Businesses are reliant on data to survive in the competitive market, and data is constantly in danger of loss or theft. Loss of valuable data leads to negative consequences for both individuals and organizations. Cybersecurity is the process of protecting sensitive data from damage or theft. To successfully achieve the objectives of implementing cybersecurity at different levels, a range of procedures and standards should be followed. Cybersecurity standards determine the requirements that an organization should follow to achieve cybersecurity objectives and facilitate against cybercrimes. Cybersecurity standards demonstrate whether an information system can meet security requirements through a range of best practices and procedures. A range of standards has been established by various organizations to be employed in information systems of different sizes and types. However, it is challenging for businesses to adopt the standard that is the most appropriate based on their cybersecurity demands. Reviewing the experiences of other businesses in the industry helps organizations to adopt the most relevant cybersecurity standards and frameworks. This study presents a narrative review of the most frequently used cybersecurity standards and frameworks based on existing papers in the cybersecurity field and applications of these cybersecurity standards and frameworks in various fields to help organizations select the cybersecurity standard or framework that best fits their cybersecurity requirements.
- cybersecurity framework
- cybersecurity standard
- information security framework
- information security standard
- cybersecurity requirements
- information security requirements
1. Introduction
2. Cybersecurity Standards and Frameworks
|
Standard |
Framework |
|---|---|
|
|
3. Cybersecurity Standards—Information Security Standards
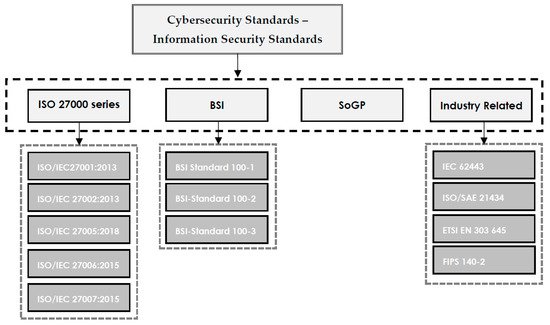
3.1. ISO/IEC 27000 Series
3.2. ISF Standard of Good Practice for Information Security
3.3. BSI IT-Grundschutz
3.4. Industry Related Standrads
4. Cybersecurity Frameworks—Information Security Frameworks
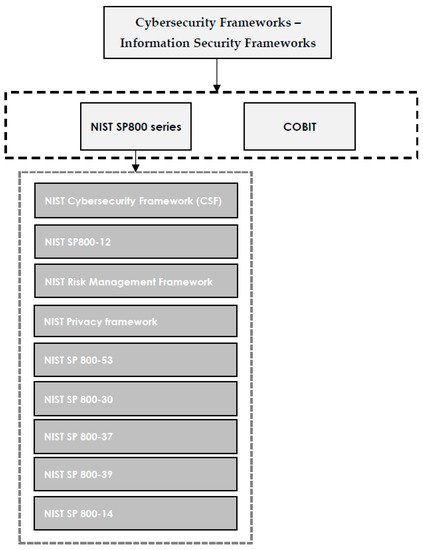
4.1. COBIT
4.2. The SP800 Standard Series
4.2.1. NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
The “cybersecurity framework” was established by NIST after the executive order was signed by President Obama in 2014. Furthermore, the role of the NIST was updated by the Cybersecurity Enhancement Act of 2014 (CEA) aiming to cover the identification and development of cybersecurity risk frameworks for critical infrastructure operators and owners. Existing business operations and cybersecurity concerns are covered in this framework. Thus, it can be referred to as a foundation for a new a mechanism or cybersecurity program to improve an existing program, which can be adopted as the best practices by organizations or private sectors to secure their own critical organization [44].
The NIST cyber security framework (CSF) helps organizations to increase their cybersecurity measures and provides an integrated organizing structure for different approaches in cybersecurity through collecting best practices, standards, and recommendations. In other words, a framework providing a means of expressing cybersecurity requirements can be effective to point out gaps in the cybersecurity practices of an organization.
4.2.2. NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF)
Every organization is required to follow a process with seven steps, including preparing, categorizing, selecting, implementing, assessing, authorizing, and monitoring in order to manage its privacy and information security risks [7]. This process is designed to be a comprehensive and measurable process that is repeatable at different times. This framework can be also employed in IoT-based environments to address growing privacy and security challenges.
4.2.3. NIST Privacy Framework
The NIST privacy framework [45] concentrates on addressing the concerns of organizations to detect and respond to concerns related to privacy and establish innovative services and products while considering individual privacy [7]. This framework is based on five major functions including identifying, governing, controlling, communicating, and protecting. This framework can also help managers to address privacy concerns in IoT-based environments.
4.2.4. NIST SP800-12
The core principles of cyber security are covered in detail in SP800-12 [10]. It was initially developed to be used in governmental and federal agencies; however, it can also be employed in other organizations focusing on computer security and controls [7]. The approach of the NIST is summarized in the SP800-12 series of standards clarifying the main elements, including the role of computer security in supporting the mission of the business, emphasizing the role of computer security in sound management, the importance of performing cost effective computer security, the importance of clearly defining accountability and responsibilities in computer security, emphasizing the role of system owners outside of the organization, emphasizing the employment of an integrated and comprehensive approach, the importance of assessing computer security on a regular basis, as well as the relationship between computer security and societal factors [7]. Thus, the handbook covers cost considerations, significant concepts, and the correlation between different security controls, eventually offering solutions to ensure that resources are secure [43].
4.2.5. NIST SP 800-53
This standard mainly concentrates on privacy and controls in information systems and organizations aiming to secure assets, individuals, and operations in organizations from different cyber threats, including human error, hostile attacks, failures in structure, natural disasters, privacy risks, and threats from foreign intelligence entities [7].
4.2.6. NIST SP 800-30
This standard mainly concentrates on providing guidance for the development of information systems risk assessment. Risk assessment plans are conducted using NIST SP 800-30 based on the recommendations and principles of the NIST standard. This standard facilitates the understanding of cyber risks for decision makers in the organization [43]. When decision makers realize the risks and issues mentioned by a technician, they can make smart decisions based on the available resources and budget [7].
4.2.7. NIST SP 800-37
This standard mainly concentrates on providing guidelines to apply a risk management framework in information systems and organizations. This standard presents guidelines for organizations to implement and manage privacy and security risks regarding the best practices in information systems. The responsibility to manage privacy and security based on this standard belongs to the top management team [7].
4.2.8. NIST SP 800-39
This standard mainly concentrates on guiding organizations to develop a program that is integrated with the aim of managing information security risks regarding the organizational mission, operations, reputation, functions, individuals, image, and organizational assets [43]. This structured and flexible approach specifically concentrates on assessing and monitor risks and responding accordingly. Moreover, this guide towards risk is not intended to take the place of other risk-related measures in organizations [7].
4.2.9. NIST SP 800-14
Commonly used security principles are described in NIST SP 800-14 to help users realize policies in cybersecurity. This standard equips organizations with requirements that they should follow to secure resources of information technology. Employment of NIST SP 800-14 ensures organizations of the readiness of their information technology security solutions in case of cyber threats [43].5. Discussion and Conclusion
Cybersecurity standards are significant for consideration in different organizations since they help businesses to identify best practices and methods for use to be equipped against cyber threats and the loss of valuable data [61,62]. These standards provide businesses with consistent metrics-based measures to ensure the effectiveness of methods and procedures that are employed to prevent and mitigate cyber threats [63].
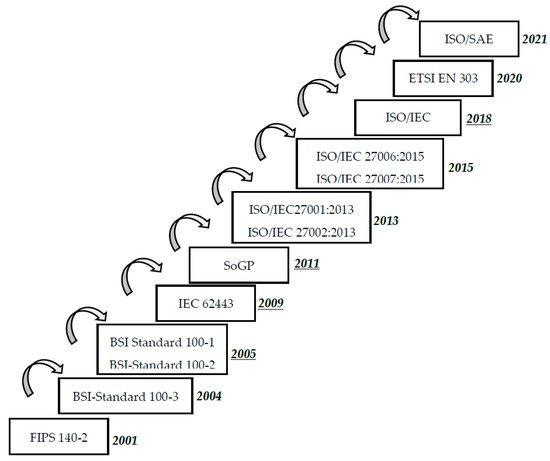
As noted in this study, there are plenty of cyber security standards to be employed that are different in scope and features. In this study, an overview of the most frequently used cyber security standards based on existing papers in the cyber security field, their features and application areas, has been developed and a narrative literature review was conducted by extracting 17 relevant papers that were published from 2000 to 2022 regarding cyber security standards considering the aim of each research, its main findings, relevant industry, and employed standards. Based on the review of these 17 papers in this study, several key contributions in information security standards have been investigated.
Breda and Kiss [46] introduced MIL STD 285 and IEEE-299-2006 as two appropriate standards to implement in electromagnetic shielding emission security in manufacturing based on the design of protected areas by investigating the appropriate standard to provide protective measures. However, among 17 reviewed papers, these two standards were the main focus of just on one article.
Referring to the findings of Siponen and Willison [47] in comparing validation and application of cyber security standards, BS ISO/IEC17799: 2000, BS7799, SSE-CMM, and GASPP/GAISP are standards that are universal and general to be employed in organizations of different sizes and natures.
According to Humphreys [48], who analyzed ISO/IEC 27001 in terms of following the management PDCA cycle and controls in response to insider threats in organizations of different sizes and natures, training personnel regarding security, handling critical information, access controls, the separation of duties, regular back-ups, social engineering, and mobile devices are recognized as major controls in ISO/IEC 27001 to deal with insider threats. Additionally, another study [58] has demonstrated the effectiveness of ISO17799 in addressing insider threats.
Moreover, Hemphill and Longstreet [49] have focused on data breaches in the U.S. retail economy, considering PCI DSS that is the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. PCI DSS is a standard in cyber security that is employed in the finance and banking industry for credit cards, debit cards, and pre-paid cards that are issued by Discover, American Express, MasterCard and Visa, and JCB International, among others. This standard is not compulsory to be implemented in the U.S.; however, the combination of self-regulation and market forces in industries that use cards significantly motivates the response to cyber threats.
Security management guidelines and network security guidelines including ISO/IEC 17799, ISO/IEC 24743, ISO/IEC TR 13335-5, ISO/IEC 18028, and ISO/IEC TR 15947 are reviewed by Fumy [28], who concluded that the role of human awareness to combat cyber threats is the most significant issue to be considered.
Moreover, Srinivas [27] analyzes cyber-attacks, along with security requirements and measures, and discusses CIMF, which is the architecture of the cybersecurity incident management framework. Then, introduces the main purpose of CIMF that is to develop an integrated management mechanism to respond cyber threats and incidents.
To compare PCI DSS and ISO17799 [50], both standards were reviewed by Rowlingson and Winsborrow, who finally concluded that although both standards have a lot in common in terms of aim and objectives, they differ significantly in terms of scope. ISO17799 is a general standard that can be employed in a wide range of organizations; however, PCI is applicable for a limited range of information systems, and its implication costs depend on the maturity of the systems and the security processes and controls within a system.
In studies that have been developed regarding security in the micro grid industry [51], an overview of cyber security standards that may be found useful in this regard has been developed. However, in all these studies, it was concluded that there is no significant standard to guarantee the security of a smart grid, and a combination of standards [53], or the one that is the best match based on the case, should be employed [59].
Broderick [52] analyzed security standards and security regulations, and BS-7799, ISO-17799, ISO-27001, and COBIT were recognized as the most popular information security frameworks and standards that are oriented toward each other. Moreover, the ISO-17799:2005 standard does not include any guide to implement network isolation except for auditing network physical isolation. Additionally, Lai and Dai [56] suggested the provision of a technique viewpoint and a management viewpoint for network isolation purposes.
From the review, it was also concluded that despite the fact that ISO 27500 and ISO 31000 complete each other [54], they do not make explicit reference to each other. Thus, ISO 27500 is just a framework that does not specify any certain method or control.
To evaluate the performance of standards in mobile and wireless communication [55], a prototype implementation has been designed to compare CSI, ADOPT, CPC-OCSP, CRLs, and SCVP standards and relevant resulting parameters, concluding that OCSP-based schemes perform better in comparison to other standards in the ICT industry. Considering security breaches as the result of employing the Internet of Things in smart homes, one study on cybersecurity standards [60] has concentrated on ENISA and DCMS standards as applicable standards for smart homes.
The paper presented the various types of information security standards and their applications in different fields to ensure the security of data against cyber threats. Based on their nature, some standards are considered mandatory for organizations to follow in order to become certified; however, some standards, such as ISO17799, are applicable to all types of organizations, regardless of their size and type. Moreover, in some cases, the application of one standard may not fulfill all the demands of an organization, and it may be necessary to employ a combination of standards in order to ensure security against cyber threats and data loss.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/electronics11142181
