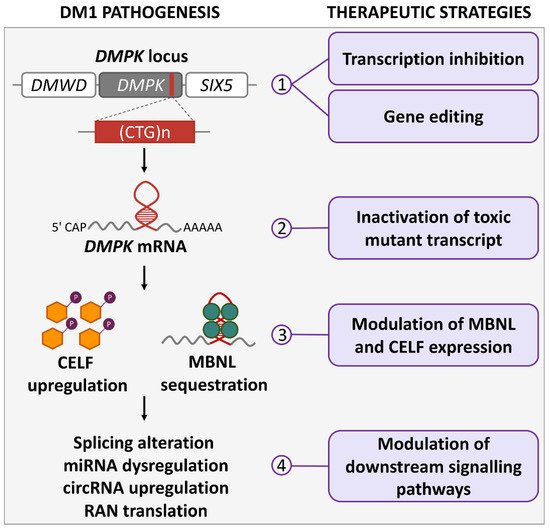
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) is the most common muscular dystrophy affecting many different body tissues, predominantly skeletal and cardiac muscles and the central nervous system. The expansion of CTG repeats in the DM1 protein-kinase (DMPK) gene is the genetic cause of the disease. The pathogenetic mechanisms are mainly mediated by the production of a toxic expanded CUG transcript from the DMPK gene. With the availability of new knowledge, disease models, and technical tools, much progress has been made in the discovery of altered pathways and in the potential of therapeutic intervention, making the path to the clinic a closer reality.
- myotonic dystrophy
- trinucleotide-expansion disease
- DM1 mice
- antisense oligonucleotides
- molecular therapy
- gene editing
1. Introduction
2. Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1: Clinical Features and Pathogenetic Mechanisms
3. DM1 Cell and Animal Models
| (A) Knockout and Overexpressing Models | ||||||||||||
| Mouse Model | Generation Strategy | DM1-Like Features | Limitations | Research Application | Ref | |||||||
| DMPK-/- | Dmpk KO via replacement of 5′-UTR and exons 1-7 with hygromycin cassette | Late-onset mild myopathy and altered Ca++ homeostasis | Mild phenotype; possible confounding insertional effects on flanking genes; mixed genetic background | Relevance of absence of DMPK protein to DM1 phenotype | [52][66] | |||||||
| DMPK-/- | Dmpk KO via replacement of 5′-UTR and exons 1-7 with neomycin cassette | Late-onset mild myopathy; decreased force generation; altered Na+ currents in skeletal muscles; cardiac conduction defects | Mild phenotype; possible confounding insertional effects on flanking genes; mixed genetic background | Relevance of absence of DMPK protein to DM1 phenotype | [51][67] | |||||||
| DMPK-/- | Dmpk KO via replacement of 5′-UTR and exons 1-7 with hygromycin cassette | No phenotype | Failure to replicate the DM1 phenotype | Relevance of absence of DMPK protein to DM1 phenotype | [53] | |||||||
| Mbnl1ΔE3/ΔE3 | Mbnl1 KO via targeted deletion of Mbnl1 exon 3 | Mild myotonia and myopathy (centralized nuclei, split fibers); heart conduction defects; progressive cataracts; AS alterations | Mild muscle phenotype; mild brain alterations; limited spliceopathy | Evaluation of MBNL1 splicing regulation to DM1 phenotype | [56][57] | |||||||
| Mbnl2ΔE2/ΔE2 | Mbnl2 KO via targeted deletion of Mbnl2 exon 2 | Development of several CNS alterations (REM sleep propensity, deficit in spatial memory, decreased synaptic plasticity), AS alterations | Failure to replicate the DM1 muscular phenotype | Evaluation of MBNL2 splicing regulation to DM1 phenotype | [55] | |||||||
| Mbnl3ΔE2 | Mbnl3 KO via targeted deletion of Mbnl3 exon 2 (X-linked) | Progressive delay in muscle regeneration; abnormalities in embryonic muscle differentiation leading to neonatal hypotonia | Possible compensation by MBNL3 truncated isoform or other MBNl family members | Evaluation of MBNL3 contribution to DM1 phenotype | [58] | |||||||
| Mbnl1ΔE3/ΔE3; Mbnl2C/C; Myo-Cre+/- |
Mbnl1 KO; skeletal-muscle specific Cre-mediated Mbnl2 KO | Small size at birth and skeletal abnormalities; myopathy and severe motor deficits; AS alterations also in brain tissues | High neonatal mortality and reduced lifespan | Evaluation of MBNL1 and MBNL2 contribution to DM1 muscular phenotype | [60] | |||||||
| Mbnl1ΔE3/ΔE3; Mbnl3ΔE2 |
Mbnl1 and Mbnl3 KO via targeted deletion of Mbnl1 exon 3 and Mbnl3 exon 2 | Myotonia and myopathy; reduction in muscle strength; chloride currents alteration; AS alterations; translation defects | AS alterations similar to Mbnl1 single knock out; lack of brain alterations | Evaluation of MBNL1 and MBNL3 contribution to DM1 phenotype | [59] | |||||||
| Mbnl1ΔE3/ΔE3; Mbnl2C/C; Mbnl3C; Myo-Cre+/- |
Mbnl1 KO; muscle-specific Cre-mediated Mbnl2 and Mbnl3 KO | Severe congenital myopathy and spliceopathy, severe respiratory difficulties and muscle wasting in adults; gene expression changes | High neonatal mortality and reduced lifespan | Evaluation of all MBNL proteins loss contribution to DM1 muscular phenotype | [61] | |||||||
| MCKCUGBP1 | Insertion of human CELF1 transgene under striated-muscle-specific MCK mouse promoter | Chains of central nuclei in myofibers, increased NADH reactivity, degenerating fibers and AS alterations | Neonatal lethality in mice expressing high levels of CELF1 | Contribution of CELF1 overexpression to DM1 muscular phenotype | [62] | |||||||
| TRECUGBP1 | Insertion of Tet-responsive human CELF1 transgene; heart-specific rtTA expression | Left ventricular systolic dysfunction and dilatation, AS alterations | DM1-like phenotype limited to heart defects | Contribution of CELF1 overexpression to DM1 heart phenotype | [63] | |||||||
| TRECUGBP1 | Insertion of Tet-responsive human CELF1 transgene; skeletal-muscle-specific rtTA expression | Myofibers containing central nuclei, decreased muscle weight, impaired muscle function, AS alterations | DM1-like phenotype limited to skeletal-muscle defects | Contribution of CELF1 overexpression to DM1 skeletal-muscle phenotype | [65] | |||||||
| TRECUGBP2 | Insertion of Tet-responsive human CELF2 transgene; heart-specific rtTA expression | No observed heart pathology; AS alterations similar to those observed in TRECUBP1 mice | Mild heart phenotype | Contribution of CELF2 overexpression to DM1 heart phenotype | [64] | |||||||
| (B) Transgenic Models with Repeat Expansion | ||||||||||||
| Mouse Model | Generation Strategy | (CTG)n | DM1-Like Features | Limitations | Research Application | Ref | ||||||
| DM200 | Insertion of a Tet-responsive expanded DMPK transgene where DMPK coding region is replaced by GFP | 200 | Ribonuclear foci; MBNL1 sequestration; AS alterations; myotonia, progressive cardiac conduction abnormalities | Splicing alterations in the heart have not been described | Study of DM1 phenotype associated with toxic CUG repeats; modeling muscle regeneration; test of therapeutic strategies | [68][69][70] | ||||||
| DM300 | Insertion of a 45Kb human genomic fragment containing DMWD, DMPK and SIX5 genes from a DM1 patient | ~300 | Ribonuclear foci (skeletal muscle, heart and brain); myotonia; muscle atrophy; morphological abnormalities; changes in the distribution of MAPT/Tau protein isoform; defect in glucose metabolism | High mortality; mild splicing alterations; intergenerational instability of CTG-repeat numbers | Evaluation of DMPK transcript toxicity in different tissues | [71][72] | ||||||
| DMSXL | Insertion of a 45Kb human genomic fragment containing DMWD, DMPK and SIX5 genes from a DM1 patient | >1000 | Ribonuclear foci; MBNL1 sequestration; AS alterations; deficits in motor performance; behavioral abnormalities; synaptic dysfunction; inhibition of exploratory activity and cerebellar glial dysfunction | High mortality; severe body-weight reduction; interindividual variability; decreased transgene expression with aging; mild muscular phenotype | Evaluation of DMPK transcript toxicity in different tissues and in multiple brain cell types; test of therapeutic strategies | [23][73][74] | ||||||
| HSALR | Insertion of the human skeletal actin (HSA) gene including CTG repeats in the 3’ UTR | ~250 | Ribonuclear foci; AS alterations; myotonia and muscle histopathology abnormalities (increase in central nuclei and variability in fiber size) after six months of age |
Limited to skeletal muscle; does not contain DMPK gene sequence; absence of muscle weakness | Investigation of expanded-CUG-repeat toxicity in muscle fibers; test of therapeutic strategies |
[75][76] | ||||||
| LC15 | Insertion of CTG expanded DMPK 3’ UTR downstream Luciferase gene driven by CMV-βA promoter | 250–400 | Ribonuclear foci, AS alteration and MBNL2 upregulation in the heart; reduced Na+ and K+ channel activity; ventricular arrhythmias | DM1-like phenotype limited to heart defects | Evaluation of biophysical mechanisms reproducing DM1-like electrocardiograph abnormalities | [77] | ||||||
| EpA960/ 𝛼-MHC-Cre |
Insertion of CTG expanded DMPK exon 15 transgene containing Cre-responsive loxP sequences; heart-specific myosin Cre expression | 960 (CTCGA-interrupted) |
Ribonuclear foci; MBNL1 sequestration; CELF1 protein upregulation; AS alterations; cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias; systolic and diastolic dysfunction |
Does not reproduce CTG-repeat continuity; mouse model no longer available | Evaluation of DMPK transcript toxicity and CELF1 overexpression in heart tissue | [78] | ||||||
| EpA960/ HSA-Cre |
Insertion of CTG expanded DMPK exon 15 transgene containing Cre-responsive loxP sequence; skeletal-muscle-specific Cre expression | 960 (CTCGA-interrupted) |
Ribonuclear foci; MBNL1 sequestration; CELF1 protein upregulation; AS defects; myotonia and progressive muscle wasting, deficits in muscle performance and histopathological abnormalities | Does not reproduce CTG-repeat continuity; mouse model no longer available | Evaluation of DMPK transcript toxicity and CELF1 overexpression in skeletal tissue | [79] | ||||||
| EpA960/ CamKII-Cre |
Insertion of CTG expanded DMPK exon 15 transgene containing Cre-responsive loxP sequence; brain-specific Cre expression | 960 (CTCGA-interrupted) |
Ribonuclear foci; MBNL1 sequestration; AS alterations; learning disability; neurotransmission dysfunction; brain atrophy and aging | Does not reproduce CTG-repeat continuity; mouse model no longer available | Identify mechanisms involved in CTG-dependent neuronal degeneration | [80] | ||||||
| TREDT960I/𝛼-MHC-rtTA | Insertion of Tet-responsive expanded DMPK exons 11–15 transgene; heart-specific rtTA expression | 960 (CTCGA-interrupted) |
Ribonuclear foci; MBNL1 sequestration; CELF1 protein upregulation; AS alterations ; arrhythmias | Does not reproduce CTG-repeat continuity | Study of alteration of ion transport and action potential in cardiomyocytes expressing toxic CUG | [81][82] | ||||||
| TREDT960I/ MDAF-rtTA |
Insertion of Tet-responsive expanded DMPK exons 11–15 transgene; skeletal-muscle-specific rtTA expression | 960 (CTCGA-interrupted) |
Ribonuclear foci; MBNL1 sequestration; CELF1 protein upregulation; AS alterations; muscle wasting and myopathy | Does not reproduce CTG-repeat continuity | Study the mechanisms of CUG-repeat-induced muscle tissue loss | [83] | ||||||
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms23094622
References
- Johnson, N.E.; Butterfield, R.J.; Mayne, K.; Newcomb, T.; Imburgia, C.; Dunn, D.; Duval, B.; Feldkamp, M.L.; Weiss, R.B. Population-Based Prevalence of Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 Using Genetic Analysis of Statewide Blood Screening Program. Neurology 2021, 96, e1045–e1053.
- Bird, T.D. Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1165/ (accessed on 21 March 2022).
- Harper, P.; van Engelen, B.; Eymard, B.; Wilcox, D. Myotonic Dystrophy. Present management, future therapy; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004; ISBN 9780198527824.
- Meola, G.; Cardani, R. Myotonic dystrophies: An update on clinical aspects, genetic, pathology, and molecular pathomechanisms. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 594–606.
- Brook, J.D.; McCurrach, M.E.; Harley, H.G.; Buckler, A.J.; Church, D.; Aburatani, H.; Hunter, K.; Stanton, V.P.; Thirion, J.P.; Hudson, T.; et al. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: Expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3′ end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell 1992, 68, 799–808.
- Mahadevan, M.; Tsilfidis, C.; Sabourin, L.; Shutler, G.; Amemiya, C.; Jansen, G.; Neville, C.; Narang, M.; Barcelo, J.; O’Hoy, K.; et al. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: An unstable CTG repeat in the 3′ untranslated region of the gene. Science 1992, 255, 1253–1255.
- Ashizawa, T.; Dunne, C.J.; Dubel, J.R.; Perryman, M.B.; Epstein, H.F.; Boerwinkle, E.; Hejtmancik, J.F. Anticipation in myotonic dystrophy. I. Statistical verification based on clinical and haplotype findings. Neurology 1992, 42, 1871–1877.
- Overend, G.; Legare, C.; Mathieu, J.; Bouchard, L.; Gagnon, C.; Monckton, D.G. Allele length of the DMPK CTG repeat is a predictor of progressive myotonic dystrophy type 1 phenotypes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 2245–2254.
- Miller, J.N.; van der Plas, E.; Hamilton, M.; Koscik, T.R.; Gutmann, L.; Cumming, S.A.; Monckton, D.G.; Nopoulos, P.C. Variant repeats within the DMPK CTG expansion protect function in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neurol. Genet. 2020, 6, e504.
- Andre, L.M.; Ausems, C.R.M.; Wansink, D.G.; Wieringa, B. Abnormalities in Skeletal Muscle Myogenesis, Growth, and Regeneration in Myotonic Dystrophy. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 368.
- Visconti, V.V.; Centofanti, F.; Fittipaldi, S.; Macri, E.; Novelli, G.; Botta, A. Epigenetics of Myotonic Dystrophies: A Minireview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12594.
- Alwazzan, M.; Newman, E.; Hamshere, M.G.; Brook, J.D. Myotonic dystrophy is associated with a reduced level of RNA from the DMWD allele adjacent to the expanded repeat. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 1491–1497.
- Thornton, C.A.; Wymer, J.P.; Simmons, Z.; McClain, C.; Moxley, R.T., 3rd. Expansion of the myotonic dystrophy CTG repeat reduces expression of the flanking DMAHP gene. Nat. Genet. 1997, 16, 407–409.
- Brouwer, J.R.; Huguet, A.; Nicole, A.; Munnich, A.; Gourdon, G. Transcriptionally Repressive Chromatin Remodelling and CpG Methylation in the Presence of Expanded CTG-Repeats at the DM1 Locus. J. Nucleic Acids 2013, 2013, 567435.
- Wang, E.T.; Cody, N.A.; Jog, S.; Biancolella, M.; Wang, T.T.; Treacy, D.J.; Luo, S.; Schroth, G.P.; Housman, D.E.; Reddy, S.; et al. Transcriptome-wide regulation of pre-mRNA splicing and mRNA localization by muscleblind proteins. Cell 2012, 150, 710–724.
- Nutter, C.A.; Bubenik, J.L.; Oliveira, R.; Ivankovic, F.; Sznajder, L.J.; Kidd, B.M.; Pinto, B.S.; Otero, B.A.; Carter, H.A.; Vitriol, E.A.; et al. Cell-type-specific dysregulation of RNA alternative splicing in short tandem repeat mouse knockin models of myotonic dystrophy. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 1635–1640.
- Kalsotra, A.; Xiao, X.; Ward, A.J.; Castle, J.C.; Johnson, J.M.; Burge, C.B.; Cooper, T.A. A postnatal switch of CELF and MBNL proteins reprograms alternative splicing in the developing heart. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20333–20338.
- Imbriano, C.; Molinari, S. Alternative Splicing of Transcription Factors Genes in Muscle Physiology and Pathology. Genes 2018, 9, 107.
- Lopez-Martinez, A.; Soblechero-Martin, P.; de-la-Puente-Ovejero, L.; Nogales-Gadea, G.; Arechavala-Gomeza, V. An Overview of Alternative Splicing Defects Implicated in Myotonic Dystrophy Type I. Genes 2020, 11, 1109.
- Kuyumcu-Martinez, N.M.; Wang, G.S.; Cooper, T.A. Increased steady-state levels of CUGBP1 in myotonic dystrophy 1 are due to PKC-mediated hyperphosphorylation. Mol. Cell. 2007, 28, 68–78.
- Castro, A.F.; Loureiro, J.R.; Bessa, J.; Silveira, I. Antisense Transcription across Nucleotide Repeat Expansions in Neurodegenerative and Neuromuscular Diseases: Progress and Mysteries. Genes 2020, 11, 1418.
- Cho, D.H.; Thienes, C.P.; Mahoney, S.E.; Analau, E.; Filippova, G.N.; Tapscott, S.J. Antisense transcription and heterochromatin at the DM1 CTG repeats are constrained by CTCF. Mol. Cell. 2005, 20, 483–489.
- Huguet, A.; Medja, F.; Nicole, A.; Vignaud, A.; Guiraud-Dogan, C.; Ferry, A.; Decostre, V.; Hogrel, J.Y.; Metzger, F.; Hoeflich, A.; et al. Molecular, physiological, and motor performance defects in DMSXL mice carrying >1000 CTG repeats from the human DM1 locus. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1003043.
- Kearse, M.G.; Wilusz, J.E. Non-AUG translation: A new start for protein synthesis in eukaryotes. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 1717–1731.
- Zu, T.; Gibbens, B.; Doty, N.S.; Gomes-Pereira, M.; Huguet, A.; Stone, M.D.; Margolis, J.; Peterson, M.; Markowski, T.W.; Ingram, M.A.; et al. Non-ATG-initiated translation directed by microsatellite expansions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 260–265.
- Koehorst, E.; Nunez-Manchon, J.; Ballester-Lopez, A.; Almendrote, M.; Lucente, G.; Arbex, A.; Chojnacki, J.; Vazquez-Manrique, R.P.; Gomez-Escribano, A.P.; Pintos-Morell, G.; et al. Characterization of RAN Translation and Antisense Transcription in Primary Cell Cultures of Patients with Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5520.
- Falcone, G.; Perfetti, A.; Cardinali, B.; Martelli, F. Noncoding RNAs: Emerging players in muscular dystrophies. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 503634.
- Perbellini, R.; Greco, S.; Sarra-Ferraris, G.; Cardani, R.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Meola, G.; Martelli, F. Dysregulation and cellular mislocalization of specific miRNAs in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD 2011, 21, 81–88.
- Perfetti, A.; Greco, S.; Cardani, R.; Fossati, B.; Cuomo, G.; Valaperta, R.; Ambrogi, F.; Cortese, A.; Botta, A.; Mignarri, A.; et al. Validation of plasma microRNAs as biomarkers for myotonic dystrophy type 1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38174.
- Rau, F.; Freyermuth, F.; Fugier, C.; Villemin, J.P.; Fischer, M.C.; Jost, B.; Dembele, D.; Gourdon, G.; Nicole, A.; Duboc, D.; et al. Misregulation of miR-1 processing is associated with heart defects in myotonic dystrophy. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 840–845.
- Czubak, K.; Taylor, K.; Piasecka, A.; Sobczak, K.; Kozlowska, K.; Philips, A.; Sedehizadeh, S.; Brook, J.D.; Wojciechowska, M.; Kozlowski, P. Global Increase in Circular RNA Levels in Myotonic Dystrophy. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 649.
- Greco, S.; Cardinali, B.; Falcone, G.; Martelli, F. Circular RNAs in Muscle Function and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3454.
- Voellenkle, C.; Perfetti, A.; Carrara, M.; Fuschi, P.; Renna, L.V.; Longo, M.; Sain, S.B.; Cardani, R.; Valaperta, R.; Silvestri, G.; et al. Dysregulation of Circular RNAs in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1938.
- Ozimski, L.L.; Sabater-Arcis, M.; Bargiela, A.; Artero, R. The hallmarks of myotonic dystrophy type 1 muscle dysfunction. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2021, 96, 716–730.
- Espinosa-Espinosa, J.; Gonzalez-Barriga, A.; Lopez-Castel, A.; Artero, R. Deciphering the Complex Molecular Pathogenesis of Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 through Omics Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1441.
- Philips, A.V.; Timchenko, L.T.; Cooper, T.A. Disruption of splicing regulated by a CUG-binding protein in myotonic dystrophy. Science 1998, 280, 737–741.
- Warf, M.B.; Berglund, J.A. MBNL binds similar RNA structures in the CUG repeats of myotonic dystrophy and its pre-mRNA substrate cardiac troponin T. RNA 2007, 13, 2238–2251.
- Arandel, L.; Polay Espinoza, M.; Matloka, M.; Bazinet, A.; De Dea Diniz, D.; Naouar, N.; Rau, F.; Jollet, A.; Edom-Vovard, F.; Mamchaoui, K.; et al. Immortalized human myotonic dystrophy muscle cell lines to assess therapeutic compounds. Dis. Models Mech. 2017, 10, 487–497.
- Pantic, B.; Borgia, D.; Giunco, S.; Malena, A.; Kiyono, T.; Salvatori, S.; De Rossi, A.; Giardina, E.; Sangiuolo, F.; Pegoraro, E.; et al. Reliable and versatile immortal muscle cell models from healthy and myotonic dystrophy type 1 primary human myoblasts. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 342, 39–51.
- Provenzano, C.; Cappella, M.; Valaperta, R.; Cardani, R.; Meola, G.; Martelli, F.; Cardinali, B.; Falcone, G. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Deletion of CTG Expansions Recovers Normal Phenotype in Myogenic Cells Derived from Myotonic Dystrophy 1 Patients. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 9, 337–348.
- Renna, L.V.; Bose, F.; Iachettini, S.; Fossati, B.; Saraceno, L.; Milani, V.; Colombo, R.; Meola, G.; Cardani, R. Receptor and post-receptor abnormalities contribute to insulin resistance in myotonic dystrophy type 1 and type 2 skeletal muscle. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184987.
- Franck, S.; Couvreu De Deckersberg, E.; Bubenik, J.L.; Markouli, C.; Barbe, L.; Allemeersch, J.; Hilven, P.; Duque, G.; Swanson, M.S.; Gheldof, A.; et al. Myotonic dystrophy type 1 embryonic stem cells show decreased myogenic potential, increased CpG methylation at the DMPK locus and RNA mis-splicing. Biol. Open 2022, 11.
- Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Santostefano, K.; Wang, Y.; Reid, T.; Zeng, D.; Terada, N.; Ashizawa, T.; Xia, G. Genome Therapy of Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 iPS Cells for Development of Autologous Stem Cell Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 1378–1387.
- Ueki, J.; Nakamori, M.; Nakamura, M.; Nishikawa, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Tanaka, A.; Morizane, A.; Kamon, M.; Araki, T.; Takahashi, M.P.; et al. Myotonic dystrophy type 1 patient-derived iPSCs for the investigation of CTG repeat instability. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42522.
- Martineau, L.; Racine, V.; Benichou, S.A.; Puymirat, J. Lymphoblastoids cell lines—Derived iPSC line from a 26-year-old myotonic dystrophy type 1 patient carrying (CTG)200 expansion in the DMPK gene: CHUQi001-A. Stem Cell Res. 2018, 26, 103–106.
- Spitalieri, P.; Talarico, R.V.; Caioli, S.; Murdocca, M.; Serafino, A.; Girasole, M.; Dinarelli, S.; Longo, G.; Pucci, S.; Botta, A.; et al. Modelling the pathogenesis of Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 cardiac phenotype through human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 118, 95–109.
- Fernandez-Garibay, X.; Ortega, M.A.; Cerro-Herreros, E.; Comelles, J.; Martinez, E.; Artero, R.; Fernandez-Costa, J.M.; Ramon-Azcon, J. Bioengineeredin vitro3D model of myotonic dystrophy type 1 human skeletal muscle. Biofabrication 2021, 13.
- de Haro, M.; Al-Ramahi, I.; De Gouyon, B.; Ukani, L.; Rosa, A.; Faustino, N.A.; Ashizawa, T.; Cooper, T.A.; Botas, J. MBNL1 and CUGBP1 modify expanded CUG-induced toxicity in a Drosophila model of myotonic dystrophy type 1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 2138–2145.
- Houseley, J.M.; Wang, Z.; Brock, G.J.; Soloway, J.; Artero, R.; Perez-Alonso, M.; O’Dell, K.M.; Monckton, D.G. Myotonic dystrophy associated expanded CUG repeat muscleblind positive ribonuclear foci are not toxic to Drosophila. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 873–883.
- Picchio, L.; Plantie, E.; Renaud, Y.; Poovthumkadavil, P.; Jagla, K. Novel Drosophila model of myotonic dystrophy type 1: Phenotypic characterization and genome-wide view of altered gene expression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 2795–2810.
- Reddy, S.; Smith, D.B.; Rich, M.M.; Leferovich, J.M.; Reilly, P.; Davis, B.M.; Tran, K.; Rayburn, H.; Bronson, R.; Cros, D.; et al. Mice lacking the myotonic dystrophy protein kinase develop a late onset progressive myopathy. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 325–335.
- Jansen, G.; Groenen, P.J.; Bachner, D.; Jap, P.H.; Coerwinkel, M.; Oerlemans, F.; van den Broek, W.; Gohlsch, B.; Pette, D.; Plomp, J.J.; et al. Abnormal myotonic dystrophy protein kinase levels produce only mild myopathy in mice. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 316–324.
- Carrell, S.T.; Carrell, E.M.; Auerbach, D.; Pandey, S.K.; Bennett, C.F.; Dirksen, R.T.; Thornton, C.A. Dmpk gene deletion or antisense knockdown does not compromise cardiac or skeletal muscle function in mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 4328–4338.
- Pandey, S.K.; Wheeler, T.M.; Justice, S.L.; Kim, A.; Younis, H.S.; Gattis, D.; Jauvin, D.; Puymirat, J.; Swayze, E.E.; Freier, S.M.; et al. Identification and characterization of modified antisense oligonucleotides targeting DMPK in mice and nonhuman primates for the treatment of myotonic dystrophy type 1. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 355, 329–340.
- Charizanis, K.; Lee, K.Y.; Batra, R.; Goodwin, M.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Shiue, L.; Cline, M.; Scotti, M.M.; Xia, G.; et al. Muscleblind-like 2-mediated alternative splicing in the developing brain and dysregulation in myotonic dystrophy. Neuron 2012, 75, 437–450.
- Kanadia, R.N.; Johnstone, K.A.; Mankodi, A.; Lungu, C.; Thornton, C.A.; Esson, D.; Timmers, A.M.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Swanson, M.S. A muscleblind knockout model for myotonic dystrophy. Science 2003, 302, 1978–1980.
- Matynia, A.; Ng, C.H.; Dansithong, W.; Chiang, A.; Silva, A.J.; Reddy, S. Muscleblind1, but not Dmpk or Six5, contributes to a complex phenotype of muscular and motivational deficits in mouse models of myotonic dystrophy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9857.
- Poulos, M.G.; Batra, R.; Li, M.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Darnell, R.B.; Swanson, M.S. Progressive impairment of muscle regeneration in muscleblind-like 3 isoform knockout mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3547–3558.
- Choi, J.; Personius, K.E.; DiFranco, M.; Dansithong, W.; Yu, C.; Srivastava, S.; Dixon, D.M.; Bhatt, D.B.; Comai, L.; Vergara, J.L.; et al. Muscleblind-Like 1 and Muscleblind-Like 3 Depletion Synergistically Enhances Myotonia by Altering Clc-1 RNA Translation. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1034–1047.
- Lee, K.Y.; Li, M.; Manchanda, M.; Batra, R.; Charizanis, K.; Mohan, A.; Warren, S.A.; Chamberlain, C.M.; Finn, D.; Hong, H.; et al. Compound loss of muscleblind-like function in myotonic dystrophy. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1887–1900.
- Thomas, J.D.; Sznajder, L.J.; Bardhi, O.; Aslam, F.N.; Anastasiadis, Z.P.; Scotti, M.M.; Nishino, I.; Nakamori, M.; Wang, E.T.; Swanson, M.S. Disrupted prenatal RNA processing and myogenesis in congenital myotonic dystrophy. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 1122–1133.
- Ho, T.H.; Bundman, D.; Armstrong, D.L.; Cooper, T.A. Transgenic mice expressing CUG-BP1 reproduce splicing mis-regulation observed in myotonic dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 1539–1547.
- Koshelev, M.; Sarma, S.; Price, R.E.; Wehrens, X.H.; Cooper, T.A. Heart-specific overexpression of CUGBP1 reproduces functional and molecular abnormalities of myotonic dystrophy type 1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 1066–1075.
- Wang, E.T.; Ward, A.J.; Cherone, J.M.; Giudice, J.; Wang, T.T.; Treacy, D.J.; Lambert, N.J.; Freese, P.; Saxena, T.; Cooper, T.A.; et al. Antagonistic regulation of mRNA expression and splicing by CELF and MBNL proteins. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 858–871.
- Ward, A.J.; Rimer, M.; Killian, J.M.; Dowling, J.J.; Cooper, T.A. CUGBP1 overexpression in mouse skeletal muscle reproduces features of myotonic dystrophy type 1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 3614–3622.
- Benders, A.A.; Groenen, P.J.; Oerlemans, F.T.; Veerkamp, J.H.; Wieringa, B. Myotonic dystrophy protein kinase is involved in the modulation of the Ca2+ homeostasis in skeletal muscle cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 1440–1447.
- Berul, C.I.; Maguire, C.T.; Aronovitz, M.J.; Greenwood, J.; Miller, C.; Gehrmann, J.; Housman, D.; Mendelsohn, M.E.; Reddy, S. DMPK dosage alterations result in atrioventricular conduction abnormalities in a mouse myotonic dystrophy model. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, R1–R7.
- Mahadevan, M.S.; Yadava, R.S.; Yu, Q.; Balijepalli, S.; Frenzel-McCardell, C.D.; Bourne, T.D.; Phillips, L.H. Reversible model of RNA toxicity and cardiac conduction defects in myotonic dystrophy. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1066–1070.
- Yadava, R.S.; Mandal, M.; Giese, J.M.; Rigo, F.; Bennett, C.F.; Mahadevan, M.S. Modeling muscle regeneration in RNA toxicity mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 1111–1130.
- Yadava, R.S.; Yu, Q.; Mandal, M.; Rigo, F.; Bennett, C.F.; Mahadevan, M.S. Systemic therapy in an RNA toxicity mouse model with an antisense oligonucleotide therapy targeting a non-CUG sequence within the DMPK 3′UTR RNA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 1440–1453.
- Seznec, H.; Agbulut, O.; Sergeant, N.; Savouret, C.; Ghestem, A.; Tabti, N.; Willer, J.C.; Ourth, L.; Duros, C.; Brisson, E.; et al. Mice transgenic for the human myotonic dystrophy region with expanded CTG repeats display muscular and brain abnormalities. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 2717–2726.
- Seznec, H.; Lia-Baldini, A.S.; Duros, C.; Fouquet, C.; Lacroix, C.; Hofmann-Radvanyi, H.; Junien, C.; Gourdon, G. Transgenic mice carrying large human genomic sequences with expanded CTG repeat mimic closely the DM CTG repeat intergenerational and somatic instability. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 1185–1194.
- Hernandez-Hernandez, O.; Guiraud-Dogan, C.; Sicot, G.; Huguet, A.; Luilier, S.; Steidl, E.; Saenger, S.; Marciniak, E.; Obriot, H.; Chevarin, C.; et al. Myotonic dystrophy CTG expansion affects synaptic vesicle proteins, neurotransmission and mouse behaviour. Brain J. Neurol. 2013, 136, 957–970.
- Sicot, G.; Servais, L.; Dinca, D.M.; Leroy, A.; Prigogine, C.; Medja, F.; Braz, S.O.; Huguet-Lachon, A.; Chhuon, C.; Nicole, A.; et al. Downregulation of the Glial GLT1 Glutamate Transporter and Purkinje Cell Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Myotonic Dystrophy. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2718–2729.
- Kimura, T.; Nakamori, M.; Lueck, J.D.; Pouliquin, P.; Aoike, F.; Fujimura, H.; Dirksen, R.T.; Takahashi, M.P.; Dulhunty, A.F.; Sakoda, S. Altered mRNA splicing of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor and sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 2189–2200.
- Mankodi, A.; Logigian, E.; Callahan, L.; McClain, C.; White, R.; Henderson, D.; Krym, M.; Thornton, C.A. Myotonic dystrophy in transgenic mice expressing an expanded CUG repeat. Science 2000, 289, 1769–1773.
- Tylock, K.M.; Auerbach, D.S.; Tang, Z.Z.; Thornton, C.A.; Dirksen, R.T. Biophysical mechanisms for QRS- and QTc-interval prolongation in mice with cardiac expression of expanded CUG-repeat RNA. J. Gen. Physiol. 2020, 152.
- Wang, G.S.; Kearney, D.L.; De Biasi, M.; Taffet, G.; Cooper, T.A. Elevation of RNA-binding protein CUGBP1 is an early event in an inducible heart-specific mouse model of myotonic dystrophy. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2802–2811.
- Orengo, J.P.; Chambon, P.; Metzger, D.; Mosier, D.R.; Snipes, G.J.; Cooper, T.A. Expanded CTG repeats within the DMPK 3′ UTR causes severe skeletal muscle wasting in an inducible mouse model for myotonic dystrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2646–2651.
- Wang, P.Y.; Lin, Y.M.; Wang, L.H.; Kuo, T.Y.; Cheng, S.J.; Wang, G.S. Reduced cytoplasmic MBNL1 is an early event in a brain-specific mouse model of myotonic dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2247–2257.
- Rao, A.N.; Campbell, H.M.; Guan, X.; Word, T.A.; Wehrens, X.H.; Xia, Z.; Cooper, T.A. Reversible cardiac disease features in an inducible CUG repeat RNA-expressing mouse model of myotonic dystrophy. JCI Insight 2021, 6.
- Valencik, M.L.; McDonald, J.A. Codon optimization markedly improves doxycycline regulated gene expression in the mouse heart. Transgenic Res. 2001, 10, 269–275.
- Morriss, G.R.; Rajapakshe, K.; Huang, S.; Coarfa, C.; Cooper, T.A. Mechanisms of skeletal muscle wasting in a mouse model for myotonic dystrophy type 1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 2789–2804.
