3. Aldose Reductase Inhibitors
Due to the involvement of AKR1B1 in the etiology of diabetic complications, a great effort has been devoted in the last fifty years to the design and the synthesis of molecules able to inhibit AKRB1. More recently, the inhibition of AKR1B1 has been also considered a tool to intervene in the inflammation processes that contribute to the complications in the diabetic patients
[20].
The inhibitors of AKR1B1 have multiple structures, but some common features can be identified. ARIs usually present a polar moiety, that interacts with the aforementioned “anion binding pocket” of the enzyme and a hydrophobic moiety, that interacts with the non-polar region of the AKR1B1 active site
[6][7][21][22][23].
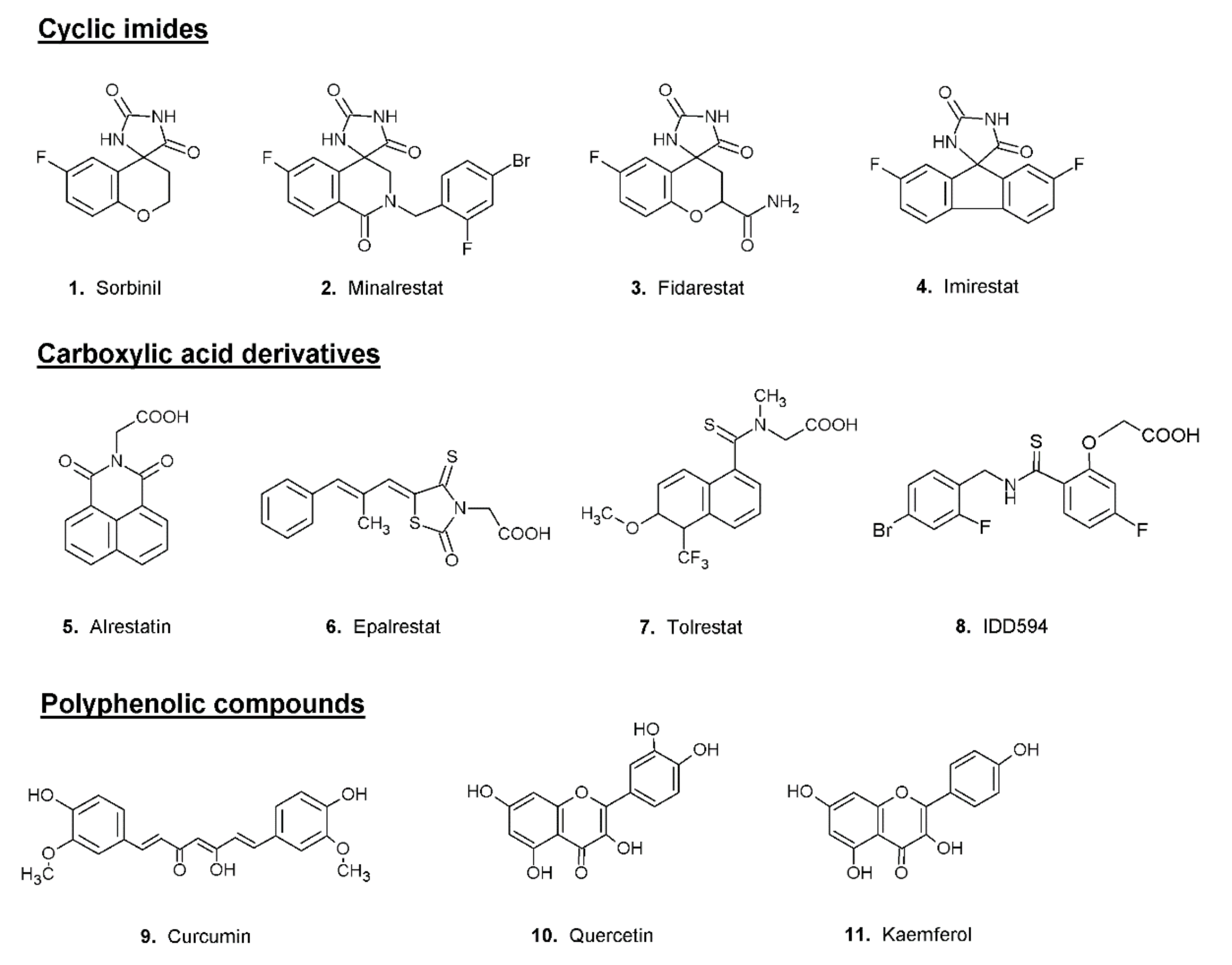
Most aldose reductase inhibitors can basically be divided into three main classes: compounds that contains cyclic imides, carboxylic-acid derivatives and polyphenolic compounds (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Structures of classical examples of aldose reductase inhibitors.
Sorbinil (compound
1 of
Figure 2), first introduced by Pfizer, can be considered the progenitor of the class of cyclic imides
[24]. Even though this inhibitor is able to efficiently inhibit the in vitro activity of the enzyme, by binding to the active site through the formation of hydrogen bonds
[7], the treatment of diabetic patients with Sorbinil showed no significant amelioration of secondary diabetic complications such as polyneuropathy
[25]. The ineffectiveness of Sorbinil in diabetic subjects, combined with the occurrence of hypersensitivity reactions to the drug
[26], led to the design of new inhibitors, whose structure was based on that of Sorbinil; among them the most effective were found to be Fidarestat, Minalrestat and Imirestat (compounds
2–
4 of
Figure 2)
[27].
The structure of Alrestatin (compound
5 of
Figure 2), one of the first carboxylic acid derivatives proposed as aldose reductase inhibitors, has been used as a model for the developing of a series of new ARIs. One of the most effective carboxylic derivatives is Epalrestat (compound
6 of
Figure 2), a potent AKR1B1 inhibitor capable of lowering the concentrations of fructose and sorbitol produced from the polyol pathway with a consequent reduction of the levels of oxidative stress. Experimental evidence showed the efficacy of Epalrestat in the treatment of diabetic neuropathies and nephropathies
[28]. Tolrestat (compound
7 of
Figure 2) is another potent AKR1B1 inhibitor of the class of carboxylic acid derivatives. Studies conducted on humans have demonstrated the ability of this inhibitor to improve neuropathy and nephropathy in diabetic subjects
[29][30][31]. After its commercialization in several countries, Tolrestat was withdrawn because of serious effects and reduced efficacy in subsequent clinical trials
[32]. Among the most studied molecules, tested as AKR1B1 inhibitors, are the compounds of the IDD series. These inhibitors, all designed starting from a common scaffold, are potent and specific with IC
50 in the low micromolar or nanomolar range
[33][34]. The analysis of the crystal structure of the ternary complex of human AKR1B1, NADP
+ and inhibitor IDD594 (compound
8 of
Figure 2) provided valuable information of the molecular mechanism of the opening of the specificity pocket involved in the binding of several AKR1B1 inhibitors. Even though many ARIs of the class of carboxylic acid derivatives show a great affinity for the enzyme in vitro, their potency is highly reduced in vivo. The reduced effectiveness in vivo is related to the very low pK
a of these inhibitors, which causes them to be ionized at physiological pH. The negative charge makes it difficult for these compounds to pass through the cell membrane
[3].
A great variety of polyphenolic compounds, for example, curcumin, quercetin and kaempferol (compounds
9–
11 of
Figure 2), have been shown to possess a potent inhibitory effect on AKR1B1 activity in various in vitro and in vivo systems
[35][36].
The search for new inhibitors of AKR1B1 is an active and constantly evolving field of research and every year several new molecules for the inhibition of AKR1B1 are designed and proposed
[11][37][38][39][40].
4. Aldose Reductase Differential Inhibitors
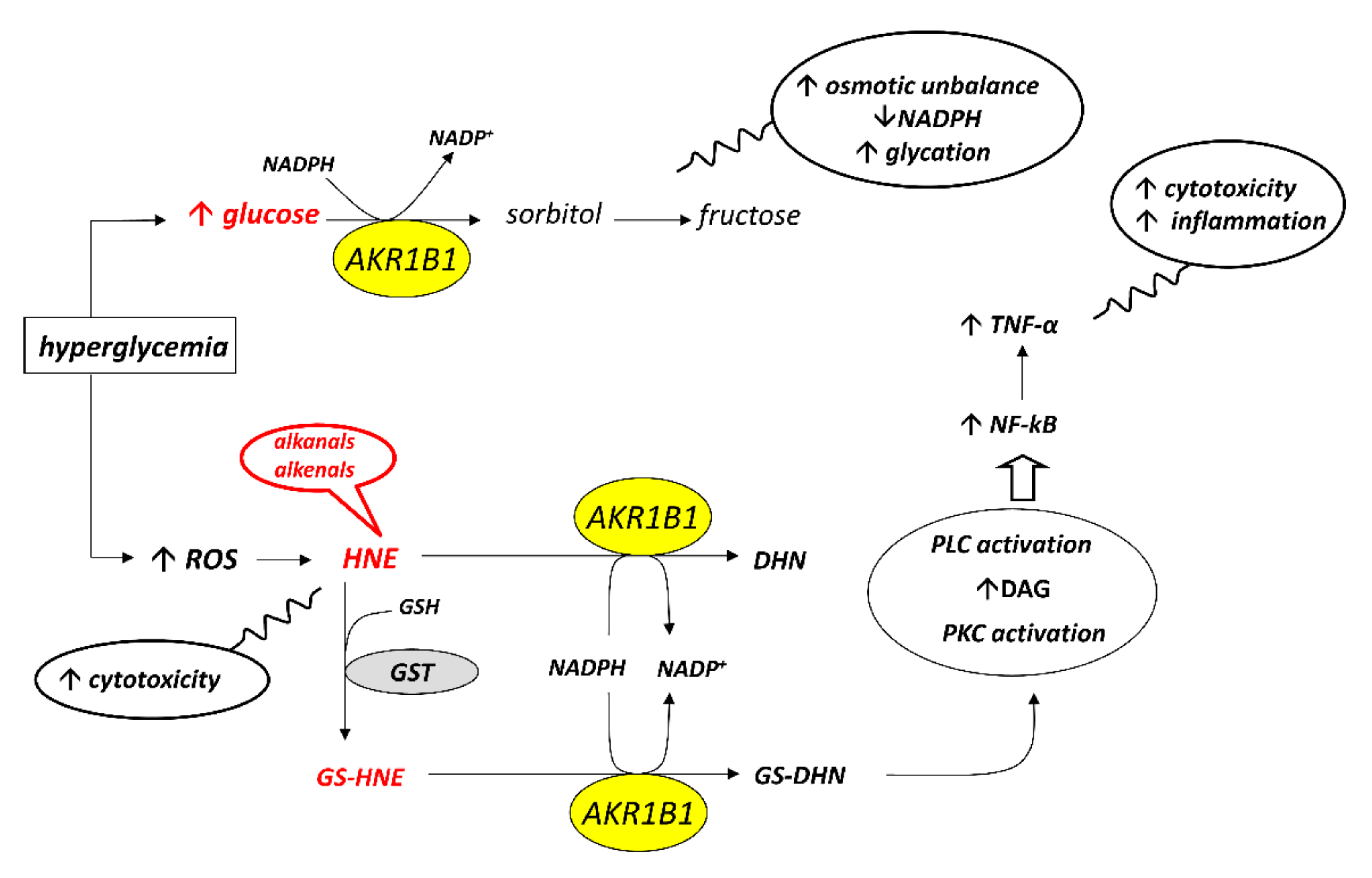
Despite the considerable effort devoted in the last decades to the synthesis of AKR1B1 inhibitors, virtually all synthesized compounds failed as drugs for the treatment of diabetic complications. To date, the only drug marketed is Epalrestat, for sale only in eastern countries. The reasons for this failure may be various and range from a reduced bioavailability of the molecules proposed as aldose reductase inhibitors to the onset of important side effects associated with the use of such inhibitors. On the other hand, a possible explanation could lie in the fact that the activity of AKR1B1 under hyperglycemic conditions, in addition to potential harmful effects, can have a beneficial effect, since, as reported above, AKR1B1 is capable of reducing toxic aldehydes, such as HNE and other alkenals and alkanals, which are formed during the lipid peroxidation process. Due to the failure of classical AKR1B inhibitors, a new strategy for inhibiting this enzyme has recently been proposed, based on the possibility of an inhibitory action dependent on the substrate to be transformed
[41]. AKR1B1 is a multispecific enzyme since it can catalyze the reduction of hydrophilic as well of hydrophobic substrates (
Table 1). However, if researchers consider the specificity of the enzyme towards its multiple substrates, it appears evident that AKR1B1 is not simply a permissive enzyme but is able to discriminate among different substrates of the same class
[42][43]. Emblematic in this regard is the comparison among different isomers and stereoisomers of aldoses (
Table 1); in the case of glucose, for instance, the activity of the enzyme towards
l-glucose is almost negligible. It is also noteworthy that in the case of glucose and other aldoses the reaction rate of AKR1B1 as a function of substrate concentrations appears biphasic. Believed to be associated with the heterogeneity of the used enzyme preparations supposed to contain two oxidative states of the enzyme
[44], the biphasic behavior observed with glucose and other aldose substrates turned out to depend on an incomplete inhibition exerted on the aldehyde reduction by the hemiacetal form of the sugar
[45].
Table 1. a List of AKR1B1 substrate examples. The specificity constant KS is reported for each substrate.
| Hydrophobic Substrates and Derivatives |
Ks
mM−1min−1 |
Aldoses |
Ks
mM−1min−1 |
| propanal |
5.5 |
d-glyceraldehyde |
1860 |
| butanal |
439 |
l-glyceraldehyde |
6840 |
| hexanal |
3657 |
d-threose |
114 |
| nonanal |
1157 |
l-threose |
276 |
| trans-2-pentenal |
61.7 |
d-arabinose |
0.24 |
| trans-2-nonenal |
2058 |
l-arabinose |
10.8 |
| 4-hydroxy trans-2-pentenal |
199 |
d-xylose |
8.4 |
| 4-hydroxy trans-2-nonenal |
921 |
l-xylose |
0.48 |
| trans-4-decenal |
1108 |
d-idose |
4.2 |
| cis-4-decenal |
862 |
l-idose |
35.75 |
| 4-hydroxy trans-2,3-nonenal |
2320 |
d-glucose |
0.61 |
| 3-glutathionyl-4-hydroxy-nonanal |
1376 |
l-glucose |
n.d. b |
a Adapted from [46]; b Not determinable; l-glucose is not a substrate up to 30 mM concentration.
The very fact that the enzyme can reduce both hydrophobic and hydrophilic aldehydes suggests that different molecules may interact with the enzyme following alternative pathways. Indeed, a molecular modelling study has highlighted the different ways in which the substrates glucose, HNE and GS-HNE interact with the active site of the enzyme
[47]. The computational analysis revealed that, in addition to the hydrogen bonds with the catalytic residues H110 and Y48, glucose forms other hydrogen bonds with residues W111 and L300, present in the active site of the enzyme and with the cofactor NADPH. HNE, besides the two hydrogen bonds with the catalytic residues H110 and Y48, seems to induce the opening of the “specificity pocket” that accommodates the hydrophobic tail of HNE. As for GS-HNE, the HNE moiety of the molecule interacts with the “specificity pocket” in a similar way to that of HNE, while the glutathionyl moiety forms hydrogen bonds with V47, W20 and Q49 residues located in the upper part of the active site
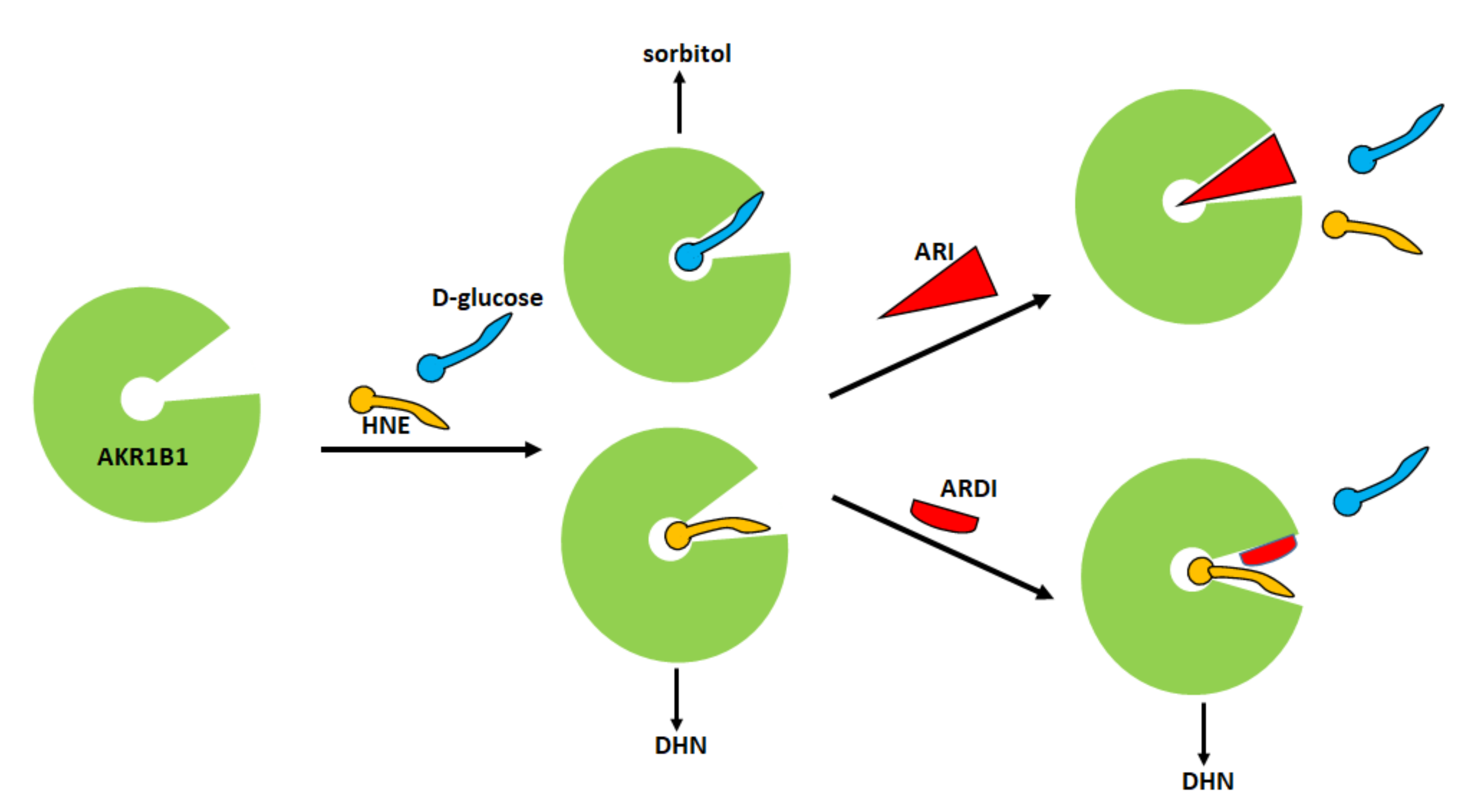
[47]. The consideration that different molecules may bind to the catalytic site of the enzyme following alternative ways supports the idea that it might be possible to act selectively on the enzyme by blocking its unwanted activities and preserving the advantageous ones. Thus, a useful aldose reductase differential inhibitor (ARDI) should preferentially inhibit the activity of AKR1B1 on glucose and/or GS-HNE, leaving unaltered or less affected the detoxifying action of the enzyme against HNE. Therefore, an ARDI would prevent the diabetic complications related to the activation of the polyol pathway and the pro-inflammatory effect of AKR1B1; on the other hand, it would maintain the detoxification capacity of the enzyme, contributing to the reduction of oxidative stress. The schematic representation of the ARDI action reported in
Figure 3 emphasizes the different positioning of the substrate at the active site as the rational base of a possible differential inhibitory action.
Figure 3. Classical and differential inhibition of AKR1B1. A classic inhibitor of AKR1B1 binds to the enzyme preventing both glucose and HNE from binding. A differential inhibitor binds to the enzyme and prevents glucose from binding but leaves the enzyme’s ability to transform HNE unaffected. HNE: 4-hydroxy-2,3-nonenal; DHN: 1,4-dihydroxy-2,3-nonene.
As highlighted in a theoretical study, a differential inhibitor of a multispecific enzyme should be able to preferentially bind to the free enzyme, that is, it should behave as a competitive inhibitor, or, alternatively, while being able to bind to both the free enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex, in a mixed type inhibition, it should still have a significant affinity for the free enzyme
[48].
Generally speaking, it is conceivable that, irrespective of the mechanism of action, a very powerful inhibitor, strongly interfering with the key catalytic function of Tyr-48, could hardly act as an ARDI, being unable to discriminate between different substrates.
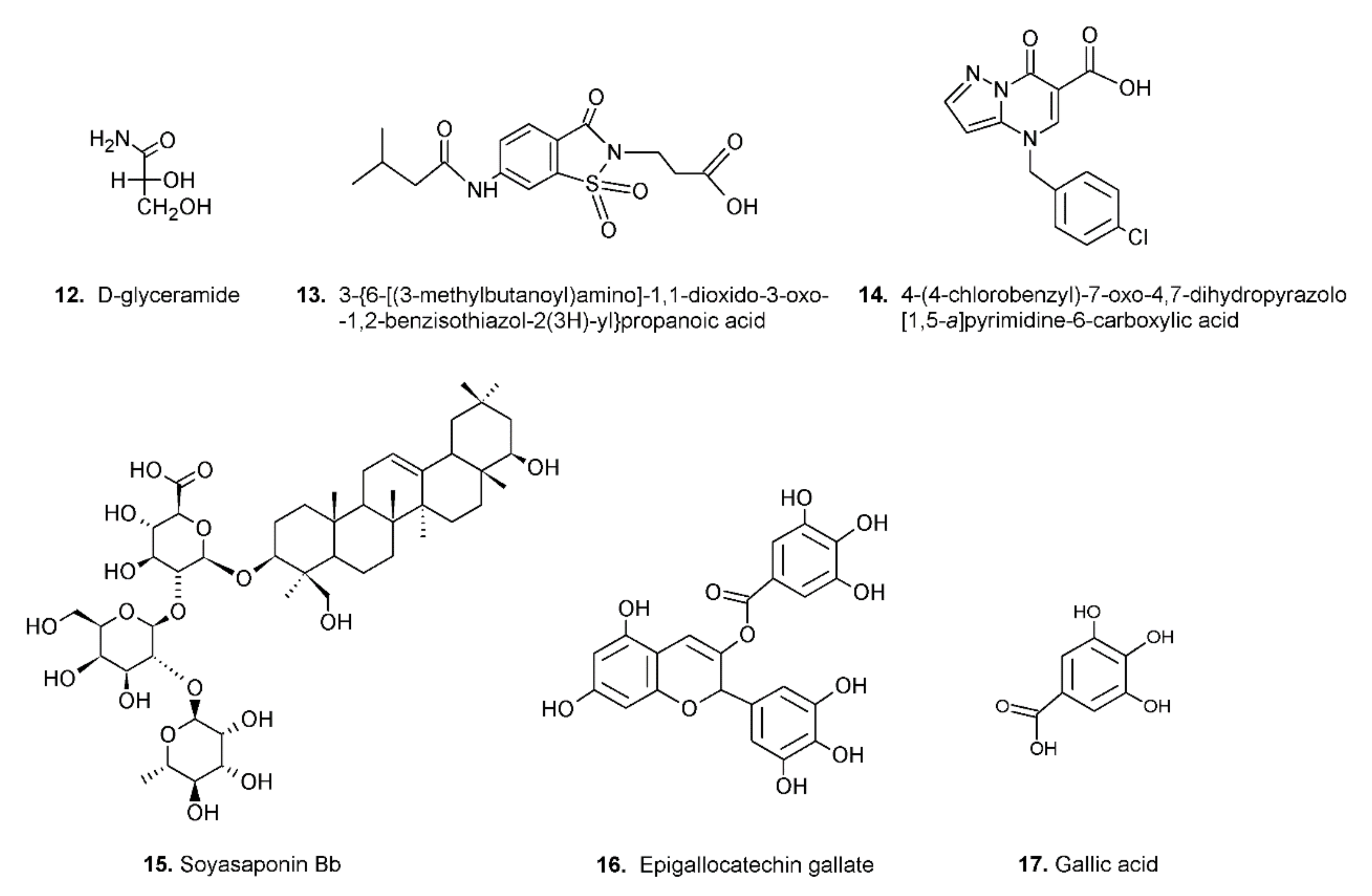
Despite the above mentioned restrictions, in a precursor study, clear kinetic evidence was obtained that some molecules are able to preferentially inhibit the reduction of the hydrophilic substrates (e.g.,
d-glyceramide, compound
12 of
Figure 4), while others are more efficient at inhibiting the reduction of the hydrophobic ones (e.g., compound
13 of
Figure 4)
[41].
Figure 4. Structures of molecules acting as ARDIs.
Starting from this first experimental evidence, a subsequent screening has been undertaken on a series of compounds previously developed as classical inhibitors of AKR1B1, in order to test the possibility that some of them could act as ARDIs. The possibility that different substrates bind differently to specific parts of the enzyme
[47] and the fact that the hemiacetal form of long-chain aldoses can modulate the activity of AKR1B1
[45] has raised the more general question of which substrate should be used in screening studies of AKR1B1 inhibitors. Most inhibition studies use
d,l-glyceraldehyde, a triose, which, in the light of the above considerations, cannot be considered the model substrate of the enzyme. Thus, in studies in which molecules for the inhibition of the reduction of
d-glucose by AKR1B1 are searched for,
d-glucose should be used as the appropriate substrate. However,
d-glucose, due to the very high K
M of AKR1B1 for this sugar, is a very poor substrate for the enzyme. Therefore, either large amounts of enzyme or extremely high glucose concentrations are required to have acceptable rate measurements. To circumvent the methodological limitations posed by the use of
d-glucose,
l-idose, the C-5 epimer of
d-glucose, which mimics the structure of
d-glucose, has been proposed as a good substrate alternative to
d-glucose
[49] and should be routinely used for searching for ARDIs. Furthermore, the evidence that dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)—the solvent most frequently used to solubilize compounds during AKR1B1 inhibition studies—affects
l-idose and HNE reduction through different inhibition mechanisms
[50] highlighted the need to strictly control the solvent concentration especially in studies looking for ARDIs.
The search for ARDIs among some previously described AKR1B1 inhibitors evidenced that classical potent AKR1B1 inhibitors, such as Epalrestat and Sorbinil, showed no ability to differentially inhibit AKR1B1. At the same time, it has been shown that other molecules are able to modulate the activity of the enzyme depending on the specific substrate (
l-idose, HNE or GS-HNE adduct). In particular, when screening molecules of a class of acid derivatives of pyrazolo[1,5-
a] pyrimidine compounds (compound
14 of
Figure 4), characterized by the presence of a pyrazolo[1,5-
a] pyrimidine core and a carboxylic moiety, it has been reported that some compounds in this class can preferentially inhibit the reduction of sugars and GS-HNE adduct with respect to HNE
[51]. Explaining the structural features required for a molecule capable of inhibiting a certain mechanism of action while leaving an alternative pathway unaffected is not easy. The extensive structural information available for AKR1B1 is less helpful than one would expect, since it is lacking the most relevant information concerning the reciprocal influence between the substrate and the inhibitor both positioned on the enzyme. At the level of pure speculation, one might hypothesize that compounds able to preferentially inhibit the reduction of HNE over the reduction of glucose are able to somehow block the opening of the specificity pocket that allocates the hydrophobic tail of the HNE. This hypothesis might not be valid in the case of molecules which preferentially inhibit the reduction of glucose. In this case, the picture is further complicated by the presence of the hemiacetal form of glucose that influences the activity of AKR1B1.