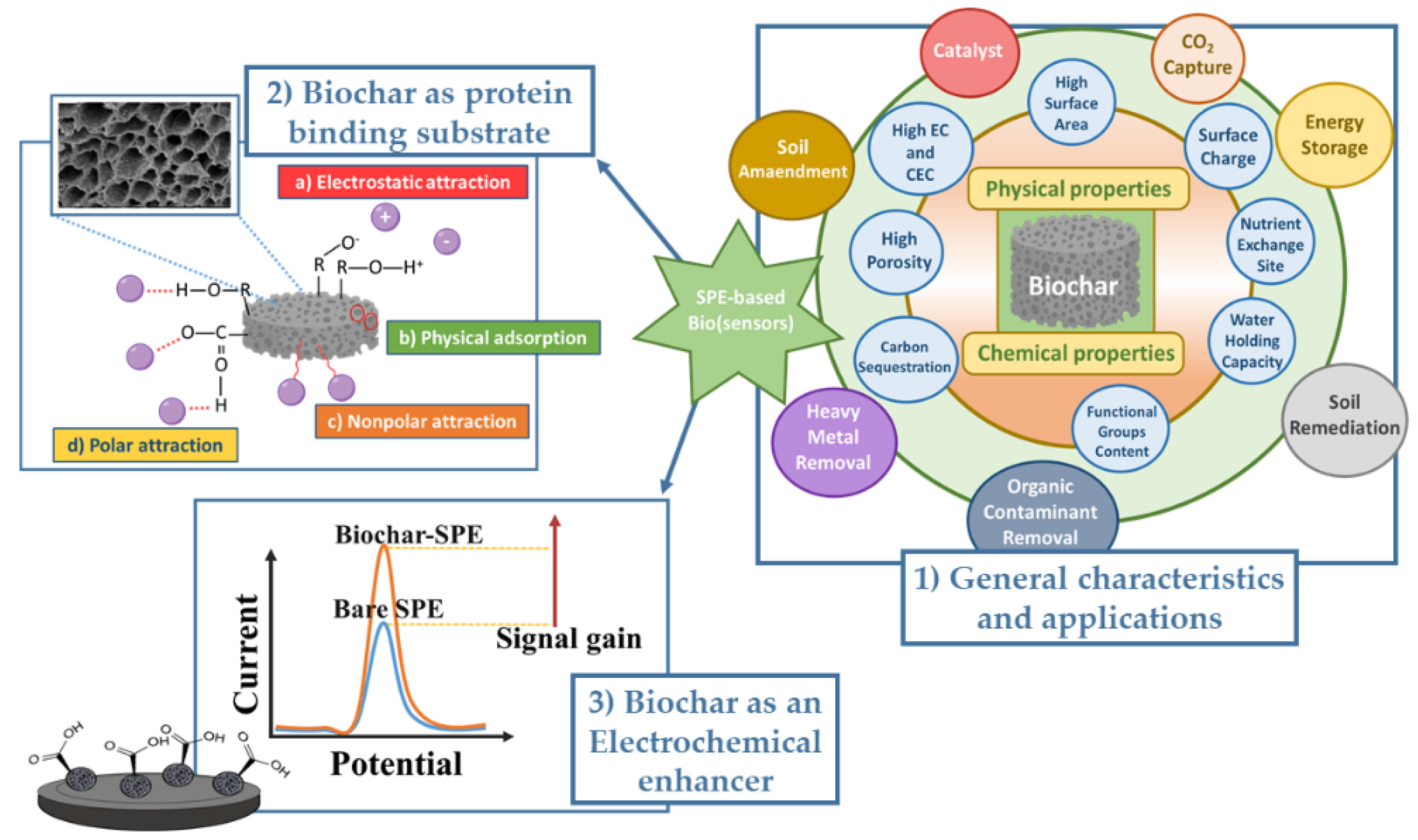
With the continuous progress in technology, understanding carbon nanomaterials (CNMs) has reached a new level of interest. Their excellent electrical conductivity, stability, potential high-throughput screening and easy-to-use assay procedure make these compounds suitable for the fabrication of realizing sensors and energy storage devices [
1,
2]. The production of carbon nanostructures has greatly increased the use of these devices, creating a wide range of applications based on their use, ranging from the creation of miniaturized printed electrodes to the development of flexible electronic devices, humidity sensors or passive sampling systems [
3,
4,
5]. Until now, several electronic and electrochemical tools are developed and applied at the lab scale. Nevertheless, to allow the deployment of these technologies on a large scale, it is necessary for a cost-production reduction and their actual health safety. In addition, CNMs are rather energy-intensive and expensive and require long syntheses, and studies on their toxicity are not yet concluded [
6]. For example, activated carbon is conventionally derived from coal, while CNMs such as carbon nanotubes and graphene can be produced through specific techniques (i.e., chemical vapor deposition, electric arc discharge, etc.) using gaseous petrochemicals (i.e., methane, acetylene, ethylene, hydrogen, etc.) at high temperatures (>800 °C) [
7]. These high-temperature and resource-intensive processes can be suitable for large-scale production in industrial settings but are not compliable with a fully sustainable solution or production in smaller installations. Alternative eco-friendly carbon material, produced at low cost, competes to replace CNMs, widely used at the industrial level [
8]. Recently, attention is being focalized on green recycling carbon material, called biochar. The latter is an inexpensive, solid, recycling carbonaceous material obtained by pyrolysis of renewable sources (i.e., wood chips and pellets, bark, straw, walnut shells and rice husks, bagasse, sewage sludge, etc.) [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16], and its production requires a lower overall energy input than activated carbon, resulting in lower net energy consumption with a low net cost. Its morphological and physicochemical properties can strongly vary with the feedstock source choice and the conditions of the pyrolysis treatment [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23]. In addition, the high porosity combined with its surface being rich in functional groups on one side and its excellent electrical conductivity and biocompatibility on the other expand its applications in different fields. A schematic representation of biochar’s applications and its most exploited qualities is reported in
Figure 1.
Until a few years ago, biochar has been used in a large number of applications such as adsorbent for wastewater treatment and agronomic applications (i.e., immobilizing organic and inorganic pollutants), or as an amendment in agricultural soils (effects on soil, agricultural yields, and nitrogen leaching and emissions) [
18,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26]. However, recently, its potential as an eco-friendly and smart nanomaterial for several electrochemical applications is increasingly exploited [
27]. In 2015, Joseph et al. reported the redox properties of different biochar, which are rich in carbon (amorphous and graphitic C, labile organic compounds, and minerals) in this regard [
28]. In particular, they underlined that the electrochemical properties of biochar are a function of the concentration and composition of the various redox-active minerals and organic compounds and, at the same time, of their production method [
29,
30]. Many electrochemical studies, present in the literature, reported the use of biochar as a surface modifier of electrodes (i.e., carbon paste, glassy carbon, etc.) [
31,
32,
33], but only a few of them concern SPEs [
34,
35,
36]. Precisely with that in mind, the present work aims to illustrate the recent applications of biochar as a sustainable nanomaterial for electrochemical applications in the field of SPEs. Before all else, its capabilities to act as an electrochemical enhancer (improving the electron transfer process when used for the modification of SPEs), as a booster of the active surface area of the electrodes and as a protein binding substrate (i.e., enzyme, antibody, etc.) in the production of biosensors were carefully studied and discussed [
37].
2. Application of Biochar in Sensing
Since the application of biochar as a soil conditioner, catalyst and carbon sequester has been successfully reported, other strategies based on this recycling material to promote sensors with improved analytical performances continue to be widely studied today. In 2020, an inspiring review about sustainable materials for the design of sensors, reporting how the pyrolysis and activation process can affect biochar features, was published [
94]. Here, different applications of biochar underlining the potentiality and the promising features of these carbonaceous and recycled materials for electrochemical applications have been reported (
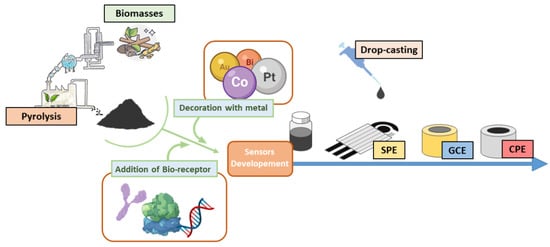
Figure 2). In
Figure 2, a general scheme for the modification of screen-printed and bulk electrodes using biochar is reported. Moreover, a few examples of works reported in the literature are discussed below.
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the steps involved in the fabrication of biochar-modified electrodes.
2.1. Carbon-Paste and Glassy-Carbon Electrodes
In recent years, an increasing number of publications were centered on biochar-modified glassy-carbon electrodes (GCEs) and carbon paste electrodes (CPEs) [
95,
96,
97,
98,
99,
100]. In these papers, biochar was used for its adsorbent properties and as a highly effective electrode modifier for the pre-concentration of organic contaminants. In these studies, the porous surface of biochar, rich in chemical groups (i.e., carboxyl, hydroxyl, phenolic groups, etc.), which can interact in several ways with the target analytes, was exploited for the pre-concentration and voltammetric determinations of inorganic ions and organic species [
98,
101,
102,
103]. Another interesting use of biochar is that in which it was deposited alone or decorated with metallic nanoparticles (i.e., mercury, bismuth, gold, etc.) or electrocatalytic potential nanostructures (i.e., nickel hydroxide, copper hexacyanoferrate, etc.) for the construction of a powerful electrochemical sensor. These methods, based on voltammetric procedures (i.e., stripping, differential pulse, square wave voltammetry, etc.), have provided significant improvement in the performances (sensitivity and selectivity) of the sensor developed.
Table 1 reports significant works in which biochar-modified CPE and GCE were used. In these works, biochar was exploited to electrochemically determine heavy metal ions and organic compounds, including hormones, insecticides, herbicides or antibiotics, in different matrices.
Table 1. Main source, preparation, application and limit of detection (LOD) obtained from biochar-modified CPE and GCE.
Several papers, present in the literature, reported the use of Castor oil biochar to develop voltammetric sensors for the detection of heavy metals in water or food [
95,
96,
97,
98,
99,
100,
101]. In this regard, one of the first applications of biochar was reported by Suguhiro et al. in 2013 [
95]. In this work, the authors exploited both the high affinity for heavy metals [
99,
100] and the electrocatalytic capacity of biochar to develop a voltammetric sensor for the determination of lead (II) and cadmium (II). Chiefly, they proposed, for the first time, the characterization of adsorptive properties of biochar, typical of bio-carbon obtained under low-temperature pyrolysis conditions [
112], using differential pulse adsorptive voltammetry (DPAdSV). The sensors showed excellent analytical performances with a low LOD (nanomolar range), excellent sensitivity, stability and recovery (>94%), with the absence of significant interference by common cations present in waters. Comparable results were obtained by Olivera et al. (2015) for the determination of copper using biochar (form the same feedstock)-modified CPE. Moreover, for organic compounds, interesting results were obtained when biochar by bamboo was modified with inorganic salts such as ZnCl
2 [
113] or carbonate minerals dolomite (DM) [
114] or used to modify the electrodic surface of GCE. The electrochemical performance of these modified electrodes improved in terms of sensitivity (lower LOD) and stability, especially when used in clinical and food matrices. Another remarkable application is that of L. He and coworkers (2020). They developed a sensitive and reusable electrochemical biosensor for bisphenol A (BPA) based on newly synthesized biochar nanoparticles (BCNPs) [
115]. In this work, a stable immobilization of the tyrosinase (Tyr) enzyme using the carboxyl functionality of the highly conductive magnetic biochar nanoparticles was proposed. This biosensor, based on GCEs, presented very promising analytical performances with a detection limit (LOD) of 2.78 nM with linear ranges from 0.01 to 1.01 μM [
115].
Moreover, this is not the only biochar-based biosensor for the detection of bisphenol A. Indeed, Y. Liu and coworkers (2019) presented an electrochemical tyrosinase enzyme (Tyr)-based biosensor using a highly conductive sugarcane-derived biochar nanoparticle (BCNP) for the detection of BPA [
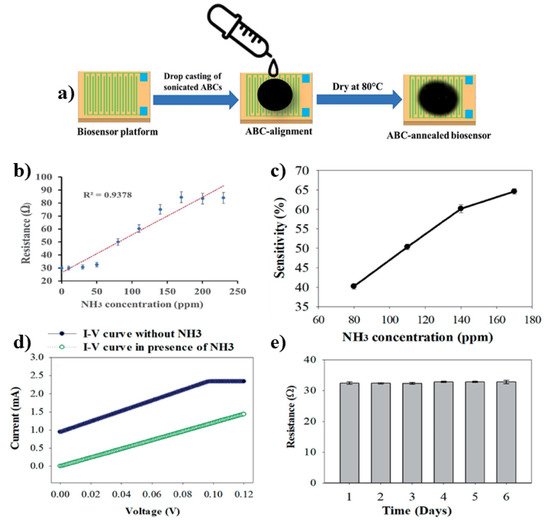
110]. In this biosensor (BCNPs/Tyr/Nafion/GCE), a higher sensing signal (improved amperometric current responses) due to the conductivity property of biochar nanoparticles was observed. Precisely, a decreased charge transfer resistance and lowered reduction potential were obtained if compared with the biosensor based on bare GCE (Tyr/Nafion/GCE). Moreover, biochar-based biosensors showed robust analytical performances with a sensitivity of 3.18 nM and a linear range from 0.2 to 10 μM. These results were confirmed when the device was employed in real water detection, as evidenced by the high accuracy compared to that of high-performance liquid chromatography. Another attention-grabbing application of biochar is that proposed by A. Sobhan and coworkers (2021). In this work, they employed activated biochar (activated by steam-activation method) from corn stover for the development of a biosensor (ABC/PLA-based platform) selective for NH
3. The analytical performances reported in
Figure 3 [
116] demonstrate the robustness of the method when used in smart food packaging control. Moreover, careful characterization in terms of polylactic acid (PLA, ranging from 15 to 50%), electrical conductivity and tensile strength were reported.
Figure 3. Schematic representation of ABC/PLA-based biosensor fabrication (a) and its analytical performances (from (b–e)). In particular, in (b) the resistance response to NH3 concentrations, in (c) the sensitivity, in (d) the comparison of I-V data of 85% ABC/PLA-based biosensor in the presence/absence of NH3 and (d) the stability of the biosensor using a fixed concentration of NH3 (50 ppm) was reported.
Q. Zhou et al. (2021) reported on the fabrication of a sensor based on corncob biochar-modified GCE for the determination of dibutyl phthalate (DBP) [
117]. In this tool, functional corncob biochar (F-CC
3) and MIP were combined, achieving high sensitivity (detection limit of 2.6 nM), reproducibility and successful application in the detection of DBP in rice wine [
117]. However, there are also many examples of biochar-modified CPE-based biosensors. For instance, C. Kalinke and her co-workers proposed an electronic tongue based on biochar-modified CPE for the detection of phenolic compounds using stripping voltammetry (see
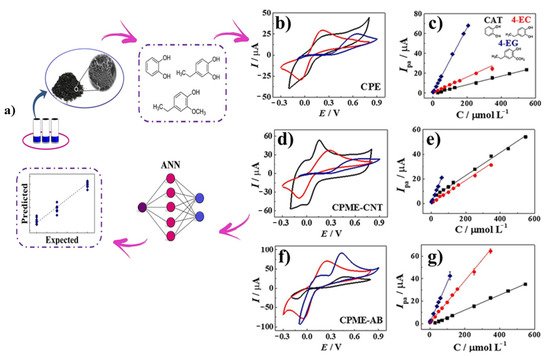
Figure 4). In particular, this artificial neural network (2019)-based electronic tongue used stripping voltammetry as a discrimination technique for the analysis of a mixture of several phenolic compounds, such as catechol (CAT), 4-ethylcatechol (4-EC) and 4-ethylguaiacol (4-EG), showing good sensitivity (LOD in the micromolar range) and reproducibility [
118].
Figure 4. (a) Schematic representation of voltammetric electronic tongue-based biochar-modified CPE for phenolic compounds stripping detection. Cyclic voltammograms and analytical curves obtained for catechol (CAT), 4-ethylcatechol (4EC) and ethylguaiacol (4-EG) using CPE, CPME-CNT and CPME-AB (b–g, respectively).
Furthermore, other works based on biochar have been proposed by the same research group. For example, they developed a non-enzymatic sensor based on nickel-supported activated biochar modified-CPE (NiAB-CPME) for the determination of glucose [
108]. The biosensor showed good performances in terms of repeatability (RSD% = 3.84%), sensitivity (LOD 0.137 µM) and linear range from 5.0 to 100.0 µM. Moreover, they applied this feasible green analytical procedure for the determination of glucose in human saliva and blood serum, also obtaining satisfactory results when a microfluidic methodology was used, thus proving to be a simple, robust and accurate method. In addition, in a second work, they presented a quick electrochemical immunoassay for the detection of pathogens based on biochar-modified CPE [
119]. In this paper, the authors developed an immunosensor to detect Hantaviruses (single-stranded RNA viruses belonging to the Hantaviridae family) [
119]. Matins and his co-workers exploited the highly functionalized surface of biochar able to bind covalently (by EDC/NHS conjugation) the specific antibody for Hantavirus in the construction of the immunosensor. The device showed good analytical performances with a LOD of 0.14 ngmL
−1 and a linear range ranging from 5.0 to 1.0 μgmL
−1. Other biosensors dealing with biochar-modified CPE and GCE are reported in
Table 2.
Table 2. Main source, preparation, application, limit of detection (LOD) and biosensors based on biochar.
2.2. Biochar Application in Screen-Printed-Based Platforms
In the literature, several papers report the comparison of the analytical performances (using the same electroanalytical techniques) of SPEs with those of traditional (bulk) carbon or graphite electrochemical systems (GCE or CPE). The results underlined that, under the same experimental conditions, the combination of SPEs with portable electrochemical instruments represents the best possibility to have new reliable, reproducible, mass-producible and cost-effective electro-chemical tools [
27,
130,
131]. Indeed, they can be easily modified with carbonaceous nanomaterials to improve their analytical performances [
132,
133]; in particular, this statement is confirmed by some examples of SPE modified with biochar, reported in the literature [
13,
17,
27], used for its fascinating morphological and electrochemical features. In comparison with the bulk electrodes (the one reported in the previous paragraph, GCE and CPE), SPEs offer other advantages to coupling with cost-effective instrumentation, the capability of miniaturization and automation. However, it is well-known that these transducers, particularly when the working electrode (WE) is made of graphite-based materials, have serious issues due to their sluggish surface kinetics, which severely affect their performances [
35]. Carbon materials and nanomaterials (CNMs) represent the most valid solution to overcome this problem, within which biochar is undoubtedly the most innovative and eco-friendly alternative. The modification of SPEs with CNMs and thus also with biochar provides several advantages. Among them, improved surface kinetics, enhanced electroactive surface area and amended adsorption and functionalization capability are, undoubtedly, the most important [
132,
133,
134]. This represents a whole new field of research in full flow, but there are still few works dealing with sensors and biosensors based on SPE-modified with biochar.
Table 3 reports the latest research works published about the development of biochar-based biosensors, and some examples of them are discussed in detail hereafter.
Table 3. Main source, preparation, application, limit of detection (LOD) and sensors based on biochar.
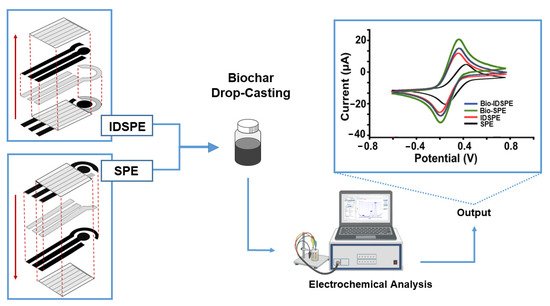
An example of the electrochemical application of biochar as a serigraphic platform modifier (traditional SPE and inverse-designed IDSPE) was proposed by Cancelliere et al. (2019) [
36]. The study, reported in
Figure 5, showed the potentiality of biochar when used as a modifier of the WE with a remarkable improvement of the electrochemical performances in terms of electroanalytical parameters, such as peak-to-peak separation (ΔE), heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant (k
0) and current peak ratio (Ipa/Ipc). In this work, by comparing the analytical performances between biochar-modified and unmodified SPEs, an enormous gain in sensitivity and repeatability was assessed. This is ascribable to the actual benefits provided by this recycling material once cast on the WE surface, thereby demonstrating its effectiveness as an electrochemical enhancer.
Figure 5. Two different configurations of serigraphic platforms and enhancing effect of the biochar.
The same research group also proposed two biochar-based biosensors. In one, they developed a tyrosinase-based amperometric biosensor (Ty/biochar-SPE) in which the enzyme was directly immobilized on biochar-modified SPEs. This biosensor showed very promising analytical performances when assessed for the detection of catecholamines, with a linear working range for epinephrine from 0.05 up to 0.5 mM and a LOD of 2 × 10
−4 mM [
34]. In the other, they used biochar both as an anchoring system and as an electrochemical enhancer, fabricating an ultrasensitive voltammetric label-free immunosensor for interleukin-6 (IL-6). The immunosensing platform was evaluated both in serum and in whole blood samples, showing excellent analytical assessment with LOD in the pico-molar range (5.4 pgmL
−1), good reproducibility (RSD% < 11%) and recovery (always >85%). The peculiarity of this immunosensor resides in its time-saving ability coupled with powerful performances when compared with commercial spectrophotometric ELISA kits [
35]. Another interesting work, reported in
Figure 6, is that developed by the research group of Compagnone [
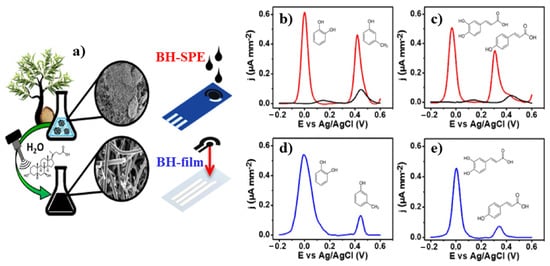
134]. Precisely, they presented water-phase exfoliated biochar nanofibers from Eucalyptus scraps that they used both for the modification of the screen-printed electrodes (BH-SPE) and for the fabrication of a conductive film (BH-film). The BH-based sensors exhibited robust analytical performances with good repeatability (RSD ≤ 7%, n = 5), reproducibility (RSD ≤ 10%; n = 3), sensitivity for hydroxytyrosol (LOD ≤ 0.6 μM) and tyrosol (LOD ≤ 3.8μM) and recovery in the real sample matrix (91–111%, RSD ≤ 6%; n = 3) [
134].
Figure 6. (a) Schematic representation of BH-SPE (red lines) and BH-film (blue lines) preparation and (b–e) their application in the detection of caffeic acid and dopamine (25 μM).
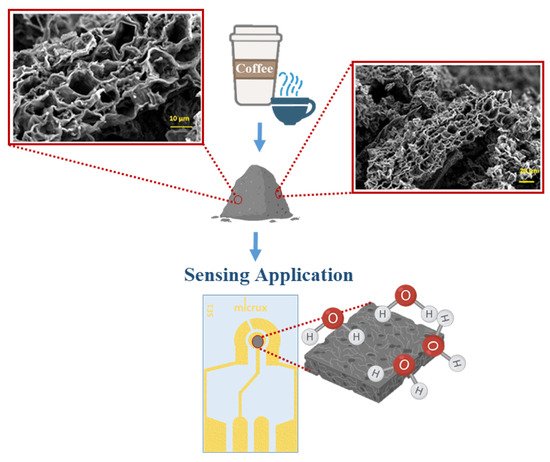
However, there are different works in which biochar is exploited for the development of powerful humidity sensors. Among them, one of the most promising is that of Jagdale et al. (2019) [
135]. They proposed biochar from waste coffee as a material for the development of impedimetric humidity sensors (see
Figure 7). The sensing platforms were produced (heated at 300 °C) using an ink-containing CGB with polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which acts as a temporary binder and ethylene glycol monobutyral ether, as an organic vehicle. The sensitivity tests (humidity), performed at room temperature under a flow of 1.7 Lmin
−1 in a relative humidity range from 0 to 100%, showed an initial impedance of the film of 25.2 ± 0.15 MΩ, which changes to 12.3 MΩ under 98% humidity exposure, with a sensor response above 20% [
135].
Figure 7. Schematic representation of humidity sensor based on biochar from waste coffee.