Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
DARPP-32 is an integrator of dopamine and glutamate. It is an interesting potential target in the pursuit of improving current pharmacological treatment options for addiction.
- DARPP-32
- addiction
- nicotine
- alcohol
- opioid
- stimulant
1. DARPP-32 Discovery
The late Paul Greengard discovered DARPP-32 during his pioneering work that proved the same mechanisms used in the endocrine system are used for communication between nerve cells [1]. Within glycogenolysis, for example, epinephrine binds to a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) causing a subunit to activate adenylyl cyclase and result in an increased cytosolic concentration of cAMP (the second messenger). cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA) and this causes a cascade of phosphorylation that results in decreased glycogen synthesis and increased glycogen breakdown (see Figure 1) [2].
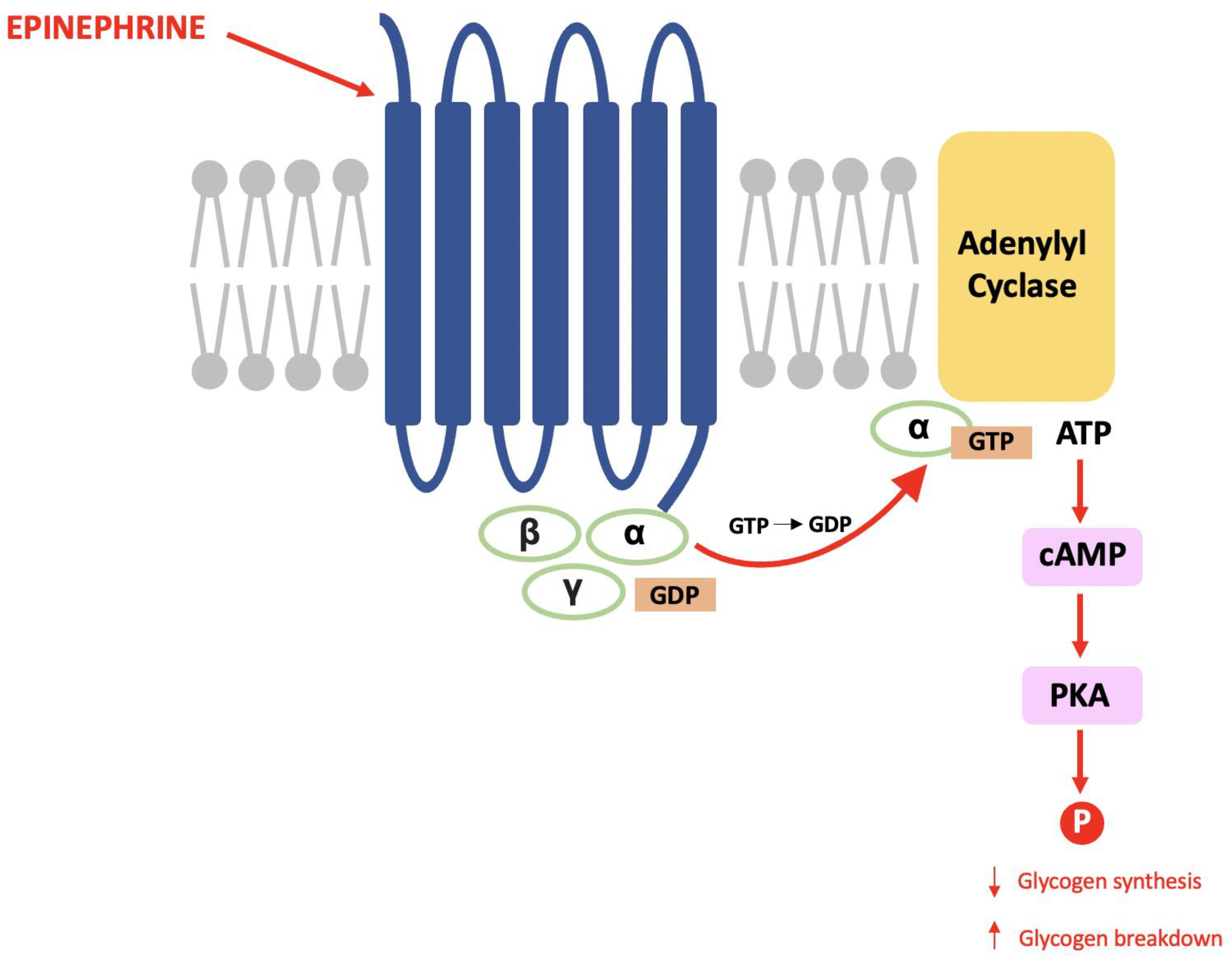
Figure 1. The glycogenolysis pathway: This is a second messenger pathway in which epinephrine binds to a GPCR, activates PKA and stimulates a cascade of phosphorylation that decreases glycogen synthesis and increases glycogen breakdown.
In DARPP-32 modulation, dopamine binds to D1 receptors located in the striatum and causes a Gs subunit to interact with adenylyl cyclase and result in the same pathway; increased intracellular cAMP, activation of PKA and, in this case, phosphorylation of DARPP-32 at the threonine-34 (Thr34) residue [3]. The result of this pathway is the conversion of DARPP-32 into a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1 (PP-1) (see Figure 2). PP-1 is a multifunctional protein affecting a variety of signalling pathways, making DARPP-32 an effector of downstream changes in physiological function and a promising target for pharmacological intervention [4].
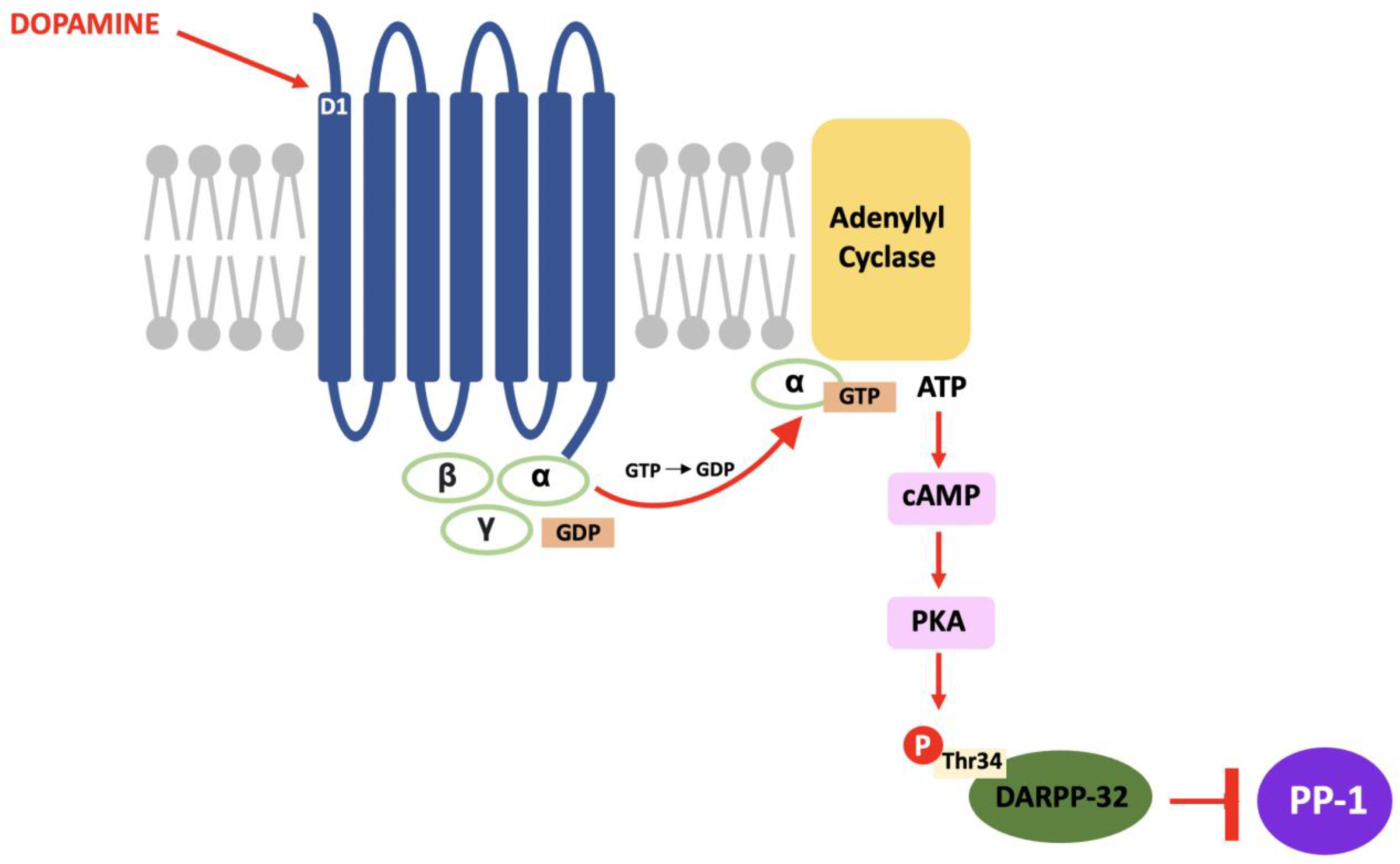
Figure 2. The D1/DARPP-32/PKA pathway: Dopamine binds to D1 receptors, activates PKA and stimulates a cascade of phosphorylation that results in the inhibition of PP-1.
2. DARPP-32 Phosphorylation
As discussed in 4.1, DARPP-32 is phosphorylated via PKA at the Thr34 residue. This occurs primarily through the actions of dopamine (and D1-selective agonists) on striatal neurons expressing the D1 class of receptors, such as within striatonigral subpopulations [5]. Adenosine acting on A2A-expressing regions such as within striatopallidal neurons has the same effect; increased activity of adenylyl cyclase to stimulate cAMP formation and activate cAMP-dependent PKA [6]. The effect of these two neurotransmitters is additive as they both activate the cAMP/PKA/DARPP-32 signalling pathway and cause PP-1 inhibition [7]. In contrast, D2-receptor activation via dopamine and D2-selective agonists reduces levels of DARPP-32 phosphorylation at the Thr34 residue, through adenylyl cyclase inhibition that results in decreased PKA activity [8]. As PKA regulates a variety of cAMP-dependent physiological processes, the ability to act as either a PKA or PP-1 inhibitor gives rise to the unique switch function of DARPP-32.
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK-5) phosphorylates DARPP-32 at the threonine-75 (Thr75) residue [9]. This prevents the actions of PKA at the Thr34 site [10]. Opposingly, casein kinase I (CK1) and casein kinase II (CK2) act to attenuate the actions of DARPP-32 as a PP-1 inhibitor [11]. CK2 phosphorylates DARPP-32 at Serine-97 (Ser97) and increases the efficiency of Thr34 phosphorylation whilst phosphorylation of Serine-130 (Ser130) via CK1 acts to inhibit protein phosphatase-2B (calcineurin) [12][13]. Calcineurin and protein phosphatase-2A (PP-2A) act synergistically to dephosphorylate DARPP-32 at Thr34 [14]. Therefore, reducing calcineurin-dependent dephosphorylation of DARPP-32 would increase levels of Thr34-phosphorylated DARPP-32.
Glutamate can also regulate DARPP-32 phosphorylation. Acting at both NMDA and AMPA receptors, glutamate causes calcium-dependent activation of calcineurin to result in dephosphorylation of DARPP-32. Opposingly, glutamate at I mGlu-5 receptors (mGlu5) potentiates cAMP formation coupled to A2A receptors and increases Thr34 phosphorylation. It can also increase phosphorylation at Ser130 and Thr75 through group I mGlu receptors [15]. The ability of DARPP-32 to alter downstream signalling depending on phosphorylation site is indicative of the central role it plays in signal transduction (see Figure 3).
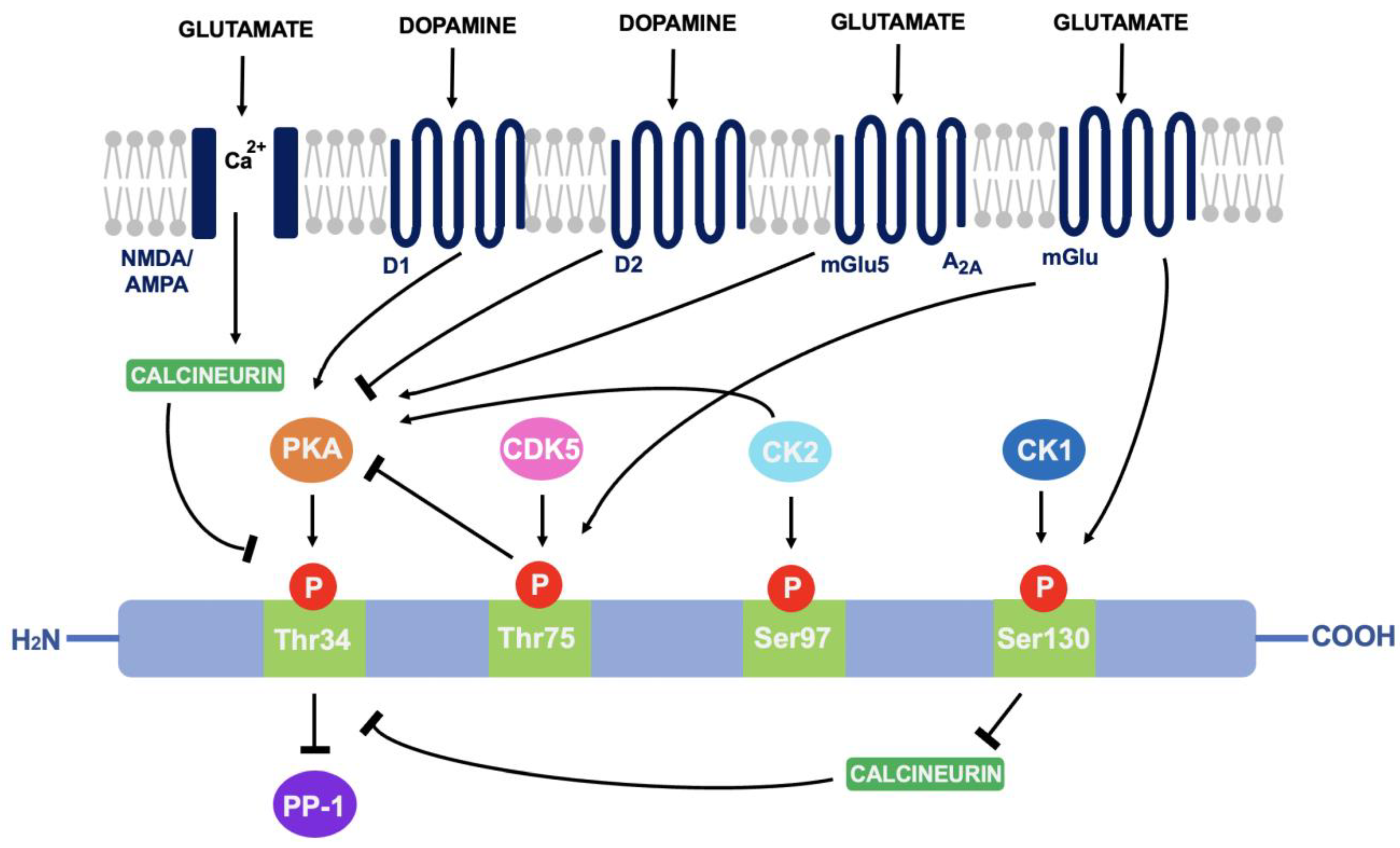
Figure 3. A summary of the actions of dopamine and glutamate on DARPP-32 phosphorylation: Through phosphorylation of DARPP-32 at four main amino acid sites (Thr34, Thr75, Ser97 and Ser130), DARPP-32 acts as either a PP-1 or PKA inhibitor.
3. DARPP-32 Localisation
Through immunohistochemistry investigations, expression of DARPP-32 has been identified in the brain, adrenal medulla, kidney, and parathyroid cells [16]. However, immunocytochemistry localization experiments and biochemical studies proved that DARPP-32 is predominantly localised in medium spiny neurons (MSNs) within the striatum [17]. The striatum is a site of major dopaminergic innervation within the central nervous system. The dorsal striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen) receives dopaminergic input from the substantia nigra pars compacta that contributes to coordination and response, whilst the ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens) is innervated from the VTA and contributes to the reward pathway [18].
Excitatory neurons from the cortex, thalamus and limbic areas of the brain input high levels of glutaminergic innervation to the (predominantly GABAergic) striatal neurons through both NMDA and non-NMDA classes of glutamate receptors [19]. The localisation of DARPP-32 within neurons expressing high levels of dopaminergic and glutaminergic innervation is indicative of the importance of these neurotransmitters in regulating DARPP-32. As both dopamine and glutamate neurotransmission is critical to addiction pathophysiology, it is also indicative of the involvement of DARPP-32 in substance abuse.
4. DARPP-32 and Neuroplasticity
Changes in neural plasticity discussed in Section 3 are strongly associated with a pathway known as the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) cascade [20]. This results in the activation of downstream transcription factors such as cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) and subsequent expression of proteins that cause structural dendritic and synaptic changes that are associated with all forms of substance abuse [21]. For example, opioids and psychostimulants have opposing effects on neuronal plasticity in response to this pathway. Opioids decrease the number and complexity of dendritic spines on MSNs and the prefrontal cortex, alongside hippocampus neurons and dopaminergic neurons in the VTA. Cocaine, methylphenidate and amphetamines do the reverse [22].
Dopaminergic and glutaminergic pathways modulate both DARPP-32 and the MAPK/ERK cascade, and ERK is a downstream effector of DARPP-32 [23]. Furthermore, PP-1 is usually responsible for activation of striatal-enriched tyrosine phosphatase (STEP); a phosphatase that dephosphorylates and deactivates ERK. Thus, through DARPP-32 dependent PP-1 inhibition, ERK is activated. ERK activation in response to d-amphetamine (an amphetamine salt), cocaine, morphine, THC and nicotine abuse was lacking in DARPP-32 knock out (KO) mice, highlighting the importance of DARPP-32 involvement in this pathway [24].
5. DARPP-32 and Substances of Abuse
In addition to the integration of dopaminergic and glutaminergic transmission that makes DARPP-32 so relevant to addiction pathophysiology, the protein itself is also differentially influenced by the various drugs of abuse (see Figure 4).
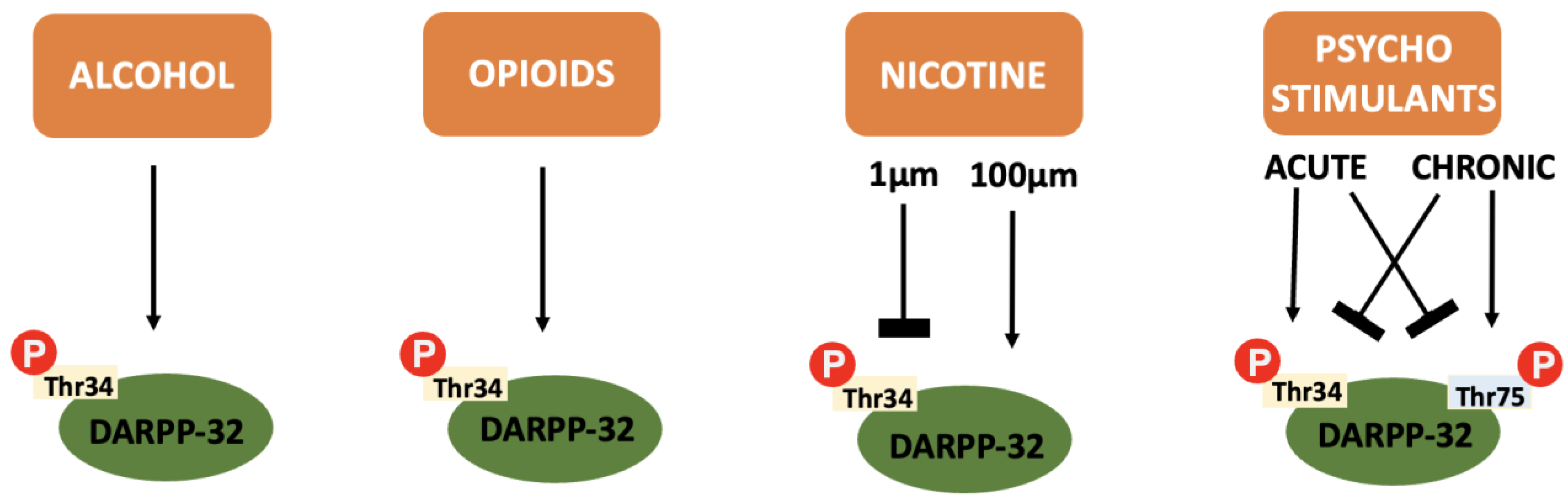
Figure 4. A summary of the effect of various drugs of abuse on DARPP-32 phosphorylation: Alcohol, opioids and cannabinoids cause an increase in Thr34 independent of concentration or repeated administration. Nicotine causes inhibition of Thr34 phosphorylation at low concentrations and increases Thr34 phosphorylation at higher concentrations. Psychostimulants cause increased Thr34 phosphorylation and decreased Thr75 phosphorylation after acute administration and the reverse after chronic administration.
5.1. DARPP-32 and Alcohol
Moderate levels of alcohol (ethanol) are proven to increase Thr34 phosphorylation, thus activating D1 dependent cAMP/PKA/DARPP-32 signalling pathways and inhibiting PP-1 [25]. A downstream effect of this reduced phosphatase activity is phosphorylation of the NR1 subunit on NMDA receptors [26]. Usually, ethanol is a potent inhibitor of NMDA receptors [27]. However, within DARPP-32 expressing brain regions via the mechanism discussed above, NMDA sensitivity to ethanol is reduced [28]. Disinhibition of NMDA receptors allows enhanced glutaminergic transmission that contributes to the reward pathway and allows long term synaptic plasticity to promote ethanol dependence. Somewhat expectantly, investigations into ethanol motivation using DARPP-32 KO mice proved it to be key in modulating ethanol-seeking behaviour [29].
Further studies into levels of DARPP-32 mRNA in rats with genetic preference or avoidance showed significant differences in genetic expression, implying the importance of DARPP-32 in genetic probability of addictive tendencies [30]. Another study showed that ethanol sensitized mice (who consumed more alcohol and were therefore more susceptible to addiction) had higher DARPP-32 phosphorylation when co-administered a D1 receptor agonist [31]. This highlights a potential role of the D1/DARPP-32/Thr34 pathway in ethanol sensitization.
DARPP-32 therefore exists as a promising therapeutic target, due to prevalent involvement in ethanol dependence pathophysiology. Modulation of the phosphorylation pathways associated with it could reduce plasticity changes and ethanol reinforcement
5.2. DARPP-32 and Opioids
Some evidence shows that acute administration of opioids increases D1 dependent phosphorylation of Thr34 and has no effect on Thr75 phosphorylation [32]. It is suggested that this Thr34 phosphorylation augments hyperlocomotor responses to opioids, but seemingly has no effect on behavioural sensitisation [33].
Hyperlocomotion is a heightened state of locomotive activity; the forward progression carrying a person from one destination to the other [34]. It is often used as a phenotypical representation of substance abuse because all drugs of abuse have locomotor enhancing effects. Accordingly, increases in locomotor activity often parallel the progression of substance dependence, due to repeated administration progressively increasing the effect [35].
This dependence on DARPP-32 to cause hyperlocomotion in opioid use therefore supports the involvement of DARPP-32 in addiction progression. However, there are discrepancies in this knowledge. Locomotor activity is increased through opioid interaction with μ opioid receptors [36]. In striatonigral neurons within the striatum, activation of the μ receptor causes an interaction with D1 receptors that inhibits the increase in DARPP-32 phosphorylation [37]. This would therefore reduce Thr34 phosphorylation and contradict the effect of this on motor response. Supporting this, acute morphine administration to morphine-sensitised rats has shown a delayed increase in Thr75 phosphorylation, hence PKA inhibition of and reduction in Thr34 phosphorylation [38].
An interrelation of opioid effecting DARPP-32 and vice versa is clear. Further clarity of whether the mechanisms of this interaction progress addiction would clarify whether DARPP-32 is a potential target for opioid dependence treatment.
5.3. DARPP-32 and Nicotine
The effect of nicotine on DARPP-32 is dose-dependent, causing a sustained decrease in Thr34 phosphorylation at low concentrations (1 µm) and transient increases at higher concentrations (100 µm). This is likely due to D2 or D1 receptor signalling at low or high concentrations, respectively [39]. In vivo arterial concentrations of nicotine are usually closer to the lower value; approximately 0.5 µm [40]. Hence, an educated guess would be to assume Thr34 phosphorylation is low within human smokers.
Investigations using DARPP-32 KO mice displayed heightened nicotine intake, responsiveness to motor depressant effects and a generally enhanced behavioural response to nicotine [41]. It could therefore be hypothesised that low levels of Thr34 phosphorylation could exert behavioural control of nicotine through its phosphorylation state. Modulation of DARPP-32 to influence this behavioural control would in this sense be a promising therapeutic target.
5.4. DARPP-32 and Cannabinoids
Evidence of the effect of cannabinoids on DARPP-32 phosphorylation are somewhat less concrete and explored than that of other substances of abuse. This is perhaps responsive to earlier discussions in previous content regarding the unacknowledged severity of CUD. Despite this, there is evidence to show that agonists for the CB1 receptor (a neural cannabinoid receptor) do increase Thr34 phosphorylation in MSNs [42].
This phosphorylation has been linked to the cataleptic effects of high dose cannabinoids [43]. Through genetic inactivation of receptors involved in the DARPP-32/PKA pathway and resulting decreases in motor depression, it is clear Thr34 is involved in the suppressive psychomotor effects of cannabinoids [44]. To what extent this is relevant to DARPP-32 as a therapeutic target for addiction would require more understanding of DARPP-32 involvement in CUD pathophysiology.
Interaction between the CB1 receptor and D2 receptors to increase ERK phosphorylation and enhance CB1 expression (thus increasing cannabinoid signalling) has been proven [45]. It is likely that DARPP-32 is an integrator within this cross talk and DARPP-32 shows promise as a potential target for CUD, but further clarifications are required.
5.5. DARPP-32 and Psychostimulants
Psychostimulants exhibit different degrees of DARPP-32 phosphorylation depending on acute or chronic administration. Acutely, Thr34 phosphorylation is increased whilst Thr75 phosphorylation decreases. After chronic administration, CDK-5 (and p53, another transcription factor) are upregulated to result in reversal of this ratio [46]. DARPP-32 KO mice show reduced sensitivity, reward and locomotor activity acutely, and increased locomotor sensitivity after chronic use [47]. It is therefore plausible that these changes are dependent on the phosphorylation state of DARPP-32. This supports use as a therapeutic target.
Further investigations have highlighted the importance of DARPP-32 phosphorylation in psychostimulant dependence. Acutely, interrelations between cocaine, DARPP-32 and the ERK pathway have been realised. High levels of Thr34 and decreased Thr75 phosphorylation corresponds to increased ERK signalling, thus contributing to both genetic expression and behavioural response [48]. This enhanced signalling is associated with cocaine-conditioned place preference behaviour, which represents contextual drug reward [49]. Meanwhile, high levels of Thr75 phosphorylation after chronic administration are intrinsically linked to psychostimulant-induced locomotion and behavioural sensitisation [50][51].
DARPP-32 is undoubtably integral to psychostimulant dependence. Arguments for application as a therapeutic target are most well-supported for psychostimulants as opposed to other abusable substance groups.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/neurosci3030035
References
- Hemmings, H.; Greengard, P.; Tung, H.; Cohen, P. DARPP-32, a dopamine-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein, is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1. Nature 1984, 310, 503–505.
- Feher, J. ATP Production I. In Quantitative Human Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017.
- Wang, H.; Farhan, M.; Xu, J.; Lazarovici, P.; Zheng, W. The involvement of DARPP-32 in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53791–53803.
- Saidy, B.; Kotecha, S.; Butler, A.; Rakha, E.A.; Ellis, I.O.; Green, A.R.; Martin, S.G.; Storr, S.J. PP1, PKA and DARPP-32 in breast cancer: A retrospective assessment of protein and mRNA expression. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 5015–5024.
- Fernandez, É.; Schiappa, R.; Girault, J.; Novère, N. DARPP-32 Is a Robust Integrator of Dopamine and Glutamate Signals. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2006, 2, e176.
- Svenningsson, P.; Lindskog, M.; Rognoni, F.; Fredholm, B.; Greengard, P.; Fisone, G. Activation of adenosine A2A and dopamine D1 receptors stimulates cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of DARPP-32 in distinct populations of striatal projection neurons. Neuroscience 1998, 84, 223–228.
- Nishi, A.; Snyder, G.; Greengard, P. Bidirectional Regulation of DARPP-32 Phosphorylation by Dopamine. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 8147–8155.
- Dagda, R.; Das Banerjee, T. Role of protein kinase A in regulating mitochondrial function and neuronal development: Implications to neurodegenerative diseases. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 26, 359–370.
- Bibb, J.A.; Snyder, G.L.; Nishi, A.; Yan, Z.; Meijer, L.; Fienberg, A.A.; Tsai, L.-H.; Kwon, Y.T.; Girault, J.-A.; Czernik, A.J.; et al. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 by Cdk5 modulates dopamine signalling in neurons. Nature 1999, 402, 669–671.
- Svenningsson, P.; Nishi, A.; Fisone, G.; Girault, J.-A.; Nairn, A.C.; Greengard, P. DARPP-32: An Integrator of Neurotransmission. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 269–296.
- Bibb, J.A.; Nishi, A.; O’Callaghan, J.P.; Ule, J.; Lan, M.; Snyder, G.L.; Horiuchi, A.; Saito, T.; Hisanaga, S.-I.; Czernik, A.J.; et al. Phosphorylation of Protein Phosphatase Inhibitor-1 by Cdk5. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 14490–14497.
- Girault, J.; Hemmings, H.; Williams, K.; Nairn, A.; Greengard, P. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32, a dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein, by casein kinase II. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 21748–21759.
- Desdouits, F.; Siciliano, J.; Greengard, P.; Girault, J. Dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein DARPP-32: Phosphorylation of Ser-137 by casein kinase I inhibits dephosphorylation of Thr-34 by calcineurin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 2682–2685.
- Nishi, A.; Snyder, G.; Nairn, A.; Greengard, P. Role of Calcineurin and Protein Phosphatase-2A in the Regulation of DARPP-32 Dephosphorylation in Neostriatal Neurons. J. Neurochem. 2016, 72, 2015–2021.
- Nishi, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Higashi, H.; Tanaka, M.; Nairn, A.; Greengard, P. Glutamate regulation of DARPP-32 phosphorylation in neostriatal neurons involves activation of multiple signaling cascades. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1199–1204.
- Belkhiri, A.; Zhu, S.; El-Rifai, W. DARPP-32: From neurotransmission to cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 17631–17640.
- Ouimet, C.; Miller, P.; Hemmings, H.; Walaas, S.; Greengard, P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. III. Immunocytochemical localization. J. Neurosci. 1984, 4, 111–124.
- Dupre, K. A Potential Neuroanatomical Dissociation of DARPP-32 in Striatal ERK Signaling. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 10783–10785.
- Greengard, P.; Allen, P.; Nairn, A. Beyond the Dopamine Receptor. Neuron 1999, 23, 435–447.
- Impey, S.; Obrietan, K.; Storm, D. Making New Connections. Neuron 1999, 23, 11–14.
- Wiegert, J.; Bading, H. Activity-dependent calcium signaling and ERK-MAP kinases in neurons: A link to structural plasticity of the nucleus and gene transcription regulation. Cell Calcium 2011, 49, 296–305.
- Russo, S.; Dietz, D.; Dumitriu, D.; Morrison, J.; Malenka, R.; Nestler, E. The addicted synapse: Mechanisms of synaptic and structural plasticity in nucleus accumbens. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 267–276.
- Gould, T.; Manji, H. DARPP-32: A molecular switch at the nexus of reward pathway plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 253–254.
- Valjent, E.; Pascoli, V.; Svenningsson, P.; Paul, S.; Enslen, H.; Corvol, J.-C.; Stipanovich, A.; Caboche, J.; Lombroso, P.J.; Nairn, A.C.; et al. From the Cover: Regulation of a protein phosphatase cascade allows convergent dopamine and glutamate signals to activate ERK in the striatum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 102, 491–496.
- Svenningsson, P.; Nairn, A.; Greengard, P. DARPP-32 mediates the actions of multiple drugs of abuse. AAPS J. 2005, 7, E353–E360.
- Snyder, G.; Fienberg, A.; Huganir, R.; Greengard, P. A Dopamine/D1 Receptor/Protein Kinase A/Dopamine- and cAMP-Regulated Phosphoprotein (Mr32 kDa)/Protein Phosphatase-1 Pathway Regulates Dephosphorylation of the NMDA Receptor. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 10297–10303.
- Hoffman, P.; Rabe, C.; Grant, K.; Valverius, P.; Hudspith, M.; Tabakoff, B. Ethanol and the NMDA receptor. Alcohol 1990, 7, 229–231.
- Maldve, R.E.; Zhang, T.A.; Ferrani-Kile, K.; Schreiber, S.S.; Lippmann, M.J.; Snyder, G.L.; Fienberg, A.A.; Leslie, S.W.; Gonzales, R.A.; Morrisett, R.A. DARPP-32 and regulation of the ethanol sensitivity of NMDA receptors in the nucleus accumbens. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 641–648.
- Risinger, F.; Freeman, P.; Greengard, P.; Fienberg, A. Motivational Effects of Ethanol in DARPP-32 Knock-Out Mice. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 340–348.
- Nuutinen, S.; Kiianmaa, K.; Panula, P. DARPP-32 and Akt regulation in ethanol-preferring AA and ethanol-avoiding ANA rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 503, 31–36.
- Abrahao, K.; Oliveira Goeldner, F.; Souza-Formigoni, M. Individual Differences in Ethanol Locomotor Sensitization Are Associated with Dopamine D1 Receptor Intra-Cellular Signaling of DARPP-32 in the Nucleus Accumbens. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98296.
- Borgkvist, A.; Usiello, A.; Greengard, P.; Fisone, G. Activation of the cAMP/PKA/DARPP-32 Signaling Pathway is Required for Morphine Psychomotor Stimulation but not for Morphine Reward. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 1995–2003.
- Yger, M.; Girault, J. DARPP-32, Jack of All Trades? Master of Which? Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 56.
- Konsolaki, E.; Skaliora, I. Motor vs. cognitive elements of apparent “hyperlocomotion”: A conceptual and experimental clarification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 112, E3–E4.
- Zhang, J.; Kong, Q. Locomotor activity: A distinctive index in morphine self-administration in rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174272.
- Smith, M.; Greene-Naples, J.; Lyle, M.; Iordanou, J.; Felder, J. The Effects of Repeated Opioid Administration on Locomotor Activity: I. Opposing Actions of μ and κ Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 330, 468–475.
- Lindskog, M.; Svenningsson, P.; Fredholm, B.; Greengard, P.; Fisone, G. μ- and δ-opioid receptor agonists inhibit DARPP-32 phosphorylation in distinct populations of striatal projection neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 2182–2186.
- Scheggi, S.; Crociani, A.; De Montis, M.; Tagliamonte, A.; Gambarana, C. Dopamine D1 receptor-dependent modifications in the dopamine and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of Mr 32 kDa phosphorylation pattern in striatal areas of morphine-sensitized rats. Neuroscience 2009, 163, 627–639.
- Hamada, M.; Higashi, H.; Nairn, A.; Greengard, P.; Nishi, A. Differential regulation of dopamine D1 and D2 signaling by nicotine in neostriatal neurons. J. Neurochem. 2004, 90, 1094–1103.
- Lee, A.; Picciotto, M. Effects of nicotine on DARPP-32 and CaMKII signaling relevant to addiction. A Tribute to Paul Greengard (1925–2019). Adv. Pharmacol. 2021, 90, 89–115.
- Zhu, H.; Lee, M.; Guan, F.; Agatsuma, S.; Scott, D.; Fabrizio, K.; Fienberg, A.A.; Hiroi, N. DARPP-32 Phosphorylation Opposes the Behavioral Effects of Nicotine. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 58, 981–989.
- Borgkvist, A.; Marcellino, D.; Fuxe, K.; Greengard, P.; Fisone, G. Regulation of DARPP-32 phosphorylation by Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 31–35.
- Polissidis, A.; Chouliara, O.; Galanopoulos, A.; Rentesi, G.; Dosi, M.; Hyphantis, T.; Marselos, M.; Papadopoulou-Daifoti, Z.; Nomikos, G.G.; Spyraki, C.; et al. Individual differences in the effects of cannabinoids on motor activity, dopaminergic activity and DARPP-32 phosphorylation in distinct regions of the brain. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 13, 1175–1191.
- Andersson, M. Cannabinoid Action Depends on Phosphorylation of Dopamine- and cAMP-Regulated Phosphoprotein of 32 kDa at the Protein Kinase A Site in Striatal Projection Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8432–8438.
- Chiang, Y.; Lo, Y.; Chen, J. Crosstalk between Dopamine D2 receptors and cannabinoid CB1 receptors regulates CNR 1 promoter activity via ERK1/2 signaling. J. Neurochem. 2013, 127, 163–176.
- Girault, J.; Nairn, A. DARPP-32 40 years later. A Tribute to Paul Greengard (1925–2019). Adv. Pharmacol. 2021, 90, 67–87.
- Zachariou, V.; Sgambato-Faure, V.; Sasaki, T.; Svenningsson, P.; Berton, O.; Fienberg, A. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 at Threonine-34 is Required for Cocaine Action. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 31, 555–562.
- Sun, W.; Zhou, L.; Hazim, R.; Quinones-Jenab, V.; Jenab, S. Effects of acute cocaine on ERK and DARPP-32 phosphorylation pathways in the caudate-putamen of Fischer rats. Brain Res. 2007, 1178, 12–19.
- Tropea, T.; Kosofsky, B.; Rajadhyaksha, A. Enhanced CREB and DARPP-32 phosphorylation in the nucleus accumbens and CREB, ERK, and GluR1 phosphorylation in the dorsal hippocampus is associated with cocaine-conditioned place preference behavior. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 1780–1790.
- Engmann, O.; Giralt, A.; Gervasi, N.; Marion-Poll, L.; Gasmi, L.; Filhol, O.; Picciotto, M.R.; Gilligan, D.; Greengard, P.; Nairn, A.C.; et al. DARPP-32 interaction with adducin may mediate rapid environmental effects on striatal neurons. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10099.
- Scheggi, S.; Raone, A.; De Montis, M.; Tagliamonte, A.; Gambarana, C. Behavioral expression of cocaine sensitization in rats is accompanied by a distinct pattern of modifications in the PKA/DARPP-32 signaling pathway. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 1168–1183.
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
