Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) is a common cause of acute kidney injury in patients with malignancies, and it is a frequent condition for which the nephrologist is consulted in the case of the hospitalized oncological patient. Recognizing the patients at risk of developing TLS is essential, and so is the prophylactic treatment. The initiation of treatment for TLS is a medical emergency that must be addressed in a multidisciplinary team (oncologist, nephrologist, critical care physician) in order to reduce the risk of death and that of chronic renal impairment. TLS can occur spontaneously in the case of high tumor burden or may be caused by the initiation of highly efficient anti-tumor therapies, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, dexamethasone, monoclonal antibodies, CAR-T therapy, or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. It is caused by lysis of tumor cells and the release of cellular components in the circulation, resulting in electrolytes and metabolic disturbances that can lead to organ dysfunction and even death.
- cancer
- chemotherapy
- toxicity
- tumor lysis syndrome
1. Introduction
2. Definition and Classification
| Cairo–Bishop Definition of Tumor Lysis Syndrome | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory TLS = modification of at least 2 parameters within 24 h |
|
Or 25% increase | within 3 to 7 days after chemotherapy initiation |
|
Or 25% decrease | ||
| Clinical TLS = laboratory TLS + 1 organ dysfunction or death |
|
||
-
changes of the laboratory parameters must be simultaneous within 24 h because the patient may develop one abnormality, and later on another, unrelated to TLS (e.g., hypocalcemia associated with sepsis);
-
symptomatic hypocalcemia has to be a criterion for clinical TLS, even when the decrease in calcium level is less than 25% of baseline;
-
a 25% variation of a parameter is significant for the diagnosis only if it causes symptoms or if the value is not within the normal range [3].
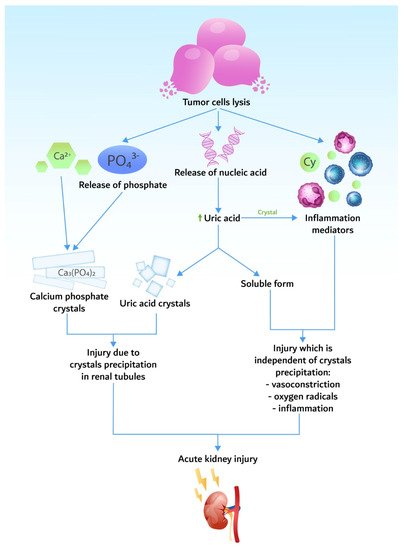
3. Pathogenesis
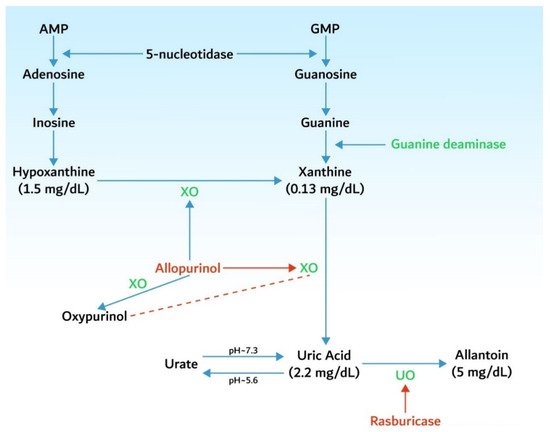
3.1. Hyperuricemia
3.2. Hyperkalemia
3.3. Hyperphosphatemia and Hypocalcemia
4. Epidemiology
| Germ cell tumors |
| Neuro- and medulla blastomas |
| Small cell carcinoma and other lung tumors |
| Breast, ovarian, and vulvar neoplasms |
| Hepatoblastoma and hepatocellular carcinoma |
| Colorectal and gastric carcinoma |
| Melanoma |
| Sarcoma |
5. Identification of Patients at Risk
| Tumor Risk Factors | Patient-Related Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| Type of tumor | Male gender |
| Tumor volume (tumors > 10 cm) | Age > 65 years |
| Metastatic disease | Pretreatment serum creatinine > 1.4 mg/dL |
| Tumor growth rate (LDH > 2 times NV) | Renal obstruction |
| Level of leukocytosis (>25,000/mm3) | Pretreatment serum uric acid > 7.5 mg/dL |
| Sensitivity to chemotherapy (germ cell tumors, small cell lung cancer, etc.) | Associated conditions (hypotension, hypovolemia, nephrotoxic drugs, CKD) |
6. Tumor Lysis Syndrome Management
6.1. Prophylaxis
-
every 4 to 6 h after antitumor therapy initiation for patients at high risk;
-
every 8 to 12 h for patients at intermediate risk;
-
daily for patients at low risk.
-
to avoid the nephrotoxic drugs (NSAIDs, contrast agents);
-
to stop the treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers.
6.2. Treatment
Renal Replacement Therapy
-
daily hemodialysis;
-
continuous veno-venous hemofiltration;
-
combination of intermittent hemodialysis and continuous hemofiltration/hemodiafiltration for an efficient clearance of phosphate, which is time dependent. These techniques use dialysis membranes with large pores, which allow for rapid clearance of molecules that otherwise are not efficiently removed by conventional hemodialysis.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/biomedicines10051012
