Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Pharmacology & Pharmacy
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is known as an autoimmune disease that damages the neurons in the central nervous system. MS is characterized by its most common symptoms of spasticity, muscle spasms, neuropathic pain, tremors, bladder dysfunction, dysarthria, and some intellectual problems, including memory disturbances. Several clinical studies have been conducted to investigate the effects of cannabis on the relief of these symptoms in MS patients.
- Cannabis sativa
- marijuana
- cannabinoids
- 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
- multiple sclerosis (MS)
1. Introduction
MS is a neurological disease with an autoimmune origin that affects and damages the central nervous system and affects 2.3 million people worldwide [1][2]. This demyelinated disease leads to severe impairment of nerve signal transmission between the brain and spinal cord that causes a loss of myelin sheath [1][2].MS has been characterized by symptoms of spasticity, muscle spasms, tremors, bladder dysfunction, neuropathic pain, dysarthria, and some intellectual problems, including memory disturbances [3,4]. Some drugs have been licensed to slow down disease progression and reduce relapse frequency [3]. However, more studies are needed to further alleviate the disabling symptoms of MS patients.
In the 21st century, the Sativa plant has become the most widely used illicit drug [5]. It isalso known as hemp, cannabis, or marijuana, and comes in a variety of forms, including cigarettes or hash pipes and sweets or brownies [5,6]. The cannabis plant, which includes over 560 identified components, is primarily composed of phytochemicals [5]. The two prominent species of Cannabis plant, which are mostly used for recreational and medical, are Cannabis indica and Cannabis sativa (C. Sativa) [7,8]. Both plants are composed of different cannabinoid compositions of THC and CBD [9,10]. Previous research hasshown the different effects of each species due to the different concentrations of the two main components [11]. C. Sativa has a higher ratio of CBD to THC and the reverse is seen for C.indica [10]. There are about 100 cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa [12], the most well-known of which are 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) (Figure 1a,b). The endogenous cannabinoid system, which includes CB1 and CB2 receptors, is where cannabinoids get their effects. The psychotropic effects of THC are primarily mediated by a CB1 receptor agonist actions. CBD, on the other hand, is hypothesized to bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors and act as an antagonist [5,13].
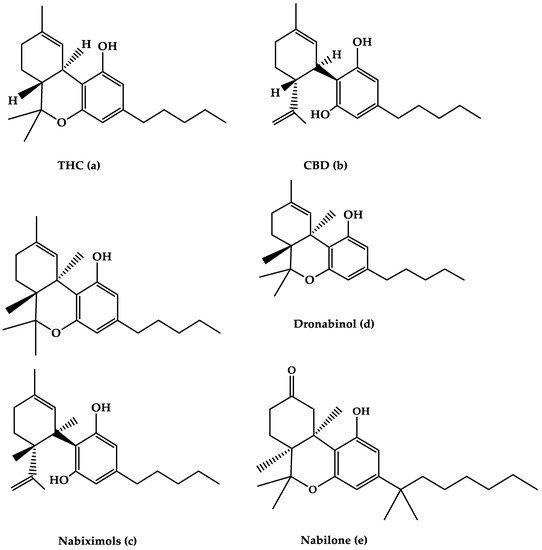
Figure 1. The molecular structures of (a) THC, (b) CBD, (c) Nabiximols, (d) Dronabinol, and (e) Nabilone are depicted in this diagram.
Cannabis has been used for over 5000 years, with the discovery of the endogenous cannabinoid system occurring more than a decade ago. CB1 and CB2 are cannabinoid receptors that are linked to adenylyl cyclase negatively and mitogen-activated protein kinase positively through the Gi/o protein [14,15]. CB1 and CB2 are distributed in the central and peripheral nervous systems and immune systems [16]. CB1 receptors are found mostly in nerve terminals in the central nervous system and some peripheral tissue and are linked to a specific type of calcium and potassium channel via a G protein. Because it blocks pain pathways in the brain and spinal cord, the CB1 receptor’s main function is to suppress neurotransmitter release, and it plays a crucial role in mediating the pain-relieving effect of cannabis [17].
Phytocannabinoids, endocannabinoids, and synthetic cannabinoids are the three types of cannabinoids. The major chemical components of cannabis are phytocannabinoids, which include a variety of non-cannabinoid C21 terpenes phenolic compounds, or C22 for the carboxylate group, which is largely synthesized in cannabis [18,19]. Heat can decarboxylate phytocannabinoids, which are biosynthesized in carboxylated form [20].
Cannabis isconsidered a promising anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agent due to its central and peripheral actions on CB1 and CB2 receptors that mediate different intracellular pathways when activated [21]. In addition to the effects of the cannabinoids on CB1 and CB2 receptors, cannabinoids have effects on nuclear receptors and ion channels by their activity on other transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and have a modulating activity on opioid and serotonin receptors [16]. THC is a psychoactive component of cannabis with the highest potency. THC can be utilized to treat neuropathic and chronic pain because of its intoxicating, anti-emetic, and anti-inflammatory properties [22]. CBD does not cause psychosis, although it does have pharmacological effects on pain and spasticity [23].
The main psychoactive constituent of the C. Sativa plant, 9-THC, was discovered in the late 1980s and was shown to have activity on a specific cannabinoid receptor in the brain (the cannabinoid CB1 receptor), which had a huge impact on the development of cannabinoid therapeutic drugs and their potential to relieve MS spasticity symptoms [24]. Preclinical animal studies of MS suggested that cannabinoids have anti-septic effects due to the activation of CB1 receptors, which inhibit the release of classical neurotransmitters, such as glutamine, while also decreasing neuronal excitability by activating somatic and dendrite potassium channels [25,26].
CBD is a key non-psychotropic cannabinoid present in C. Sativa that accounts for up to 40% of the cannabis plant’s extract and binds to a wide range of physiological targets of the endocannabinoid system in the human body. CBD has shown potential in the treatment of MS symptoms. CBD, in particular, has been shown in numerous trials to reduce stiffness, discomfort, inflammation, exhaustion, and depression in MS patients, resulting in increased mobility [27,28]. CBD also affects the non-cannabinoids receptors GPCRs and ion channels that will lead to pain regulation and anti-inflammatory effects through receptor modulation [16].
Several attempts have been made to determine the primary genetic factor contributing to MS progression and severity [29,30,31]. Although it was demonstrated that genetic effects on MS disease severity and susceptibility are polygenic with modest influence [30,31], more studies are needed to further understand the pharmacogenetics of MS disease and to define the molecular target of CBD in MS patients by performing the ex vivo/in vitro research in human immune cells as reported by Furgiuele et al. [31].
2. Cannabinoid Agents for the Treatment of MS
2.1. Nabiximols
Nabiximols is the generic name for Sativex®, an oromucosal spray containing a 1:1 molecular ratio of THC and CBD (Nabiximols (c), Figure 1) [76]. It has been licensed in several countries for the treatment of severe spasticity in MS patients [5]. The THC, CBD, and the small number ofother constituents of the plant extract, including other cannabinoids and terpenoids dissolved in ethanol, make up around 70% of the constituents in Nabiximols [76]. There are 2.7 mg, 2.5 mg, and 0.04 g of THC, CBD, and ethanol, respectively, in each dose of oromucosal spray. Its administration has a favorable pharmacokinetic profile, with fewer first-pass effects and a low plasma concentration, resulting in the avoidance of psychoactive effects that are caused by smoked cannabis [76,77,78].Furthermore, its maximum plasma concentration would rise gradually within 2–4 h after administration, while the quick onset effect will appear after 15–40 h, making treatment adjustments easier [77].The synergistic interaction is based on a low-dose combination of THC and CBD, which results in reduced euphoric effects and improved cannabinoid-mediated anti-spasticity therapeutic benefits [76]. According to much research, starting therapy with a 14-day dose titration period is recommended to reach up to 12 sprays as the highest dose per day [78]. Individual dose distribution across a day, as well as dose change over the treatment course, is possible depending on the intensity of the disease. The recommended maximum daily dose is 12 sprays with at least 15 min between each spray [77]. Nabiximols were tested in MS patients with a variety of symptoms, such as stiffness, pain, tremor, and bladder function, in several clinical investigations [56,79,80,81]. Nabiximols were found to have good effects on spasticity, pain, and quality of life in MS patients in the majority of trials (Table 1) [56,79,80,81].
Table 1. The efficacy of oromucosal spray nabixiomol, oral dronabinol, and oral nabilone forms of cannabis on MS-related symptoms and their adverse effects.
| Cannabinoid Agents | Therapeutic Actions | Adverse Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Nabiximols |
|
|
| Dronabinol |
|
|
| Nabilone |
|
|
2.1.1. Effects of Nabiximols on MS-Related Spasticity
Wade and colleagues reported an open-label extension trial in 2006 that included 137 patients diagnosed with MS after 6-week placebo-controlled research, in which the efficacy and tolerability of Sativex for the management of spasticity and other symptoms were assessed for about 15 weeks [82]. The primary outcome was assessed using a visual analog scale, which revealed a consistent reduction in spasticity. Furthermore, it had unfavorable effects on MS pain, tremor, and bladder symptoms, and 58 patients dropped out due to ineffectiveness [82].
Collin et al. conducted a 6-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled research on 189 patients in 2007, comparing the effects of Sativex between the groups [83]. There was a significant difference in spasticity reduction between the active and placebo groups, with a decrease in the numerical rating scale (NRS) score of p = 0.048 [83]. As a secondary endpoint, however, there was no therapeutic impact among other Ashworth scores [83].
Novotna and colleagues conducted a large multicenter phase III trial in 2011 that included two phases of study design: phase A began with a four-week single-blind treatment phase to identify early responders to oromucosal spray Nabixomols, followed by phase B, which was a 12-week randomized, double-blind study phase [77]. The recommended highest daily dose of nabiximols was 12 sprays. In a study comparing oral mucosal spray to placebo, the oral mucosal spray was linked to a 51% reduction in MS spasticity. In addition, the NRS ratings decreased by 20% [77].
Based on a series of randomized controlled clinical trials vs. placebo, Nabiximols were given and licensed for their therapeutic efficacy and relief of spasticity-related symptoms [56,79,83]. The first line anti-spastic study was recently designed and implemented using an enriched–design methodology as proof of the German authority’s request that add-on Nabixomolsweremore effective than readjusting the anti-spasticity medication regimen alone in providing symptomatic relief of MS spasticity during a 4-week trial period compared to placebo [84]. SAVANT, a well-designed research of oromucosalNabixomol as an add-on therapy for the treatment of MS spasticity in MS patients, found that it had a promising effect in reducing moderate to severe spasticity symptoms [85].
Nabiximols are approved and advised as an add-on treatment for adult patients with moderate to severe resistant MS spasticity in several Western countries [86,87].
2.1.2. Effect of Nabiximols on MS-Related Pain
Nabiximols (oromucosal spray): randomized, placebo-controlled research in which 66 patients were randomly assigned to Nabiximols or placebo found that Nabiximols was effective in alleviating both central pain associated with MS and pain-related sleep disruption [88]. In a different double-blind experiment conducted in 2013, 339 patients with central neuropathic pain associated with MS were randomized to 167 Nabiximols and 172 placeboes, with the Nabiximols showing a statistically significant response rate at week 10 compared to the placebo [80]. The authors explained the findings by stating that their patient population may represent a particularly treatment-resistant group because they had long-standing pain spanning more than 5 years on average, and they demonstrated that those with a less than 4-year history of neuropathic pain were more likely to be resistant to treatment [80]. Nine randomized controlled studies with 1289 individuals were included in a recent systematic meta-analysis of THC: CBD oromucosal spray and placebo for the treatment of chronic neuropathic pain. Nabiximols were found to relieve chronic neuropathic pain more effectively than placebo, with a small effect size [89]. This suggests that further research into the full potential of Nabiximols in these people could be very interesting.
2.2. Dronabinol
The primary THC isomer present in the cannabis plant, (−)-trans-9-THC(Dronabinol(d), Figure 1), is known by the generic name Dronabinol. Dronabinol is available in three strength formulations: oral soft gelatin capsule, oral soft gelatin capsule, and oral soft gelatin capsule (2.5, 5, and 10 mg). It was first used to treat chemotherapy-induced vomiting and nausea, as well as anorexia and weight loss in AIDS patients, and it was tested in ten clinical trials for its efficacy and safety in treating MS symptoms including spasticity, pain, tremor, bladder function, sleep, quality of life, and side effects [57,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105]. Dronabinol appears to be highly effective in the treatment of pain in MS patients, according to the bulk of clinical evidence, although other symptoms showed only little improvement (Table 1) [95].
2.2.1. Effects of Dronabinol on MS-Related Spasticity
Zajick et al. conducted a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled research on 630 patients aged 18 to 64 in 2003 [57]. The effect of orally administered Marinol (Dronabinol) and Cannador on MS symptoms were studied for 15 weeks in this design study [57]. Weight-adjusted 0.25 mg/kg 9-THC (Dronabinol, supplied orally in 2.5 mg capsules), natural Cannabis oil (Cannador), or placebo were used to provide the dose [57]. The study assessed the effects of orally delivered cannabis extract (Cannador), Dronabinol, or placebo on spasticity following 28 days dose-titration phase using the Ashworth scale. Over a year, 80% of the subjects demonstrated a moderate reduction in spasticity [57]. There was no significant therapeutic impact between the active and placebo groups in the primary outcome. In comparison to the placebo group, the groups who took Dronabinol or Candor in spasticity demonstrated better improvement in the secondary result. They discovered that subjects who took Dronabinol exhibited a slight improvement on the Ashworth scale (p = 0.003) after 12 months of follow-up, which was not detected in the canned or placebo groups [57].
2.2.2. Effects of Dronabinol on MS-Related Pain
Schimrigk et al. published a study that found Dronabinol to be superior to placebo in the treatment of neuropathic pain [106]. They discovered a clinically relevant difference between the treatment and placebo groups without statistical significance. They also discovered that it is a safe long-term management choice for MS with pain, since the number of side effects was comparable to that of normal treatment [106].
2.3. Nabilone
Nabilone (Figure 1e) is the generic name for the primary synthetic analog of 9-THC carrying dibenzopyran-9-one structure with a racemic combination of (S,S)-(+)- and (R,R)-(−)-isomers. Nabilone was approved in 1985 for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced vomiting and nausea in individuals who did not respond to standard anti-emetic drugs; however, serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonists have partially supplanted Nabilone for this use. Nabilone is also approved for the treatment of neuropathic and chronic cancer pain, as well as MS spasticity. It comes in three dosages in pill form (0.25, 0.5, and 1 mg). The effectiveness of nabilone in the treatment of MS spasticity was investigated in three clinical studies published between 1995 and 2015 [108,109,110] and reviewed in four reviews published between 2006 and 2015 [40,44,46,111]. Nabilone appears to be beneficial in lowering most MS symptoms, including stiffness, pain, bladder dysfunction, and quality of life, according to the majority of trials (Table 1).
2.3.1. Effects of Nabilone on MS-Related Spasticity
Martyan et al. studied the effects of Nabilone on MS-related spasticity for four weeks [108]. Their findings indicated that MS spasticity symptoms have improved [108]. A meta-analysis of three parallel groups based on the GRADE rating approach revealed that Nabilone has a moderate effect on MS-related spasticity [75].
2.3.2. Nabilone Effects on MS-Related Pain
A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials found sufficient evidence to support the improved impact of Nabilone on MS-related pain [75]. In 2015, a randomized double-blind study looked at the effects of Nabilone as an adjunctive to gabapentin for neuropathic pain caused by relapsing-remitting MS. It found that Nabilone combined with gabapentin is an effective, novel, and well-tolerated treatment for MS patients with neuropathic pain [110].
2.3.3. Effects of Nabilone on MS-Related Tremor
Oral Nabilone was shown to have no meaningful effect on tremors in a class III trial [55]. In a systemic evaluation of 630 individuals, Koppel et al. concluded that oral Nabilone does not affect MS-related tremors [40].
3. Adverse Effects
Several studies that employed cannabis in MS patients reported the side effects of the drugs [72,82,112,113]. The severity of these side effects was typically described as ‘mild’ to ‘moderate’, depending on a variety of factors, such as the dose, type, and quantities of cannabinoids in the products used, and the individuals [72,82,112,113]. Dizziness/lightheadedness (14–59%), gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting) (13–37% in active groups), dry mouth (4–26% in active groups), urinary tract infections (15.4–34%), and other adverse effects, such as fatigue, headache, attention disturbance, and disorientation, are the most commonly reported adverse effects in MS patients treated with cannabinoids [56,57,77,112]. A recent study tookadvantage of The Epistemonikos database, and analyzed 25 systematic reviews on the use of cannabinoids in MS patients; they concluded that the benefit–risk ratio of using cannabinoids in these patients is unfavorable, because there is a high level of evidence about the lack of benefits, and adverse effects are common [114]. The majority of assessments of these studies found no evidence that any of these side effects limit clinical use [72].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/life12050682
References
- Trapp, D.B.; Nave, K.-A. Multiple sclerosis: An immune or neurodegenerative disorder? Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 31, 247–269.
- Schwab, N.; Schneider-Hohendorf, T.; Wiendl, H. Therapeutic uses of anti-α4-integrin (anti-VLA-4) antibodies in multiple sclerosis. Int. Immunol. 2015, 27, 47–53.
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
 Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia
