Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Immunology
Fungal spores are ubiquitous in the environment and are encountered on a daily basis. Fungi that enter the body are usually controlled by our innate immune system, preventing disease from developing. Detection of fungal surface ligands by Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) triggers a pro-inflammatory response, resulting in innate immune activation and elimination of fungi when the immune response is effective, or ineffective clearance and development of disease when immunity fails.
- fungal infections
- antifungal immunity
- host–pathogen interaction
- immune dysregulation
- host-directed therapy
1. Barriers to Fungal Entry
The first components of our protection against invading fungi are the physical and anatomical barriers that prevent entry of pathogens, primarily skin and mucosal membranes [17]. The skin is colonised by a range of commensal microorganisms, the main fungal species being members of the Malassezia genus [19,20]. Tight junctions in the epithelia form a physical barrier to fungal entry, while C. albicans colonisation on the skin has been shown to be controlled by skin-resident dendritic cells [17,21].
The primary mechanism of pulmonary exposure to fungi is inhalation of fungal spores, most commonly Aspergillus spp. [22]. Once in the respiratory tract, tight junctions between epithelial cells prevent fungal invasion into the host. A layer of mucus helps trap fungal spores, allowing cilia to move trapped fungi out of the respiratory tract to be coughed up or swallowed into the digestive tract to be destroyed by stomach acid [23].
2. Host Recognition of Fungi
Fungal pathogens can circumvent physical barriers and gain entry to the host in the case of a barrier break, e.g., injury. PRRs are able to detect a range of conserved structures on pathogens, known as pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), as well as detecting the damage caused by pathogens, known as damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) [24]. This triggers an intracellular signalling cascade, leading to production of effector proteins and recruitment of innate immune cells (Table 1). There has been a large effort to increase our understanding of PRRs involved in antifungal immunity. C-type lectin receptors (CLRs), such as Dectin-1 and Mincle, are PRRs that have been demonstrated to detect fungi. Dectin-1 specifically detects β-1,3-glucan, a fungal cell wall carbohydrate, stimulating NF-κB signalling, inflammasome activation, phagocytosis and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [25]. Double stranded RNA (a PAMP usually associated with viral infections) in A. fumigatus infection is detected by RIG-I-like receptors, which stimulates MDA5/MAVS signalling. Type III interferon expression is entirely reliant on MDA5/MAVS, whereas Type I interferon expression was also triggered through alternative mechanisms [26]. Type III interferon appears to be a critical regulator in neutrophil activation and antifungal immunity [27], suggesting MDA5/MAVS signalling is critical in the antifungal immune response.
Table 1. Pattern recognition receptors in fungal infection.
| Pattern Recognition Receptor | Localisation | Cell Expression | Adaptor Proteins | Effectors | Pathogen-/Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns Recognised | Fungal Species | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLR2 | Plasma membrane | Monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, mast cells, neutrophils | MyD88, Mal | NF-κB, TNF, TGFβ, IL-10, IL-12, IFNγ | Phospholipomannan, β-glucans | C. albicans, A. fumigatus, P. brasiliensis | [28,29,30,31] |
| TLR4 | Plasma membrane, endosome membrane | Monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, mast cells, neutrophils, B cells, intestinal epithelium | MyD88, Mal, TRIF, TRAM | NF-κB, TNF, IL-8, Type I IFN | O-linked mannosyl, Mannan, Glucuronoxylomannan | C. albicans, A. fumigatus | [28,29,30,31] |
| TLR7 | Endosome membrane | Monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, B cells | MyD88 | IFN-β, Type I IFN | ssRNA | C. albicans | [28,30,31,32] |
| TLR9 | Endosome membrane | Monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, B cells | MyD88 | NF-κB, IL-12, TNFα | Unmethylated DNA with CpG motif | Candida spp., C. neoformans, A. fumigatus, P. brasiliensis, M. furfur | [28,30,31,33,34] |
| Dectin-1 | Plasma membrane | Monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, mast cells, some T cells | hemITAM | IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, IL-23 | β-1,3-glucans | Candida spp., C. neoformans, A. fumigatus, H. capsulatum, S. cerevisiae, P. brasiliensis | [28,30,31] |
| Dectin-2 | Plasma membrane | Monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils | ITAM-FcRγ | TNFα | Mannose | C. albicans, C. glabrata, C. neoformans, A. fumigatus, H. capsulatum | [28,30,31] |
| Mincle | Plasma membrane | Monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, mast cells, some B cells | ITAM-FcRγ | NF-κB, IL-1, IL-6, IL-10 IL-12, IL-23 | α-mannose, glyceroglycolipid, mannosyl fatty acids, MSG/gpA | A. fumigatus, C. albicans, P. carinii, Malassezia spp. | [30,31,35] |
| DC-SIGN | Plasma membrane | Macrophages, dendritic cells, activated B cells | LSP1 | IL-10 | Mannose, N-linked mannans, galactomannans | C. albicans, C. neoformans, A. fumigatus, S. cerevisiae | [28,30,31] |
| Mannose Receptor | Plasma membrane | Macrophages, Kupffer cells, endothelial cells | Associated with FcRγ and GBR2, exact mechanism unknown | TNF, IL-1β | Mannose, α-glucans, chitin | C. albicans, C. neoformans, A. fumigatus, H. capsulatum, S. cerevisiae, P. brasiliensis | [28,30,36,37] |
| MDA5 | Cytoplasm | Monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, B cells, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts | CARDs, MAVs | NF-κB, Type I IFN, Type III IFN, TNFα, IL-12, | dsRNA | C. albicans, A. fumigatus | [26,30] |
3. Macrophages
Macrophages are a key innate immune cell type in fungal infection control. Recruitment of macrophages to sites of fungal infection is a highly dynamic process. Macrophages cluster around A. fumigatus infection in zebrafish and play a role in preventing the yeast-to-hyphae transition, which is associated with increased pathogenicity [38]. The number of macrophages in clusters was highly dynamic, though whether decreases in macrophage density was caused by reverse migration, apoptosis/pyroptosis or cell death was not revealed. In silico analysis of Mucor circinelloides infection, supported by observations in zebrafish models of infection, revealed the number of phagocytes present at the site of infection is critical to infection control [39]. The size of macrophage clusters may play a crucial role in control of fungal infections. Resident tissue macrophages have been demonstrated to congregate and “cloak” tissue microlesions with pseudopods in an in vivo mouse sterile injury model, which concealed pro-inflammatory debris, prevented neutrophil swarming and reduced collateral tissue damage caused by neutrophil-mediated inflammation [40]. Though not yet shown in a model of fungal infection, macrophage clustering may similarly facilitate cloaking of damage caused by fungi, limiting the pro-inflammatory neutrophil response and preventing excess tissue damage. Conversely, damage caused by fungi could be too large to effectively cloak, permitting the hyperinflammatory response and collateral tissue damage observed in alternative models of fungal infection [41].
Following recruitment, the primary mechanism of pathogen clearance by macrophages is phagocytosis. Macrophage PRRs or Fc receptors bind to fungal PAMPs or opsonising antibodies, respectively, triggering engulfment of the fungus [42]. Two mechanisms of fungal engulfment have been described: zipper phagocytosis and coiling phagocytosis (Figure 1) [43,44]. Phagocytosis of C. neoformans is typically facilitated by crosslinking of Fcγ receptors and C. neoformans bound IgG antibodies. Inability to form lipid rafts with closely localised Fcγ receptors prevents IgG mediated phagocytosis, though complement mediated phagocytosis is unaffected [45]. Following investigation in mouse knockout models, Anion Exchanger 2 has been suggested as a critical regulator of engulfment, through regulation of Dectin-1 expression, and fungal killing, by affecting intracellular pH homeostasis in macrophages [46]. Engulfed fungi are held in the phagosome, which fuses with the lysosome to form a phagolysosome. Acidification of the phagolysosome allows fungal degradation by acid-dependent proteases (such as Cathepsin D), combined with fungal killing by ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) [42,47,48]. Hatinguais et al., demonstrated mitochondrial ROS, produced via reverse electron transport, not only contribute to the destruction of phagocytosed A. fumigatus conidia, but also trigger production of TNF-α and IL-1β in vitro, stimulating further antifungal responses [49]. Although inhibition of mitochondrial H2O2 impaired phagocytosis of A. fumigatus by alveolar macrophages in a mouse model, neutrophil activity was not impaired and survival and fungal burden were not affected [50]. Hence, while mitochondrial ROS are important in for the antifungal activity of alveolar macrophages, NADPH oxidase activity is able to compensate effectively, displaying redundancy in the host antifungal response. While lysosomal degradation is the typical outcome of phagocytosis, macrophage-to-macrophage transfer (termed “Dragotcytosis”) of C. neoformans has also been observed in vitro [51]. Shah et al., observed a similar phenomenon in A. fumigatus infection. Hyphal growth of phagocytosed A. fumigatus caused macrophage necrosis, triggering macrophage-to-macrophage transfer of germinating A. fumigatus, preventing fungal escape [52]. Unlike dragotcytosis, transfer of A. fumigatus was macrophage necrosis-dependent. However, the biological significance of these phenomena is unknown. Vomocytosis (also referred to as nonlytic exocytosis) is the expulsion of phagocytosed particles without degradation into the extracellular environment and occurs in macrophages in vitro during C. albicans and C. neoformans infection [53,54]. In mammalian in vitro and zebrafish in vivo models of cryptococcosis, vomocytosis is regulated by the MAP kinase ERK5. Viral infection and type I interferon signalling have been associated with enhanced rates of vomocytosis in vitro [55,56]. It is possible that the expulsion phase of dragotcytosis operates by a similar mechanism.
Phagocytosis of fungi is not always possible: C. albicans and A. fumigatus hyphae may become too long to phagocytose and Cryptococcus neoformans titan cells are too large to phagocytose [57,58,59]. Inability to phagocytose a pathogen typically leads to frustrated phagocytosis, a process in which there is downregulation of phagocytosis mechanisms and a strong inflammatory response mediated by IL-1β [60,61].
Phagocytosis of C. albicans can trigger a yeast-to-hyphae transition, leading to macrophage killing through mechanical piercing by hyphae or induction of pyroptosis, allowing escape of C. albicans [62]. To counteract this, macrophages are able to fold phagocytosed fungal hyphae at septal junctions (Figure 1), resulting in significantly reduced hyphal growth and disruption to the cell wall [63]. Exactly how much hyphal folding contributes to fungal clearance is unknown, however, this represents a previously uncharacterised macrophage function, which may be relevant to other hyphal pathogens.
Macrophages are a highly heterogenous population, existing on a spectrum of behaviours between M1, pro-inflammatory phenotypes and M2, wound healing phenotypes [64]. Proteomic analysis revealed a pro-inflammatory to wound healing phenotypic switch in C. albicans infection, whereas C. neoformans infection drives macrophages into a naïve M0 phenotype [65,66]. Stimulating an M1 phenotype led to decreased fungal burden and increased survival of mouse models in C. albicans and C. neoformans infection [67,68]. Promotion of an M2 phenotype in A. fumigatus infection reduces control of infection, corresponding with the other fungal pathogens [69]. This reveals a mechanism to avert pro-inflammatory macrophage polarisation to the detriment of the host, driven by immunosuppressive drugs (e.g., steroids) or interactions with fungal pathogens. It could be possible to improve outcomes of fungal infection by therapeutically promoting M1 macrophage polarisation, though this must be done with caution to prevent excess, harmful inflammation.
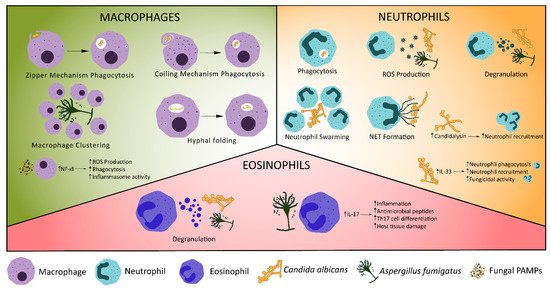
Figure 1. Cellular Innate Immune Control of Fungal Infections. Various mechanisms exist for the control of fungal infections by the innate immune system. Macrophages phagocytose fungi, undergo macrophage clustering or fold phagocytosed hyphae. Recognition of fungal ligands, such as candidalysin, stimulates production of IL-1β, triggering neutrophil recruitment [70]. Increased expression of IL-33 in C. albicans infection triggers neutrophil recruitment and phagocytosis [71]. Neutrophils may also release reactive oxygen species (ROS) or neutrophil extracellular traps, degranulate, phagocytose fungi or undergo swarming. Eosinophils have antifungal effects through degranulation [72] and production of IL-17, which stimulates pro-inflammatory signalling, production of antimicrobial peptides and Th17 cell differentiation [73,74].
4. Neutrophils
Neutrophil recruitment to fungi, like macrophages, is driven by detection of PAMP/DAMPs by PRRs (Table 1). Mincle binds α-mannose and other fungal cell wall components, resulting in pro-inflammatory signalling and recruitment of neutrophils [30,75]. RIG-I-like receptor detection of double stranded RNA stimulates a strong neutrophil-mediated antifungal response via MDA5/MAVS signalling [26,27]. Candidalysin, produced by hyphal C. albicans, appears to be a potent stimulator of innate immune responses in mucosal, central nervous system and systemic infections [70,76,77]. Candidalysin stimulates IL-1β production via a CARD9-dependent mechanism, which in turn leads to CXCL1-mediated recruitment of neutrophils [70]. TRAF1 (induced by the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF) inhibits CXCL1 in C. albicans infection [78,79], suggesting a regulatory role for TRAF1 to prevent excess neutrophil recruitment and activation. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) may also be key for immune responses to candidalysin. Inhibition of EGFR in mouse models of oral candidiasis reduces IL-1β and CXCL1 [80,81], suggesting EGFR may be the initial receptor responsible for CXCL1-mediated neutrophil recruitment. Neutrophil recruitment and survival are also reduced by EGFR inhibition, providing strong evidence of the link between candidalysin, EGFR and CXCL1-mediated neutrophil recruitment. IL-33 is another key mediator of neutrophil recruitment [82] and IL-33 knockout mice have increased mortality in C. albicans infection. Based on in vitro primary cell models, IL-33 operates via IL-23 and GM-CSF to promote phagocytosis by neutrophils [71]. IL-33 also suppresses IL-10 expression, resulting in superior fungicidal activity by neutrophils in vitro. IL-10 expression has been associated with persistent C. albicans infection in other in vitro data [83], which may be due to reduced neutrophil activity. IL-23 has additional mechanisms of aiding antifungal immunity. IL-23 deficient mice have increased myeloid cell apoptosis, resulting in reduced survival in systemic C. albicans infection [84]. Interestingly, this occurred independent of IL-17 and was unique to fungal infections.
Neutrophils have been shown to coordinate their migration to sites of infection through a process called neutrophil swarming [85]. Swarming inhibits the growth of several fungal pathogens in vitro: C. albicans, C. auris, Candida glabrata, C. neoformans and A. fumigatus [86,87,88]. Swarms were smaller for yeast-locked C. albicans, C. auris and C. glabrata (which are unable to hyphate) compared to wild type C. albicans [87]. Furthermore, using an in vitro model of A. fumigatus infection, swarms appeared to preferentially form around hyphae [88]. This implies a potential correlation between hyphae formation and neutrophil swarming, which requires further investigation. Swarming in fungal infections is dependent on LTB4, meaning it operates by the same mechanism as swarming in other infections or injury [86,89,90].
Following migration to sites of infection, neutrophils have several mechanisms to eliminate fungal pathogens, including phagocytosis and degradation in the phagolysosome, degranulation, production of ROS and neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) release (Figure 1). Neutrophils produce granules containing a range of bactericidal and fungicidal effectors, including myeloperoxidase, cathepsins, defensins and lactoferrin [91]. The secretion of effectors in degranulation leads to fungal killing and is preferentially used in Candida infections with pseudo-hyphae [92]. Degranulation was dependent on CXCR1 in C. albicans infection in a mouse model, demonstrating a novel function of murine CXCR1 which correlates with evidence that human CXCR1 promotes oxidative and non-oxidative bactericidal activity by neutrophils [93,94]. Neutrophils also produce ROS, such as superoxide or hydrogen peroxide, which can be used intracellularly to kill phagocytosed fungi, or extracellularly to target hyphae [95,96]. Neutrophils are capable of expelling chromatin covered in antimicrobial proteins, leading to entrapment and killing of extracellular pathogens [97]. These neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs; Figure 1) are host protective against C. albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans and Aspergillus nidulans in in vitro human neutrophil models [87,97,98,99] and may be involved in swarm initiation [87,100]. NETs have also been demonstrated to directly stimulate Th17 cell differentiation, via TLR2 and RORγt, corresponding with increasing IL-17 and GM-CSF production [101]. IL-17 and GM-CSF both stimulate neutrophil activity in fungal infection [71,102], creating a feedback loop, in which NETs promote an adaptive immune response and additional neutrophil activity. A subpopulation of neutrophils also produce IL-17, which may further feed into this positive feedback loop [103]. Recent evidence suggests NETosis induced by C. albicans can occur independent of Peptidylarginine deiminase 4 (PAD4), contradicting established literature that NETosis is PAD4-dependent [104,105,106,107]. Alternative studies demonstrated PAD4 is not necessary for NET formation or neutrophil-mediated control of A. fumigatus infection [108,109]. Further research is needed to clarify whether PAD4-independent NETosis is a non-canonical mechanism of NETosis for all stimuli or is a phenomenon unique to fungal infections. Despite their fungicidal role, NETs may have an overall detrimental effect on the host. NET proteins intended to eliminate fungi have been observed bound to, but not killing, C. albicans and inducing apoptosis of host cells [110]. Furthermore, inhibition of NETosis reduced A. fumigatus burden in mouse models of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis [111]. However, these experiments inhibited NETosis by generating PAD4 knockout mice, which does not account for the possibility of PAD4-independent NETosis. Alternative methods of NETosis inhibition may be required to provide greater support to these conclusions.
Transfer of phagocytosed A. fumigatus conidia from neutrophils to macrophages by a β-glucan dependent mechanism has been observed in zebrafish [112]. The function of shuttling, and significance in fungal clearance, remains unclear, with conflicting arguments stating shuttling is a fungal strategy to avoid degradation by neutrophils or that shuttling is a host strategy to facilitate antigen presentation and initiate adaptive immune responses [38,112].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/jof8080805
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
