Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology
|
Microbiology
Biohydrogen is a sustainable energy form and a preferable substitute for fossil fuel. Biohydrogen production is eco-friendly compared to other methods of hydrogen production. It has the potential to replace conventional fossil fuels without releasing greenhouse gases. Hydrogen production from biomass depends upon the type of feedstock utilized.
- biohydrogen
- feedstock
- fermentation
- fossil fuel
- global warming
- substrate pretreatment
1. Algae Biomass-Based Biohydrogen Production
Algae can be either prokaryotic or eukaryotic, performing photosynthesis such as higher plants and contributing to approximately 50% of global carbon fixation depending on the amount of light captured and photosynthesis [1][2]. Algal carbohydrates constitute 15–70% of dry cell mass and have a unique basic composition in every algal strain. As algae are rich in proteins, free amino acids can be obtained by hydrolysis of proteins. The cultivation medium and environment also affect the composition of the algal biomass. The cultivation of N. oleobundans in freshwater raises the carbohydrate content of the cell wall, whereas glucose content rises when grown in seawater [3]. Arthrospira platensis total carbohydrate content was reported to be 64.3%, mainly in the form of glucan [4]. The α-glucan is made up primarily of glucose (>90%), with negligible other simple sugars [5]. To obtain useful raw material to produce biohydrogen, suitable pretreatment must be used to extract both structural and storage microalgal carbohydrates from biomass after harvesting [6].
Pretreatment is obligatory for releasing fermentable sugars from algal biomass, as hydrogen-producing bacteria (HPB) typically have less hydrolytic enzymatic activity. To improve the efficiency of the fermentative biohydrogen production from algal biomass, pretreatment is imperative to liberate simple fermentable sugars from complex substrates and make them readily biodegradable. Methods employed for algal biomass pretreatment are physical (mechanical, heat, microwave irradiation, and ultrasonic treatment), chemical (acid, alkali, chloroform, ozonolysis), and biological (enzymatic treatment). These pretreatment methods are supposed to break down the cell wall and facilitate organic substances to be released from the cells [2]. After appropriate pretreatment, the HPB could consume simple substrates to produce hydrogen.
The production of biohydrogen primarily requires algae with high carbohydrate content. To avoid carbohydrate loss during pretreatment processes, the pretreatment method should be chosen very carefully, keeping in mind energy, environmental and economic indicators to achieve maximum efficiency with maximum hydrogen yield. Before selecting a pretreatment method for algal biomass, the following factors should be considered [6]. The efficiency of the pretreatment method is one of the major factors, depending in part on cell disruption efficiency and product yield. Energy demand is also important, as mechanical methods have high energy demands. Hence, to reduce the energy demand and improve performance, a combination of chemical and thermal processes may be used in combination with mechanical methods. Such an approach may reduce environmental impact. Cost is also an important factor. Microwaves or pulsed electric fields have high associated costs, while continuous systems with wet microalgal biomass may reduce costs by eliminating drying and dewatering processes. Product quality is another relevant factor. Although the selected pretreatment method should not ideally influence the quality of the product, it may be compromised in methods involving cavitation or oxidation, where free radicals are generated, or in chemical pretreatment, where excess salts are produced due to neutralization reactions. Another factor is the pollution generated from the solvents used in chemical pretreatment methods [7]. Specific criteria should be followed for selecting the pretreatment technology; the chosen approach should avoid biomass size reduction; the proportion of hemicellulose must be conserved and should be less energy-intensive [8].
2. Substrates for Biohydrogen Production and Their Pretreatment
Various pretreatment strategies have been studied to use waste materials for bio-hydrogen production. Pretreatment of the substrate is essential for efficient bio-hydrogen production. Pretreatment facilitates the substrate breakdown into simple sugars, a prerequisite for microbial growth. Fermentation at high operating temperatures (65–70 °C) improves the substrate degradation rate and thus increases H2 production rate [9]. Various wastes or wastewaters, such as olive mill effluent [10], are ideal for photo-biological H2 production as they contain ethanol, acetate, butyrate, and propionate. Sewage sludge and tofu wastewater are regarded as the most promising substrates for the production of H2. Before being utilized as a substrate, sewage sludge is pretreated for 1 h at 150 °C temperature under 10 atm after alkali treatment. During photo-fermentation, 0.17–0.28 L H2/L broth/day is constantly produced [11]. Cassava pulp is a by-product of the starch industry that contains up to 60% starch as dry matter and contains carbohydrates, including cellulose and hemicelluloses. Cassava pulp’s cellulose and hemicellulose may be acid hydrolyzed and utilized as a substrate for fermentative hydrogen production by anaerobic mixed cultures, under optimum hydrolysis conditions; 0.5% H2SO4 at a ratio of 1:15 (dry w/v) for 30 min, resulting in 27.4 g/L of total sugar yield [5]. Using various organic-rich domestic, agricultural, and industrial waste products for biohydrogen production decreases the cost of scaling up while also effectively removing the organic load [12]. Cheese whey is an excellent substrate for fermentative H2 generation since it comprises 4.6%lactose, 1.2% crude protein, 0.6% ash, 0.3% fat, 5–8% total solids, and 92.7% water [13][7]. Dairy wastewaters contain polysaccharides, proteins, and lipids, which undergo hydrolysis to sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids [11]. During fermentation, they are transformed into volatile fatty acids (VFAs), which are then degraded by acetogens to produce acetate, CO2, and H2 [14]. Pretreatment of complex biomass containing lignocelluloses is prevalent, as most complex substrates are unsuitable and must be broken down into simple components for easier access during fermentation [15] (Figure 1).
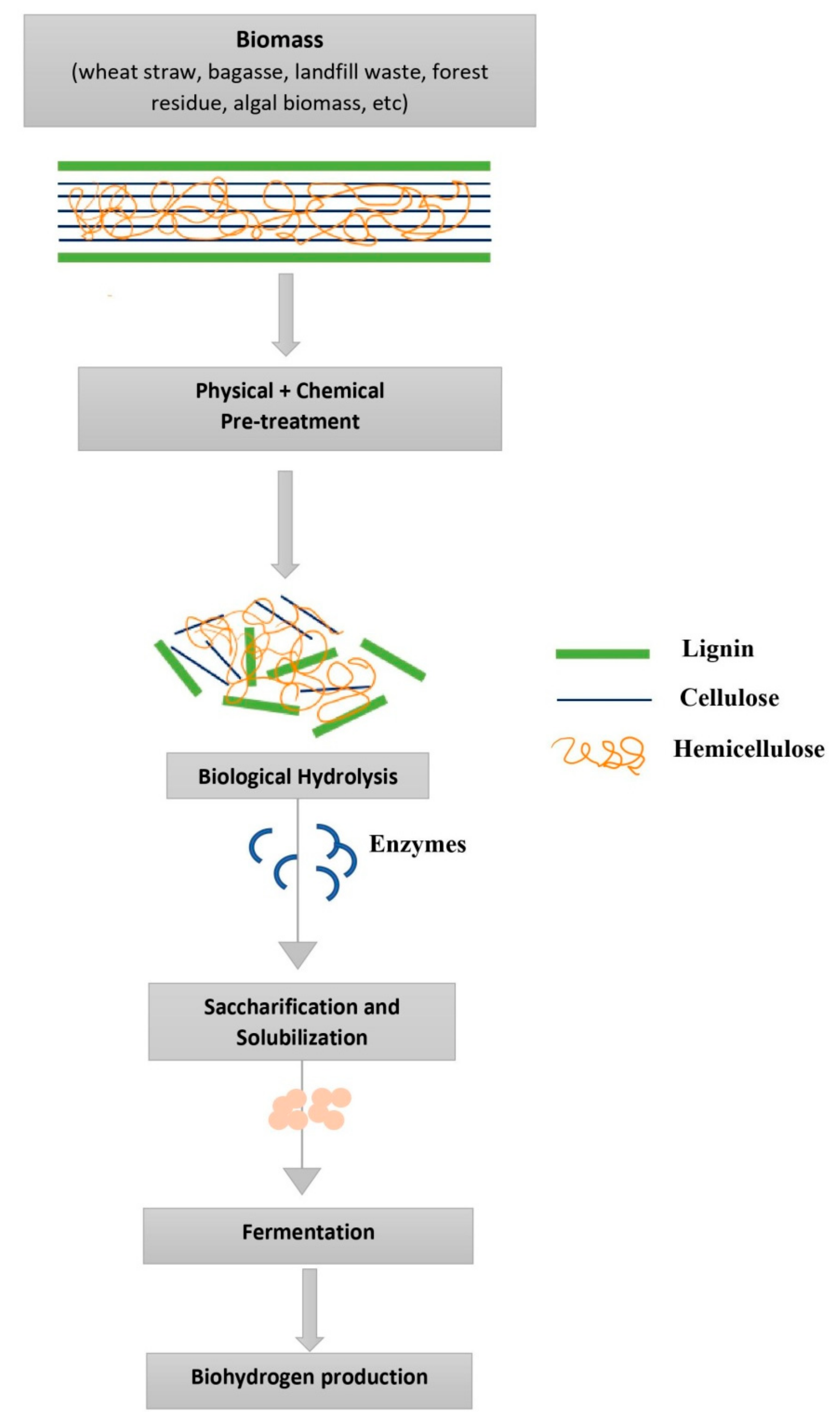
Figure 1. Schematic representation of biomass hydrolysis for biofuel production using physical, chemical, and biological pretreatment methods.
After selecting a microbial consortium enriched in hydrogen-producing ability, the accessibility of easily decomposable substrate is essential for the growth of microbes and hydrogen production. Algal biomass is enriched in large sugar residues and is considered an ideal substrate for H2 production [16]. Algal biomass (such as other organic waste) can be used for H2 generation due to its high protein, fat, and carbohydrate content [17][5]. Nguyen et al. (2010) used accumulated starch present within the green algae C. reinhardtii as a substrate. Later, the hyperthermophilic eubacterium T. neapolitana was used to convert that accumulated starch into H2 gas [17]. The algal starch could be directly fermented into H2 by a bacterium with amylase activity (1.8–2.2 mol H2/mol) [16]. These wastes’ cellulose and hemicellulose percentages must be hydrolyzed to degrade carbohydrates to achieve high H2 production. The resultant treated waste may be regarded as the potential substrate for fermentative hydrogen production. The main purpose of substrate pretreatment technology is to break down the complex structure of less degradable organic compounds and improve their solubility, thereby upgrading H2 yield. The type of substrate and pretreatment method used may affect the yield of hydrogen and the characteristics of the effluents. Ideally, the best substrate pretreatment method should be selected, with high hydrogen yield, cost efficiency, process sustainability, and low energy requirements.
3. Inoculum Pretreatment
Inoculum pretreatment technologies are also utilized to enhance the H2 production yield (Figure 2). These pretreatment technologies help to improve H2 yield by suppressing the hydrogen-consuming bacteria (HCB) and methane production. Inoculum pretreatment is proven to select micro-flora for better hydrogen production [18] (Table 1). Many studies have reported that pretreatment of sludge to avoid methane production and suppress the action of HCB leads to higher H2 production [19][20][21][22]. Pretreatment of inoculum or substrate may result in enhanced hydrogen content in the range of 43–69% [23]. Pretreatment of anaerobic inoculum accelerates hydrolysis, reducing the effect of the rate-limiting step and improving process stability, thus enhancing anaerobic digestion for effective H2 production [24][25][26]. Various inoculum pretreatment methods exist to enhance hydrogen production, including heat pretreatment, acid/alkali-treatment, ultrasonic waves, chloroform, and iodopropane [18][24][25]. Among these methods, the first three are more effective. Pretreatment steps vary, depending on the inoculum and substrate utilized and their unique properties that affect the H2 yield.

Figure 2. Inoculum pretreatment approaches for biohydrogen production by mixed microbial culture.
Table 1. List of various substrate pretreatment methods used for biohydrogen production.
| Substrate | Pretreatment | Pretreatment Conditions | Hydrogen Yield | Increase in H2 Yield (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice mill wastewater | Thermal | 121 °C temp Time: 15 min |
Control: 90 mL of hydrogen Pretreated: 200 mL of hydrogen |
55 | [27] |
| Beetroot pulp |
Microwave | 700 W; 170 °C temp Time: 30 min |
Control: 95.7 mL of hydrogen Pretreated: 108.7 mL of hydrogen |
12 | [28] |
| Palm oil mill effluent (POME) |
Acid | 0.8% (w/v) phosphoric acid and 1% (w/v) nitric acid. Time: 10 min |
Control: 0.64 mol H2/mol Pretreated: 1.24 mol H2/mol |
48.4 | [29] |
| Bio-methenated distillery wastewater |
Ozone | Ozone dose: 4.6 g/h Time: 160 min |
Control: 0.37 mL/h of hydrogen yield with 44.19 mL/g COD Pretreated: 1.18 mL/h of H2 yield with 185.5 mL/g COD |
68.6 | [30] |
| Cassava wastewater | Enzymatic | α-amylase (Incubation temperature: 37 °C) OPTIMASH BG® (Incubation temperature: 60 °C) Incubation period: 10 day |
Control: 2.06 mol/g COD Pretreated: 5.02 mol/g COD (α-amylase) 4.24 mol/g COD (OPTIMASH BG®) |
58.9 51.4 |
[31] |
| Rice mill wastewater | Combined (acid followed by enzymatic) |
Acid −1.5% H2SO4 Reaction time: 60 min Enzyme: A. niger Incubation temperature: 29 °C |
Control: 0.128 mol/L of hydrogen Pretreated: 5.34 mol/L of hydrogen. |
97.6 | [32] |
| Textile desizing wastewater | Combined pretreatment (flocculation and coagulation) |
Coagulant GGEFloc-653 −1 g/L Rapid mixing 100 rpm (3 min), Slow mixing 30 rpm (20 min), Sludge settling time: 1 h |
Control: 0.88 L/L-d H2 production rate Pretreated: 3.8 L/L-d H2 production rate |
76.8 | [33] |
4. New Approaches to Biomass-Based Biohydrogen Production
Three processes have been studied based on the pretreatment method, hydrolysis, and fermentation process being carried out in the same/separate reactor.
4.1. Separate Hydrolysis and Fermentation (SHF)
Separate Hydrolysis and Fermentation (SHF) is an effective approach that involves sequential enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation (Figure 3). However, to obtain a better biohydrogen yield, the conditions for hydrolysis should be optimal [34]. The sugars hexose and pentose are found in lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysate; to further enhance H2 yield, microbes are essential to ferment both sugars. The bacterium Thermoanaerobacterium thermosaccharolyticum W16 uses fermentable sugars obtained from hydrolysis to produce biohydrogen. Biomass pretreatment procedures produce inhibitors, which should be removed during the detoxification step. Biological pretreatment and saccharification methods have been reported to avoid the production of inhibitors. In the case of enzymatic saccharification, Trichoderma viride crude cellulase was utilized to produce reducing sugar [35]. When steam-exploded switchgrass was used for H2 production, the yield obtained by using the hydrolysate was 99.8 mL/g of substrate [36]. Pretreatment methods involving acid and alkali have a significant influence on grass saccharification for producing H2. In the case of grass with acid pretreatment, the H2 produced was 72.2 mL/g of the substrate.
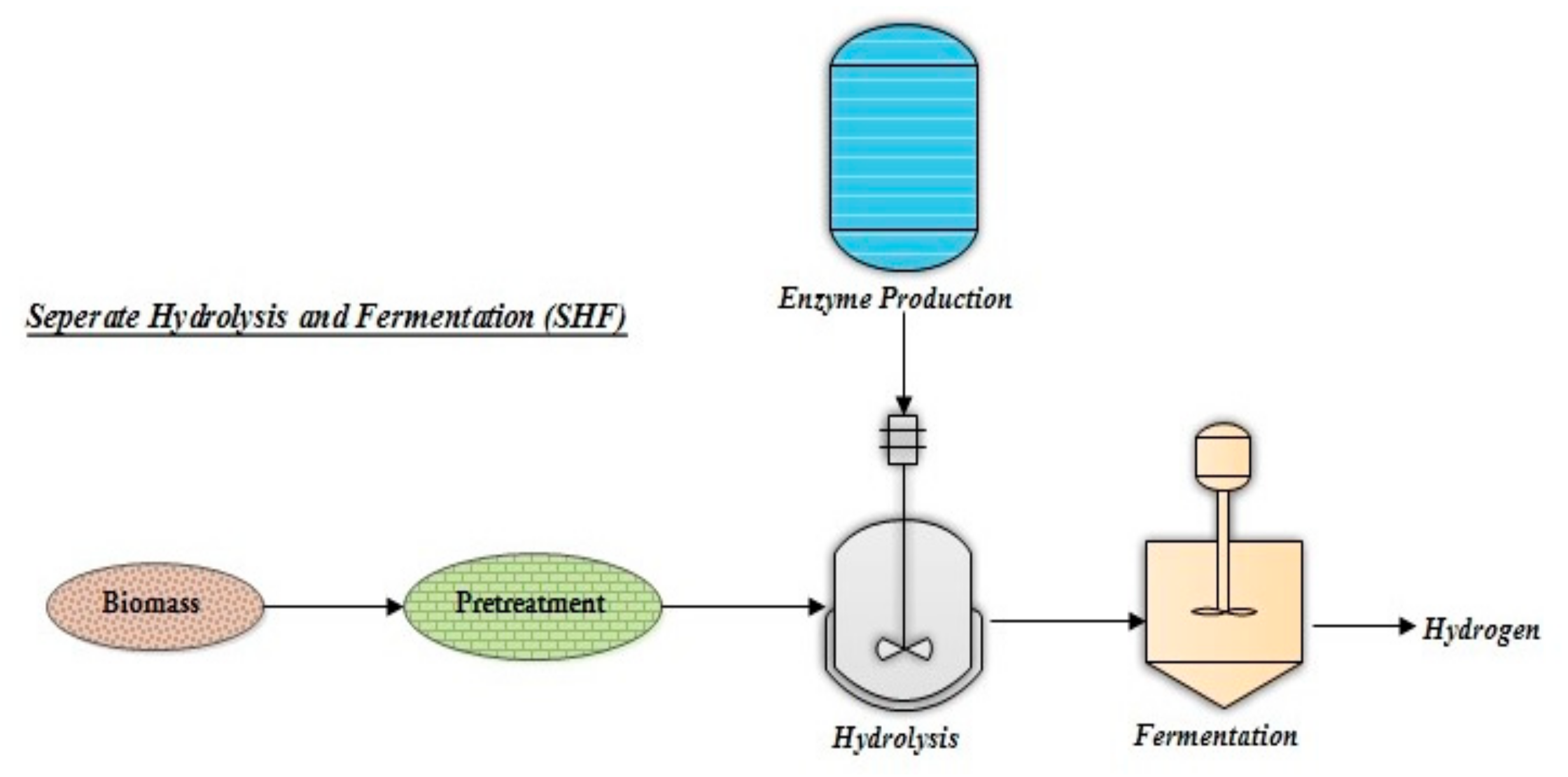
Figure 3. Schematic representation of separate hydrolysis and fermentation (SHF) for biohydrogen production.
4.2. Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation (SSF)
Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation (SSF) is carried out in the same reactor by utilizing different enzymes for saccharification and H2 fermentation (Figure 4). SSF can improve process time and cost while also removing product inhibition during cellulose hydrolysis [37]. Using SSF, Clostridium butyric ASI 209 was selected to produce H2 from steam-exploded corn, and the effect of variables such as pH or enzyme-loading on the productivity of H2 was noted. Some other studies noted how acetic acid and enzyme-loading affected H2 production. When the acetic-acid steam-exploded procedure was used to increase the production of H2, Ethanoligenes harbinese B49 resulted in high H2 yield and production [34]. SSF produced biohydrogen from fermentable sugars derived from fungal-pretreated cornstalk using enzymes from T. viride and T. thermosaccharolyticum W16. After studying various process parameters, a maximum yield of 89.3 mL H2/gm substrate was reported [35].
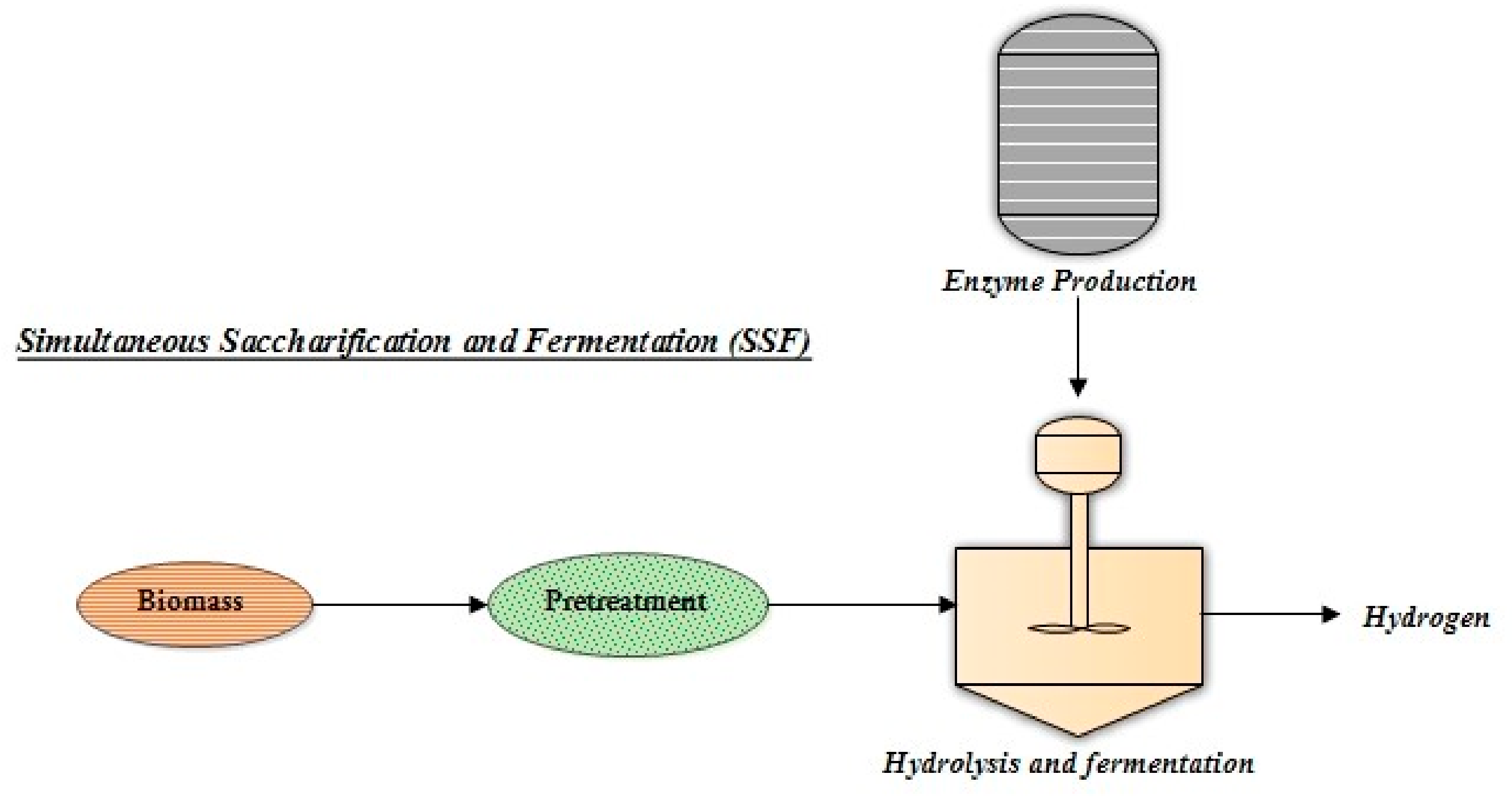
Figure 4. Schematic process of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) for biohydrogen production.
4.3. Consolidated Bioprocessing (CBP)
CBP is an integrated and economically feasible single-step process (Figure 5). Compared with fermentation, the pH and temperature required here for enzymatic hydrolysis are different. Compared to SHF and SSF technologies, the CBP operating technique is more straightforward. No enzyme is added, the chances of contamination are less, the energy requirement is low, and minimal investment is required. CBP encompasses a mixed-culture activity producing a synergistic effect, thus giving a high H2 yield. Reduced time for fermentation, high substrate conversion, and eliminated inhibitory compounds are some of the benefits of using mixed culture in this process [38].
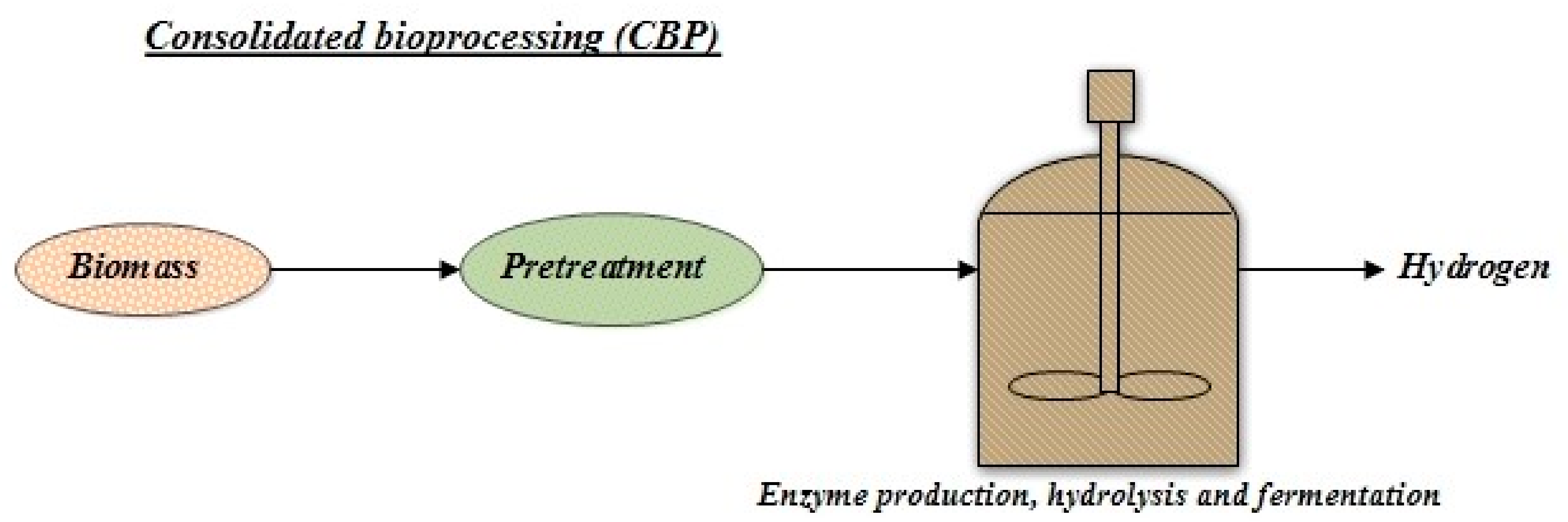
Figure 5. Process outlook of consolidated bioprocessing (CBP) for hydrogen production.
4.4. Integrated Strategy for Alternative Bioenergy Resources in Addition to H2
Along with hydrogen, several byproducts such as lactic acid, ethanol, and lactic acid are also produced during fermentation. Recovery of these products is desirable to make the process more feasible and economical.
4.4.1. Co-Production of Bio Alcohols and VFAs
Complex lignocellulosic biomass is prefered to be utilized as a substrate to minimize the impact on the environment. In aerobic bacteria, extracellular enzymes break down cellulose, while in anaerobic bacteria, hydrolysis of cellulose is mediated by the cellulosome, a multi-enzyme extracellular complex. Alcohols, VFAs, and H2, can be produced simultaneously using mixed culture [39]. Cellulolytic E. coli have been utilized on bovine rumen to produce 0.36 g/L of ethanol and an H2 yield of 4.41 mL/gm from corn straw. Sweet sorghum stalk, plant-based biomass, contains structural carbohydrates, e.g., cellulose, hemicellulose, and nonstructural sugars, e.g., fructose, glucose, sucrose, that affect the yield of H2. A two-step dark fermentation method has been used with Clostridium thermosaccharolyticum to utilize carbohydrates (structural and nonstructural) of sweet sorghum stalk to produce VFAs and hydrogen. In the first step, nonstructural sugars were used by C. thermosaccharolyticum to give 3.27 mmol H2/g substrate, 1.18 g/L of acetic acid, and 0.97 g/L of butyric acid. The remaining biomass, when treated with dilute H2SO4 before being refermented with C. thermosaccharolyticum, produced 2.5 mmol H2/gm of the substrate, 0.99 g/L acetic acid, and 1.09 g/L butyric acid [40].
4.4.2. Co-Production of Methane and Hydrogen
The energy density of hydrogen is high (142 kJ/g), followed by methane having 55.5 kJ/g [41]. Acidogenic microorganisms utilize lignocellulosic biomass to produce CO2, H2, and VFAs after hydrolyzing them into free sugars. Hydrogenotrophic methanogens use CO2 and H2 dissolved in the medium to generate CH4, whereas acetogenic bacteria do conversion of acetic acid into methane and CO2. H2 is scavenged by hydrogenotrophic methanogens, which reduces H2 production. Dark fermentation is preferred over anaerobic fermentation to prevent the formation of methane and methanogens, resulting in increased H2 and CO2 production. Lignin amount was decreased on pretreatment with alkaline H2O2, accompanied by an increase in substrate conversion efficiency to around 86 percent, resulting in H2 yields of 303 mL/g COD. In recirculated-two-phase anaerobic digestion (R-TPAD), both dark fermentation and methane-producing processes are combined. Hydrogen is produced in the first stage, and the used material of 1st stage that contains byproducts is then subjected to methane production in the second stage. After this, the effluent from methanogenesis is recirculated to the dark fermentation unit [42].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/en15030999
References
- Ho, K.-L.; Lee, D.-J.; Su, A.; Chang, J.-S. Biohydrogen from lignocellulosic feedstock via one-step process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 15569–15574.
- Rai, P.K.; Kadier, A.; Kumar, M.; Singh, S.P. Utilization of Microalgal Biomass as a Source of Bioenergy. In Role of Photosynthetic Microbes in Agriculture and Industry; Tripathi, K., Kumar, N., Abraham, G., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-153-614-033-0.
- Rashidi, B.; Dechesne, A.; Rydahl, M.G.; Jorgensen, B.; Trindade, L.M. Neochlorisoleoabundans cell walls have an altered composition when cultivated under different growing conditions. Algal Res. 2019, 40, 101482.
- Cheng, J.; Xia, A.; Liu, Y.; Lin, R.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Combination of dark- and photo-fermentation to improve hydrogen production from Arthrospira platensis wet biomass with ammonium removal by zeolite. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 13330–13337.
- Liu, Q.; Yao, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, W.; Tan, H.; Cao, X.; Xue, S.; Yin, H. Production and structural characterization of a new type of polysaccharide from nitrogen-limited Arthrospira platensis cultivated in outdoor industrial-scale open raceway ponds. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 131.
- Nagarajan, D.; Chang, J.-S.; Lee, D.-J. Pretreatment of microalgal biomass for efficient biohydrogen production—Recent insights and future perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122871.
- Rai, P.K.; Asthana, R.K.; Singh, S.P. Optimization of photo-hydrogen production based on cheese whey spent medium. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 7597–7603.
- Wyman, C.E. Biomass ethanol: Technical progress, opportunities, and commercial challenges. Ann. Rev. Energy Environ. 1999, 24, 189–226.
- Agler, M.T.; Wrenn, B.A.; Zinder, S.H.; Angenent, L.T. Waste to bioproduct conversion with undefined mixed cultures: The carboxylate platform. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 70–78.
- Eroglu, E.; Gunduz, U.; Yucel, M.; Turker, L.; Eroglu, I. Photobiological hydrogen production from olive mill wastewater as sole substrate sources. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2004, 29, 163–171.
- Rai, P.K. Recent Advances in substrate utilization for fermentative hydrogen Production. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 59–67.
- Mohan, S.V.; Babu, V.L.; Sarma, P.N. Anaerobic biohydrogen production from dairy waste water treatment in sequencing batch reactor (AnSBR): Effect of organic loading rate. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2007, 41, 506–515.
- Rai, P.K.; Singh, S.P.; Asthana, R.K. Biohydrogen Production from Cheese Whey Wastewater in a Two-Step Anaerobic Process. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 1540–1549.
- Rai, P.K.; Singh, S.P.; Asthana, R.K. Prospects of utilizing dairy waste for biohydrogen production. Int. J. Biotech. Biosci. 2011, 1, 263–270.
- Rossi, D.M.; Da Costa, J.B.; De Souza, E.A.; Peralba, M.d.C.R.; Samios, D.; Ayub, M.A.Z. Comparison of different pre-treatment methods for hydrogen production using environmental microbial consortia on residual glycerol from biodiesel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 4814–4819.
- Kumar, G.; Bakonyi, P.; Periyasamy, S.; Kim, S.H.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bélafi-Bakó, K. Lignocellulose biohydrogen: Practical challenges and recent progress. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 728–737.
- Nguyen, T.A.D.; Kim, K.R.; Nguyen, M.T.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, D.; Sim, S.J. Enhancement of fermentative hydrogen production from green algal biomass of Thermotoganeapolitanaby various pretreatment methods. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 13035–13040.
- Venkata Mohan, S. Fermentative hydrogen production with simultaneous wastewater treatment: Influence of pretreatment and system operating conditions. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2008, 67, 950–961.
- Yetis, M.; Gunduz, U.; Eroglu, I.; Yucel, M.; Turker, L. Photoproduction of hydrogen from sugar refinery wastewater by Rhodobacter sphaeroides OU 001. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2000, 25, 1035–1041.
- Rai, P.K.; Singh, S.P. Integrated dark- and photo-fermentation: Recent advances and provisions for improvement. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 19957–19971.
- Rai, P.K.; Singh, S.P. Biological production of clean energy: Hydrogen. In Advances in Microbiology; Tiwari, S.P., Rajesh Sharm, R., Rajeeva Gaur, R., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 55–83. ISBN 978-1-62808-633-1.
- Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, J.B.; Meng, L. Effects of volatile fatty acid concentrations on methane yield and methanogenic bacteria. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 848–853.
- Xie, B.F.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, J.H.; Song, W.L.; Liu, J.Z.; Cen, K.F. Production of hydrogen and methane from potatoes by two-phase anaerobic fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 99, 5942–5946.
- Zhu, H.; Beland, M. Evaluation of alternative methods of preparing hydrogen producing seeds from digested wastewater sludge. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2006, 31, 1980–1988.
- Hu, B.; Chen, S. Pretreatment of methanogenic granules for immobilized hydrogen fermentation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 3266–3273.
- Luste, S.; Luostarinen, S.; Sillanpää, M. Effect of pre-treatments on hydrolysis and methane production potentials of by-products from meat-processing industry. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 247–255.
- Haridoss, S. Studies on biohydrogen production from rice mill waste water using Enterobacter aerogenes MTCC 2822 by Dark Fermentation Process. J. Pet Environ. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 312.
- Ozkan, L.; Erguder, T.H.; Demirer, G.N. Effects of pretreatment methods on solubilization of beet-pulp and bio-hydrogen production yield. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 382–389.
- Mahmod, S.S.; Jahim, J.M.; Abdul, P.M. Pretreatment conditions of palm oil mill effluent (POME) for thermophilic biohydrogen production by mixed culture. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27512–27522.
- Malik, S.N.; Ghosh, P.C.; Vaidya, A.N.; Mudliar, S.N. Ozone pretreatment of biomethanated distillery wastewater in a semi batch reactor: Mapping pretreatment efficiency in terms of COD, color, toxicity and biohydrogen generation. Biofuels 2018, 11, 1–9.
- Leano, E.P.; Babel, S. Effects of pretreatment methods on cassava wastewater for biohydrogen production optimization. Renew. Energy 2012, 39, 339–346.
- Ramprakash, B.; Muthukumar, K. Comparative study on the performance of various pretreatment and hydrolysis methods for the production of biohydrogen using Enterobacter aerogenes RM 08 from rice mill wastewater. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 9106–9112.
- Lin, C.-Y.; Lay, C.-H.; Sen, B.; Chu, C.-Y.; Kumar, G.; Chen, C.-C.; Chang, J.-S. Fermentative hydrogen production from wastewaters: A review and prognosis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 15632–15642.
- Ren, N.-Q.; Zhao, L.; Chen, C.; Guo, W.-Q.; Cao, G.-L. A review on bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass to H2: Key challenges and new insights. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 92–99.
- Zhao, L.; Cao, G.-L.; Wang, A.-J.; Ren, H.-Y.; Xu, C.-J.; Ren, N.-Q. Enzymatic saccharification of cornstalk by onsite cellulases produced by Trichoderma viride for enhanced biohydrogen production. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 591–598.
- Reginatto, V.; Antônio, R.V. Fermentative hydrogen production from agroindustrial lignocellulosic substrates. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 323–335.
- Ibrahim, M.F.; Abd-Aziz, S.; Yusoff, M.E.M.; Phang, L.Y.; Hassan, M.A. Simultaneous enzymatic saccharification and ABE fermentation using pretreated oil palm empty fruit bunch as substrate to produce butanol and hydrogen as biofuel. Renew. Energy 2015, 77, 447–455.
- Nagarajan, D.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Recent insights into consolidated bioprocessing for lignocellulosic biohydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 14362–14379.
- Pang, J.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Hao, M.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Qi, Q.-S. An isolated cellulolytic Escherichia coli from bovine rumen produces ethanol and hydrogen from corn straw. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 165.
- Islam, S.; Guo, C.; Liu, C.-Z. Enhanced hydrogen and volatile fatty acid production from sweet sorghum stalks by two-steps dark fermentation with dilute acid treatment in between. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 659–666.
- Rai, P.K.; Singh, S.P.; Asthana, R.K.; Singh, S. Biohydrogen production from sugarcane bagasse by integrating dark- and photo-fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 140–146.
- Qin, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Xiao, B.; Hojo, T.; Kubota, K.; Cheng, J.; Li, Y.-Y. Co-production of biohydrogen and biomethane from food waste and paper waste via recirculated two-phase anaerobic digestion process: Bioenergy yields and metabolic distribution. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 276, 325–334.
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
