The GAZ Tigr (Russian: Тигр and English: Tiger) is a Russia n 4x4, multipurpose, all-terrain infantry mobility vehicle manufactured by GAZ, first delivered to the Russian Army in 2006. Primarily used by the Russian Federation's armed forces, it is also used by numerous other countries.
- multipurpose
- gaz
- tigr
1. History
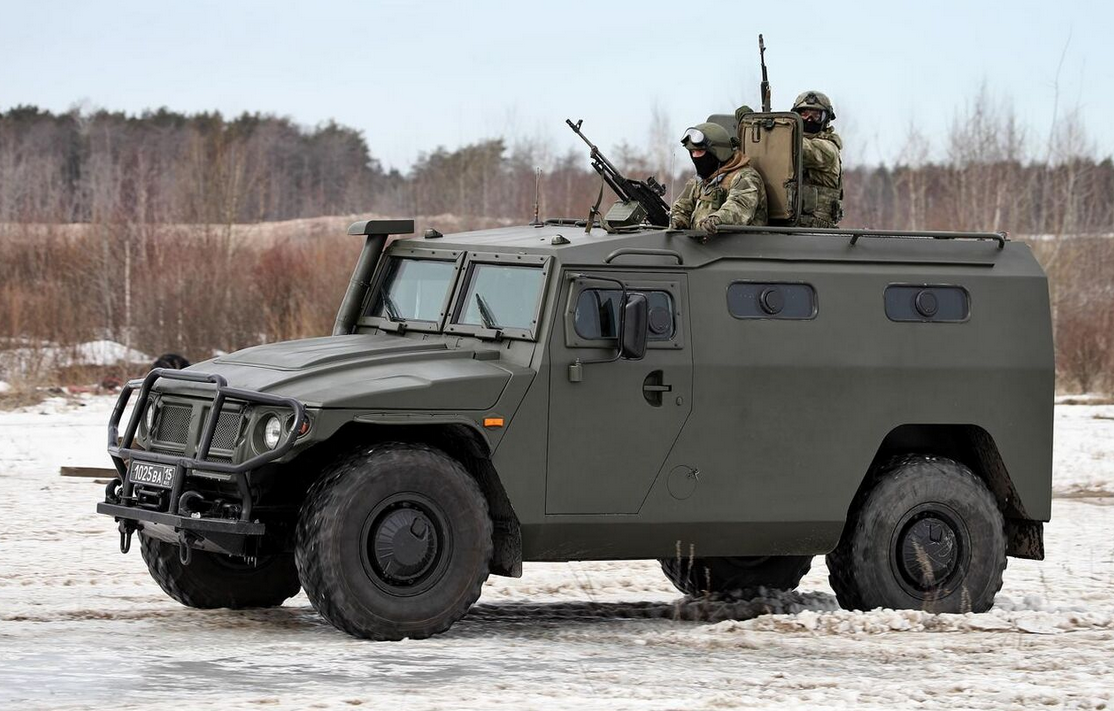
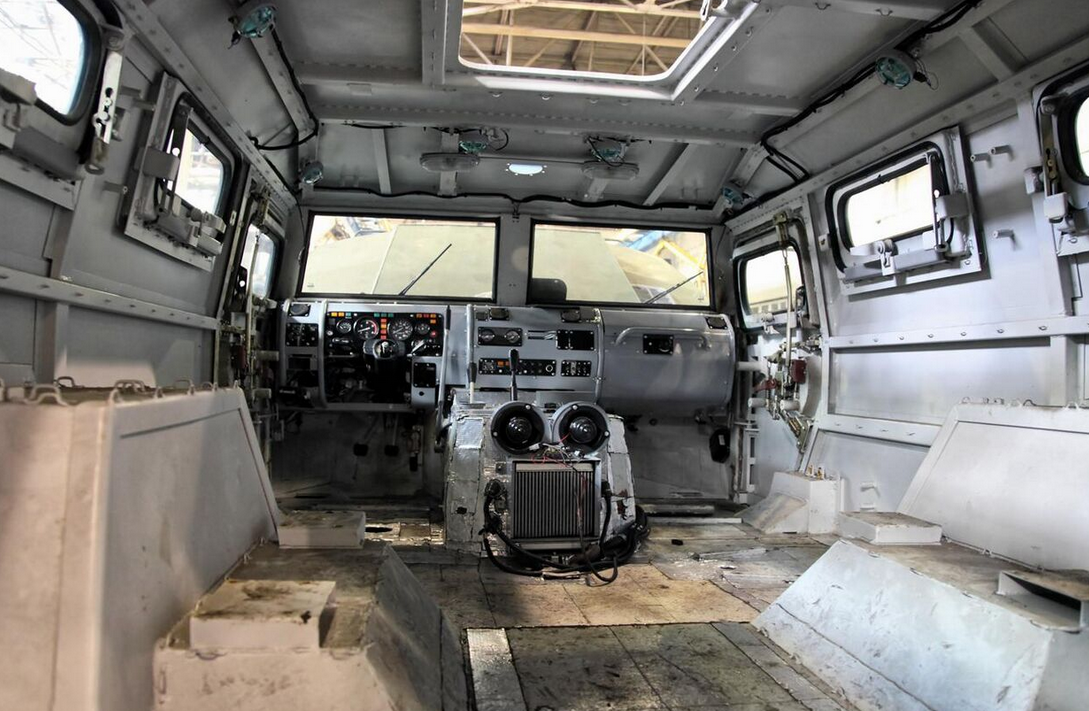


The Tigr was first shown at the IDEX exhibition in 2001.[1] Pilot production started in 2004 with 96 vehicles. The Russian Army officially adopted the GAZ-2975 into service at the end of 2006.[2] The vehicle was then officially manufactured in 2007.[2]
China co-produced the GAZ Tigr with Russia after it initially refused to grant them a full license.[3] 110 Tigrs were delivered from 2008-2010 and are in service with the Chinese Public Security police.[4] Some saw use publicly in the 2008 Beijing Olympics and in the 2009 Xinjiang riots.[4][5]
5 Tigrs, fully assembled, were delivered with five more in kit form for assembly while 100 were assembled in China under Beijing Yanjing Motor Company.[4][6] Yanjing Motor-made vehicles are known as YJ2080C and YJ2081C, the differences are the engine installed and the weight.[7]
During the 2010 Interpolitex exhibition, MIC presented the upgraded version of GAZ Tigr-the VPK-233114 Tigr-M-with a new YaMZ-534 diesel engine, additional armour and an NBC protection system. This new GAZ Tigr-M entered service with the Russian army during the first half of the 2013. Mass production and the export version have already been launched with a 205 hp engine.[8][9]
Tigr armoured cars were reported to be among the AFV's deployed by Russia in the Crimean crisis.[10] In early March 2015, OSCE inspectors spotted "a camouflaged GAZ TIGRA-type armoured personnel carrier" guarding a DPR Checkpoint, close to the village Shyrokyne east of Mariupol.[11]
In 2011, "Rosoboronexport" has offered Azerbaijan to create a licensed production of armored vehicles on its territory.[12][13]
Since 2015, Tigr vehicles are used by the Syrian Army in fight with opposition and extremist groups.[14]
The Minsk Wheel Tractor Plant unveiled the Lis-PM (Fox-PM in English from Russian), a variant of the Tigr, in a public relations event on April 30, 2015.[15] It's made from parts supplied from VPK-233136 Tigr kits.[16] Parts made in Belarus are around 85 percent with plans to have the Lis-PM made with all the components made in Belarus.[17] The vehicle was previously seen at the 7th International Exhibition of Armament and Military Equipment or MILEX-2014 event.[15] They were then shown on May 9, 2015 in a Belarusian military parade.[15]
BYMC announced on November 8, 2016 that an unnamed country has purchased 177 YJ2080s, winning its first export order.[18]
In January 2017, Tigr-Ms entered service with the Russian Army mounting the Arbalet-DM remote weapon station (RWS). It can hold a Kord 12.7 mm machine gun carrying 150 rounds of ammunition or a PKTM 7.62 mm machine gun carrying 250 rounds. The module has TV and thermal imaging cameras allowing target identification out to 2.5 km and 1.5 km respectively, an integral laser rangefinder, and the ability to lock on and track targets.[19]
As of May 2020, Tigr has been exported to 16 states and since 2005 over 2,000 vehicles have been built in various configurations and delivered to Russia and foreign countries.[20][21]
2. Design
The vehicle was designed to transport troops and various equipment quickly on road and off-road. It has a chassis frame construction, with a traditional layout of front engine, middle crew compartment, and rear cargo area. Standard features include: power steering, independent all-wheel torsion suspension with hydraulic shock absorbers and stabilizer bars, a transfer case with a locking center differential, limited slip differentials, two-speed transfer case, automatic tire inflation, engine block heater, and electric winch.
The GAZ-233001 has optional air conditioning, stereo, electric windows, and an anti-lock braking system.
Armored versions of the Tigr feature 5 mm (0.20 in) (7 mm (0.28 in) for the SPM-2) heat-treated and stress-relieved armor plates. The Tigr can carry a half ton of cargo.
The available engines are a Cummins 5.9 L (360 cu in) B180 turbodiesel with 180 hp (130 kW); a Cummins 5.9 L (360 cu in) B205 turbodiesel producing 180 hp (130 kW); a Cummins 5.9 L (360 cu in) B-214 turbodiesel making 215 hp (160 kW); or a GAZ-562 3.2 L (200 cu in) turbodiesel with 197 hp (147 kW).
Designed for performance in mountain, arctic, and desert environments, the Tigr is capable of operating at ambient temperatures ranging from −14–50 °C (7–122 °F). Moreover, the vehicle has approach and departure angles of 52 degrees and a wading depth of 1.2 m (3.9 ft).
3. Variants
3.1. Russian Variants
The Tigr is produced in multiple variants.
GAZ-2975
- GAZ-2975-A prototype unarmored three-door station wagon sport utility vehicle
- GAZ-29751 - 3 door wagon,
- GAZ 29752 - 5-door wagon designed to carry four people and from 500 to 1000 kilograms of cargo,
- GAZ-297533 - two door with tilt covered load platform.[22]
Specifications:
- Ground clearance, mm - 400
- Capacity in kg - 1500
- Tire dimension - 335/80 R20
- Curb weight, kg - 5300
- Allowable tilt when the slope, deg. - thirty
- The angle of overhang front / rear, deg. - 52/52
- The turning radius, m - 8.9
- The cost - about 60 thousand US dollars.[23]
- Transmission - 6 speed manual transmission or five speed automatic
GAZ-2330
Standard unarmoured production variant
- GAZ-2330-Multipurpose unarmoured SUV, made in two and three-door versions
- GAZ-23304-Multipurpose unarmoured five-door wagon with rear hinged doors
- GAZ-233001/GAZ-233011-Multipurpose unarmoured four-door pickup truck
- GAZ-233002/GAZ-233012-Multipurpose unarmoured two-door pickup truck
- GAZ-233003/GAZ-233013-Multipurpose unarmored three-door SUV with a sedan body with optional undivided/divided interior
Tigr-2
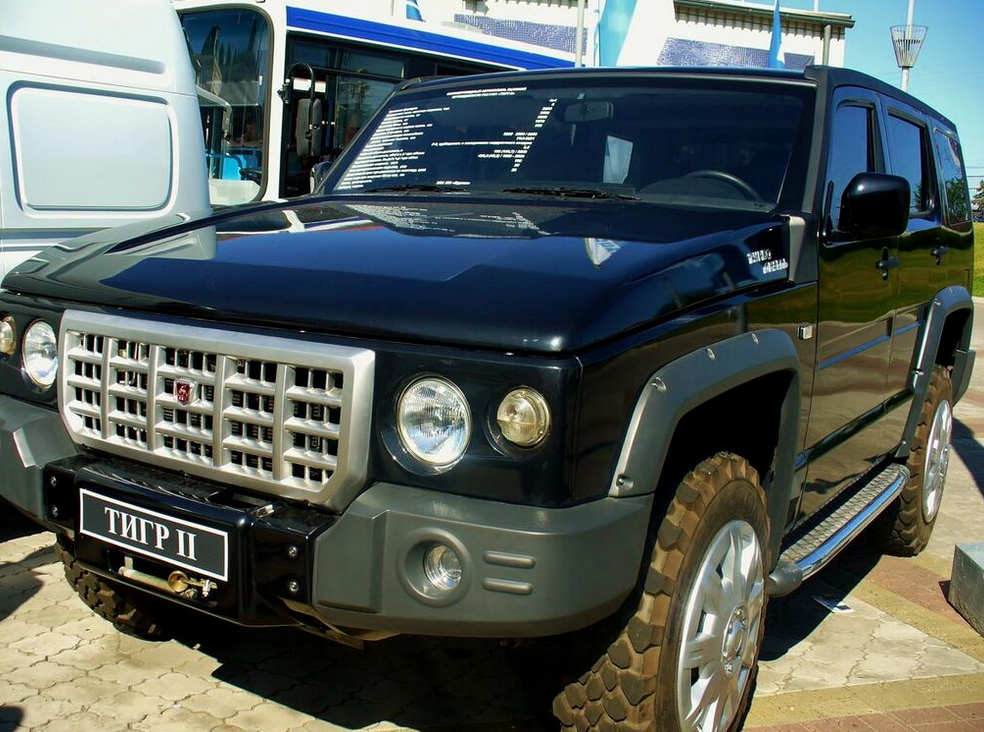

GAZ-3121 "Tiger-2" - an experimental rebodied civilian style SUV, presented for the first time in September 2006 at the Moscow Motor Show in the exhibition "Russian cars". Released in a small series from 2008, mainstream sales at dealers were planned to start in 2009 with the car available in two trim levels-luxury and regular.
The standard SUV is mechanically very similar to the military Tigr. It is packaged with a Steyr turbodiesel with 190 hp (140 kW) or six-cylinder Cummins B205 with 205 hp (153 kW) and is designed for speeds of up to 160 km/h (99 mph). Interior details are borrowed from the GAZ Volga and GAZ Gazelle.
With a weight of 3,500 kg (7,700 lb), the civilian Tiger-2 fuel consumption is 15 L/100 km. Its length is 5.7 m (19 ft), its width and height is 2.3 m (7.5 ft), and its ground clearance is 330 mm (1.08 ft). Compared with the military version, the civilian Tigr is 2,800 kg (6,200 lb) lighter. The price was planned at $270,000/17,600,000 rubles.
SP46
In 2007, a ceremonial parade variant was designed, the СП46 (SP 46) ceremonial Tigr is a two-door convertible with a removable rigid roof. It features two seats in the front and one in the back, and is finished with modern luxury car appointments. This Tigr is equipped with an automatic Allison 1000 series transmission and Cummins B205 turbodiesel. Vehicle weight was reduced to 4,750 kg (10,470 lb), as this version is unarmoured.
In November 2008, a prototype of the parade Tigr was presented to the Minister of Defense Anatoly Serdyukov. Subsequently, three vehicles were ordered and used in the Victory Day parade on May 9, 2009 at the Palace Square in St. Petersburg and also at the 64th anniversary of Russia's World War II victory.
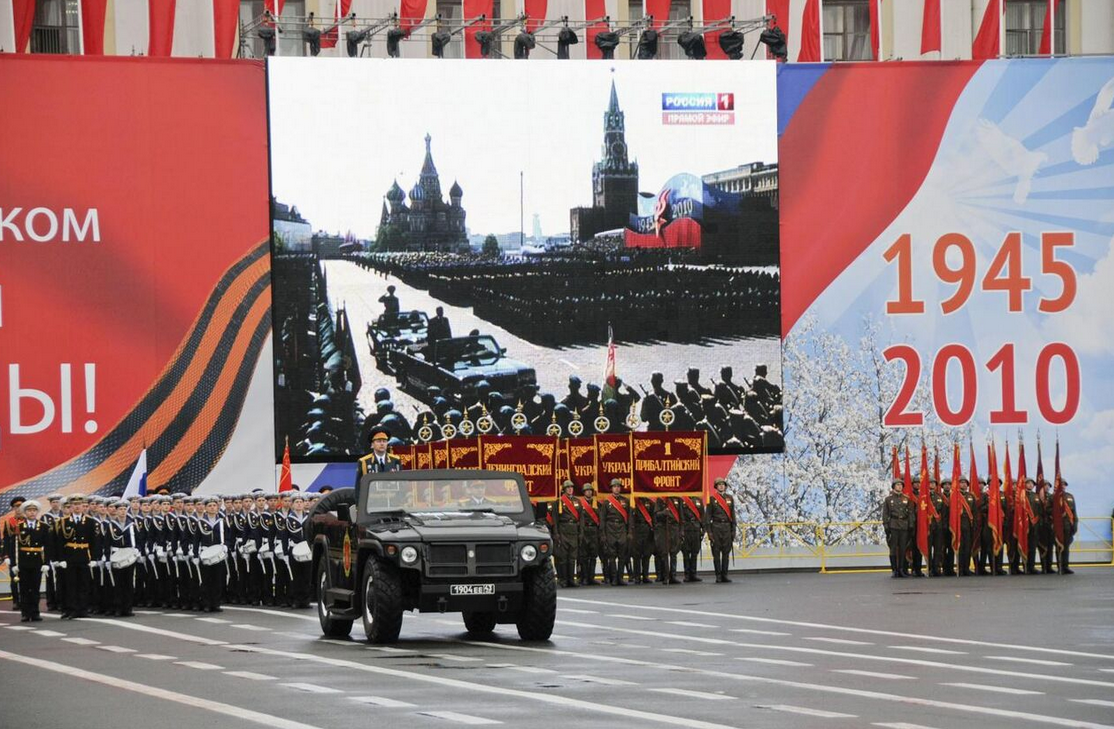

SP46 in 2010 Moscow Victory Day Parade in St. Petersburg.
STS
The CTC (English:STS) GAZ-233014 "Tigr" - a special vehicle - The Russian Army's armored version. Winged sheathed hull with an anti-splinter coating made of aramid fiber. 4-stroke turbocharged diesel engine Cummins B 205. STS GAZ-233014 was accepted for supply to units of the General Staff of the Russian Federation by Order of the Minister of Defense of the Russian Federation from March 6, 2007. The STS took part in the 2014 Crimean operation.[24]
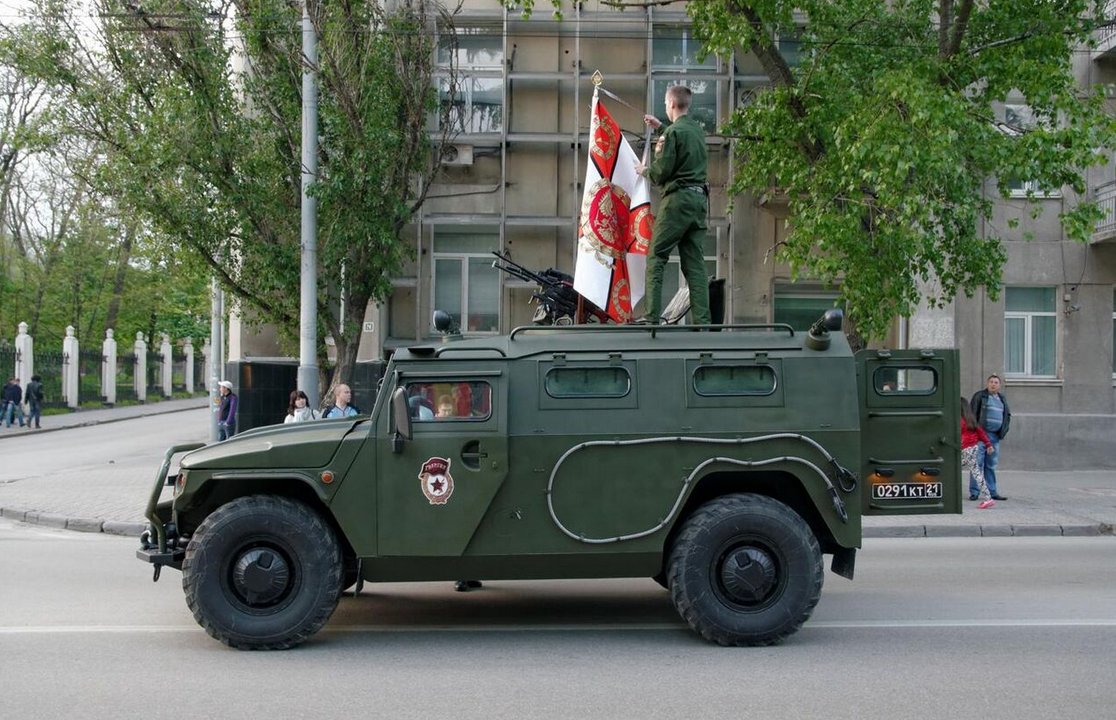

GAZ-233014 "Tigr" at 2014 Rostov-on-Don Victory Day Parade Rehearsal
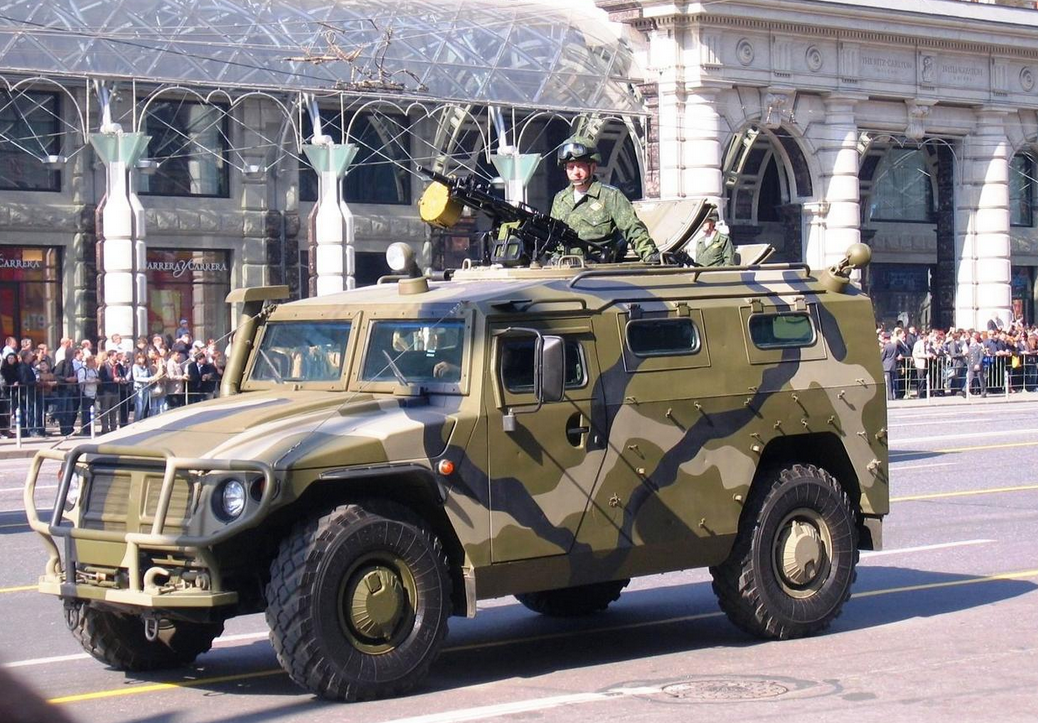

GAZ-233014 during 2008 Moscow May Day Parade Rehearsal
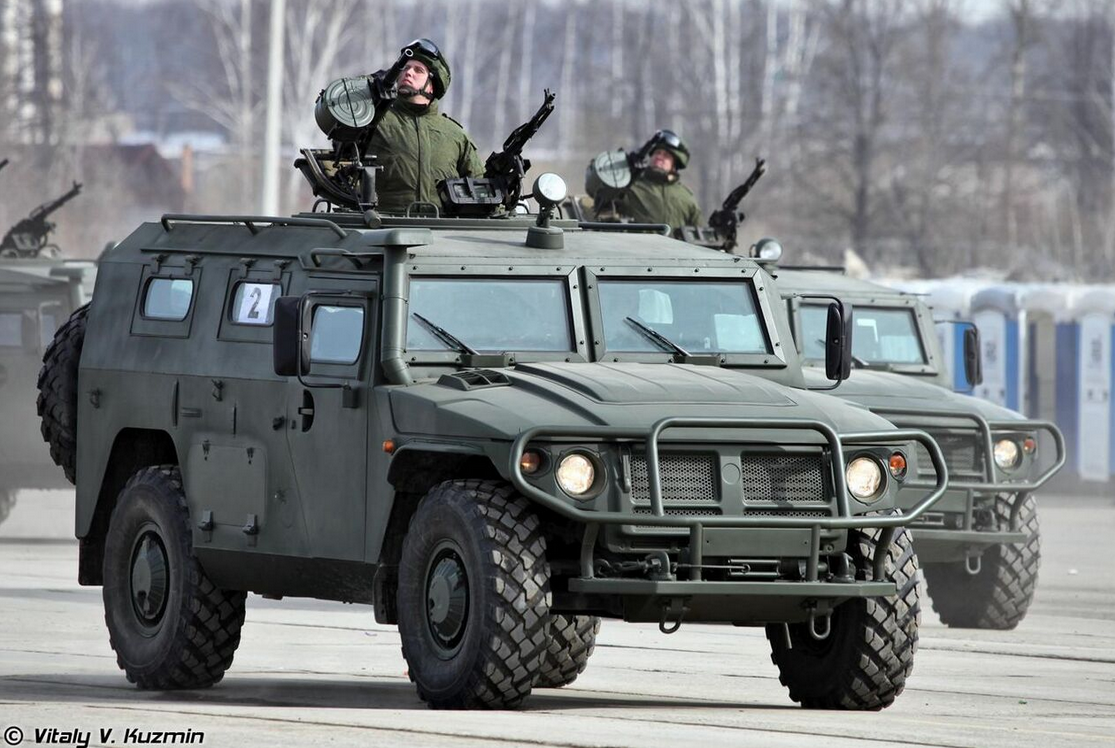

GAZ-233014 during 12 April 2013 Victory Day Parade rehearsal
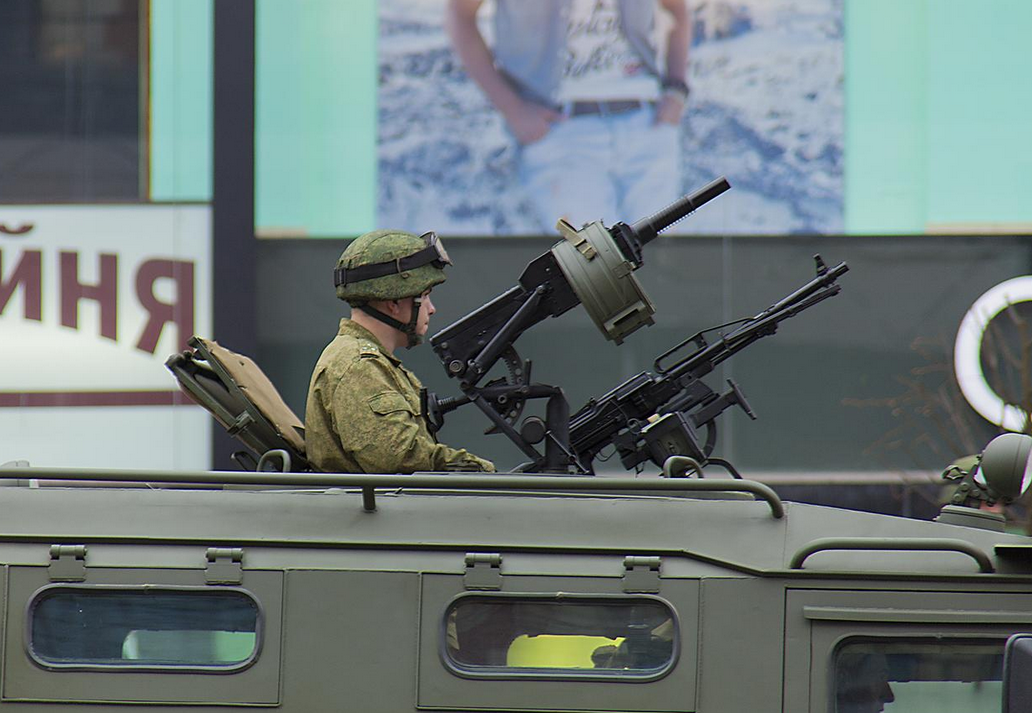

closeup of GAZ-233014 weapons station
SPM-1
Специальная полицейская машина СПМ-1 (Special police car SPM-1) GAZ-233034 Tigr is used by the Russian Interior Ministry OMON in counter-terrorism operations and territorial defense. It is armoured, with IEC 50963-96 Class 3 side/rear protection and Class 5 frontal protection (GOST P 50963-96, level 1 corresponds to the STANAG 4569). The vehicle has accommodations for seven occupants including the driver. Early models permit the firing of personal weapons through one-way portholes in the body. In later models personal weapons can be fired through portholes in the armored glass. An automatic gun carriage can be fitted to the roof, along with radio signal jamming equipment.
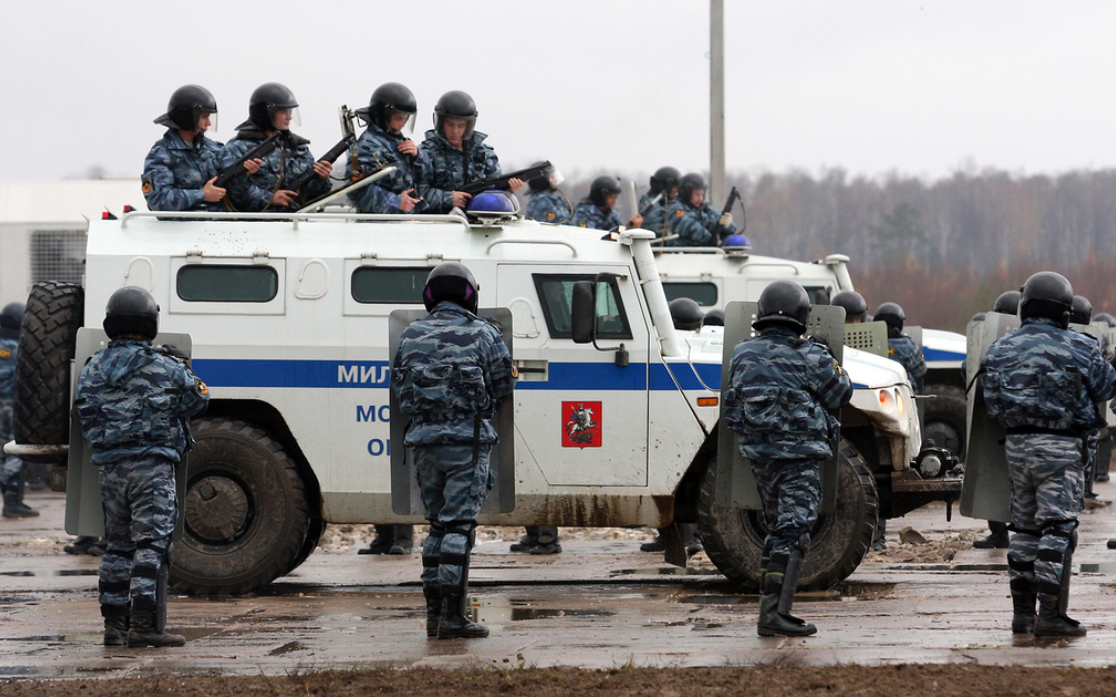

OMON SPM-1 vehicle during antiriot training in Moscow
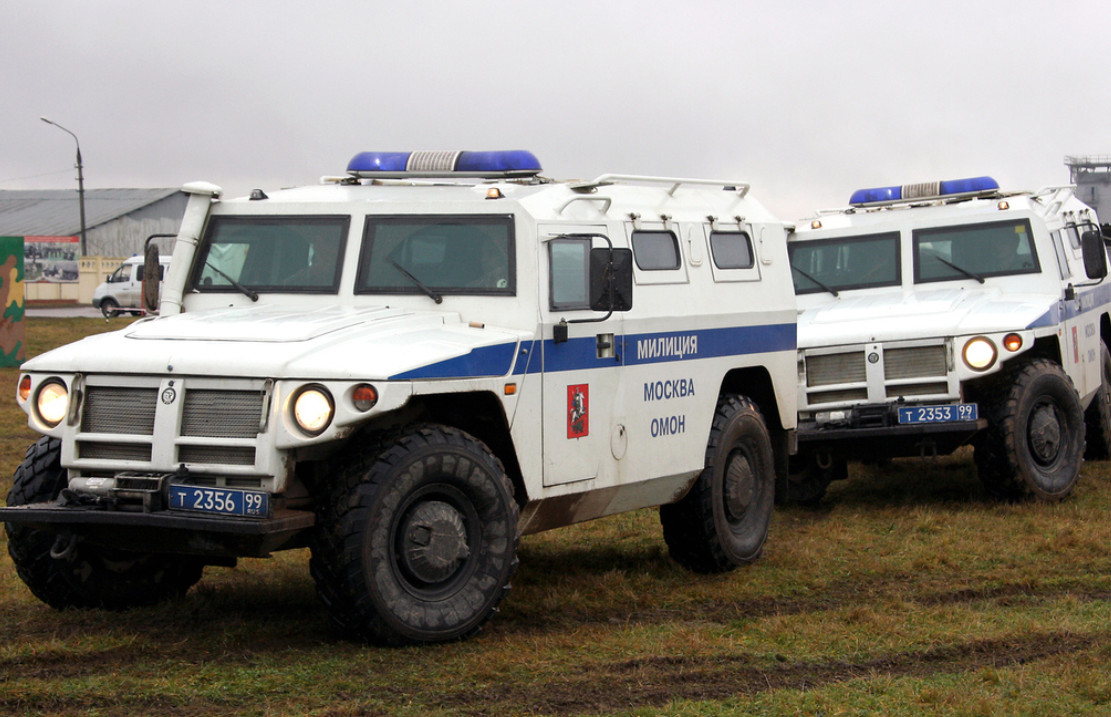

OMON SPM-1 vehicle during antiriot training in Moscow
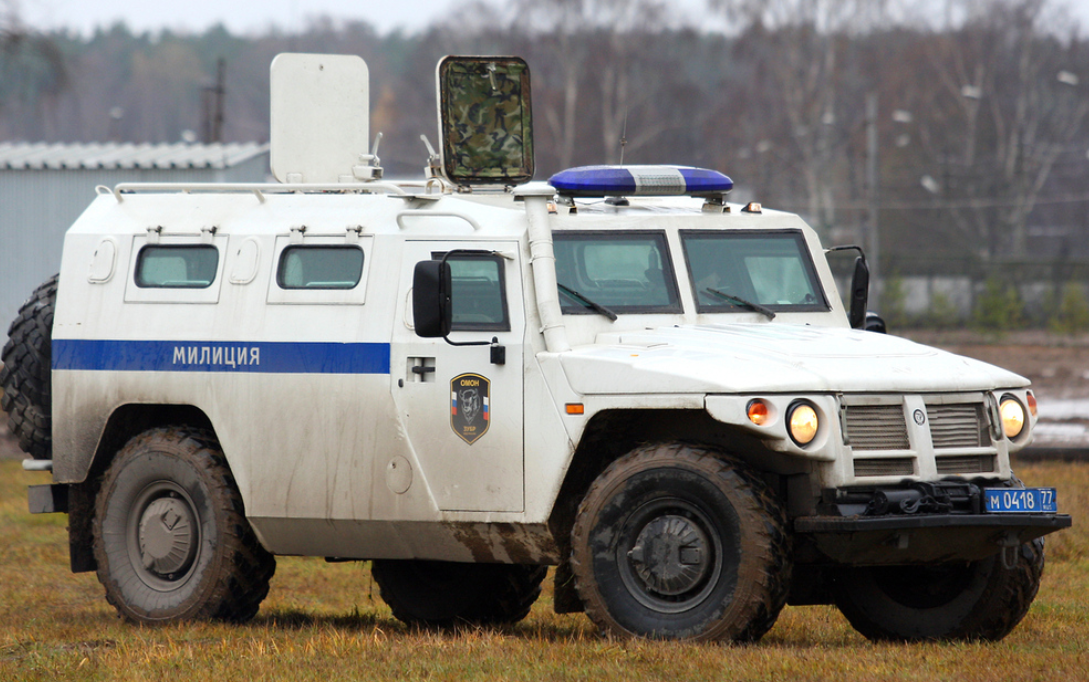

SPM-1 AAV
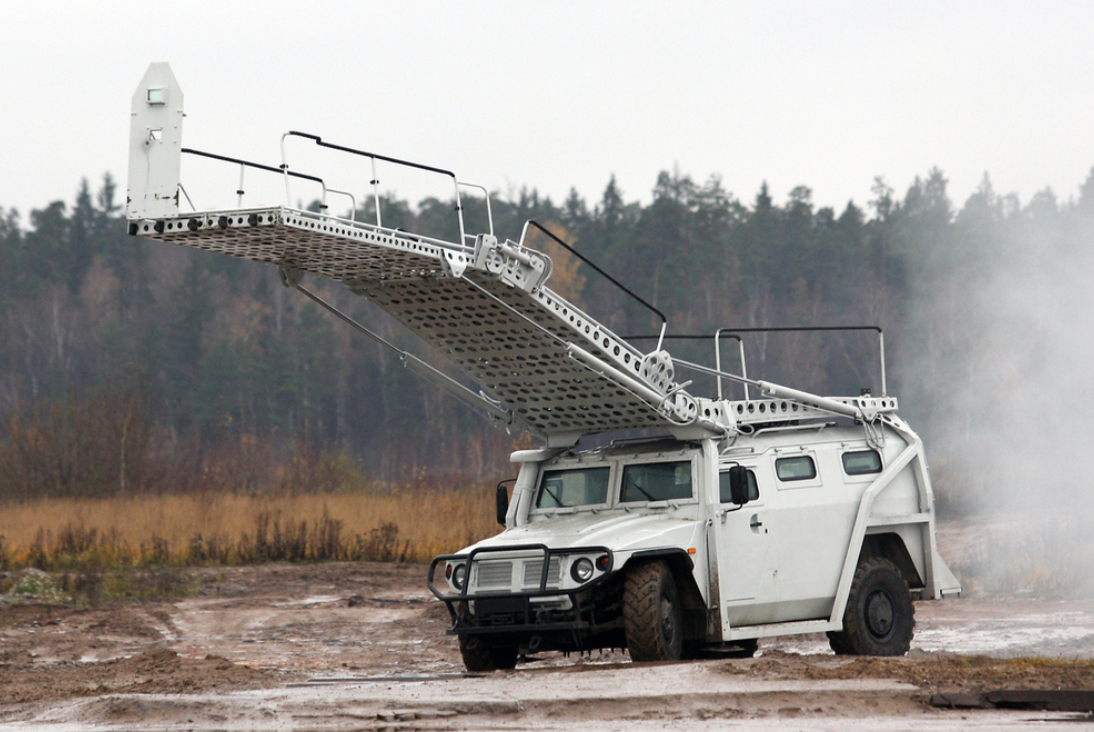

The SPM-1 Aircraft Assault Vehicle is an SPM-1 fitted with a large remote-control hydraulic ladder system. It is designed to provide access to the second or third floors of buildings and aircraft.
SPM-2 "Tigr-Alpha-BB"
Специальная полицейская машина СПМ-2 (Special Police Vehicle SPM-2) ГАЗ-233036 Tigr-Alfa-BB (Tiger-Alpha-VV) is an SPM-1 with GOST 50963-965 level 5 ballistic protection all around (instead of a mixture of level 3 and 5). Two additional glass hatches on the roof allow for the firing of personal weapons.
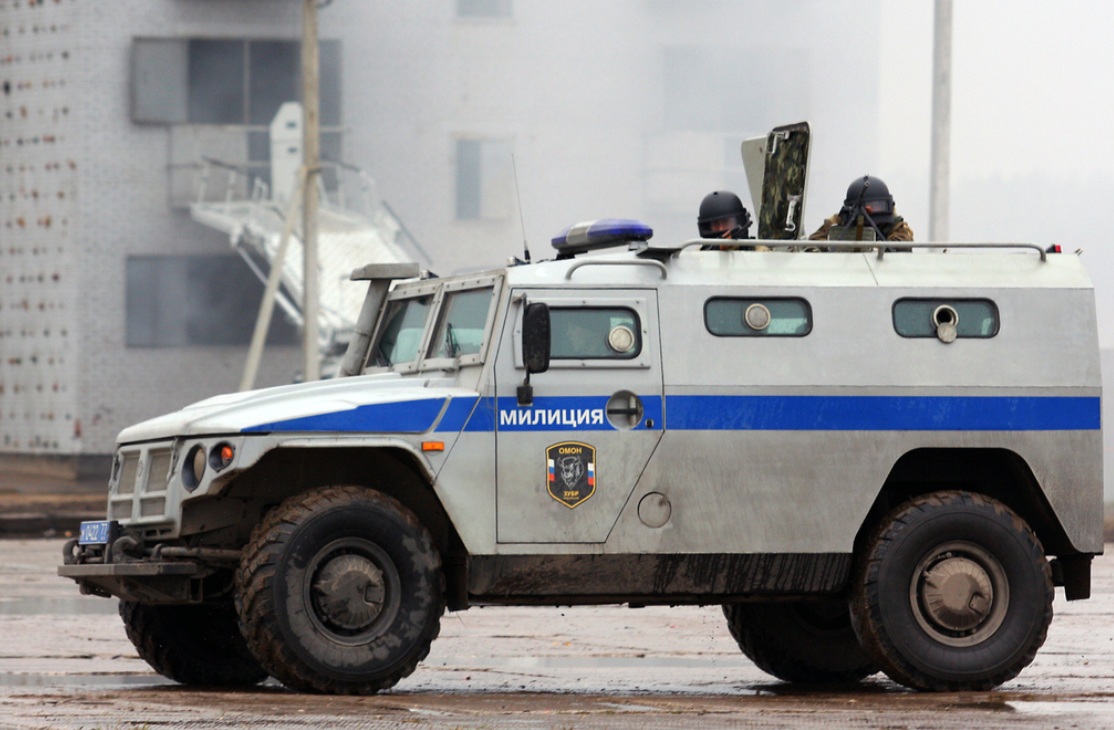

OMON Zubr SPM-2 vehicle
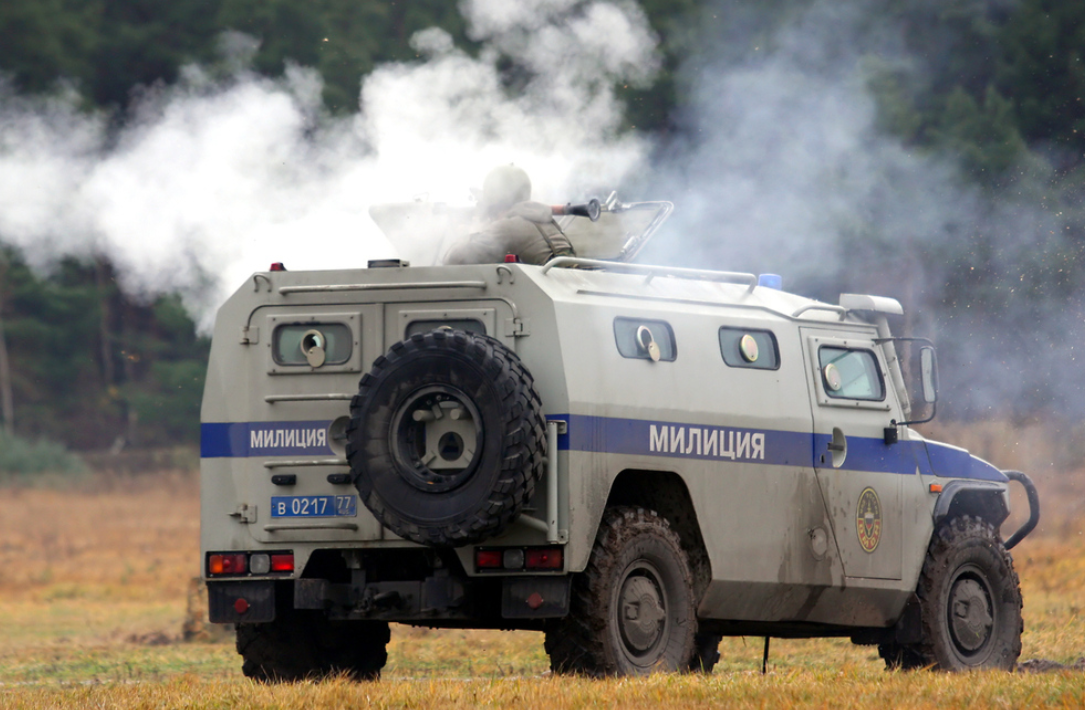

OMON Zubr SPM-2 vehicle
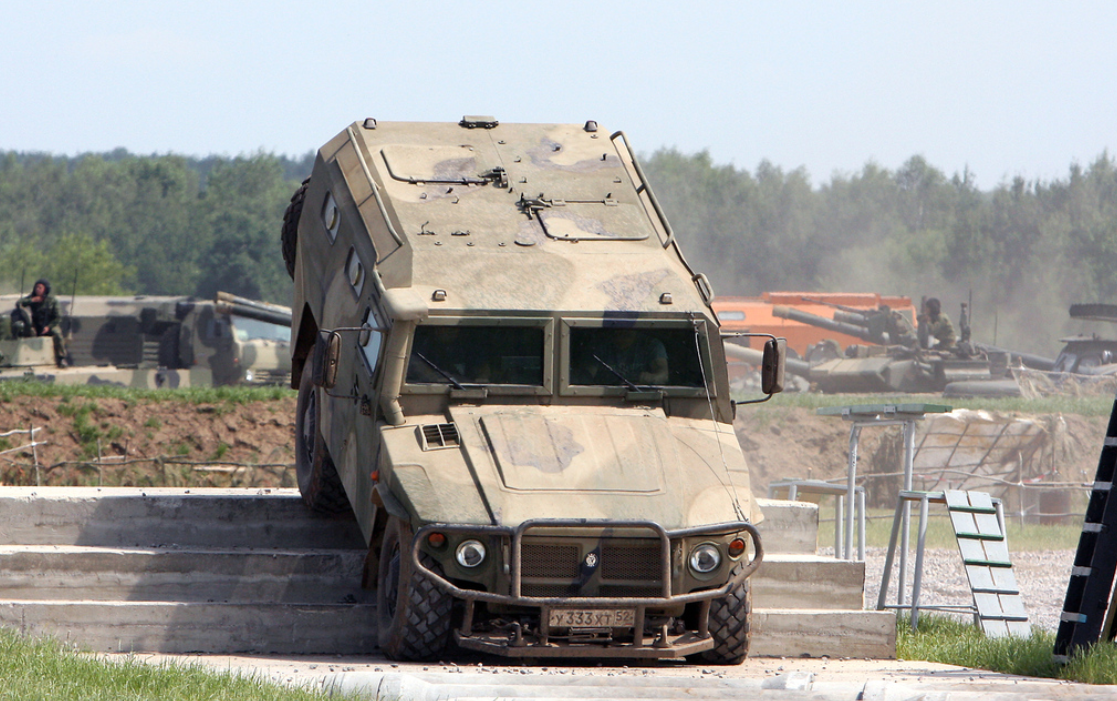

SPM-2 demonstrator at IDELF in 2010
R-145BMA
This variant is designed as a command center for special events and crises. It is a SPM-2 fitted with extensive communications equipment.
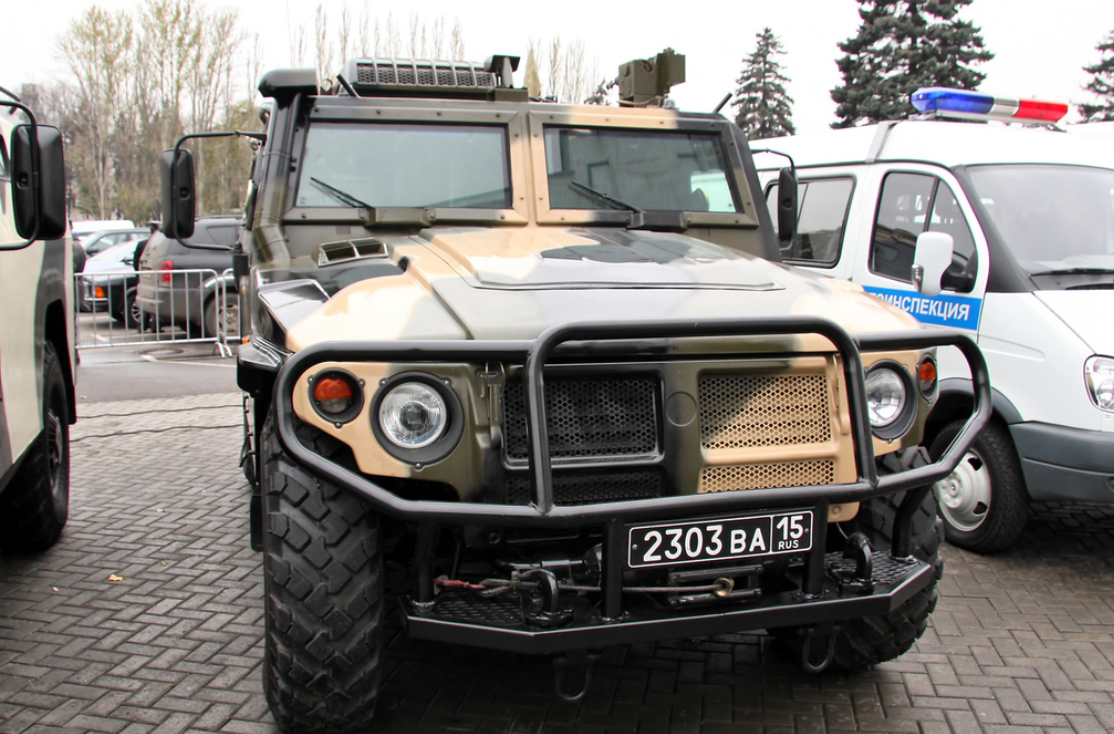

R-145BMA command vehicle
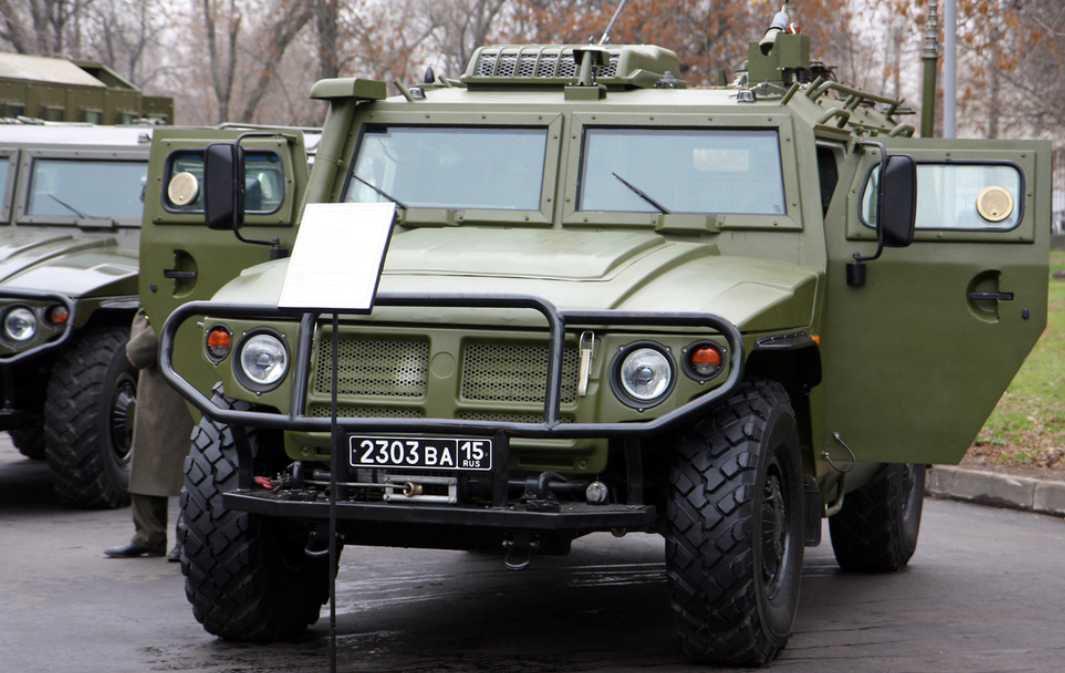
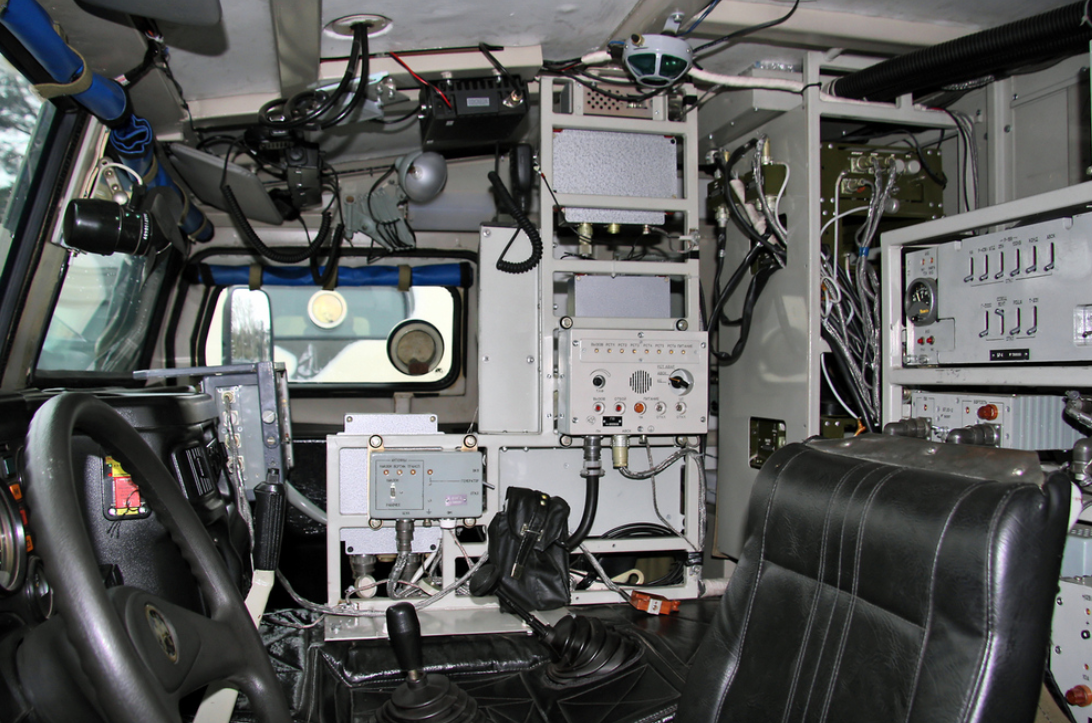


Kornet-D
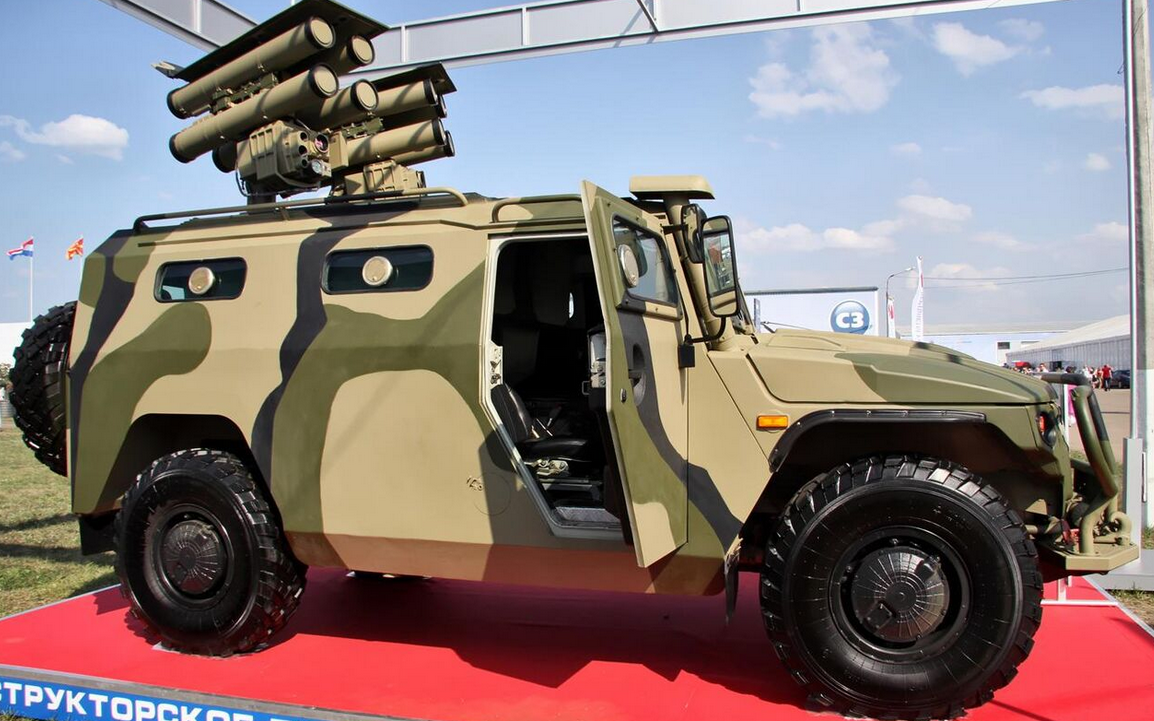

In 2011, the Tula Instrument Design Bureau demonstrated an upgraded Kornet-EM antitank missile system. Two such units were mounted on a modified chassis of the SPM-2 Tigr. The machine is equipped with two retractable launchers for 8 missiles and gunnery equipment (remote weapons control with screens to display images from the sighting systems), as well as 8 additional missiles. This antitank system tested at Kapustin-Yar. The missile complex when mounted on a Tigr is known as the Kornet-D, and it is meant to replace the 9P148 missile carrier. Deliveries started in 2015.[25]
"Project 420"
In early 2010, an improved Tigr armored vehicle with a 420-horsepower 5.9 litres (360.0 cu in) Cummins ISB and a Chrysler 545RFE automatic transmission was created. This engine/transmission combination was originally designed for a Dodge Ram pickup. Externally, the vehicle featured an additional air intake on the bonnet and enlarged brakes. Acceleration time to 100 km/h (62 mph) was reduced from 35 to 23 seconds compared to the standard version, and the top speed increased from 140 km/h (87 mph) to 160 km/h (99 mph).
Tigr-M
During the 2010 Interpolitex exhibition, the Multi-purpose Armored Vehicle (Ru:автомобиля многоцелевого назначения (АМН)) AMS 233 114 Tigr-M was presented by the Military Industrial Company. It featured a new YaMZ-534 diesel engine,[26] a new armored hood, air filter installation, an increase in the number of rear passenger seats (from 8 to 9) and the replacement of the bicuspid rear hatch with a large square hatch.
Currently, the Tigr-M is mass-produced and supplied to the Russian Army, including with the new Arbalet-DM remote control weapons station which is composed of 12.7mm Kord or 7.62mm PKTM machine guns.[27][28]
The upgraded Tigr 4x4 armoured vehicle with increased protection displayed at the Army 2018 defence show in Kubinka, near Moscow, on 21–26 August. The upgrade is based on combat experience gained during operations in Syria and designated the ASN 233115 Tigr-M SpN.[29]
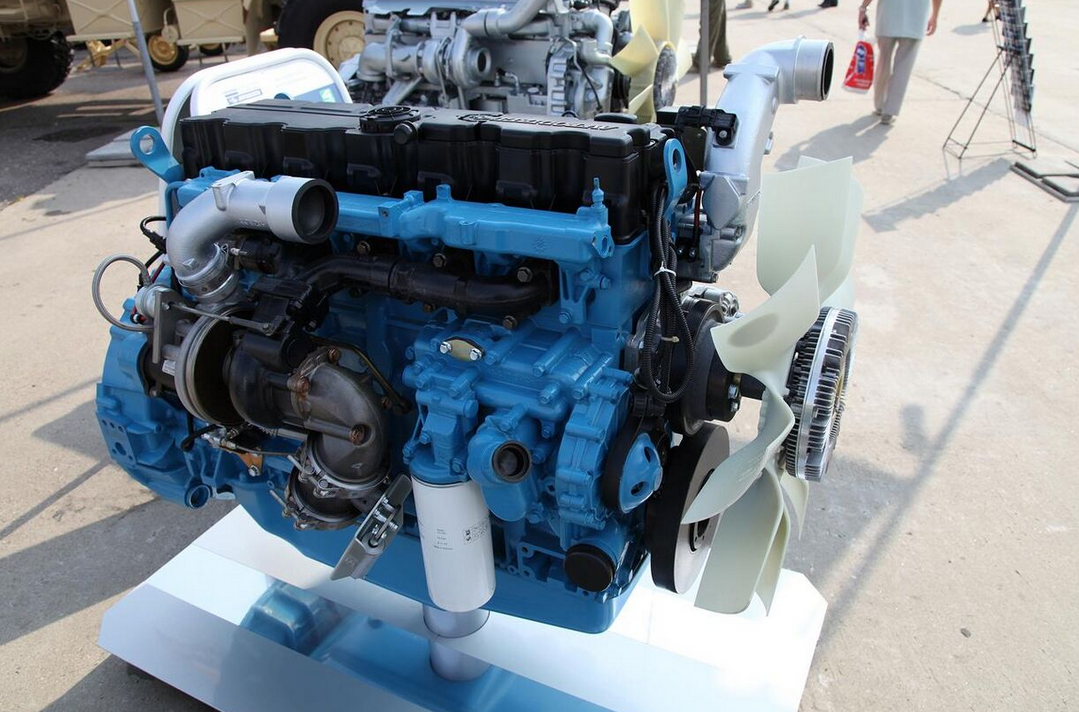

YaMZ-5347-10 diesel of the Tiger-M
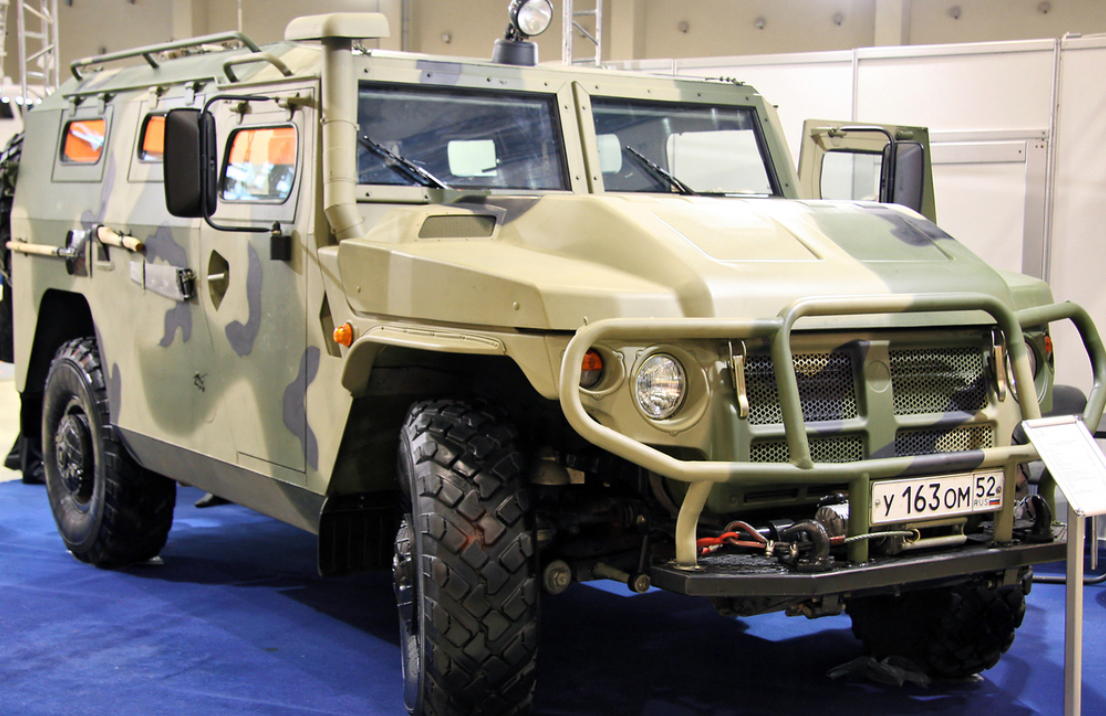

VPK-233114 Tiger-M
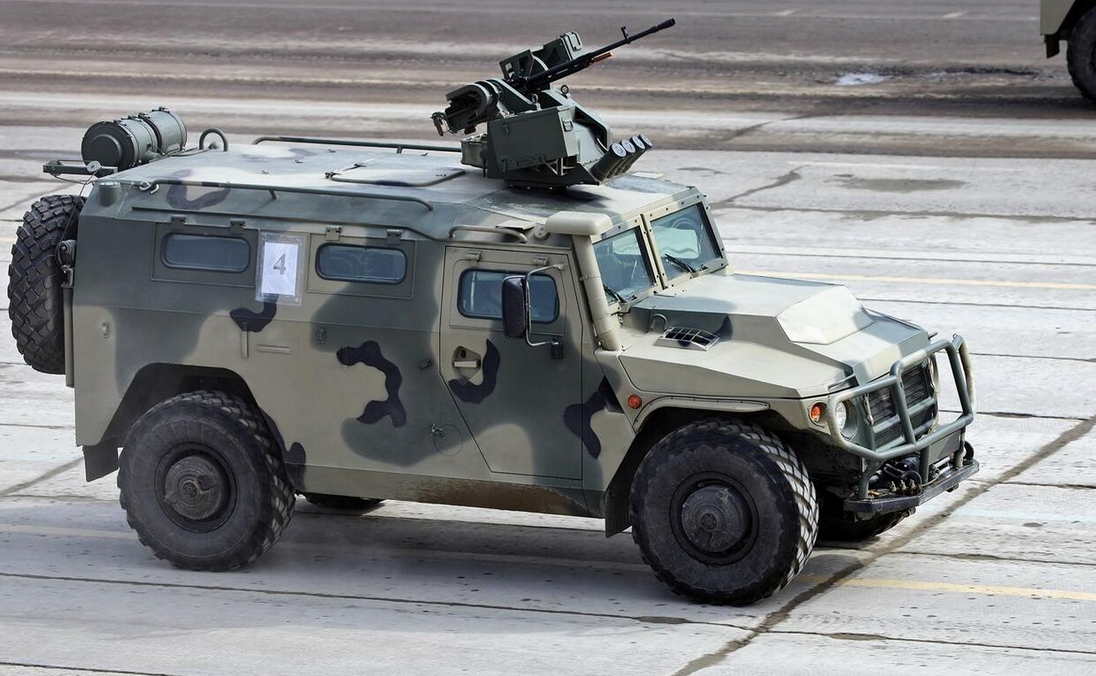

AMN 233114 Tigr-M with remote controlled turret Arbalet-DM
Tigr-6A SPV
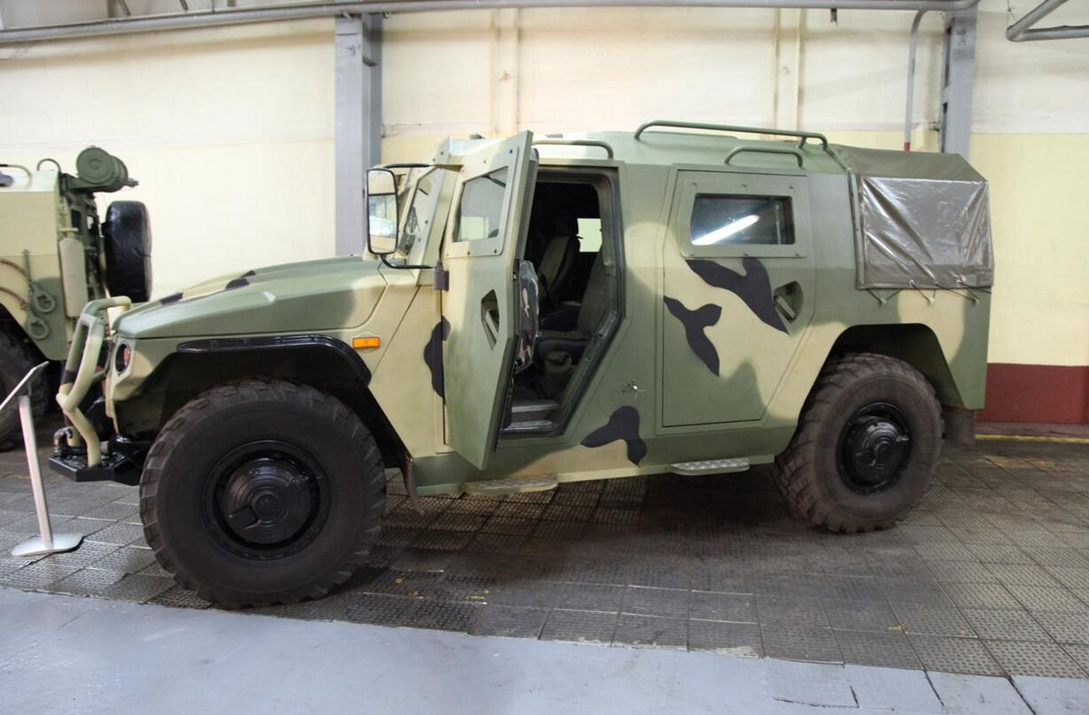

The CTC GAZ-233014 "Tiger" SPV prototype vehicle was first shown at the Bronnitsi Armoured Vehicles Show on June 10, 2011. Based on the SPM-2, the SPV is designed for combat officer transport. It has a four-door station wagon body with increased GOST 6A armor protection (heavy mine protection and special shock-absorbing seats/footrests which are not attached to the floor). As of November 2012, tests are being conducted. The roof of the car has a large rotating hatch with folding a folding lid and two brackets for mounting weapons. Firing from the personal weapons of the crew and the assault group carried out through open armored glass in the doors and on the sides of the vehicle. There are places for stowage of ammunition, rocket-propelled grenade launchers such as the RPG-26, a radio station and a radio-controlled explosive devices blocker.
Characteristics:
- Length, mm - 5700
- Width, mm - 2300
- Height, mm - 2200
- Wheelbase, mm - 3300
- Ground clearance, mm - 400
- Drive formula - 4 × 4
- Load capacity, kg - 1200
- Capacity, people. - 6
- Tires dimension - 335/80 R20
- Curb weight, kg - 5300
- Maximum speed, km / h - no more than 125
- Angle of climbing ability, deg. - thirty
- Acceptable roll when driving on the slope, deg. - 20
- Fording depth, m - 1.2
- Overhang angle front / rear, deg. - 52/52
- Minimum turning radius, m - 8.9
- Transmission - 5-speed manual
Anti-aircraft vehicles
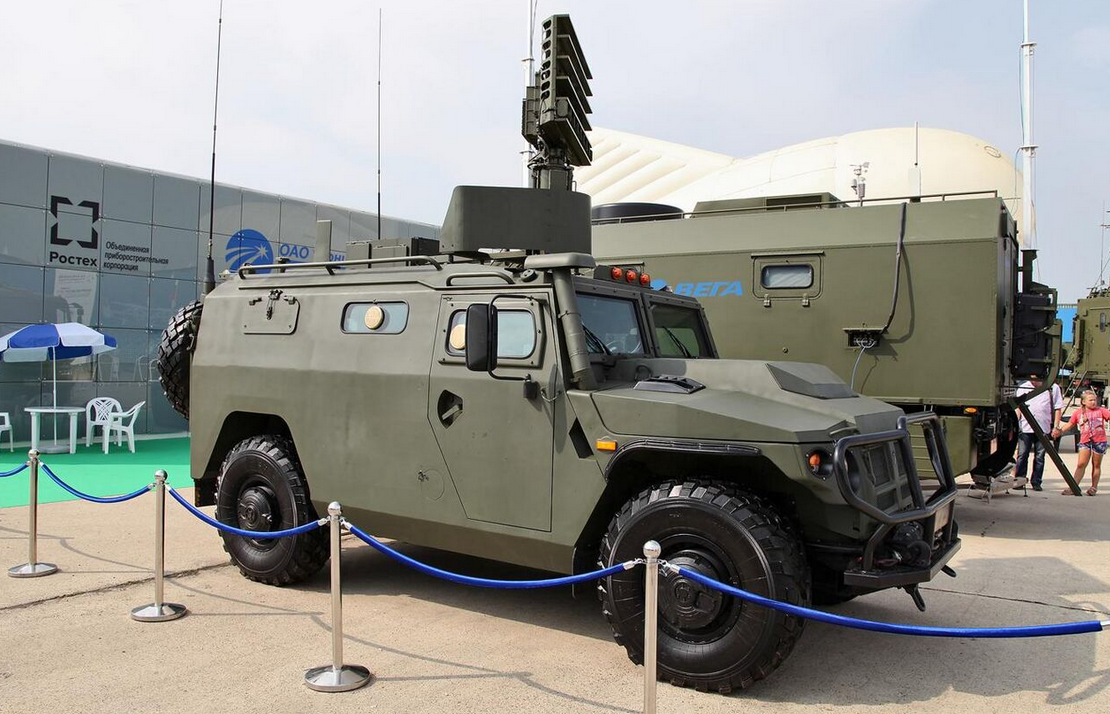

The Tigr chassis has been fitted with the 1L122E radar to allow the vehicle to simultaneously locate 15 aerial targets per second and perform target assessment in one second. Its purpose is to give Russian soldiers armed with MANPADS a command and target indication vehicle to receive more precise target data. The vehicle can deploy within five minutes and operate in temperatures from -50 to 60 degrees Celsius (-58 to 132 degrees Fahrenheit). Development started in mid-2013, with the first prototype delivered in May 2014. The vehicle is currently an independently developed prototype, with talks being held for trials and the follow-up launch of series line production.[30]
The Gibka-S is an anti-aircraft Tigr variant carrying four Igla-S or 9K333 Verba MANPADS tubes on a retractable launching station. By January 2017, the system was being prepared for preliminary trials.[31] State tests were completed in December 2019.[32][33]
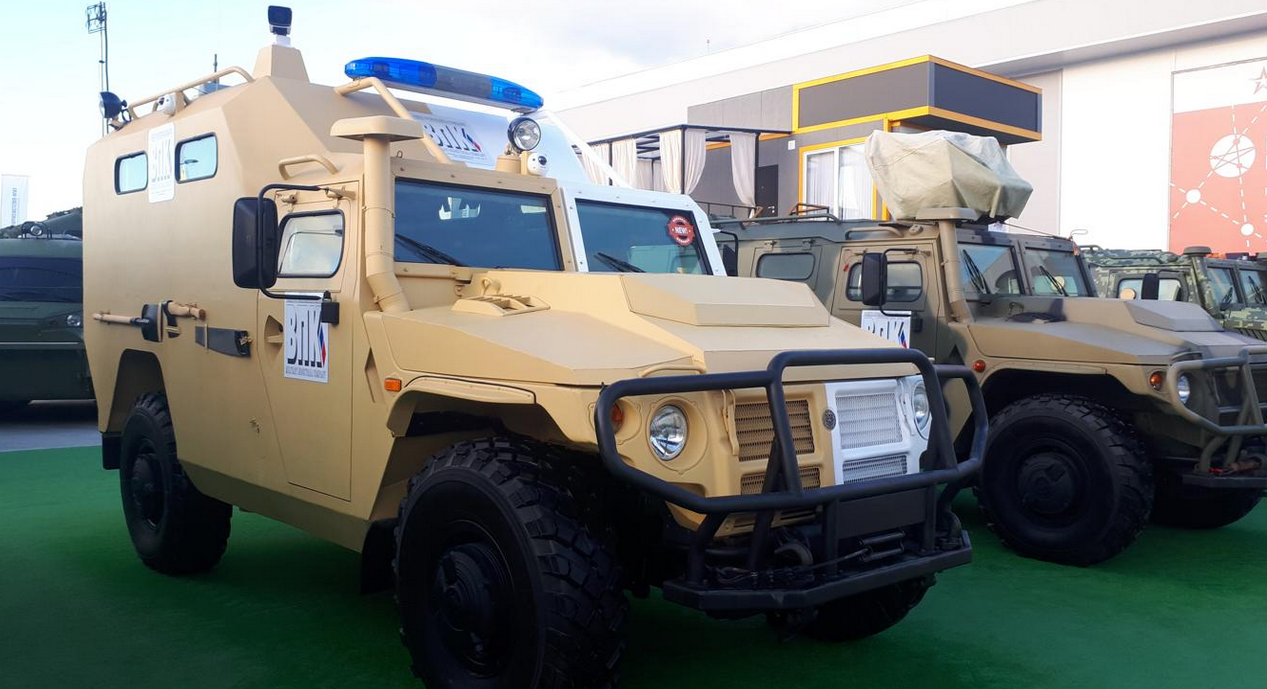
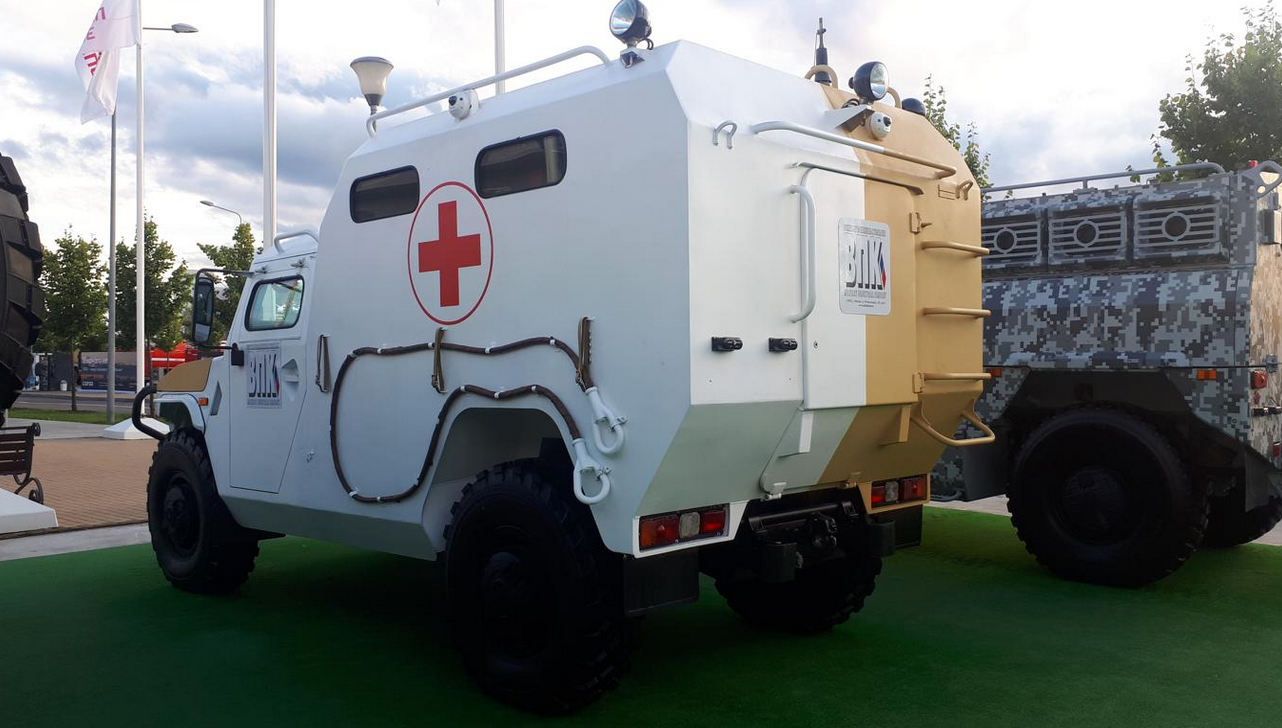
Armored ambulance
BNK has developed an armored ambulance version of the Tigr


3.2. Belarusian Variants
Lis-PM

Lis-PM is a Belarusian-made version of the Tigr produced by the Minsk Wheel Tractor Plant (MZKT Volat).[34] The Lis-PM has a weight of up to 7.5 t and transports eight soldiers. The vehicle is armed with an NSVT Utyos 12.7 mm heavy machinegun (HMG).[34]
They're usually equipped with a NSV HMG and an AGS-17 AGL.
Shershen ATGM
A variant with the twin-barreled Shershen ATGM[35] mounted on top was developed by Belarus .[36]
3.3. Chinese Variants
Yanjing Guardian
- YJ2081C Protected Assault Vehicle - A 4x4 vehicle equipped with a RWS mount on top, two doors at the front and doors at the back.[37]
- YJ2081A Command Car Vehicle - A basic 4x4 vehicle with four doors at the front and doors at the back with a winch mounted.[38]
- YJ2081B Recon Vehicle - A 4x4 vehicle that looks like the YJ2081A model, meant to be used for recon missions.[39]
- YJ2120D Protection Support Vehicle - A 6x6 equipped with a load handling system allowing the loading/unloading of different load platforms and containers. [40]
Yanjing Defender
- YJ2080B Recon Vehicle - A basic 4x4 vehicle used for recon vehicles, appears similarly to the YJ2081A/B Guardian models.[41]
- YJ2080C1 Anti-Riot Vehicle[42]
- YJ2080C Protected Assault Vehicle - A 4x4 vehicle equipped with a RWS mount on top, two doors at the front and doors at the back.[43]
- YJ2080C Missile Launcher Vehicle - A 4x4 vehicle equipped with an 8-rocket launcher module mounted on top.[43]
4. Russian Producers
4.1. BNK
BNK (Military Industrial Company)
- AMS 233 114 "Tigr-M"
4.2. Arzamas
At PJSC AMZ (part of the " Military-Industrial Company ") serially produced following models of "Tigr" vehicle:
- GAZ-233034 - SPM-1 "Tigr" level of ballistic protection Class 3 ;
- GAZ-233036 - SPM-2 "Tigr" level of ballistic protection Class 5 ;
- GAZ-233014 - STS "Tigr" special vehicle, the Army version of the armored vehicle, the level of ballistic protection Class 3 ;
- GAZ-233001 Tigr - all-terrain vehicle with the five-door unarmoured body
5. Tigr-Based Developments
5.1. Russia
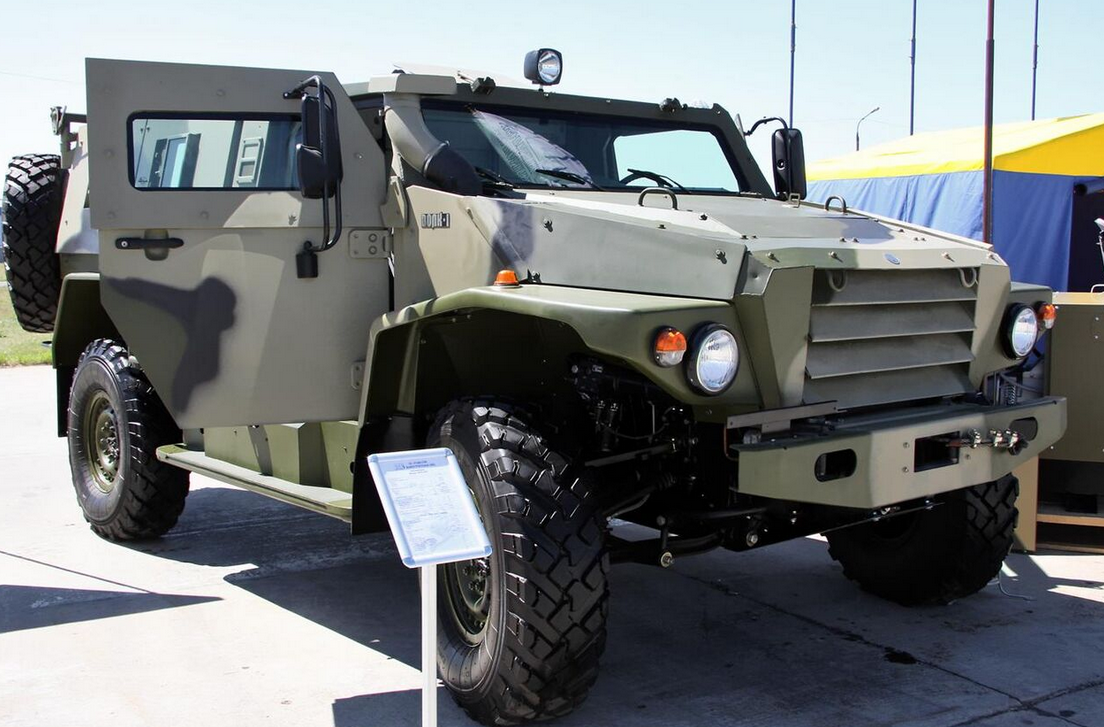

In 2010, an international forum in Zhukovsky publicly presented three prototypes of a modular all-wheel drive family of vehicles, called the MIC-3927 Volk (the Russian word Volk (Волк) translates to Wolf). Like the Tigr, it was developed by the Military Industrial Company of Russia.
Th Volk is available as a 4×4 (MIC-3927) or 6×6 (MIC-39273) and has increased bulletproofing (Class 6A to GOST 50963-96) and mine protection (STANAG Level 2a/2b).
In 2012, orders of the Tigr were cancelled in favour of the Volk; however, orders were resumed.
5.2. United Arab Emirates
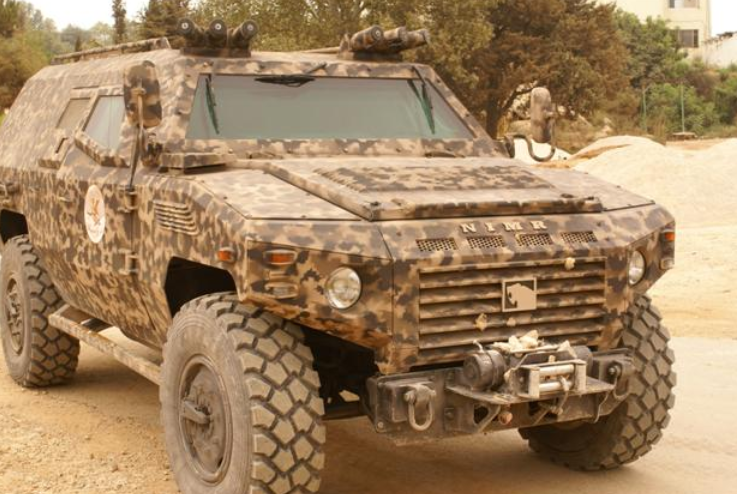

Emirates Defense Technology (EDT) initially started the Nimr (Arabic for tiger) project in the UAE. Engineers from the Industrial Computer Technologies engineering firm (a subsidiary of GAZ) were then subcontracted to complete the detailed engineering and prototyping of the first Nimr 1 prototype. Further developments of the Nimr prototype and the complete development of the first generation Nimr vehicles was carried out in the UAE by the Bin Jabr Group.
The Nimr is a scaled-down Tigr, designed specifically for the harsh desert climates found in the Middle East.
6. Operators
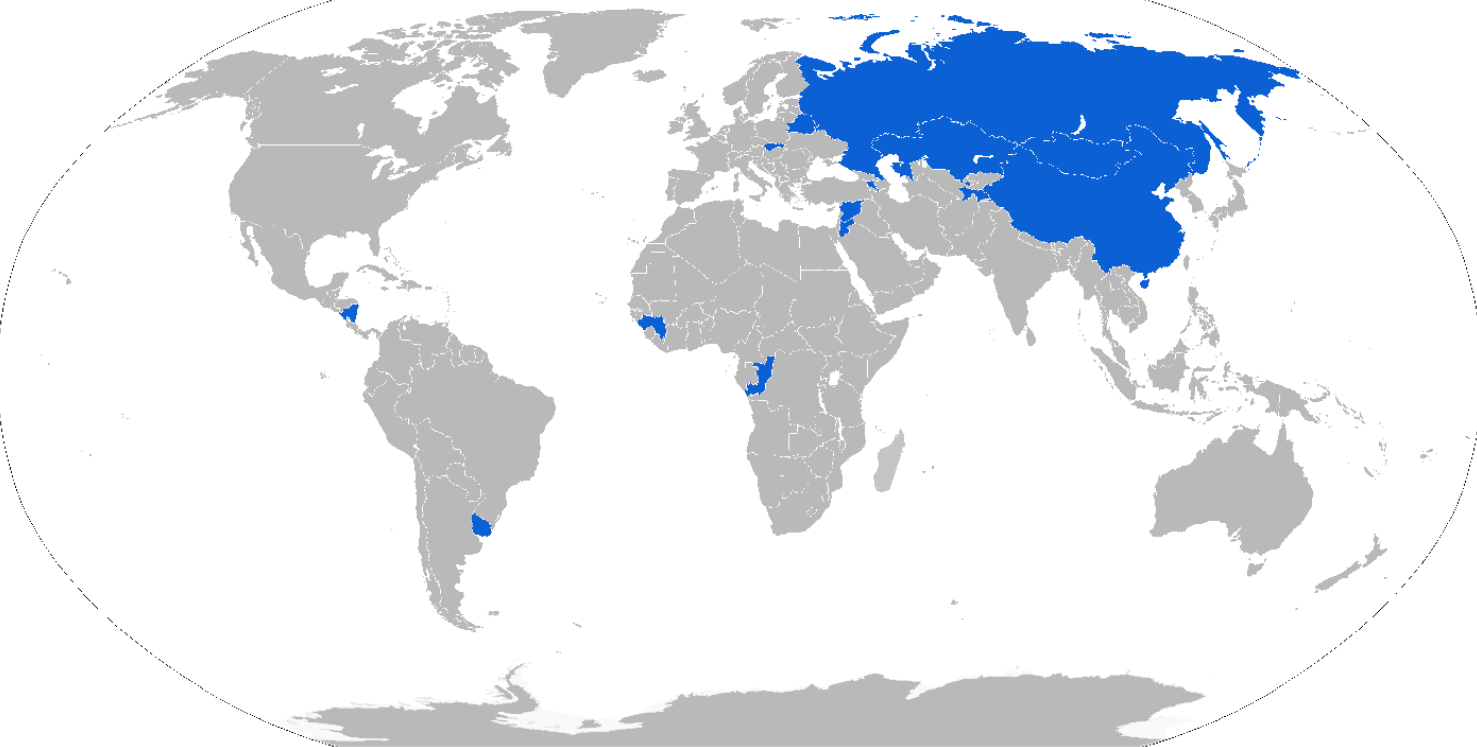
6.1. Current Operators
- Armenia: Used by the Armenian Army.[44]
- Belarus: Known to be used by Belarussian special forces units.[16][36]
- China: In Chinese service, it's known as the YJ2080 Sentinel.[45] 110 YJ2080s delivered from 2008–10, currently in service with Ministry of Public Security.[4]Congo: Tigrs are in use by the Congolese National Police.[46][47]
- Guinea: 3 Tigrs were known to be purchased for the Guinean Presidential Guard in 2011.[4]
- Kazakhstan[48]
- Mongolia: Used by special police units.[49]
- Nicaragua: An agreement was signed in 2012 to supply Tigrs. It is not known how many were produced for Nicaragua.[50]
- Russia: 2,000+. Purchases were discontinued in 2012 in favour of the Wolf, but orders were later resumed.[51][52] 500 vehicles were placed into service by 2011.[4] 20 Tigr-Ms with Arbalet-DM combat module were delivered in 2016.[53] Known service users include the Russian Army and the Russian Naval Infantry. Russian airborne forces were equipped with Tigr-Ms.[54][55] 175 Tigr-Ms were delivered in 2018-19.[56]
- Slovakia[57]
- Tajikistan[36]
- Uruguay: 3 Tigrs were delivered to the Uruguayan Repulican Guard in April 2011 for $600,000.[4] They are equipped with bull bars, air conditioning, window grilles and a video surveillance system.[4] 3 Tigrs were delivered in February 2017 to the National Police of Uruguay.[58] There were 10 Tigr vehicles in use by the URG in late 2017.[59]
- Uzbekistan: Tigr-Ms were delivered to the Uzbekistan National Guard in April 2019.[26]
- Zambia: 35 supplied and used by the Zambian Army.[60][61]
- Yemen: Yemeni Republican Guard.[62][63]
6.2. Future Operators
- Egypt: Egypt announced plans to purchase 50 Tigers for the Interior Ministry in 2017.[64]
6.3. Evaluation-Only Operators
- Brazil: The Military Police of Rio de Janeiro State in September 2010 received a 4x4 armored GAZ-233036 TIGR model for testing until March 2011.[4]
- India: 2 Tigrs ordered for field tests in 2008.[4][65]
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Engineering:GAZ_Tigr
References
- John Pike. "GAZ 2975 Tigr". http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/russia/gaz-2975.htm.
- "Tigr GAZ-2330 light armoured vehicle personnel carrier". Army Recognition. http://www.armyrecognition.com/russia_russian_army_wheeled_armoured_vehicle_uk/tigr_gaz-2330_military-industrial_company_technical_data_sheet_specifications_information_uk.html.
- "Russia have successfully concluded a deal to supply China with armoured vehicle Tigr - Army Recognition". Armyrecognition.com. 2010-11-05. http://www.armyrecognition.com/november_2010_army_military_defense_industry_news/russia_have_successfully_concluded_a_deal_to_supply_china_with_armoured_vehicle_tigr.html.
- "TIGR (GAZ 2330)" (in fr). http://red-stars.org/spip.php?article253.
- "La Chine sur le point d'acheter des 4x4 russes TIGR pour sécuriser les jeux olympiques" (in fr). http://red-stars.org/spip.php?breve1073.
- "Confirmation de l'achat de 4x4 blindés russes TIGR par la Chine" (in fr). http://red-stars.org/spip.php?breve1093.
- Administrator. "China Yanjing Auto produces locally Russian Tigr 4x4 armored under license called YJ2080 YJ2081 11812163 - Airshow China 2016 online show daily news coverage - Defence security military exhibition 2016 daily news category". http://www.armyrecognition.com/airshow_china_2016_online_show_daily_news_coverage/china_yanjing_auto_produces_locally_russian_tigr_4x4_armored_under_license_called_yj2080_yj2081_11812163.html.
- "The new Tigr-M GAZ-233114 multipurpose 4x4 armoured will enter in service with Russian army 1002134 - Army Recognition". http://www.armyrecognition.com/february_2013_army_military_defense_industry_news/the_new_tigr-m_gaz-233114_multipurpose_4x4_armoured_will_enter_in_service_with_russian_army_1002134.html.
- "Псковский спецназ получил бронеавтомобили "Тигр" - Еженедельник "Военно-промышленный курьер"". http://vpk-news.ru/news/33542.
- Mackey, Robert (5 March 2014). "Russia's Defense Minister Calls Evidence of Troop Presence in Crimea 'Complete Nonsense'". https://thelede.blogs.nytimes.com/2014/03/05/russias-defense-minister-calls-evidence-of-troop-presence-in-crimea-complete-nonsense/.
- "Latest from OSCE Special Monitoring Mission (SMM) to Ukraine based on information received as of 18:00 (Kyiv time), 3 March 2015" OSCE 4. March 2015 http://www.osce.org/ukraine-smm/143801
- ""Рособоронэкспорт" предложил Азербайджану бронемашины "Тигр"". http://lenta.ru/news/2011/02/24/tiger/.
- ""Рособоронэкспорт" предложил Азербайджану бронемашины "Тигр"". http://army.lv/ru/tigr/356/28697.
- "В Сирии "Тигры" могут вывести из строя БМП - Еженедельник "Военно-промышленный курьер"". http://vpk-news.ru/news/33602.
- https://web.archive.org/web/20160603002452/http://vsr.mil.by/2015/04/30/goskomvoenprom-k-paradu-gotovy/
- "Janes | Latest defence and security news". https://www.janes.com/article/81569/belarus-expands-armoured-vehicle-fleet.
- https://web.archive.org/web/20150508044101/http://www.military-informant.com/army/8949-vpervye-byl-pokazan-novejshij-broneavtomobil-lis-pm-belorusskoj-armii.html
- "燕京汽车 官方网站". http://www.yanjingauto.com/NewsView.aspx?ClassID=1&ID=28.
- Tigr-M armored car with remote-controlled Arbalet-DM module enters Russian Army inventory - Armyrecognition.com, 7 March 2017 https://www.armyrecognition.com/march_2017_global_defense_security_news_industry/tigr-m_armored_car_with_remote-controlled_arbalet-dm_module_enters_russian_army_inventory_80703173.html
- "ЦАМТО / Новости / Российские бронеавтомобили «Тигр» состоят на вооружении 16 стран". http://www.armstrade.org/includes/periodics/news/2019/0426/114052149/detail.shtml.
- "Defense firm delivers over 2,000 Tigr armored vehicles to Russian, foreign customers". https://tass.com/defense/1160073.
- http://русская-сила.рф/guide/army/tr/gaz2975.shtml Russian
- "ГАЗ "Тигр" будет производиться серийно RosInvest.Com - Венчур, управление, инвестиции". http://rosinvest.com/novosti/105430.
- Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation
- "Russian armed forces to receive Kornet-M and 9K115 Metis-M1 anti-tank-guided missiles TASS 12605161 | weapons defence industry military technology UK | analysis focus army defence military industry army". https://www.armyrecognition.com/weapons_defence_industry_military_technology_uk/russian_armed_forces_to_receive_kornet-m_and_9k115_metis-m1_anti-tank-guided_missiles_tass_12605161.html.
- "Archived copy". https://armyrecognition.com/april_2019_global_defense_security_army_news_industry/national_guard_of_uzbekistan_has_received_vpk-233136_4x4_armored_vehicles.html.
- "Спецназ ЦВО получил бронеавтомобили "Тигр-М СпН" - Еженедельник "Военно-промышленный курьер"". http://vpk-news.ru/news/22311.
- "ВС РФ получили первые броневики "Тигр-М" с модулем "Арбалет-ДМ" - Еженедельник "Военно-промышленный курьер"". http://vpk-news.ru/news/30298.
- "Army 2018: VPK displays upgraded Tigr-M vehicle - Jane's 360". https://www.janes.com/article/82521/army-2018-vpk-displays-upgraded-tigr-m-vehicle.
- Russia unveils Tigr 4x4 armoured vehicle fitted with 1L122 radar at Defense Exhibition Oboronexpo - Armyrecognition.com, 15 August 2014 http://www.armyrecognition.com/august_2014_global_defense_security_news_uk/russia_unveils_tigr_4x4_armoured_vehicle_fitted_with_1l122_radar_at_defense_exhibition_oboronexpo_15.html
- New Russian Gibka-S air defense missile system ready for preliminary trials - Armyrecognition.com, 24 January 2017 http://armyrecognition.com/weapons_defence_industry_military_technology_uk/new_russian_gibka-s_air_defense_system_ready_for_preliminary_trials_12401175.html
- https://www.janes.com/article/93479/russian-gibka-s-vshorad-system-completes-state-trials
- https://www.armyrecognition.com/january_2020_global_defense_security_army_news_industry/russia_completes_acceptance_trials_of_gibka-s_air_defense_missile.html
- Frahan, Alain Henry de. "Belarus parades new armored vehicles on Independence Day military parade 2018 - July 2018 Global Defense Security army news industry - Defense Security global news industry army 2018 - Archive News year". https://www.armyrecognition.com/july_2018_global_defense_security_army_news_industry/belarus_parades_new_armored_vehicles_on_independence_day_military_parade_2018.html.
- "Archived copy". http://www.military-today.com/missiles/shershen.htm.
- "Armored Cars: MIC GAZ Tigr". 29 September 2016. https://21stcenturyasianarmsrace.com/2016/09/29/armored-cars-mic-gaz-tigr/#more-211825.
- "燕京汽车 官方网站". http://www.yanjingauto.com/CarInfo.aspx?ClassID=1&ID=7.
- "燕京汽车 官方网站". http://www.yanjingauto.com/CarInfo.aspx?ClassID=1&ID=1.
- "燕京汽车 官方网站". http://www.yanjingauto.com/CarInfo.aspx?ClassID=1&ID=4.
- "燕京汽车 官方网站". http://www.yanjingauto.com/CarInfo.aspx?ClassID=1&ID=6.
- "燕京汽车 官方网站". http://www.yanjingauto.com/CarInfo.aspx?ClassID=2&ID=3.
- "燕京汽车 官方网站". http://www.yanjingauto.com/CarInfo.aspx?ClassID=2&ID=2.
- "燕京汽车 官方网站". http://www.yanjingauto.com/CarInfo.aspx?ClassID=2&ID=8.
- https://web.archive.org/web/20170728201220/http://www.panarmenian.net/arm/news/80873/
- Antoine. "Beijing Yanjing Motor Company to produce Russian GAZ Tigr Multirole Utility Vehicles under license 50607164 - July 2016 Global Defense Security news industry - Defense Security global news industry army 2016 - Archive News year". http://www.armyrecognition.com/july_2016_global_defense_security_news_industry/beijing_yanjing_motor_company_to_produce_russian_gaz_tigr_multirole_utility_vehicles_under_license_50607164.html.
- "DomRaider". http://defense-blog.fr/le-vehicule-gaz-tigre-spm-2-a-ete-repere-en-republique-du-congo/.
- https://www.defenceweb.co.za/land/land-land/congo-buys-tigr-armoured-vehicles/
- "Казахстан купил российские бронеавтомобили Тигр". 9 September 2010. http://military-informant.com/army/kazahstantigr-sp-1517565667.html.
- orientalist_v (19 January 2016). "Монгольский полицейский SWAT. Немного редких фото.". https://orientalist-v.livejournal.com/932685.html.
- "Russia to supply armored vehicles to Nicaragua". http://english.ruvr.ru/2012_10_04/Russia-to-supply-armored-vehicles-to-Nicaragua/.
- Administrator. "ВПК с 2014 года намерена поставлять в войска бронеавтомобили "Волк" вместо "Тигр" - Военный Обозреватель". http://warsonline.info/bronetechnika/vpk-s-2014-g-namerena-postavlyat-broneavtomobili-volk.html.
- "Два "Тигра" для спецназа ВВО - Еженедельник "Военно-промышленный курьер"". http://vpk-news.ru/news/22094.
- "Archived copy". https://www.armyrecognition.com/january_2017_global_defense_security_army_news_industry/russian_armed_forces_received_two_brigades_of_buk-m3_and_buk-m2_air_defense_systems_in_2016_10901172.html.
- ngain. "Russian airborne commandos to get first batch of Tigr-M armored vehicles by year end - November 2017 Global Defense Security news industry - Defense Security global news industry army 2017 - Archive News year". https://www.armyrecognition.com/november_2017_global_defense_security_news_industry/russian_airborne_commandos_to_get_first_batch_of_tigr-m_armored_vehicles_by_year_end.html.
- "First state supply contract for Tigr armored vehicle fulfilled in Airborne Troops : Ministry of Defence of the Russian Federation". http://eng.mil.ru/en/news_page/country/more.htm?id=12175961@egNews.
- "Archived copy". https://www.armyrecognition.com/analysis_focus_army_defence_military_industry_army/russian_mod_holds_defense_hardware_delivery_day_2019.html.
- "Russia sends batch of Tigr armored vehicles to Slovakia More: http://tass.com/defense/896049". 26 August 2016. http://tass.com/defense/896049.
- Infodefensa.com (22 February 2017). "La Policía de Uruguay recibe tres nuevos vehículos blindados rusos Tigr - Noticias Infodefensa América". http://www.infodefensa.com/latam/2017/02/22/noticia-policia-uruguaya-recibe-vehiculos-blindados-rusos.html.
- "ЦАМТО / Новости / Россия поставила Уругваю партию обновленных "Тигров"". http://armstrade.org/includes/periodics/news/2017/0220/105039650/detail.shtml.
- https://www.janes.com/defence-news/news-detail/zambian-military-parades-new-equipment
- https://armstrade.org/includes/periodics/news/2021/0823/080064115/detail.shtml
- https://www.janes.com/defence-news/news-detail/zambian-military-parades-new-equipment
- https://armstrade.org/includes/periodics/news/2021/0823/080064115/detail.shtml
- https://www.middleeastmonitor.com/20170824-egypt-looks-to-buy-50-advanced-armoured-vehicles-from-russia/
- "L'Inde commande deux 4x4 blindés russes TIGR pour essais" (in fr). http://red-stars.org/spip.php?breve964.
