The Schlüsselgerät 39 (SG-39) was an electrically operated rotor cipher machine, invented by the German Fritz Menzer during World War II. The device was the evolution of the Enigma rotors coupled with three Hagelin pin wheels to provide variable stepping of the rotors. All three wheels stepped once with each encipherment. Rotors stepped according to normal Enigma rules, except that an active pin at the reading station for a pin wheel prevented the coupled rotor from stepping. The cycle for a normal Enigma was 17,576 characters. When the Schlüsselgerät 39 was correctly configured, its cycle length was [math]\displaystyle{ 2.7 x 10^8 }[/math] characters, which was more than 15,000 times longer than a standard Enigma. The Schlüsselgerät 39 was fully automatic, in that when a key was pressed, the plain and cipher letters were printed on separate paper tapes, divided into five-digit groups. The Schlüsselgerät 39 was abandoned by German forces in favour of the Schlüsselgerät 41.
- schlüsselgerät
- cycle length
- sg-39
1. Technical Description

Note: Otto Buggisch gave the technical description of the cipher unit as part of TICOM homework.
Gerät 39 is an electrically operated cipher machine. The cipher technique is derived from the Enigma cipher machine.[1] A direct current passes through 3 or 4 wheels, with 26 positions, I, II, II, a reflector wheel U, and the again through the 3 wheels in reverse order, III II and I. Unlike the Enigma, the wheels here do not control their own movement: this is done through 3 independent pin-wheels N1 N2 and N3 with periods 21,23 and 25. The figures were distributed among N1 N2 and N2 in possibly two different configurations.
| N1 | N2 | N3 | Or | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | 23 | 25 | 25 | 23 | 21 |
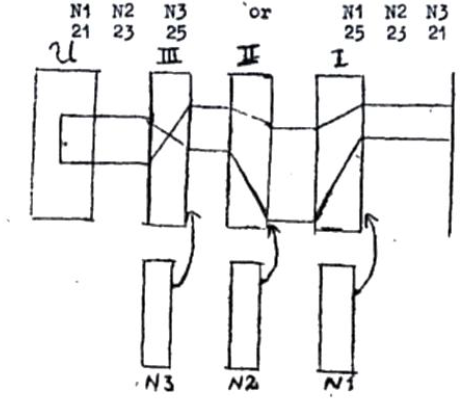
The pin wheels have a uniform motion, i.e. they move one position for every letter keyed. As for the movement of the key wheels and other details, the machine passed through different stages of development in the course of time, for which there were no specific names and which will be denoted here by a,b,c and d.
- Each of three wheels moves on one place when there is an active pin at the sensing point of the relevant pin-wheel, and it only moves then. The wheels have no moveable rings on the body of the wheel, with the result that, unlike the Enigma, the initial position of the body of the wheel is determine absolutely, at the same time as the clear message setting. The reflector wheel is pluggable like the reflector wheel D on the Enigma; it can be quickly exchanged for the second reflector wheel with prepared reflector plugging.[2]
- Wheels I, I and III, whose wiring now correspond exactly to those of the Enigma, have adjustable rings; they can be moved around the body of the wheels and have a fixed pin, which, by analogy with the Enigma, is to be called the turn-over notch, although mechanically it is not so made. Opposite the wheels I and II are two sensing points which pick up the turn-over notch as it passes. U is pluggable as in a). In addition there is between the point of input and I, a stecker S like the Enigma stecker. The following two methods of working are possible:[2]
- Working on own wiring: N1 N2 and N3 are given a certain pin arrangements, there being, it is true, certain limitations to the number of activing pins. Wheel I moves as under a) above. For wheel II there are the following 3 causes of movement:[2]
- An active pin at the sensing point of N2 causes II to move on one place as in a) above
- When the turn-over notch on the ring of I comes to the sensing point, II is caused to move on when the next letter is keyed (as with Enigma).
- When the turn-over notch comes to the sensing point of II, II turns on one place when the next letter is keyed (at the same time as III, as with the double step on Enigma)[3]
- An active pin at the sensing-point of N3 causes III to move to one place, as in the first a) above,
- When the turn-over notch on the ring of II comes to the sensing point, III moves on one place when the next letter is keyed.[3]
- Working on Enigma wiring. All the pins of N1 are set at active, the pins of N2 and N3 all remaining inactive. Then the movements identical with that of the Enigma. As all other factors also agree with the corresponding ones on the Enigma interchangeable working between both machines is possible.[3]
- Working on own wiring: N1 N2 and N3 are given a certain pin arrangements, there being, it is true, certain limitations to the number of activing pins. Wheel I moves as under a) above. For wheel II there are the following 3 causes of movement:[2]
- A sensing-point is also provided opposite wheel III. If the turn-over notch on the ring of III is touched by it, then I turns on one place when the next letter is keyed. If this movement coincides with the step caused by N1, this again results in the single step. Thus the possibility of interchangeable working with the Enigma remains. In addition, the machine now gets a fourth wheel, which is placed between III and U and does not move on when a key is touched. It corresponds to the fourth wheel on the Naval Enigma and is used for interchangeable working with this machine.[3]
- In the summer of 1944, Karl Stein of OKW/Chi told Buggisch that the reciprocal influencing of the wheels was to be altered in some way. Buggisch could not remember the details but nothing fundamental on the principle of the machine described under c) was changed. Interchangeable working with army and naval Enigma remained possible.[3]
1.1. Investigations in Periodicity
In the case of model first a) above, the question of periodicity is elementary, there are 262=276 pure periods of the length
- 21 x 23 x 25 x 26 = 313, 950
as long as the number of active pins on each of the pin wheels is prime to 2 and 13. This last condition should be laid down in the cipher regulations; otherwise the 676 periods would be further broken in a manner easily seen.[4]
Things are much more complicated in the case of Model b). Investigations into this problem in the winter of 1942/1943 were only partly successful; above all it was not possible exactly to calculate the lengths of the pure periods and the pre-periods. Estimates which were quite adequate for practical purposes were however given. Buggisch could not remember the details of these somewhat investigations. The extraordinary length of many pre-periods (lengths of some thousands were not uncommon) and the complication of their branches were remarkable. The general type can be illustrated by the following diagram:[4]
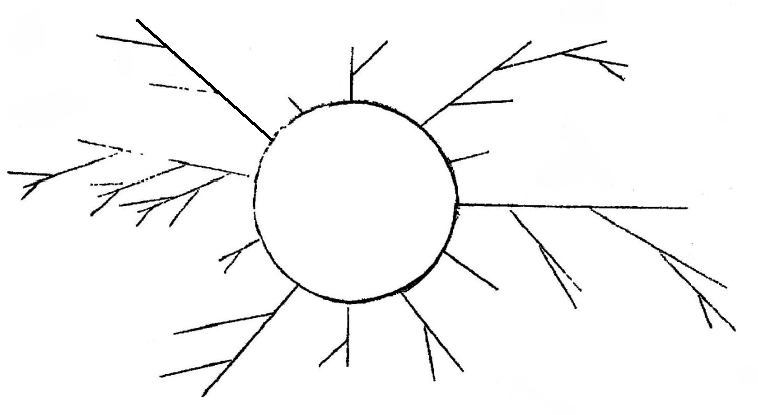
In this circle represents the pure period and the straight lines the pre-periods. There were usually several pure periods, each one of them having a complicated system of pre-periods branching into it. Several separate figures of the above type side by side are then necessary to give a graphic representation of the periodicities. A lower limit for the lengths of the pure periods was, as far as I remember: 252 x 21 x 23 x 25 = 8,162,700.
The questions of periodicities in the case of model c) was still more involved. It was just not possible to calculate the lengths of the pure periods and pre-periods, let alone give the lower limits which are themselves not inconsiderable.[4]
1.2. Cipher Security
The principal weaknesses of the Enigma were as follows:[5]
- Wheel I moved uniformly
- Wheel II and above all, wheel III moved too infrequently.
- The period of 25 x 262 was comparatively small, so that when there was a large amount of traffic on one day, on one key, one had to reckon with the concurrence of critical depths (this applies at least to the Army Enigma; the naval machine had a fourth wheel, so that a days traffic on one key was spread out over 26 periods).
- The reflector wheel was not plugable and had remained unchanged for years (and because of (5), the enemy could easily establish by Hollerith methods for example, all of the 60 x 263 substitution alphabets of the unplugged machines.
- The number of possible wheel combinations was only 60, since the set of wheels belonging to the machine, at least in the case of the Army Enigma, only consisted of 5 different wheels.[5]
Faults 1 to 4 had already been eliminated on model a) of Schlüsselgerät 39, 5. then no longer appears vital. On the other hand, however, the giving up of the adjustable rings and of the stecker gave rise to weaknesses which the Enigma did not have. In fact, the absence of stecker S cannot be compensated for by making the reflector wheel U pluggable; investigations into Enigma had shown that it was considerably more difficult to find out the steckering S than the reflectoring wheel U.[5]
In detail, the results of the investigations were as follows:
- If the inner wiring and the clear message setting of wheels I, II and II are known, the wiring of the reflector wheel and the pin arrangement of N1 N2 N3 can be found out from a crib of 25 letters, this was a fairly laborious process.
- If the inner wiring of wheels I, I and II and of the reflector wheel U is known, it is likewise possible to find out the clear message-setting and the pin-arrangement of N1 N2 and N3 from a crib of 25 letters; this too is a laborious process.[5]
The above-mentioned weakness of model a) were eliminated by the introduction of steckering and adjustable rings of model b), although this had been done primarily for quite a different reason, namely to make interchangeable working with Enigma possible. It was not now thought that there was any longer a serious possibility of a break-in. As however the system of I and N1 still had a relatively small period of 21 x 26 it appeared desirable to destroy this too. This was done on model c) by making III react to I, and presented no technical difficulties.[6]
Finally in model c), the total number of periods was multiplied by 26 compared with a) and b), but the introduction of a fourth wheel; it was not, it is true, intended primarily for this purpose but was added to carry out interchangeable working with the Naval Enigma.[6]
2. History of Gerät 39
Model a) had been developed as early as the year 1939 or 1940 at Wa Pruef 7 at the Waffenamt. In the summer of 1942, a prototype was available at Dr. Pupp's laboratory at Wa Pruef 7, and was made by the firm Telefonbau und Normalzeit (literally 'Telephone and Standard Time', later called Tenovis). A noteworthy feature was that when the clear-text letter was keyed, the corresponding cipher letter could be sent out simultaneously by the transmitter as a Morse character. This from a technical point of view, a fairly complicated operation. The machine thus was like a cipher teleprinter except that instead of the 5-element alphabet the ordinary Morse alphabet was used. The maximum keying speed was also the same as on a current (1940s) cipher teleprinter. It could not however be made use of when working on direct transmission, because reception at the other end was not automatic as in the case of a cipher teleprinter, but had to be done aurally by the operator. That was one of the many reasons why the automatic transmission part of the machine was omitted in later models. This was done when Oberst Kahn, the director of the Pruef 7 department of the Waffenamt, left, he having especially advocated this strange principle. The second model actually constructed was like the model designated with c) in the [See 2.1.1] section above. It only printed clear text and cipher text on 2 separate strips. Buggisch saw it in January 1944 when I was visiting Wa Pruef 7 Section II at Planken.[6]
The change from cipher-technical a) to b) and also c) was made at the end of 1942. It was made at the instigation of the Kriegsmarine who laid down the principle that any newly introduced cipher machine for higher HQs should permit interchangeable working with the Enigma. The Army (Heer and Wehrmacht) also adopted this standpoint: In the first instance only the highest authorities were to be issued with the new machine, e.g. OKW, OKH and the Army groups, and only gradually, as production permitted, was the Engigma machine to be replaced by the 39 at Armies, and finally perhaps at Army Corps. There were, during 1943 and 1944 between the various HQs interested, many and lengthy discussions and arguments for and against the introduction of the 39 machine. Special wishes of the Navy had to be taken into account. The industrial firm complained of lack[6] of material and labour. Owing to these and similar difficulties, development stopped altogether at one time, and it was resumed however. At any rate the vagueness of the decisive authorities was, in addition to difficulties of production, the chief reason why the machine was never completed.[7]
3. Bibliography
- "TICOM I-137 Final report written by Wachtmeister Otto Buggisch of OKH/Chi and OKW/Chi" (pdf). TICOM. 8 October 1945. https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B_oIJbGCCNYeUExkTnlyVGdOVTg/view. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Schl%C3%BCsselger%C3%A4t_39
References
- "I-137 Final report written by Wachtmeister Otto Buggisch of OKH/Chi and OKW/Chi". TICOM. 8 October 1945. https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/0B_oIJbGCCNYeMGUxNzk0NWQtNzNhZi00YWVjLWI1NmItMzc2YWZiZGNjNjQ5. Retrieved 3 February 2018.
- I-137 p.2
- I-137 p.3
- I-137 p.4
- I-137 p.5
- I-137 p.6
- I-137, p.7
