Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Plant Sciences
Long introm-spliced hairpin RNA (ihpRNA) constructs which contained inverted repeats of the phytoene desaturase (PDS) separated by an intron, had been shown to very effective in triggering PDS silencing in Brassica napus. Using the PDS gene as a target control, it was shown that the RCA-mediated long ihpRNA construct was signicantly effective in triggering gene silence in B. napus.
- Brassica napus
- RNAi
- ihpRNA
- PDS)
The 121-PDS-ihpRNA eukaryotic expressional construct was initially transferred into Agrobacterium strain GV3101 by electroporation, which was then transformed into B. napus cultivar zhongshuang 6 [31] via Agrobacterium-mediated gene transformation [32] to generate transgenic PDS-ihpRNA plants. Currently, this method of genetic transformation is considered to be of high efficiency (about 17%) [33]. The binary vector pBI121 harbors the neomycin phosphotransferase gene (NPTII) resistance selection marker (Figure 3A). The selection marker-resistant regenerated T0 transformants were initially subjected to kanamycin-based selection and then rooted well in selective medium. The selected resistant T0 transformants were then verified by PCR-based screening using the corresponding primer pairs NPTII-F and NPTII-R, which were specific for the NPTII gene in the binary construct (Figure 3A). A total of five transgenic plants (approximately 17% transformation efficiency) were obtained, all displaying photo-bleaching phenotypic characteristics (Figure 3B).
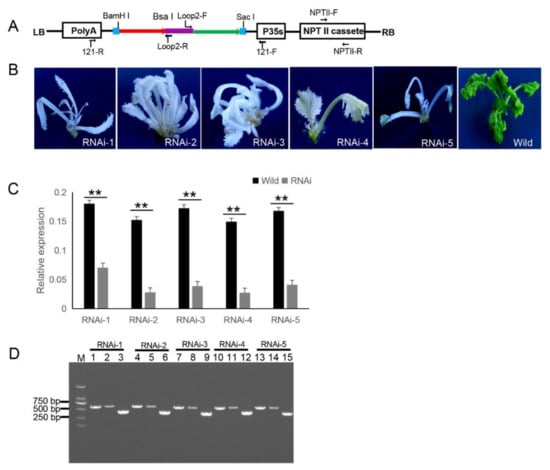
Figure 3. 121-PDS-ihpRNA-mediated silencing of the PDS gene. (A) Map of the binary vector 121-PDS-ihpRNA. NPTII-F and NPTII-R primers were used in the identification of positive transgenic plants, the primer pairs loop2-F/121-F and loop2-R/121-R were utilized to rapidly screen target genes. Blue line is the adaptor1 sequence. Purple line is the adaptor2 sequence. Red line with the arrow is the sense strand of dsDNA. Green line with the arrow is the anti-sense strand of dsDNA. (B) Interfering phenotypes of 5 PDS-ihpRNA transgenic plants. RNAi-1, RNAi-2, RNAi-3, RNAi-4, and RNAi-5 were PDS-ihpRNA transgenic plants. Wild was the transgenic negative plant. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of the PDS target gene mRNA level in the five hpRNA lines shown in (B) using the primer pair PDS-F2/PDS-R2. Data shown as mean ± s.d.,**, p < 0.05. (D) Integration into the Brassica napus genome for the PDS ihpRNA expression cassette. For the five PDS RNAi lines, loop2-F and 121-F or loop2-R and 121-R primer pair could amplify the bands with the desired size, demonstrating that the PDS ihpRNA expression cassette was successfully integrated into the B. napus plants. Lanes 3, 6, 9, 12, and 15 show the 450-bp PDS control; lanes 1, 4, 7, 10, and 13 exhibit the PCR products of loop2-F and 121-F; lanes 2, 5, 8, 11, and 14 depict the PCR products of loop2-R and 121-R.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms21197243
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
