Technoversal Leadership is a theory that goes beyond leader-follower interactions and business concerns such as growth and profit. This style has a discipline to a global understanding of biodiversity loss, climate, and environmental consciousness and the leader rising with them; Technoversal Leadership theory roots where these global crises, technology, and adaptable qualities intersect.
- Technoversal Leader
- APARTS Behaviors
- DOER Leader
- DOER Behaviors
- T-Leaders
- Self-Created-Problem-Solution Cycle
- Technology Effect on the Leader
- Skill-Based Leadership
- Big Ten of Leadership
- Gold Medalist Behaviors
The word Technoversal derives from technology and universal. While the former refers to the leader’s need to become data-driven and tech-savvy, the latter is for the Technoversal Leader’s willingness to act upon these universal crises.[1] Universal additionally refers to skills and behaviors extracted from research conducted worldwide.
Technoversal Leader employs these behaviors to improve followers’ emotional and mental condition, enhance moral principles, and task completion. The leader empathically understands their capacity and supports them. Technoversal leaders can handle troublesome tasks and situations.
The leader can create a sense of belonging and collective identity, which increase ownership of the work. Depending on mutual respect, followers tend to strive for leaders to become successful. It enhances setting goals and inspires all to achieve them.
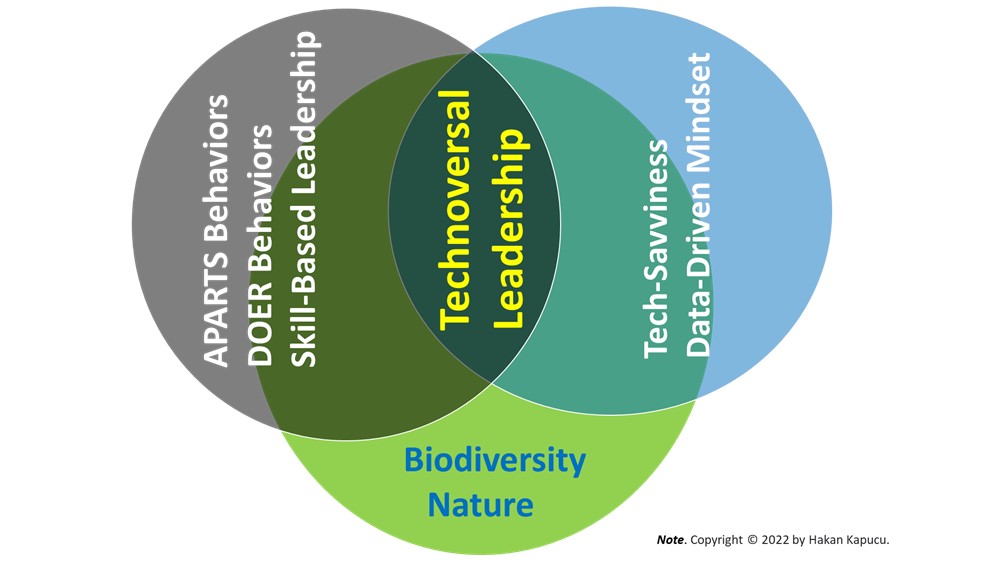
One of the core elements of this model is to connect business leadership to nature, climate, and biodiversity. It creates a new bond among leaders, animals, and natural habitats.[2] Along with a well-defined skillset, the Technoversal style becomes a promising one.
Needs and Origin
There is a need for a new perspective in leadership. While floods, fires, climate change, and resource scarcity threaten the earth, the world population has increased. Humans drove 83% of mammals and half the plants extinct since civilization. It was notably very severe in the past several decades.[3]
When the situation is so tragic, business leaders ought to take responsibility for stopping this. A leadership that places biodiversity and climate consciousness at its center become essential. When we look at it from businesses’ perspectives, the number of leaders having necessary behaviors and skills is not enough.[4] Most leaders believe their organizations need new leaders to compete in the digital age.[4][5] So, there is also a need for Skill-Based Leadership.
The need for Technoversal Leadership arises from the planet’s and businesses’ needs. Leadership styles have different definitions, and each has its core perspective. While one leader dedicates himself to serving his followers, the other transforms and another may have democracy at its core. So the core idea might differ according to style. The need that makes people gather around the leader is usually disorder or chaos. ‘’ So, leadership is the child of chaos and disorder.’’[2]
Finding and identifying these needs caused Hakan Kapucu to create Technoversal Leadership and introduce it in his dissertation in 2020.[6]
Characteristics and Skills
With changing leader-follower interactions, these times require leaders to possess new skills. Additionally, technology and digital ages open new gates and bring debates on leadership concepts. Each leadership usually comes with its core concepts and behaviors. Sometimes, it may not be easy to decide on a leadership style for prospective leaders in the abundance of styles.[7]
As different leadership styles usually have some expected behavioral properties, too many behaviors and skills eventuate. Many consultant companies and scholars define them as essential in literature. As skills and behaviors play a very significant role in leadership success, during the creation of Technoversal Leadership, the researcher conducted multifaceted research to reveal the most-needed behaviors and skills.[6]
Skill-Based Leadership
Technoversal Leadership builds on skill and behavior that have a well-defined framework. These skills allow the leader to go beyond business concerns and leader-follower interactions. Some core behaviors are empathy, respect, and perspective seeking, and they help the leader become an ideal role model for the followers. The leader is creative, inventive, and innovative. The leader tolerates and sees followers’ potential.
Technoversal Leader has two central and distinguishing behavioral sets. These behaviors facilitate and empower the leader to answer the challenges of any age and rise with ground-breaking perspectives.[8]
APARTS Behaviors
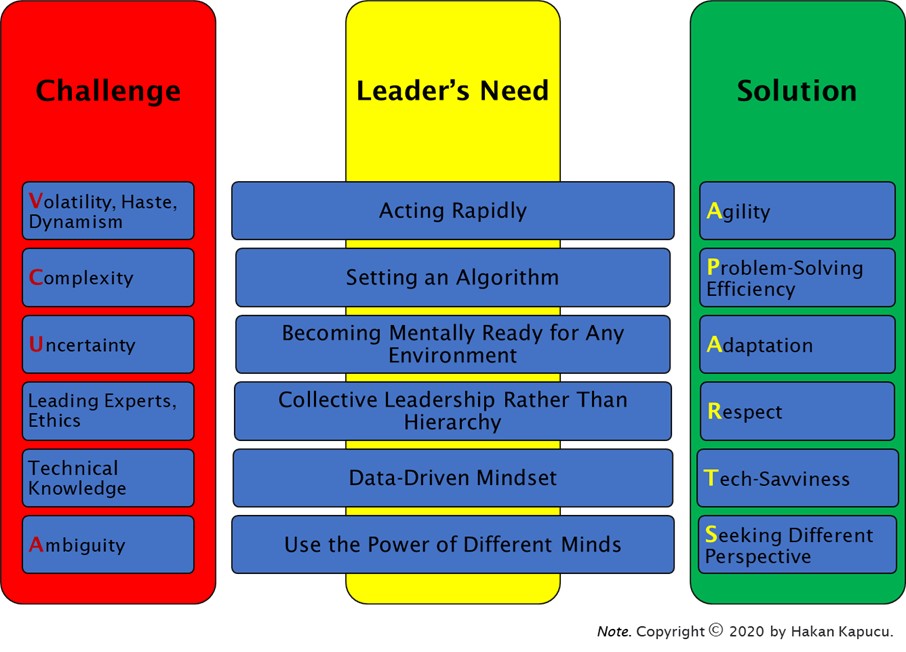
APARTS Behaviors stand for a set of skills. They are Agility, Problem solving-efficiency, Adaptation, Respect, Tech-savviness, and Seeking different perspectives. Extracted from multi-stage research that aimed to determine the in-demand behaviors of today and future leaders, they are to fill skill gap which may occur because of disruptive environments and causes poor outcomes for organizations. They link leaders and organizations to their goals and make them accomplish them.[1]
DOER Leader and DOER Behaviors
Leader and doer are words that commonly come together to denote different functions in task completion. While a doer would be a person who puts assignments into execution, a leader empowers or delegate the doer. In literature, these are not rare ‘’do not be doer, be a leader’’ or ‘’shift from doing to leading.’’ But here, DOER, an acronym in uppercase, stands for another set of specific behaviors. And the leader who embarks on DOER Behaviors is a DOER Leader.
Diligence, Opportunism, Empathy, and Resilience are notable qualities that inspire the creation of the DOER concept.[9]
These worthy behaviors make the other set that a Technoversal Leader possesses.[2][9]
Big Ten of Leadership: Gold and Silver Medalist Behaviors
APARTS Behaviors come from multi-faceted research and the first created concept. So they make Gold Medalist Behaviors in a leader’s skill set. Then DOER Behaviors are contributed, and they matter to leaders. Thus, they become Silver Medalist Behaviors. APARTS and DOER make the Big Ten of Leadership for a Skill-Based Leader. These behaviors found by research or meticulously chosen through experience and observation will make the leader meet conventional business expectations.[9]
T-Leaders
T-Leaders is the group of leaders that covers Transformational, Transactional, and Technoversal styles. Hakan Kapucu named T-Leaders to look and gain insight into business leader environment interactions.[10][2]
Transformational Leadership is a leader’s capability to impact followers’ beliefs, values, and attitudes for accomplishing the goals of an organization.[11] It is an approach that may have the potential to make changes in individuals and systems.[12]
Transactional Leadership focuses on the role of supervision and group performance. These leaders assign tasks to their employees and use reward-punishment.[13] Transactional leader incessantly monitors subordinates and take immediate action when needed.[14]
Outcomes
Like governments and people, businesses have responsibilities for biodiversity, nature, and climate. So, new business leaders must grow with this consciousness. Many parts of the earth only have a few generations to become uninhabitable.[15]
Technology is a solution mechanism to many problems, yet it may trigger environmental issues because of human errors and feelings. For example, after the industrial revolutions, businesses used new machines that polluted the environment. On the other hand, they produced other equipment to reduce this pollution’s effect. It turns into a self-created-problem-solution cycle that destroys nature.[2][1] A Technoversal Leader uses technology as a means for good.[16]
Technology Effect on the Leader
Technology vigorously keeps becoming a significant factor that shapes leadership. With rapid technological advancements, leaders change as well. The environment forces them to challenge, disrupt, and embrace new phenomena and styles.[1] With social and emotional intelligence, leaders also require a shift to technical skills.[17] Leaders need to make data-driven decision-making, which is a challenge for them.[18]
APARTS Versus VUCA
VUCA is in the business lexicon, an acronym with the components volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity.[19] It challenges and impacts governments, industries, public corporations, small-medium enterprises, organizations, and thus businesses.[20] APARTS Behaviors can take the leader beyond the time and ahead of the crowd. They enable the leader to solve VUCA challenges and many more issues that leaders face today and in the future.[21][22][7][1][6]
The Future of Leadership
A leader may adopt and employ a particular style, and a leader may exhibit the characteristics of more than one leadership style.[23] Leadership and its framework must be clear to prospectives to make a choice.
Some say Transformational is the best.[24] Others find Servant Leadership positively influences employee engagement.[25] According to the situation, there are different bests will be another approach to styles—a situational approach.[26]
One leadership style may not be enough, and one leader may not possess all the leadership styles: One is not enough, and all is not possible. It can cause a contradiction to both exhibiting one style and different leadership styles for different situations. It makes universally-accepted skills and behaviors ideal rather than leadership styles.
Servant, Laissez-faire, Democratic, Charismatic, Self-Disruptive, Transpersonal, Altrocentric, Leadership 4.0, Digital, and Agile are some old and new leadership styles. This list extends. In such a plethora, a leadership style should have a determined framework and clear guidance to prospectives to make the right choice.
Styles usually spin around leader-follower, growth, and profit circles. But a leadership style must answer to the world’s one actual issue, and it must give simple solutions to complex problems. Except for this, any leadership will be just another item on the long list of leadership styles.[7] Along with answering the businesses’ traditional expectations about leaders and followers, current global crises made the world reach a point where business leaders must pass beyond these conventional expectations and take responsibility.[2][10]
Leadership, Biodiversity, and Climate
A Technoversal Leader’s skills can fill the gap between an organization and its goals, and these skills can make the organization accomplish its goals.[1] This leadership arises both for the Earth’s needs and business needs. So it becomes a bond between business leaders and the environment, biodiversity, climate, and nature as these factors must urgently be one of the central elements of leadership.[6][2][10]
The International Union for Conservation of Nature held the first-ever IUCN CEO Summit with more than a dozen global businesses, and they addressed climate change and biodiversity loss.[27] In light of extinctions and current threats, it is clear that their ethical responsibility is to get involved in these matters much more. Environmental ethics must be part of leadership, and leaders must grow with a consciousness of biodiversity protection and nature conservancy. This need is one of the core reasons that Technoversal leadership is born.
Leader-follower interactions and growth were central for businesses when they created leadership styles. Consultant companies usually consider these aspects as the main criteria while analyzing leadership. Many decades passed, and the needs changed. The world reality is not only economic development today. Corporations hold a strong position in presiding over the world. Their leaders play a significant role, and these leaders can communicate the necessities to their followers and spread the good like a Messenger. Technoversal Leader conveys these vital messages.
‘’ If we wish to change the destiny of our planet, we must change businesses. To transform businesses into this course, we must change leaders.’’ The capacity to answer these urgent needs and do all these good things make a Technoversal Leader stand apart from the others.[2]
References
- Kapucu, H. (2020). Technology effect on the leader behaviors in the digital era. Business & IT, 10(2), pp. 12-31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14311/bit.2020.03.02
- Kapucu, H. (2022). Technoversal leadership for biodiversity and climate. Unsustainable Magazine. Retrieved from https://www.unsustainablemagazine.com/biodiversity-technoversal-leader/
- Carrington, D. (2018). Humanity has wiped out 60% of animal populations since 1970, report finds. Retrieved from https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2018/oct/30/humanity-wiped-out-animals-since-1970-major-report-finds#
- Korn Ferry. (2019). The self-disruptive leader. Retrieved from https://focus.kornferry.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/KF-Disruptive-LeaderFinal-Digital-Spreads_FINAL.pdf
- Kane, G. C. (2018, July). Common traits of the best digital leaders. MIT Sloan Management Review. Retrieved from https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/common-traits-of-the-best-digital-leaders/
- Kapucu, H. (2020). The effect of digital transformation on the leader behaviors: An implementation at intermediate goods industry. Master's Thesis, Bahcesehir University, Istanbul, Turkey, pp. 1-84. Retrieved from https://tez.yok.gov.tr/UlusalTezMerkezi/TezGoster?key=fl0Kw4p1rmMDotyKRdYv1B4RXrWKR7W0Gae_P9Uw2d0NNEF45ek-Cr5L_M3-oobZ
- Kapucu, H. (2021). A contradiction for prospective leaders: Would adopting styles confuse them? The People Development Magazine. Retrieved from https://peopledevelopmentmagazine.com/2021/11/21/prospective-leaders/
- Kapucu, H. (2021). Business leaders’ perception of digital transformation in emerging economies: On leader and technology interplay. International Journal of Advanced Corporate Learning, 14(1), pp. 43-56. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3991/ijac.v14i1.21959
- Kapucu, H. (2022). Be a leader rather than a doer. How about a DOER Leader? HCM Excellence APAC & Middle East, 4(01). Retrieved from https://www.hr.com/en/magazines/all_articles/be-a-leader-rather-than-a-doer-how-about-a-doer-le_kyjogynq.html
- Kapucu, H. (2022). Technoversal leadership for climate and biodiversity. The People Development Magazine. Retrieved from https://peopledevelopmentmagazine.com/2022/04/29/leadership-biodiversity-and-climate/
- Bass, B. & Riggio, R. (2014). Transformational Leadership. New York: Routledge.
- Langston University. Retrieved from https://www.langston.edu/sites/default/files/basic-content-files/TransformationalLeadership.pdf
- Jaqua, E. & Jaqua, T. (2021). Transactional Leadership. American Journal of Biomedical Science & Research. DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2021.14.002021
- Cole, M. S., & Bedeian, A. G. (2007). Leadership consensus as a cross-level contextual moderator of the emotional exhaustion – work commitment relationship. The Leadership Quarterly. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2007.07.002
- Young, R. & Mitchell, J. (2019). Humans have 30 years to stave off climate catastrophe, ‘Uninhabitable Earth’ author says. Retrieved from https://www.wbur.org/hereandnow/2019/05/13/climate-change-uninhabitable- earth-david-wallace-wells
- Kapucu, H. (2020). Technoversal leader: Triumphant leader of the technological era. International Journal of Progressive Sciences and Technologies, 23(1), pp. 440-446. Retrieved from http://ijpsat.es/index.php/ijpsat/article/download/2313/1330
- Cortellazzo, L., Bruni, E., & Zampieri, R., (2019). The role of leadership in a digitalized world: A review. Frontiers in Psychology, August 2019, 10, pp. 1-2, 11-13. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01938.
- Hesse, A., (2018). Digitalization and leadership – how experienced leaders interpret daily realities in a digital world. Proceedings of the 51st Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. Retrieved from https://scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/handle/10125/50121
- Bennett, N. & Lemoine, G. J. (2014). What a difference a word makes: Understanding threats to performance in a VUCA world. Business Horizons. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/263926940_What_VUCA_really_means_for_you
- Chadha, A. & Sharma, R. (2021). VUCA Challenge: Transforming Business Models in the Current Era. In Emerging Perspectives in Management, Entrepreneurship and Innovation (pp.3-8). Publisher: Falcon Publishers.
- Kapucu, H. (2021). Digital leadership: A new way of leading or a crucial skill? Leadership Excellence, 38(09). Retrieved from https://web.hr.com/jl0w
- Kapucu, H. (2021). Digital leadership: A new way of leading or a crucial skill? HCM Sales, Marketing & Alliance Excellence , 20(09). Retrieved from https://www.hr.com/en/magazines/all_articles/digital-leadership-a-new-way-of-leading-or-a-cruci_ktvgvkfr.html
- Kapucu, H. (2019). A car for everyone: An inspiring visionary made American dream come true. Project paper. DOI:10.13140/RG.2.2.28811.41768
- Manurung, H. (2018). The Best Leadership Model for Organizational Change Management: Transformational Leadership. Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3127364 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3127364
- Canavesi, A. & Minelli, E. (2021). Servant leadership and employee engagement. Employee Responsibilities and Rights Journal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10672-021-09389-9
- University of Pennsylvania. (2019). Which Leadership Style Is Best for Your Team? Retrieved from https://online.wharton.upenn.edu/blog/which-leadership-style-is-best-for-your-team/
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (2021, September). Global business leaders outline efforts to build a nature-positive future at IUCN CEO Summit. Retrieved November 12, 2021, from https://www.iucn.org/news/business-and-biodiversity/202109/global-business-leaders-outline-efforts-build-a-nature-positive-future-iucn-ceo-summit
