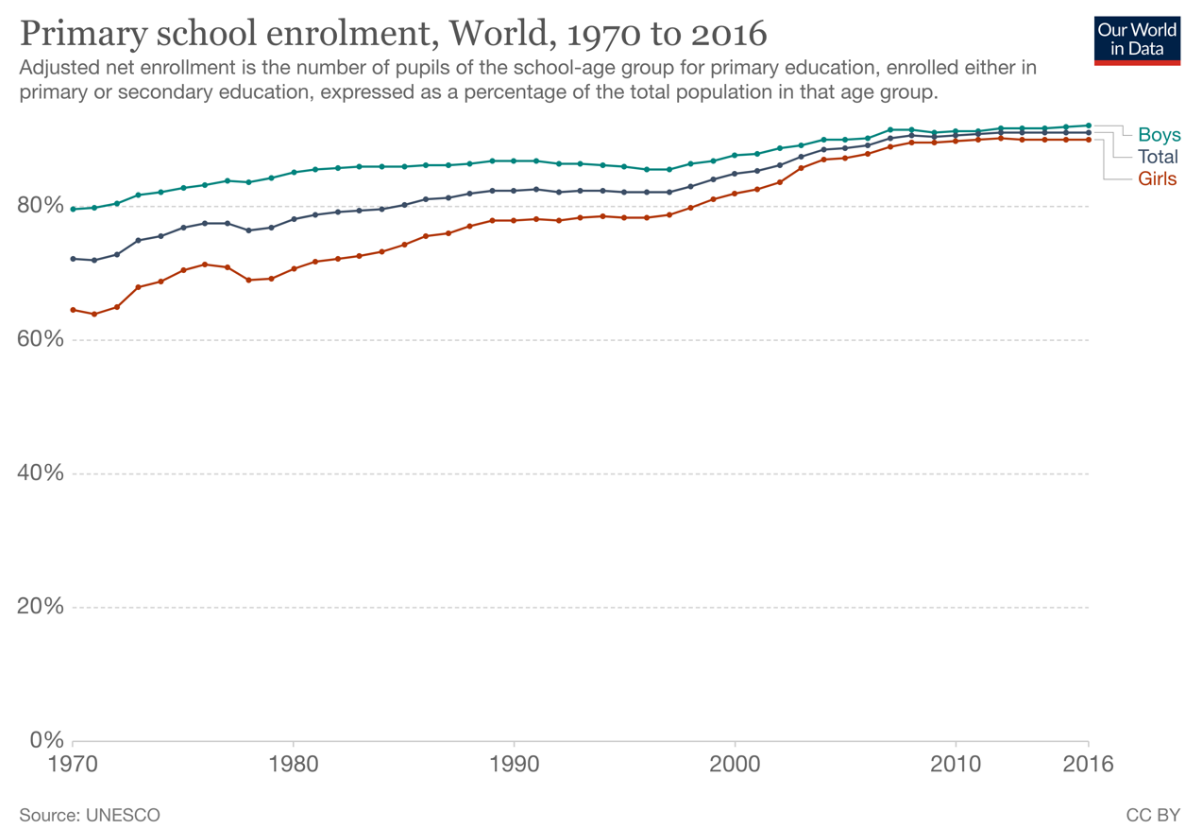
1.2. Rise of Universal Primary Schooling and the MDGs
In 2000, the Millennium Development Goals set a goal that, "by 2015, children everywhere, boys and girls alike, will be able to complete a full course of primary schooling."[3]
This once lofty goal of universal primary schooling is well on its way to completion. As of 2016, over 91 percent of children are enrolled in formal primary schooling.[4]
Furthermore, the average years of schooling completed by children in developing countries has more than tripled to greater than seven years.[5]
Education For All, a global movement led by UNESCO, expanded this schooling goal to address learning by aiming to meet the learning needs of all children, youth, and adults by 2015.[6]
1.3. "Schooling ain't Learning"[7]
Although primary schooling has rapidly increased in recent decades, emerging data reveals a frightening learning crisis: just because children are in school, does not mean they are learning. For example, in South Africa, 40 percent of children lacked numeracy skills and 27 percent were functionally illiterate; however, only two percent had either never attended school or dropped out.[5]
Previous documents, such as the UDHR and the Millennium Development Goals, clearly set out global priorities surrounding access to a quality education for all children. However, simply getting kids into classrooms is not enough to provide a quality education: there is a gap between schooling and learning that must be addressed.
1.4. Sustainable Development Goal 4
There is an increasing focus on quality of education and the learning crisis, which can be seen through Sustainable Development Goal 4 that was adopted by the United Nations in 2016. Sustainable Development Goal 4 states that countries will "ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all."[8]
The goal is then broken down into specific targets, with target 4.6 establishing that by 2030, "all youth and a substantial proportion of adults, both men and women, achieve literacy and numeracy."[9] Research on current learning trajectories in many developing countries suggests that the rate of current progress is unlikely to achieve the large gains needed to reach universal literacy and numeracy; thus, drastic changes are needed to improve learning for all students.
2. Measuring the Learning Crisis
2.1. Learning Profiles
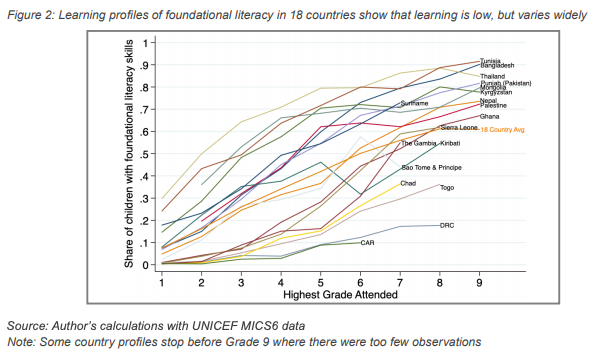
Learning profiles are an effective way to link schooling and learning, by showing the pace at which children gain the education they need as they continue through schooling. Essentially, learning profiles utilize student mastery data to link the competencies that children master and their years in school. Learning profiles can be utilized to understand the dynamics of learning over multiple ages or grades, especially in the primary years, and on progress toward universal learning goals.[11] While learning curves demonstrate individual student learning, learning profiles reveal learning data about an entire student population.
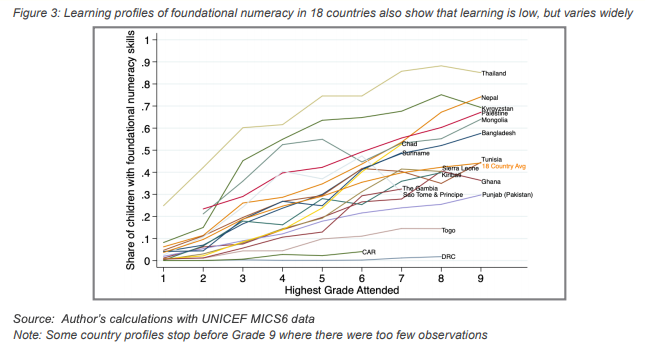
Learning profiles are visualized with the percentage of children mastering some given concept on the y-axis, usually foundational literacy or numeracy; and the years of schooling attended on the x-axis. Recent analysis using UNICEF MICS6 data reveals that the learning profiles in several low- and middle-income countries are highly variable; however, many of the learning profiles are essentially flat. A relatively flat learning profile reflects the learning crisis, in that children are spending many years in schooling, yet they are not mastering the basic concepts necessary to gain a quality education and excel in later life. This means that even if students persisted through school for many years, they would never achieve basic foundational skills in literacy and numeracy.
Several countries show flat learning profiles, including Togo, Central African Republic, and Democratic Republic of the Congo. These learning profiles also reveal that there are large variations in foundational literacy and numeracy skills for children that complete primary school. For those completing Grade 5, foundational literacy and numeracy skills vary from virtually 0 percent to as high as 80 percent.[10]
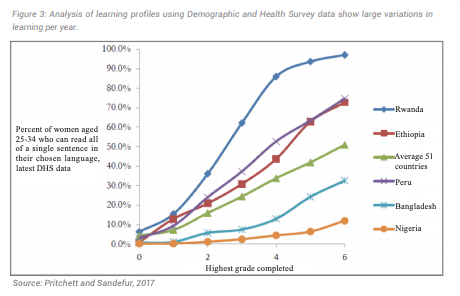
Analysis from women aged 25–34 in 51 different countries further shows variable learning profiles. In Nigeria, only about 1 in 10 women who completed Grade 6 could read a single sentence, compared to almost 100 percent in Rwanda.[12] Nevertheless, the average foundational literacy rate for women completing Grade 6 in 51 different countries was around 50 percent, revealing that half of children are leaving primary schooling without basic foundational skills.[12]
2.2. World Bank Learning Poverty Measure
The World Bank, along with the UNESCO Institute for Statistics, has developed the Learning Poverty concept and associated measure, which measures the proportion of students who are unable to read and understand a simple text by age 10.[13] This research found that 53% of children in low- and middle-income countries cannot read and understand a simple story by the end of primary school.[13] In poor countries, the level is as high as 80 percent.[13]
In fact, these new measures indicate that these startlingly high rates of illiteracy are an "early warning sign that SDG 4 for education and all related global goals are in jeopardy."[13] Current progress in improving literacy rates is much too slow to meet the SDG goals. At the current rate, approximately 43% of children will still be learning poor by 2030.[13]
2.3. Citizen-Led Assessments
The PAL Network (People's Action for Learning) is a partnership between various countries of the global south that work to conduct citizen-led assessments and improve learning outcomes for children in the developing world.[14]
In recent years, citizen-led assessments to measure learning in low- and middle-income countries have grown to better understand the learning crisis. In 2005, these citizen-led assessments began in India by the NGO Pratham through an initiative called the Annual Status of Education Report (ASER).[15]
ASER is a national household survey that is conducted throughout India, which assesses children's basic reading and math skills in 20 different regional languages. ASER Pakistan conducts similar household surveys throughout Pakistan, and Uwezo conducts assessments throughout Kenya, Uganda, and Tanzania.[16]
Recently, the PAL Network has created the International Common Assessment of Numeracy (ICAN), which is an open-source assessment tool available in 11 languages, with results aligned to SDG4 and its goal of foundational numeracy.
These citizen-led assessments have provided much deeper and detailed knowledge of the learning crisis across different countries. For example, ASER 2018 found that just 27.2 percent of Indian children in Grade 3 were able to read at a Grade 2 level, and just 28.1 percent could do basic subtraction.[17]
2.4. PISA for Development
The Programme for International Student Assessment, also called PISA, is a global study by the OECD that is conducted every three years and measures 15-year-olds academic performance in math, science, and reading. Because the OECD consists of majority developed and democratic countries, the triannual PISA studies do not measure learning in developing nations around the globe.
Thus, the OECD has encouraged the participation of low- and middle-income countries in PISA for Development testing, also called PISA-D. Seven low- and middle-income countries participated in PISA-D: Cambodia, Ecuador, Guatemala, Honduras, Paraguay, Senegal, and Zambia. The study further revealed the severity of the learning crisis:
- Only 12 percent of children who were tested met minimum proficiency levels for math, and just 23 percent for reading.[18]
- Across these countries, even the elite are receiving an inadequate education when compared to the global average: Less than a quarter of advantaged students in Senegal, Cambodia, Zambia, Guatemala, and Paraguay reach PISA-D Level 2, or minimum proficiency in reading and math as indicated by SDG4. Less than a half of advantaged students in Ecuador reach the same level.[18]
- While there are gaps in outcomes between different groups of students (girls vs. boys), the gaps are modest when compared to the gaps between the current average learning levels and the SDG4 goals for minimum proficiency.[19]
3. Severity of the Learning Crisis
3.1. India
- In rural India, almost 75 percent of third graders cannot solve a two-digit subtraction problem (like 46 minus 17).[19]
- For fifth graders, 50 percent still cannot solve the math problem.[19]
- Half of all children can read at a Grade 2 level.[17]
- 27.2 percent of Grade 3 children can read at a Grade 2 level, 28.1 percent can perform basic subtraction.[17]
3.2. Ethiopia
- Across five consecutive national learning assessments from 2000 to 2015, students in Grade 4 and Grade 8 were below the 50 percent threshold of minimum standards mastered in both literacy and numeracy.[20]
- Following the COVID-19 pandemic, student growth in numeracy slowed to about half the rate it was prior to the pandemic.[21]
3.3. Indonesia
- While Indonesia has near-universal primary school enrollment, and almost 80 percent secondary school enrollment, research shows that among Grade 12 graduates, 28 percent have Grade 1 mathematics skills and 33 percent have Grade 3 mathematics skills.[22]
- Only 11% of students who graduated from secondary school were able to answer all Grade 4 numeracy questions correctly.[23]
3.4. Nigeria
- Only about 1 in 10 women who completed Grade 6 can read a single sentence in their native language.[12]
- As of 2018, 13.2 million children do not attend school and the literacy rate among primary school graduated aged 18 to 37 was just 19 percent.[24]
3.5. Pakistan
- In 2020, the World Bank estimated that 79 percent of children in Pakistan will not learn to read by age 10.[25]
- Of people aged 15 and above, 41 percent are functionally illiterate.[26]
3.6. Tanzania
- In 2011, research found that only 30 percent of Tanzanian students could read a basic Kiswahili story and do basic math.[27]
- From 2006 to 2012, the pass rate for Tanzania's primary school exit exam declined from 70 to 31 percent; for the secondary school exit exam, from 89 to 34 percent.[27]
3.7. Vietnam
- Vietnam stands out as a developing country where primary and secondary school students are learning at impressive rates, with many children surpassing their peers in much wealthier nations.[28]
- In 2015, Vietnam ranked 21st in the globe in their average PISA score, above the United Kingdom at 23rd and the United States at 31st.[29]
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Philosophy:Learning_crisis
References
- "Universal Declaration of Human Rights." United Nations, 10 Dec. 1948, www.un.org/en/about-us/universal-declaration-of-human-rights. https://www.un.org/en/about-us/universal-declaration-of-human-rights
- Barro, R. J., & Lee, J.W. (2013). A new data set of educational attainment in the world, 1950-2010. Journal of Development Economics, 104, 184.
- "Millennium Development Goals." United Nations, Sept. 2000, www.un.org/millenniumgoals/education.shtml. https://www.un.org/millenniumgoals/education.shtml
- "Primary school enrolment, World, 1970 to 2016." Our World in Data, UNESCO Data, 2016, ourworldindata.org/grapher/primary-school-enrolment-by-sex?country=~OWID_WRL. https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/primary-school-enrolment-by-sex?country=~OWID_WRL
- "The Pivot from Schooling to Education." RISE Programme, 2016, riseprogramme.org/publications/rise-vision-document-1-pivot-schooling-education. https://riseprogramme.org/publications/rise-vision-document-1-pivot-schooling-education
- "The EFA movement". United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. Retrieved 11 Sep 2010.
- Pritchett, Lant. The Rebirth of Education: Schooling Ain't Learning. Center for Global Development, 2013. https://www.cgdev.org/sites/default/files/rebirth-education-introduction_0.pdf
- "Quality Education." Sustainable Development Goals, United Nations, 2016, www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/E_Infographic_04.pdf. https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/E_Infographic_04.pdf
- "Quality Education." Sustainable Development Goals, United Nations, 2016, www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/education/. https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/education/
- Silberstein, J. 2021. Measuring, Visualising, and Simulating Solutions to the Learning Crisis: New Evidence from Learning Profiles in 18 Countries. 2021/029. https://doi.org/10.35489/BSG-RISE-RI_2021/029
- Kaffenberger, M.2019.A Typology of Learning Proiles: Tools for Analysing the Dynamics of Learning. RISE Insight Series.2019/015. https://doi.org/10.35489/BSG-RISE-RI_2019/013.
- Pritchett, L. and Sandefur, J. 2017. Girls’ Schooling and Women’s Literacy: Schooling Targets Alone Won’t Reach Learning Goals. RISeEWorking Paper Series. 17/011. https://doi.org/10.35489/BSG-RISE-WP_2017/011
- "Learning Poverty is a combined measure of schooling and learning". World Bank. Retrieved 1 July 2021. https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/education/brief/what-is-learning-poverty
- PAL Network. https://palnetwork.org/what-we-do/
- Pratham. https://www.pratham.org/
- Uwezo. http://www.uwezo.net/
- Banerji, Rukmini. "Behind the Headlines (ASER 2018)." RISE Programme, 2019, riseprogramme.org/blog/behind-the-headlines_ASER2018. https://riseprogramme.org/blog/behind-the-headlines_ASER2018
- Pritchett, L. and Viarengo, M. 2021. Learning Outcomes in Developing Countries: Four Hard Lessons from PISA-D. RISE Working Paper Series. 21/069. https://doi.org/10.35489/BSG-RISE-WP_2021/069
- "The Education Crisis: Being in School Is Not the Same as Learning." World Bank, The World Bank, 22 Jan. 2019, www.worldbank.org/en/news/immersive-story/2019/01/22/pass-or-fail-how-can-the-world-do-its-homework. https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/immersive-story/2019/01/22/pass-or-fail-how-can-the-world-do-its-homework
- Tiruneh, Dawit T., et al. "Understanding Achievement in Numeracy Among Primary School Children in Ethiopia: Evidence from RISE Ethiopia Study." RISE Programme, 22 Jan. 2021, riseprogramme.org/sites/default/files/2021-05/Understanding_Achievement_Numeracy_Among_Primary_School_Children_Ethiopia.pdf. https://riseprogramme.org/sites/default/files/2021-05/Understanding_Achievement_Numeracy_Among_Primary_School_Children_Ethiopia.pdf
- Kim, Janice, et al. "Learning Inequalities Widen Following COVID-19 School Closures in Ethiopia." RISE Programme, 2021, riseprogramme.org/blog/learning-inequalities-widen-COVID-19-Ethiopia. https://riseprogramme.org/blog/learning-inequalities-widen-COVID-19-Ethiopia
- "Indonesia." RISE Programme, 2021, riseprogramme.org/countries/indonesia. https://riseprogramme.org/countries/indonesia
- Beatty, A. et al. 2018. Indonesia Got Schooled: 15 Years of Rising Enrolment and Flat Learning Profiles. RISE Working Paper Series. 18/026. https://doi.org/10.35489/BSG-RISE-WP_2018/026
- The World Development Report 2018. The World Bank, 2018, www.worldbank.org/en/publication/wdr2018. https://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/wdr2018
- Geven, Koen, et al. "Strengthening the fight against Pakistan’s learning crisis." World Bank, 2020, blogs.worldbank.org/endpovertyinsouthasia/strengthening-fight-against-pakistans-learning-crisis. https://blogs.worldbank.org/endpovertyinsouthasia/strengthening-fight-against-pakistans-learning-crisis
- "Literacy rate, adult total (% of people ages 15 and above) - Pakistan." World Bank, 2020, data.worldbank.org/indicator/SE.ADT.LITR.ZS?locations=PK. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SE.ADT.LITR.ZS?locations=PK
- "RISE in Tanzania: Research Overview (Technical)." RISE Programme, 2019, riseprogramme.org/publications/rise-tanzania-research-overview-technical. https://riseprogramme.org/publications/rise-tanzania-research-overview-technical
- "Vietnam." RISE Programme, 2021, riseprogramme.org/countries/vietnam. https://riseprogramme.org/countries/vietnam
- "PISA 2015 Worldwide Ranking – average score of math, science and reading." FactsMaps, 2015, factsmaps.com/pisa-worldwide-ranking-average-score-of-math-science-reading/. https://factsmaps.com/pisa-worldwide-ranking-average-score-of-math-science-reading/
