In today’s world, the problem of “white pollution” is becoming more and more serious, and many countries have paid special attention to this problem, and it has become one of the most important tasks to reduce polymer waste and to protect the environment. Due to the degradability, safety, economy and practicality of biodegradable packaging film materials, biodegradable packaging film materials have become a major trend in the packaging industry to replace traditional packaging film materials, provided that the packaging performance requirements are met. Degraded plastics are plastics that have been subjected to defined environmental conditions for a period of time and contain one or more steps that result in significant changes in the chemical structure of the material resulting in loss of certain properties (such as integrity, molecular mass, structure or mechanical strength) and/or fragmentation.
- degradable
- packaging film materials
- degradation mechanism
- modified
1. Introduction
2. Degradation Mechanism of Degradable Packaging Film Materials
| Classification | Category | Features |
|---|---|---|
| By degradation principle | Biodegradable plastics | Similar performance to traditional plastics, good degradability, high safety |
| Photodegradable plastics | Simple and low cost production process | |
| Thermal oxidative degradation plastics | Requires oxygen and heat | |
| Hydrodegradable plastics | Short degradation time, no trace, no pollution, low cost | |
| By degradation characteristics | Fully degradable plastics | Completely disintegrates and leaves no trace |
| Incomplete degradable plastics | Partial degradation |
2.1. Photodegradation
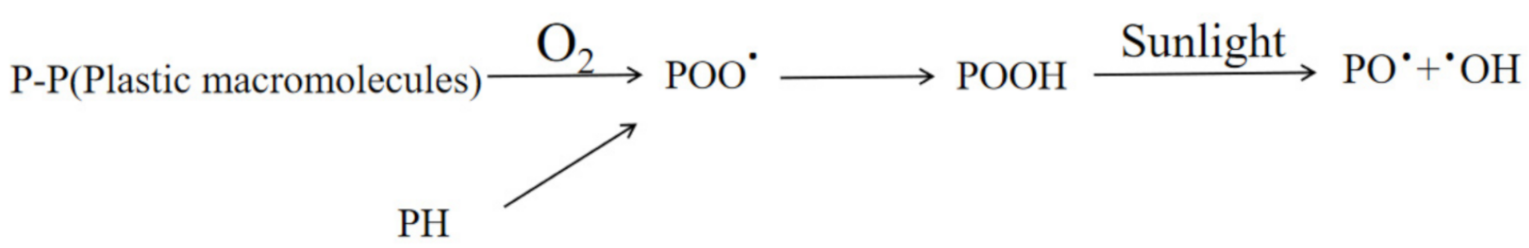
2.2. Hydrodegradation
| Material | Conditions | Weight Loss % | Number-Average Molecular Weight (Mn) | Mechanical Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polylactic acid (PLA) | Seawater | <2 | 96.60 × 103 to 83.85 × 103 | No significant change |
| Germicidal water | <2 | 96.60 × 103 to 67.98 × 103 | ||
| Poly (butyleneadipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) | Seawater | <2 | 46.67 × 103 to 20.31 × 103 | Total loss |
| Germicidal water | <2 | 46.67 × 103 to 16.02 × 103 | ||
| Poly (butylene succinate) (PBS) | Seawater | <2 | 41.56 × 103 to 30.11 × 103 | Total loss |
| Germicidal water | <2 | 41.56 × 103 to 18.63 × 103 | ||
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Seawater | 32 | 77.79 × 103 to 77.09 × 103 | Total loss |
| Germicidal water | <2 | 77.79 × 103 to 14.82 × 103 |
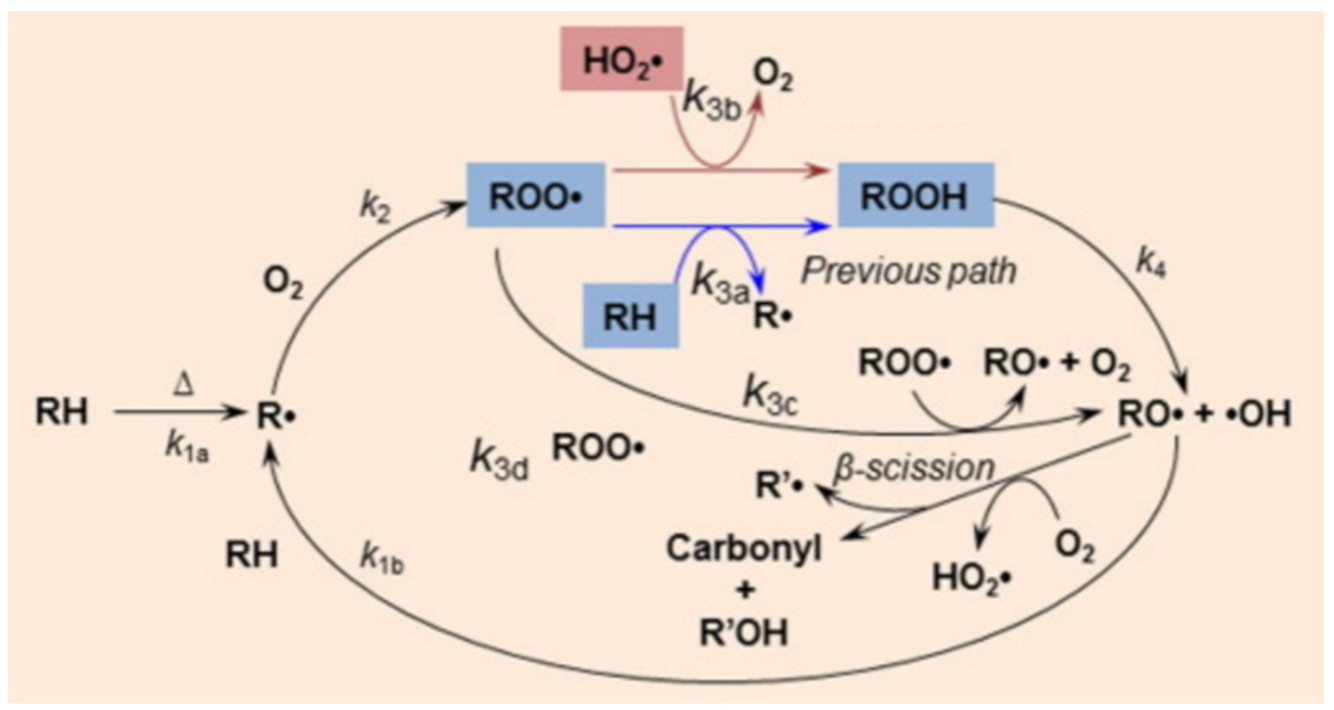
2.3. Thermal Oxidative Degradation
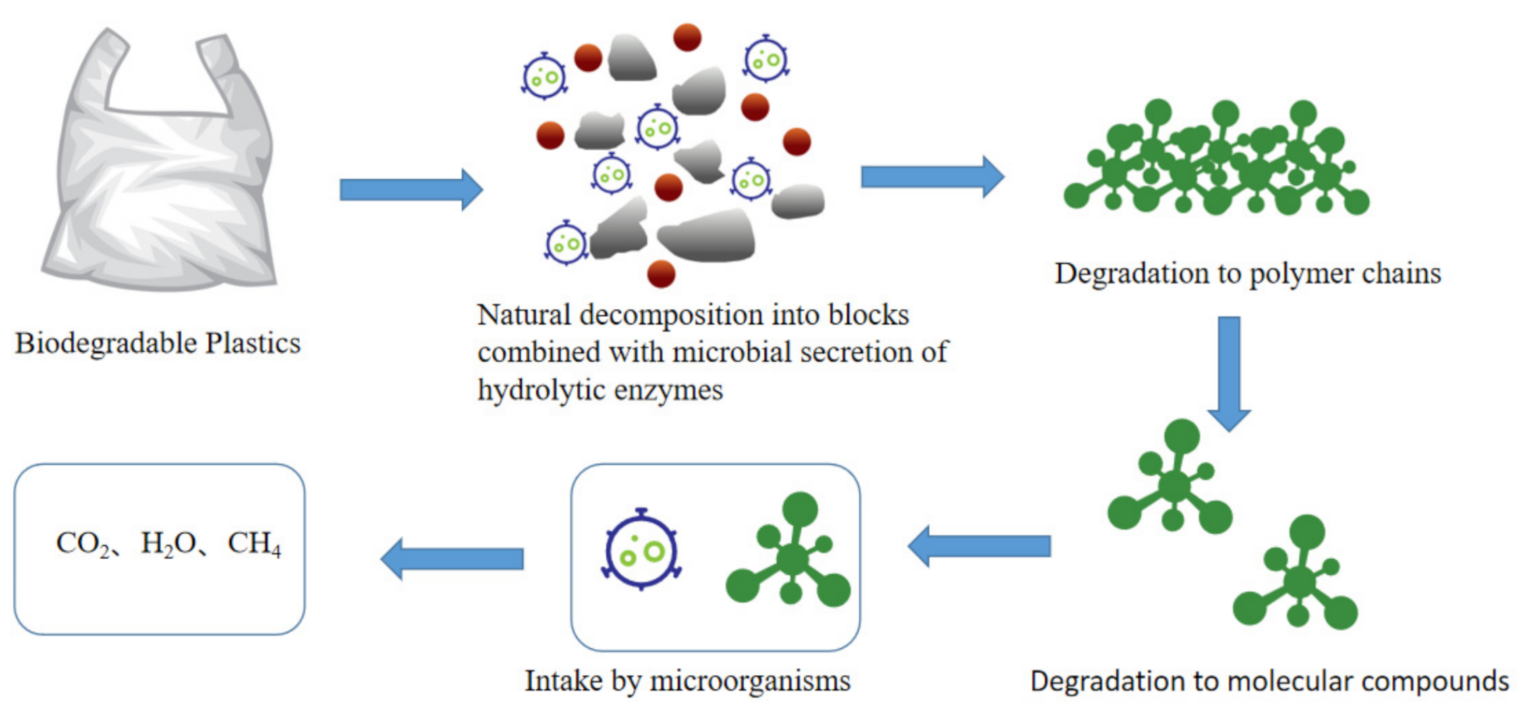
2.4. Biodegradable
| Material | Conditions | The Result of Degradation | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene | Degradation of high-density polyethylene with Aspergillus flavus PEDX3 strain for 28 days | Molecular weight reduction | [76] |
| Polypropylene | Degradation of polypropylene with microalgae Spirulina sp. for 112 days | Decrease in mechanical strength and relative molecular weight | [77] |
| Polystyrene | Degradation of polystyrene with Achatina fulica for 4 weeks | The mass loss was 30.7% on average, forming a functional group of oxidation intermediates | [78] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate | Degradation of polyethylene terephthalate with microalgae Spirulina sp. for 112 days | Decrease in mechanical strength | [77] |
| Polylactic acid | Degradation in accordance with ISO 17556 | 15% of Polylactic acid is degraded | [79] |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/membranes12050500
References
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, Use, and Fate of All Plastics Ever Made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782.
- Lin, Z.; Jin, T.; Zou, T.; Xu, L.; Xi, B.; Xu, D.; He, J.; Xiong, L.; Tang, C.; Peng, J.; et al. Current Progress on Plastic/Microplastic Degradation: Fact Influences and Mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119159.
- Ouyang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhao, M.; Wangmu, Q.; Ding, R.; Xiao, C.; Guo, X. The Aging Behavior of Polyvinyl Chloride Microplastics Promoted by UV-Activated Persulfate Process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127461.
- Paletta, A.; Filho, W.L.; Balogun, A.L.; Foschi, E.; Bonoli, A. Barriers and Challenges to Plastics Valorisation in the Context of a Circular Economy: Case Studies from Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118149.
- Enfrin, M.; Dumée, L.F.; Lee, J. Nano/Microplastics in Water and Wastewater Treatment Processes—Origin, Impact and Potential Solutions. Water Res. 2019, 161, 621–638.
- Alimi, O.S.; Farner Budarz, J.; Hernandez, L.M.; Tufenkji, N. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Aquatic Environments: Aggregation, Deposition, and Enhanced Contaminant Transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1704–1724.
- Wu, F.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Challenges and New Opportunities on Barrier Performance of Biodegradable Polymers for Sustainable Packaging. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 117, 101395.
- Andrady, A.L.; Pegram, J.E.; Nakatsuka, S. Studies on Enhanced Degradable Plastics: 1. The Geographic Variability in Outdoor Lifetimes of Enhanced Photodegradable Polyethylenes. J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 1993, 1, 31–43.
- Abu-Hilal, A.H.; Al-Najjar, T. Litter Pollution on the Jordanian Shores of the Gulf of Aqaba (Red Sea). Mar. Environ. Res. 2004, 58, 39–63.
- Lohr, A.; Savelli, H.; Beunen, R.; Kalz, M.; Ragas, A.; Belleghem, F.V. Solutions for Global Marine Litter Pollution. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2017, 28, 90–99.
- Bano, K.; Kuddus, M.; RZaheer, M.; Zia, Q.; FKhan, M.; Gupta, A.; Aliev, G. Microbial Enzymatic Degradation of Biodegradable Plastics. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2017, 18, 429–440.
- Ward, C.P.; Armstrong, C.J.; Walsh, A.N.; Jackson, J.H.; Reddy, C.M. Sunlight Converts Polystyrene to Carbon Dioxide and Dissolved Organic Carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 669–674.
- Dharma, H.N.C.; Jaafar, J.; Widiastuti, N.; Matsuyama, H.; Rajabsadeh, S.; Othman, M.H.D.; Rahman, M.A.; Jafri, N.N.M.; Suhaimin, N.S.; Nasir, A.M.; et al. A Review of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2)-Based Photocatalyst for Oilfield-Produced Water Treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 345.
- Prabhakar, P.; Sen, R.K.; Mayandi, V.; Patel, M.; Swathi, B.; Vishwakarma, J.; Gowri, V.S.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Mondal, D.P.; Srivastava, A.K.; et al. Mussel-Inspired Chemistry to Design Biodegradable Food Packaging Films with Antimicrobial Properties. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 162, 17–29.
- Jing, X.; Wen, H.; Gong, X.; Xu, Z.; Kajetanowicz, A. Recycling Waste Plastics Packaging to Value-Added Products by Two-Step Microwave Cracking with Different Heating Strategies. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 201, 106346.
- Ncube, L.K.; Ude, A.U.; Ogunmuyiwa, E.N.; Zulkifli, R.; Beas, I.N. An Overview of Plasticwaste Generation and Management in Food Packaging Industries. Recycling 2021, 6, 12.
- Webb, H.K.; Arnott, J.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Plastic Degradation and Its Environmental Implications with Special Reference to Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate). Polymers 2013, 5, 1–18.
- Rhim, J.-W.; Park, H.-M.; Ha, C.-S. Bio-Nanocomposites for Food Packaging Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1629–1652.
- Al-Thawadi, S. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Aquatic Environments: Challenges and Threats to Aquatic Organisms. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 4419–4440.
- Mao, R.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, R.; Guo, X. Microplastics in the Surface Water of Wuliangsuhai Lake, Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 137820.
- Ngo, P.L.; Pramanik, B.K.; Shah, K.; Roychand, R. Pathway, Classification and Removal Efficiency of Microplastics in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113326.
- Galloway, T.S.; Cole, M.; Lewis, C. Interactions of Microplastic Debris throughout the Marine Ecosystem. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 116.
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Jung, S.W.; Shim, W.J. Combined Effects of UV Exposure Duration and Mechanical Abrasion on Microplastic Fragmentation by Polymer Type. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4368–4376.
- Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Tian, Y.; Lin, H. Microplastic Abundance, Distribution and Composition in the Mid-West Pacific Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114125.
- Zhang, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhong, S.; Liu, J.; Qin, Y.; Gao, P. Microplastics in Freshwater and Wild Fishes from Lijiang River in Guangxi, Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142428.
- Cutroneo, L.; Reboa, A.; Besio, G.; Borgogno, F.; Canesi, L.; Canuto, S.; Dara, M.; Enrile, F.; Forioso, I.; Greco, G.; et al. Microplastics in Seawater: Sampling Strategies, Laboratory Methodologies, and Identification Techniques Applied to Port Environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 8938–8952.
- Vaughan, R.; Turner, S.D.; Rose, N.L. Microplastics in the Sediments of a UK Urban Lake. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 10–18.
- Tibbetts, J.; Krause, S.; Lynch, I.; Smith, G.H.S. Abundance, Distribution, and Drivers of Microplastic Contamination in Urban River Environments. Water Switz. 2018, 10, 1597.
- Ding, L.; Mao, R.F.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C. Microplastics in Surface Waters and Sediments of the Wei River, in the Northwest of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 427–434.
- Wang, G.; Lu, J.; Tong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Xiayihazi, N. Occurrence and Pollution Characteristics of Microplastics in Surface Water of the Manas River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136099.
- Wright, S.L.; Ulke, J.; Font, A.; Chan, K.; Kelly, F.J. Atmospheric Microplastic Deposition in an Urban Environment and an Evaluation of Transport. Environ. Int. 2019, 136, 105411.
- Prata, J.C.; Castro, J.L.; da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Cerqueira, M.; Rocha-Santos, T. An Easy Method for Processing and Identification of Natural and Synthetic Microfibers and Microplastics in Indoor and Outdoor Air. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100762.
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Du, F.; Cai, H.; Wang, G.; Shi, H. Microplastic Fallout in Different Indoor Environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6530–6539.
- Liu, M.; Lu, S.; Yang, S.; Lei, L.; Hu, J.; Lv, W.; Zhou, W.; Cao, C.; Shi, H.; Yang, X. Microplastic and Mesoplastic Pollution in Farmland Soils in Suburbs of Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 855–862.
- Ding, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Guo, X. The Occurrence and Distribution Characteristics of Microplastics in the Agricultural Soils of Shaanxi Province, in North-Western China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137525.
- Payton, T.G.; Beckingham, B.A.; Dustan, P. Microplastic Exposure to Zooplankton at Tidal Fronts in Charleston Harbor, SC USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 232, 106510.
- Wang, F.; Wong, C.S.; Chen, D.; Lu, X.; Wang, F.; Zeng, E.Y. Interaction of Toxic Chemicals with Microplastics: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 208–219.
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, A. The Impact of Microplastics on Human Health:A Review. J. Nanjing Univ. Sci. 2020, 56, 8.
- Lamberti, F.M.; Román-Ramírez, L.A.; Wood, J. Recycling of Bioplastics: Routes and Benefits. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 2551–2571.
- Panchal, S.S.; Vasava, D.V. Biodegradable Polymeric Materials: Synthetic Approach. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 4370–4379.
- Niaounakis, M. Recycling of Biopolymers—The Patent Perspective. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 114, 464–475.
- Dilkes-Hoffman, L.S.; Pratt, S.; Lant, P.A.; Laycock, B. 19—The Role of Biodegradable Plastic in Solving Plastic Solid Waste Accumulation. In Plastics to Energy; Al-Salem, S.M., Ed.; Plastics Design Library; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 469–505. ISBN 978-0-12-813140-4.
- Qin, Z.-H.; Mou, J.-H.; Chao, C.Y.H.; Chopra, S.S.; Daoud, W.; Leu, S.; Ning, Z.; Tso, C.Y.; Chan, C.K.; Tang, S.; et al. Biotechnology of Plastic Waste Degradation, Recycling, and Valorization: Current Advances and Future Perspectives. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 4103–4114.
- Zaaba, N.F.; Jaafar, M. A Review on Degradation Mechanisms of Polylactic Acid: Hydrolytic, Photodegradative, Microbial, and Enzymatic Degradation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 2061–2075.
- Liu, L.; Xu, M.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, B. On the Degradation of (Micro)Plastics: Degradation Methods, Influencing Factors, Environmental Impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151312.
- Bakbolat, B.; Daulbayev, C.; Sultanov, F.; Beissenov, R.; Umirzakov, A.; Mereke, A.; Bekbaev, A.; Chuprakov, I. Recent Developments of TiO2-Based Photocatalysis in the Hydrogen Evolution and Photodegradation: A Review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1790.
- Jin, L.; He, S.; Li, D.; Zhang, C. Status of Degradable Materials and Their Progress in Marine Research. Packag. Eng. 2020, 41, 108–115.
- Li, J.; Deng, J.; Liang, L. Application Progress of Degradable Plastics in Packaging Products. Plast. Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 94–98.
- Christensen, P.A.; Egerton, T.A.; Martins-Franchetti, S.M.; Jin, C.; White, J.R. Photodegradation of Polycaprolactone/Poly(Vinyl Chloride) Blend. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 305–309.
- Najafi, V.; Ahmadi, E.; Ziaee, F.; Omidian, H.; Sedaghat, H. Polyaniline-Modified TiO2, a Highly Effective Photo-Catalyst for Solid-Phase Photocatalytic Degradation of PVC. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 784–793.
- Krzan, A.; Hemjinda, S.; Miertus, S.; Corti, A.; Chiellini, E. Standardization and Certification in the Area of Environmentally Degradable Plastics. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 2819–2833.
- Solaro, R.; Corti, A.; Chiellini, E. Biodegradation of poly(vinyl alcohol) with different molecular weights and degree of hydrolysis. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2000, 11, 873–878.
- Lucas, N.; Bienaime, C.; Belloy, C.; Queneudec, M.; Silvestre, F.; Nava-Saucedo, J.-E. Polymer Biodegradation: Mechanisms and Estimation Techniques—A Review. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 429–442.
- Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Guo, H. Research Progress of Polyvinyl Alcohol Water-Resistant Film Materials. Membranes 2022, 12, 347.
- Saini, I.; Sharma, A.; Dhiman, R.; Aggarwal, S.; Ram, S.; Sharma, P.K. Grafted SiC Nanocrystals: For Enhanced Optical, Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 714, 172–180.
- Panda, P.K.; Yang, J.-M.; Chang, Y.-H. Water-Induced Shape Memory Behavior of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) and p-Coumaric Acid-Modified Water-Soluble Chitosan Blended Membrane. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117633.
- Yang, J.; Panda, P.K.; Jie, C.J.; Dash, P.; Chang, Y. Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Chitosan/Sodium Alginate Composite Blended Membrane: Preparation, Characterization, and Water-induced Shape Memory Phenomenon. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 1526–1537.
- Moulay, S. Review: Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Functionalizations and Applications. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2015, 54, 1289–1319.
- Abdullah, Z.W.; Dong, Y.; Davies, I.J.; Barbhuiya, S. PVA, PVA Blends, and Their Nanocomposites for Biodegradable Packaging Application. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 56, 1307–1344.
- Teodorescu, M.; Bercea, M.; Morariu, S. Biomaterials of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) and Natural Polymers. Polym. Rev. 2018, 58, 247–287.
- Liu, B.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Guo, H. Performance of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Bagasse Fibre Foamed Composites as Cushion Packaging Materials. Coatings 2021, 11, 1094.
- Lv, S.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Assessment of Structural Modification and Time-Dependent Behavior of Poly (Lactic Acid) Based Composites upon Hydrolytic Degradation. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 166, 111058.
- Wang, G.; Huang, D.; Zhang, W.; Ji, J. Degradation Performance of Typical Biodegradable Polyesters in Seawater. J. Funct. Polym. 2020, 33, 492–499.
- Shi, L.; Zhu, J.; Shi, J.; Zhao, X. Classification and Identification of Degradable Plastic Products: Current Situation and Prospect. Plast. Addit. 2021, 3, 1–5.
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, W.; Xing, R.; Xie, S.; Yang, X.; Cui, P.; Lü, J.; Liao, H.; Yu, Z.; Wang, S.; et al. Enhanced in Situ Biodegradation of Microplastics in Sewage Sludge Using Hyperthermophilic Composting Technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121271.
- Ammala, A.; Bateman, S.; Dean, K.; Petinakis, E.; Sangwan, P.; Wong, S.; Yuan, Q.; Yu, L.; Patrick, C.; Leong, K.H. An Overview of Degradable and Biodegradable Polyolefins. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1015–1049.
- Chiellini, E.; Corti, A.; D’Antone, S.; Baciu, R. Oxo-Biodegradable Carbon Backbone Polymers—Oxidative Degradation of Polyethylene under Accelerated Test Conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 2739–2747.
- Chen, L.; Yamane, S.; Sago, T.; Hagihara, H.; Kutsuna, S.; Uchimaru, T.; Suda, H.; Sato, H.; Mizukado, J. Experimental and Modeling Approaches for the Formation of Hydroperoxide during the Auto-Oxidation of Polymers: Thermal-Oxidative Degradation of Polyethylene Oxide. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2016, 657, 83–89.
- Madhu, G.; Bhunia, H.; Bajpai, P.K.; Nando, G.B. Physico-Mechanical Properties and Biodegradation of Oxo-Degradable HDPE/PLA Blends. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2016, 58, 57–75.
- Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J. Ecology of the Plastisphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 139–151.
- Elahi, A.; Bukhari, D.A.; Shamim, S.; Rehman, A. Plastics Degradation by Microbes: A Sustainable Approach. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2021, 33, 101538.
- Kyrikou, I.; Briassoulis, D. Biodegradation of Agricultural Plastic Films: A Critical Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2007, 15, 125–150.
- Reddy, R.L.; Reddy, V.S.; Gupta, G.A. Study of Bio-Plastics as Green & Sustainable Alternative to Plastics. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2013, 3, 82–89.
- Qin, M.; Chen, C.; Song, B.; Shen, M.; Gong, J. A Review of Biodegradable Plastics to Biodegradable Microplastics: Another Ecological Threat to Soil Environments? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127816.
- Liwarska-Bizukojc, E. Effect of (Bio)Plastics on Soil Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148889.
- Zhang, J.; Gao, D.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Lin, H.; Bi, Q.; Zhao, Y. Biodegradation of Polyethylene Microplastic Particles by the Fungus Aspergillus flavus from the Guts of Wax Moth Galleria mellonella. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135931.
- Khoironi, A.; Anggoro, S.; Sudarno, S. Evaluation of the Interaction Among Microalgae Spirulina sp., Plastics Polyethylene Terephthalate and Polypropylene in Freshwater Environment. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 161–173.
- Song, Y.; Qiu, R.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; He, D. Biodegradation and Disintegration of Expanded Polystyrene by Land Snails Achatina fulica. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141289.
- Cucina, M.; De Nisi, P.; Trombino, L.; Tambone, F.; Adani, F. Degradation of Bioplastics in Organic Waste by Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion, Composting and Soil Incubation. Waste Manag. 2021, 134, 67–77.
- Edaes, F.S.; De Souza, C.B. Conventional Plastics’ Harmful Effects and Biological and Molecular Strategies for Biodegradable Plastics’ Production. Curr. Biotechnol. 2020, 9, 242–254.
