Sweet potato (SP; Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam) is an edible tuber native to America and the sixth most important food crop worldwide. China leads its production in a global market of USD 45 trillion. SP domesticated varieties differ in specific phenotypic/genotypic traits, yet all of them are rich in sugars, slow digestible/resistant starch, vitamins, minerals, bioactive proteins and lipids, carotenoids, polyphenols, ascorbic acid, alkaloids, coumarins, and saponins, in a genotype-dependent manner. Individually or synergistically, SP’s phytochemicals help to prevent many illnesses, including certain types of cancers and cardiovascular disorders.
- antioxidants
- sweet potato
- Ipomoea batatas
- cancer
- carotenoids
- phenolic compounds
1. Introduction
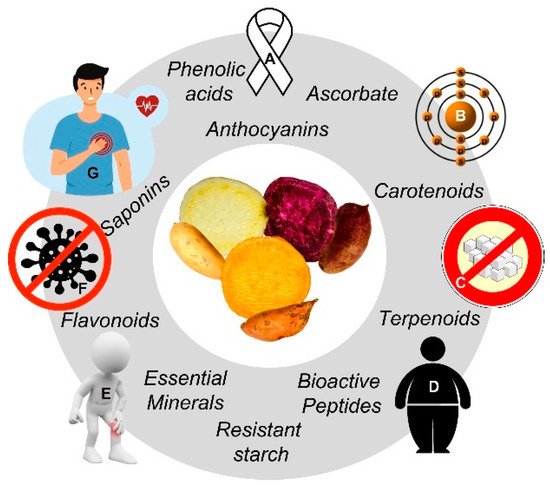
2. Health Effects and Metabolic Fate of SP’s Phytochemicals
2.1. SP and Cancer
| Variety | Phytochemical | Mechanism | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiation | |||
| Tainong 57 | Trypsin inhibitor |
DNA damage reparation |
↑ P53 leukemic cells |
| -- | Polyphenols | ↓ ROS | ↓ Oxidative damage induced by H2O2 in HepG2 cells. |
| Mixuan No. 1 | Protein hydrolysate |
↓ ROS | ↑ antioxidant activity, ↓ oxidative damage to DNA |
| Ayamurasaki | Anthocyanins | ↓ROS | ↓ Oxidative damage induced by radiation in thymocytes |
| Tainong 57 | Trypsin inhibitor | Cell cycle arrest | Phase G1 arrest |
| TU-155 | Polyphenols | Cell cycle arrest | ↓ciclin D1, A y E, ↑ Cip1/p21 |
| Promotion | |||
| NING No. 1 | Polysaccharides | Anti-inflammatory | ↓ IL-1β, IL-6 y TNF-α |
| TNG 73 | Anthocyanins | Anti-inflammatory | ↓ activation of NF-κβ in RAW 264.7 cells induced by LPS |
| -- | Caffeic acid and derivates | Inhibition in cell proliferation |
β-catenin and Tcf-4 pathway suppression |
| Progression | |||
| Bhu Krishna | Anthocyanins | Cell death induction | Apoptosis—↑ caspases |
| Diverse | Anthocyanins | Cell death induction | ↑ caspase 3 in colonic cells |
| -- | Polyphenols | Angiogenesis inhibition | ↓ VEGF165 in a dose-dependent manner |
| -- | BSG | Invasion inhibition | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway suppression |
| Zhongshu-1 | SPG-56 Glycoprotein |
Invasion inhibition | Regulation in the expression of proteins (MMP2, MMP9, VEGF, ocludin, and claudin) related with metastasis. |
| TNG 73 | Anthocyanins | Invasion inhibition | Cell migration suppression (MCF-7 cells) |
2.2. SP and Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD)
| Phytochemical | Mechanism | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Heart | ||
| Anthocyanins | ↓ Malondialdehyde | Antioxidant ↓ Lipid peroxidation |
| Flavonoids/ anthocyanin |
Vasodilation induction/ ↓ endothelin—1 |
Antihypertensive |
| Tannins/saponins/ Flavonoids/terpenoids |
↓ Creatine kinase ↓ Lactate dehydrogenase |
Prevention in ischemic damage |
| Vascular | ||
| Aqueous extracts | ↑ Telomerase activity preventing cell senescence |
Prevention of coronary artery disease |
| Anthocyanins | Inhibition of PDGF receptor-β |
Regulation of platelet aggregation |
| Chlorogenic acid | ACE Inhibition | Antihypertensive |
| Anthocyanins/ethanolic extract | ↓ VCAM | Prevention of atherosclerosis |
| SP leaves | Elongate arterial occlusion time | Prevention of thrombotic events |
| Purple SP extract | ↓ cyclooxygenase-2, ↓ inducible nitric oxide synthase ↓ tumor necrosis factor-α |
↓Inflammation |
| Brain and Kidney | ||
| Anthocyanins | ↑ BDNF | Neuroprotection after ischemic stroke |
| Flavonoids/ acetylated anthocyanins |
Blocking VEGFR2/ROS/NLRP3 signaling | ↓ Kidney damage |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/foods11071058
