Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Economics
Globalization and intense competition force organizations to be flexible and adaptable to constant changes in the market. According to many researchers, innovation is a crucial source of competitive advantage in the continuously changing environment. Many studies in the area of management present innovation as one of the most significant factors for enhancing organizational performance.
- managerial innovation
- technological innovation
- sustainable tourism development
1. Innovation Research
Innovation is considered as a crucial source of competitive advantage in a constantly changing environment [2,6]. Innovation capability is the most important determinant of organizational performance [9].
Definitions of innovation emphasize different aspects of the term. The first definition of innovation according to Schumpeter [11] is divided into “the categories of product innovation, process innovation, marketing innovation, input innovation and organizational innovation”. The European Commission [16] defined innovation as “new or renewed product/services, new markets, new production methods and changes in management”. Then, Hansen and Wakonen [17] stated that “it is practically impossible to do things identically”, which renders any change an innovation by default.
From Porter [18] until now, “not only innovation has been analyzed but also the factors that influence the ability to manage innovation”. Smith [19] identified some factors that affect the ability of a company to manage innovation. These key factors are “leadership/management style, resources, organizational structure, technology, corporate strategy, knowledge management, employees and innovation process”.
In addition, Peres [20] emphasized “the importance of innovation diffusion, as the process of new products, service market penetration that is empowered by social influences”. Many innovation studies focus on manufacturing firms [21,22,23,24,25,26,27].
However, researchers are also interested in service sector innovation [28,29,30,31,32]. Nevertheless, it must be noted that there are difficulties in measuring innovation because of the intangibility, interactivity, inseparability and variability of services [33,34]. For the above reasons, human resources (employees’ skills, abilities and experiences), organization of the innovation process, innovation outputs (service innovations can be adopted from competitors easily, so innovations must be constantly developed), communications technology (ICT) and intangibility information are the most important technologies for the service sector.
2. Innovation in the Tourism Industry
Innovation is a tool for achieving economic success, environmental sustainability and competitiveness. Thus, tourism firms should innovate constantly. It is also mentioned that innovation in tourism is quite valuable in creating a sustainable advantage for tourism destinations over other destinations [35,36,37], due to the speed with which competitors can copy successful ideas. Therefore, it is necessary that innovations be difficult for competitors to adopt. In the field of tourism, the types of innovations proposed by Abernathy and Clark [38] are
-
regular, which includes investing to increase productivity and training personnel to be more efficient in order to raise standards and quality;
-
niche, including firms taking advantage of business opportunities, increasing their network in the market and developing new products by combining existing ones;
-
revolutionary, involving applying new technologies in order to implement new methods in the market;
-
architectural, aiming to develop new attractions and events and transferring the use of new research-based knowledge, including processes performed in the most optimal way.
Later, Hjalager [39] presented five types of innovation, which are
-
product or service innovations: these include changes that can be noticed easily by customers (or tourists). They may be something “new” that they have not seen before or just new for the specific enterprise or at a particular destination;
-
process innovations: these are changes that aim to improve the levels of efficiency and productivity or technology in a company;
-
managerial innovations: these concern new ways of organizing business processes, compensating exemplary work with financial or non-financial benefits, empowering staff and improving employee satisfaction. Applying practices that retain employees are extremely beneficial in the tourism industry, as it is highly labor sensitive;
-
marketing innovations: these include new marketing concepts, such as co-production of brands and loyalty programs;
-
institutional innovations: these are new forms of co-operation and organizational structure, such as alliances, networks and clusters.
However, it is hard to differentiate among the previous types of innovation (product/service, process, managerial, institutional and marketing innovations), since there is a close relationship among them. For instance, a firm that needs to develop changes in marketing without technology investments (which belong to the process innovation) is impossible. In this paper, we focus on managerial innovations, as there is little research concerning this type of innovation in the tourism industry [40].
3. Managerial Innovations in the Tourism Industry
Managerial innovations play a meaningful role in increasing the effectiveness and competitiveness of firms to generate economic growth [41]. They provide a firm the capability to improve its structure, to adopt new managerial ideas and processes, to enable strategic renewal and to promote organizational change. Tourism organizations can easily imitate the most valuable innovations among them [42]; however, management innovation is difficult to replicate and challenging to imitate due to its organization-specific nature [43]. Hence, this kind of innovation assists companies to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage and increase competitiveness [1,44].
In particular, managerial innovations are “new organizational structures, management practices, administrative systems, processes and techniques that could create value for the organization” [45,46]. Types of this innovation include total quality management (TQM), quality circle, just-in-time production and 360-degree feedback [47]. Increasing attention is being paid to the crucial role of managerial innovation in developing strategies for increasing economic growth, organizational performance and adopting organizational changes [42,48].
The main factors that influence a firm’s ability to manage innovation are management style/leadership, organizational structure, corporate strategy, technology, knowledge management, employees and innovation processes [19]. By analyzing these elements, we are able to understand the important role of each factor that affects the competitiveness of a company and especially those in the tourism industry.
Among various leadership approaches, it seems that empowering leadership is the most efficient, since it emphasizes employees, enhances participation in decision making, eliminates bureaucratic restrictions, and cultivates a climate of creativity that gives employees the chance to take initiative, express new ideas and find efficient ways to face the daily challenges in their workplace. This attitude encourages the flexibility to change and provide employees with the necessary resources for innovation [49,50,51,52,53]. However, empowering leadership is also related positively to several outcomes, such as sales performance, work effort [54], self-leadership [55] and employee creativity [56].
Considering this context, leaders seem to play the main role in devising and implementing management innovations in a company in order to maintain a competitive advantage over its competitors [57]. Several firms in the tourism sector need employees to creatively perform their job to upgrade service quality and maintain long-term survival [58,59,60]. Thus, managers need to apply the proper type of leadership as an effective tool to implement innovation by providing adequate resources and support to employees to make necessary changes, including recognizing and rewarding their creative behaviors.
Organizational structure is “the framework of the relations on jobs, systems, operating process, people and groups making efforts to achieve the goals” [45]. Organizational structure is a set of methods dividing a task into determined duties and coordinating them. It includes models of internal relations of organization, responsibility and decision-making delegation as well as formal communication channels. Improving the information flow is one more facility provided by the structure of the organization. Organizational structure should alleviate decision making, proper reaction to environments and conflict resolution between the departments of a firm. The relationship between the main principles of a firm and coordination across its activities and internal organizational relations in terms of reporting is an element of organizational structure [45,48,61]
Corporate strategy is the scope and the direction of an organization in the long term, which achieves advantage in a changing environment through its configuration of competences and resources, with the aim of fulfilling the expectations of stakeholders [62]. Hence, a tourism firm’s strategy should promote and support innovation inside the firm, as it can support it to maintain its competitive advantage in the market, while at the same time make it more flexible to find efficient solutions to face the constant changes that arise from the external environment in which it operates. Technology can be defined at different levels [63]. Technological innovation involves the generation and adoption of a new idea concerning physical equipment, techniques/systems or tools that extend a firm’s capabilities into production systems and operational processes [63,64,65]. For instance, ICT, social media, mobile and smart phones and websites, as well as multimedia, virtual and augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and several other technological advances, especially in tourism, have helped speed up operations and have transformed the traveling process into a much more enjoyable and efficient experience.
Knowledge management is concerned with obtaining and communicating information and ideas that underline innovation competencies and include idea generation. It also covers the implicit and explicit knowledge of an organization [66,67,68] as well as the processes of gathering and using information. This is important for every firm and especially for a tourism firm, where changes are more intense and quicker. Thus, information is precious for a tourism firm, so as to be aware of such changes and to know how to act in order to maintain its privilege.
Employees and innovation processes concern the way that a firm behaves towards its employees in order for them to be satisfied and to improve their performance. In the case that the work environment enhances creativity and allows for employees to be satisfied and feel comfortable and secure to express their ideas, worries and thoughts and on the grounds that they are provided with the adequate resources, employees can be more creative, and this can lead to innovations for the company [60,69,70]. This factor is also important for tourism companies, since they mainly hire seasonal employees who are aware of the fact that they will work for a specific period of the year and that there are not many opportunities to advance in a tourism firm. This may deter them from feeling willing and motivated to do the best job that they can so as to enhance organizational performance. For these reasons, following management of employees in a tourism firm is of major importance.
Some elements that pertain to innovation as an outcome for a tourism company are form, magnitude, referent and type. More precisely, form is differentiated into service or product innovation, business model innovation and process innovation. Service or product innovation concerns a new service facility or a new product for the company [71], the customers or the market [72]. Process innovation concerns the “introduction of new management approaches, new production methods and new technologies that can be used to improve management processes and production” [72]. Business model innovation determines how a company creates and delivers value to its customers, whether it is new to the firm, customer or industry.
Magnitude indicates the degree of newness of the innovation outcome with respect to the referent [12]. Radical innovation includes fundamental changes, whereas incremental innovation represents variations in the existing practices and routines [73]. Both types of innovation are important for a tourism firm, as they help it to be more operational.
Referent defines the newness of innovation as an outcome. It can be new to the firm, to the market it serves, or to the industry. In terms of type, we can distinguish administrative and technical innovations. Administrative innovations are indirectly related to the basic work activity and more directly related to its managerial aspects, such as human resources, organizational structure, administrative processes and so on. Conversely, technical innovations include the products, processes and technologies that are used to produce products or render services related directly to the basic work activity of an organization.
Thus, the role of innovation as an outcome is essential for successful exploitation of an idea in order to improve the performance of a tourism firm. Consequently, one way for the firms to increase “quality” in the tourism sector is via managerial innovations, which lead to increased organizational performance [74,75,76,77].
Likewise, the broader elements of the tourism sector, such as restaurants, hotels, travel agencies, tourist shops, promotion/advertising agencies, transportation companies and any other kind of firm whose operation is related to the tourism sector, that aim to innovate tend to increase the possibilities to enhance their firm growth [78] and productivity [79].
Apart from these, innovation is also influenced by external and internal environmental factors [80,81], size, leadership characteristics, professionalism and entrepreneurial characteristics [82], management attitudes [83], the level of e-commerce business [84], the ability of entrepreneurs [85], the adoption and use of ICT [86], the customer relation management system, the capability of building relationships and partnerships with customers and suppliers [87] and cooperation with firms that hold the leading position in the market [88]. There are many advantages for a firm, especially in the tourism sector, to be member of a network. A network may include customers, suppliers, firms, authorities and academics.
Cooperation among the members of a network can lead to the development of ideas that can in turn improve creativity and result in the implementation of innovations. These partners contribute to the innovation process. This can influence the competitiveness of the tourism industry, since networks are incubators of innovative ideas and new businesses [89]. Through networks, scientific knowledge is transferred, and consequently, innovation can be improved and fostered [90]. The ability to absorb external knowledge is a key factor in developing competitive and original innovations [90].
The role and the importance of the relationship among innovation, innovation in the tourism industry, management innovation and technological innovations are summarized in Figure 1.
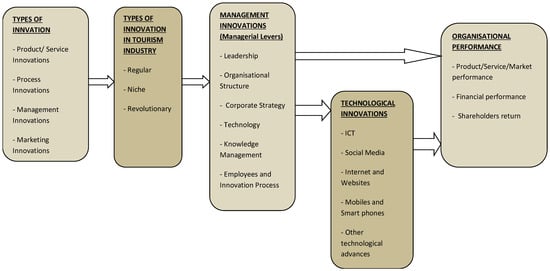
Figure 1. The framework of the links among innovation, innovation in the tourism industry, management innovation, technological innovations and organizational performance.
Figure 1 shows the links among different types of innovations, and especially management and technological innovations, which lead to an increase in organizational performance. Organizational performance encompasses three areas: financial performance, product/service or market performance and shareholder return [91,92].
The first area of financial performance describes the economic statement of the firm as profits, return on investments, return on assets and so on. The second area of product/service market performance includes the market share of the firm. The last area of shareholder return concerns the total shareholder return, the economic value added and others. There are different ways (or variables) to measure organizational performance [93]. In this paper, we refer only to the main areas of this dimension.
In addition, it must be mentioned that according to the size of the firm, its strategy, its goals, its capabilities, its needs, its budget and the market that it operates in, among other criteria, every company is able to adopt different types of innovation in order to improve its performance [94]. For instance, technological innovations are necessary, especially in tourism. Hence, further analysis of this element is provided in the following section.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/su14095182
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
