Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Biochemistry & Molecular Biology
The knowledge of the structure, function, and abundance of specific proteins related to the EMT process is essential for developing effective diagnostic approaches to cancer with the perspective of diagnosis and therapy of malignancies. The success of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) differentiation therapy in acute promyelocytic leukemia has stimulated studies in the treatment of other tumors with ATRA.
- breast cancer
- EMT
- protein
- ATRA
1. Introduction
In the last two decades, the total number of people diagnosed with cancer has almost doubled, from an estimated 10 million in 2000 to 19.3 million in 2020. Today, every 5 people around the world suffer from cancer during their lifetime. Cancer deaths have also increased, from 6.2 million in 2000 to 10 million in 2020. More than one in six deaths is caused by cancer. Breast cancer has now overtaken lung cancer as the world’s most commonly diagnosed cancer, according to statistics released by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) in December 2020 [1]. Approximately 1 in 8 women (13%) will be diagnosed with invasive breast cancer during their lifetime, and 1 in 39 women (3%) will die of breast cancer [2]. That’s why there is a growing need to learn about this disease as much as possible and the need to seek new and more effective drugs. In addition, breast cancer usually does not cause any symptoms if the tumor is small and is easiest to treat. Therefore, early cancer detection is essential for an accurate diagnosis to reduce the possibility of metastasis and relapse. The use of up-to-date analytical proteomic techniques, especially current chromatographic or electrophoretic separation methods together with mass spectrometry (MS), and the development of new analytical strategies is critical for the characterization of cancer cells and especially for identifying new diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, which have mainly protein characters. The prominent role of proteomics is to identify biomarkers for early cancer screening and predict therapeutic response [3][4][5].
Retinoids, the group of vitamin A derivatives, are currently receiving considerable attention because their properties predispose it to become an anticancer agent, as confirmed by the growing body of evidence highlighting the compound’s anticancer activity. All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) is administered orally in the first-line treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) [6] in adults and neuroblastoma (NB) in children [7]. As the promising results obtained in these diseases have not yet translated to the solid tumor clinic, there remains a large room for further in-depth studies.
2. Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer treatment has advanced significantly in the past five years. The principles of breast cancer therapy follow a curative purpose and must be determined in a multidisciplinary sense, taking into account molecular subtype and loco-regional tumor load. Advancements in therapeutic strategies make the prospect of long-term disease control in metastatic breast cancer an increasing reality.
It is well known that different combinations of the presence of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her2) status, Ki67 protein and tumor grade define five basic molecular subtypes of breast cancer, luminal A, luminal B Her2+/luminal B Her2−, basal/triple-negative, normal-like, and Her2-enriched [8][9]. The status within each subtype is summarized in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Breast cancer and its five molecular subtypes: prognosis of the disease. Reprinted with permission from [8]. Copyright 2018 ClinMed International Library.
-
Luminal A (ER+/PR+/HER2−/Ki67−): This is the most common type of breast cancer and tends to be slower-growing and less aggressive than other subtypes. Luminal A tumors are associated with the most favorable prognosis in part because they are usually responsive to hormonal therapy [10]. Tumors also show good differentiation, low grade (1 or 2), and the percentage of their recurrence is low [11]. In addition, the low level of Ki67 protein helps control of cancer growth [8].
-
Luminal B (ER+/PR+/HER2− or HER2+/Ki67+): This is a relatively small subgroup of tumors that proliferate significantly more, are less differentiated and express hormone receptors. In addition, this subtype was initially characterized clinically as always being positive for HER2, but more recently has been defined as being highly positive for the protein Ki67 and/or HER2 [12]. Luminal B breast cancers have higher histological than luminal A and recur more often.
-
Basal-like (ER−/PR−/HER2−): These cancers are also called triple-negative because they lack these receptors. This subtype, which has the most significant association with women with the BRCA1 and p53 gen mutations, offers the worst prognosis of the other subtypes, in part because treatment advances have lagged behind other molecular subtypes [13]. The majority (about 75%) of triple-negative breast cancers fall into the basal-like subtype defined by gene expression profiling. Proliferative activity is significant. Patients of luminal A and basal subtype form the regional lymph node metastases less frequently [14].
-
HER2-enriched (ER−/PR−/HER2+): In the past, this subtype had the worst prognosis; however, the widespread use of targeted therapies for HER2+ cancers have substantially improved outcomes for these patients [15].
-
Normal-like (ER+/PR+/HER2−/Ki67−): This subtype has been found to exhibit the genetic characteristics of normal breast samples, although its prognosis is often worse than the luminal A prognosis [8].
However, some data suggest that the current classification scheme for breast tumors may not fully capture cancer’s genetic and molecular status. The revised classification will allow the more accurate treatment of cancer. Today, the search for better classifiers of tumors is significantly focused on applying omic approaches, which can analyze thousands of gene sequences, gene transcripts, or proteins in a single experiment. Bouchal and colleagues [9] recently demonstrated and confirmed the suitability of sequential windowed acquisition of all theoretical fragment ion mass spectra approach (SWATH-MS) for proteotyping of human tumor samples and also identified key proteins for the classification of breast tumors. Proteins that contribute most strongly to proteotype-based classification include inositol polyphosphate-4-phosphatase, type II (INPP4B), cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1), and receptor tyrosine kinase 2 (ERBB2) are associated with estrogen receptor (ER) status, HER2 status tumor, and grade status. Although more data are needed to validate classifiers, the results suggest that proteotype-based classification may improve the current conventional classification of breast tumors and thus provide adequate treatment.
3. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a dynamic process during which epithelial cells lose their cellular polarity and phenotypic properties and acquire mesenchymal cell properties. EMT process also allows cells to disrupt the basement membrane and invade neighboring tissues or distant organs [16]. EMT occurs naturally in the body, for example, during tissue regeneration or embryogenesis. Nevertheless, EMT process has been suggested that may be closely linked to the acquisition of aggressive properties by tumor cells, facilitating the initial stages of metastasis. EMTs occur in three different biological subtypes, which have very different functional consequences [17]. Figure 2 shows different types of EMT, and at the same time, Table 1 provides an overview of some of the most common markers that demonstrate these subtypes.
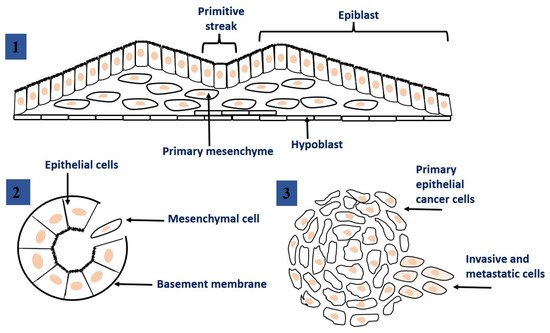
Figure 2. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition: the process of transformation of epithelial cells into mesenchymal cells. 1. EMT related to implantation, embryo formation, and organ development. 2. EMT related to cancer progression and metastasis. 3. EMT associated with tissue regeneration and organ fibrosis. This figure was adapted from ref. [17].
Table 1. An overview of some of the most common markers that demonstrate these subtypes.
| Protein Name | MW (kDa) | Up/down Regulated during Cancer | Protein Function (www.uniprot.org) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annexin 1 (ANX1) | 38.7 | UP |
|
[18] |
| Bromodomain-containing protein 7 (BRD7) | 74.1 | Up/tumor suppression |
|
[19][20] |
| E-cadherin | 97.5 | Down |
|
[21][22] |
| N-cadherin | 99.8 | Up |
|
[21][22] |
| β-Catenin | 9.2 | Up |
|
[23] |
| CD44 | 81.5 | Up |
|
[24][25] |
| Type 1 collagen | 138.9 | Promotes survival of human breast cancer cells by overexpressing Kv10.1 potassium and Orai1 calcium channels. |
|
[17][26] |
| Type IV collagen | 164.0 | Down |
|
[27][28] |
| Cytokeratin 18 | 48.1 | Down |
|
[27][29] |
| Class S100 of cytoskeletal proteins | 9.0–13.0 | Up/Down |
|
[17][30] |
| Desmin | 53.5 | Up |
|
[17] |
| Desmoplakin | 331.8 | Down |
|
[27][31] |
| Fibroblast-specific protein 1 (S100A4) | 11.7 | Up/ overexpressed in a range of different tumor types |
|
[17][32] |
| Fibronectin | 2.5 | Up |
|
[33] |
| α5 integrin | 114.5 | Up |
|
[33] |
| β6 integrin | 85.9 | Up |
|
[33] |
| Laminin 1 | 177.6 | Down |
|
[27] |
| Laminin 5 | 399.7 | Up |
|
[33][34] |
| Mucin 1 | 122.1 | Down |
|
[21][22] |
| Occludin | 59.1 | Down |
|
[27][35] |
| Smooth muscle alpha-actin (α-SMA) | 42.0 | Up |
|
[17][33] |
| Snail | 29.1 | Up |
|
[33][36] |
| Syndecan-1 | 32.5 | Up |
|
[33][37] |
| Twist | 21 | Up |
|
[33][36] |
| Vimentin (VIME) | 53.7 | Up |
|
[17][36] |
| Y-box-binding protein 1 | 35.9 | Reduces ovarian cancer cell proliferation |
|
[19][38] |
| ZEB proteins ZEB1 ZEB2 |
124.1 133.8 |
Up Up |
|
[33][36][39] |
| ZO-1 | 187.0 | Down/up |
|
[27][35][40] |
-
EMTs associated with implantation, embryo formation, and organ development are organized to generate different cell types that share common mesenchymal phenotypes. These type 1 EMTs can generate mesenchymal cells that have the potential to subsequently undergo a reverse process—a mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) to generate secondary epithelium.
-
Type 2 EMTs are associated with tissue regeneration and organ fibrosis. Organic fibrosis, which occurs in many epithelial tissues, is mediated by inflammatory cells and fibroblasts that release various inflammatory signals. Reliable markers for the characterization of mesenchymal products generated by EMT, which occur during the development of fibrosis in various organs, are the following proteins: fibroblast-specific protein 1, a class S100 of the cytoskeletal protein, α-SMA, and collagen I [41][42].
-
Type 3 EMTs are associated with cancer progression and metastasis. In the case of this EMT, the cancer cells on the invasive anterior side of the tumors transform into a mesenchymal phenotype. Many in vivo as well as in vitro experiments have shown that cancer cells can acquire a mesenchymal phenotype and express mesenchymal protein markers such as smooth muscle alpha-actin (α-SMA), fibroblast specific protein 1 (FSP1), vimentin, and desmin [43].
The incomplete EMT status in cancer cells allows them to possess more transient states and to express mixed epithelial and mesenchymal genes, so these cells can be more aggressive compared to cells with the complete EMT phenotype [44]. Cancer cells affecting metastases are similar to the epithelium and can be identified as morphologically and molecularly derived from the primary tumor. For this reason, cancer cells must reverse the mesenchymal phenotype of reverse EMT, a process known as the mesenchymal-epithelial junction (MET) [45].
At present, it is relevant to identify some essential proteins that address important, still unanswered questions. The downregulation of epithelial markers and the upregulation of mesenchymal protein markers are both characteristics of EMT (Figure 3). A critical molecular feature of this process is the downregulation of the E-cadherin expression. E-cadherin is a key protein in cell polarity and epithelial organization. The reduction or loss of E-cadherin has become one of the hallmarks of EMT and was frequently associated with metastasis and invasion in a variety of human malignancies [46]. N-cadherin, vimentin, snail, twist, and fibronectin are known as mesenchymal markers, which are closely linked to several human malignancies [47]. In addition, Snail can also inhibit the expression of other epithelial genes such as Muc1 and promote the expression of fibronectin and vimentin, which activate EMT and are associated with tumor metastasis, recurrence, and poor prognosis of breast cancer.
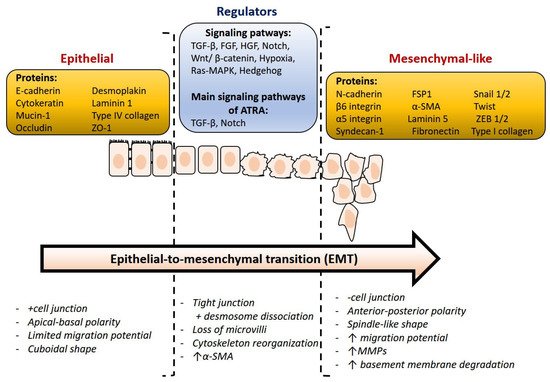
Figure 3. Overview of relevant markers and main molecular changes during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. This figure was adapted from ref. [27].
Niu et al. investigated the morphological and molecular changes that occur during the EMT process after bromodomain-containing protein 7 (BRD7) overexpression. BRD7 is a tumor suppressor known to inhibit cell proliferation and cell cycle progression and to induce apoptosis in breast cancer. In addition, in vitro tests indicated that BRD7 has the ability to inhibit mobility, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells [19]. At the same time, YB1 (Y-box-binding protein 1) was identified by nano-LC-MS/MS using LTQ Velos Orbitrap MS coupled to UltiMate RSLCnano LC as a new interacting BRD7 protein. It was further confirmed that EMT is a common change that occurs with altered expression of either BRD7 or YB1, and that BRD7 suppresses mesenchymal genes and activates epithelial genes [19]. Additionally, the possible contribution of annexin 1 (ANXA1) to breast tumorigenesis was investigated using stable quantitative MS proteomics based on isotope labeling. ANXA1 has been reported to promote migration and invasion of metastatic breast cancer cells as a modulator of EMT, such as phenotypic transition, through the transforming growth factor signaling pathway [18]. It has been revealed that ATRA modulates EMT of mammary tumor cells via the TGF-β and NOTCH pathways [48], and that modulation of the NOTCH1 signal transduction pathway plays a major role in ATRA activated anti-motility responses. The TGF pathway was also found to be a second signal transduction system that is essential for ATRA anti-migration. Doe at al. confirmed that the retinoic acid receptor alpha gene (RARA) regulates EMT-inducing transcription factors such as SLUG, FOXC2, ZEB1 and ZEB2, and factors activating TGF-β-SMAD signaling, including TGFBR1, TGFBR2, TGFB2 and SMAD3 [49].
Although it is widely believed that EMT contributes to metastasis, there is a lack of definitive in vivo evidence to support this theory. Some published papers report that although therapeutic inhibition of EMT might not prevent metastasis, combining chemotherapy with EMT inhibition might help to prevent the emergence of resistance [50][51]. Targeting EMT can serve as an effective strategy for cancer treatment, and EMT research will be promising in the coming years.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms222413345
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) in December 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/03-02-2021-breast-cancer-now-most-common-form-of-cancer-who-taking-action (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. (Eds.) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2016, Section 4: Breast Cancer; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019; Updated April 2019. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2016/results_merged/sect_04_breast.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2019).
- Qin, X.-J.; Ling, B.X. Proteomic studies in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 735–743.
- Tyanova, S.; Albrechtsen, R.; Kronqvist, P.; Cox, J.; Mann, M.; Geiger, T. Proteomic maps of breast cancer subtypes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10259.
- Yanovich, G.; Agmon, H.; Harel, M.; Sonnenblick, A.; Peretz, T.; Geiger, T. Clinical proteomics of breast cancer reveals a novel layer of breast cancer classification. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6001–6010.
- Liang, C.Y.; Qiao, G.A.P.; Liu, Y.Z.; Tian, L.; Hui, N.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.L.; Li, H.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Cao, W.Q.; et al. Overview of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and its analogues: Structures, activities, and mechanisms in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 220, 113451.
- Chlapek, P.; Slavikova, V.; Mazanek, P.; Sterba, J.; Veselska, R. Why differentiation therapy sometimes fails: Molecular mechanisms of resistance to retinoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 132.
- Sasmita, A.O.; Wong, Y.P. Organoids as reliable breast cancer study models: An update. Int. J. Oncol. Res. 2018, 1, 008.
- Bouchal, P.; Schubert, O.T.; Faktor, J.; Capkova, L.; Imrichova, H.; Zoufalova, K.; Paralova, V.; Hrstka, R.; Liu, Y.; Ebhardt, H.A.; et al. Breast cancer classification based on proteotypes obtained by SWATH mass spectrometry. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 832–843.
- Fragomeni, S.M.; Sciallis, A.; Jerus, J.S. Molecular subtypes and local-regional control of breast. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 27, 95–120.
- Abotaleb, M.; Kubatka, P.; Caprnda, M.; Varghese, E.; Zolakova, B.; Zubor, P.; Opatrilova, R.; Kruzliak, P.; Stefanicka, P.; Busselberg, D. Chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer: An update. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 458–477.
- Li, Z.-H.; Hu, P.-H.; Tu, J.-H.; Yu, N.-S. Luminal B breast cancer: Patterns of recurrence and clinical outcome. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65024–65033.
- Pan, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, G.; Wei, Y. P53 and Ki-67 as prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172324.
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.-J.; Bian, X.-W.; Yu, S.-C. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 61.
- Wang, J.; Xu, B. Targeted therapeutic options and future perspectives for HER2-positive breast cancer. Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 2019, 4, 34.
- Liskova, A.; Koklesova, L.; Samec, M.; Smejkal, K.; Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Abotaleb, M.; Biringer, K.; Kudela, E.; Danko, J.; et al. Flavonoids in cancer metastasis. Cancer 2020, 12, 1498.
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428.
- Swa, H.L.F.; Shaik, A.A.; Lim, L.H.K.; Gunaratne, J. Mass spectrometry based quantitative proteomics and integrative network analysis accentuates modulating roles of annexin-1 in mammary tumorigenesis. Proteomics 2015, 15, 408–418.
- Niu, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, C.; Duan, Y.; Wang, H.; Fan, S.; Li, Z.; Xiong, W.; et al. BRD7 suppresses invasion and metastasis in breast cancer by negatively regulating YB1-induced EMT. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 30.
- Chen, C.-L.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Q.-Z.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Q.-J.; Pan, K.; Huang, L.-X.; He, J.; Zhao, J.-J.; Jiang, S.-S.; et al. Bromodomain-containing protein 7 (BRD7) as a potential tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16248–16261.
- Prieto-García, E.; Díaz-García, C.V.; García-Ruiz, I.; Agulló-Ortuño, M.T. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in tumour progression. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 122.
- Morandi, A.; Taddei, M.L.; Chiarugi, P.; Giannoni, E. Targeting the metabolic reprogramming that controls epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in aggressive tumours. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 40.
- Wang, Y.; Qin, J.; Liu, Q.; Hong, X.; Li, T.; Zhu, Y.; He, L.; Zheng, B.; Li, M. SNF2H promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 1329–1336.
- Strouhalova, D.; Macejova, D.; Lastovickova, M.; Brtko, J.; Bobalova, J. CD44 and vimentin, markers involved with epithelial-mesenchymal transition: A proteomic analysis of sequential proteins extraction of triple-negative breast cancer cells after treatment with all-trans retinoic acid. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2020, 39, 399–405.
- Xu, H.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, Q.; Pestell, R.G.; Wu, K. The role of CD44 in epithelial–mesenchymal transition and cancer development. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 3783–3792.
- Badaoui, M.; Mimsy-Julienne, C.; Saby, C.; Van Gulick, L.; Peretti, M.; Jeannesson, P.; Morjani, H.; Ouadid-Ahidouch, H. Collagen type 1 promotes survival of human breast cancer cells by overexpressing Kv10.1 potassium and Orai1 calcium channels through DDR1-dependent pathway. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24653–24671.
- Neagu, M.; Constantin, C.; Bostan, M.; Caruntu, C.; Ignat, S.R.; Dinescu, S.; Costache, M. Proteomic technology “lens” for epithelial-mesenchymal transition process identification in oncology. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019.
- Wang, Z.N.; Xu, H.M. Relationship between collagen IV expression and biological behavior of gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 6, 438–439.
- Jung, H.; Kim, B.; Moon, B.I.; Oh, E.-S. Cytokeratin 18 is necessary for initiation of TGF-b1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition in breast epithelial cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2016, 423, 21–28.
- Donato, R.; Cannon, B.R.; Sorci, G.; Riuzzi, F.; Hsu, K.; Weber, D.J.; Geczy, C.L. Functions of S100 proteins. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 24–57.
- Zhou, G.; Yang, L.; Gray, A.; Srivastava, A.K.; Li, C.; Zhang, G.; Cui, T. The role of desmosomes in carcinogenesis. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 4059–4063.
- Orre, L.M.; Panizza, E.; Kaminskyy, V.O.; Vernet, E.; Graeslund, T.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Lehtioe, J. S100A4 interacts with p53 in the nucleus and promotes p53 degradation. Oncogene 2018, 32, 5531–5540.
- Liu, F.; Gu, L.-N.; Shan, B.-E.; Geng, C.-Z.; Sang, M.-X. Biomarkers for EMT and MET in breast cancer: An update. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4869–4876.
- Roussellea, P.; Scoazecb, J.Y. Laminin 332 in cancer: When the extracellular matrix turns signals from cell anchorage to cell. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 62, 149–165.
- Rachow, S.; Zorn-Kruppa, M.; Ohnemus, U.; Kirschner, N.; Vidal-y-Sy, S.; von den Driesch, P.; Bornchen, C.; Eberle, J.; Mildner, M.; Vettorazzi, E.; et al. Occludin is involved in adhesion, apoptosis, differentiation and Ca2+ homeostasis of human keratinocytes: Implications for tumorigenesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55116.
- Kang, E.; Seo, J.; Yoon, H.; Cho, S. The post-translational regulation of epithelial–mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors in cancer metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3591.
- Ibrahim, S.A.; Gadalla, R.; El-Ghonaimy, E.A.; Samir, O.; Mohamed, H.T.; Hassan, H.; Greve, B.; El-Shinawi, M.; Mohamed, M.M.; Götte, M. Syndecan-1 is a novel molecular marker for triple negative inflammatory breast cancer and modulates the cancer stem cell phenotype via the IL-6/STAT3, Notch and EGFR signaling pathways. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 57.
- Tailor, D.; Resendez, A.; Garcia-Marques, F.J.; Pandrala, M.; Going, C.C.; Bermudez, A.; Kumar, V.; Rafat, M.; Nambiar, D.K.; Honkala, A.; et al. Y box binding protein 1 inhibition as a targeted therapy for ovarian cancer. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021, 28, 1206–1220.e6.
- Soen, B.; Vandamme, N.; Berx, G.; Schwaller, J.; Van Vlierberghe, P.; Goossens, S. ZEB proteins in leukemia: Friends, foes, or friendly foes? Hemasphere 2018, 2, e43.
- Dekky, B.; Ruff, M.; Bonnier, D.; Legagneux, V.; Théret, N. Proteomic screening identifies the zonula occludens protein ZO-1 as a new partner for ADAM12 in invadopodia-like structures. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 21366–21382.
- Zeisberg, M.; Hanai, J.-I.; Sugimoto, H.; Mammoto, T.; Charytan, D.; Strutz, F.; Kalluri, R. BMP-7 counteracts TGFbeta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and reverses chronic renal injury. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 964–968.
- Okada, H.; Danoff, T.M.; Kalluri, R.; Neilson, E.G. Early role of Fsp1 in epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, F563–F574.
- Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 818–829.
- Roche, J. The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 52.
- Hamilton, G.; Rath, B. Mesenchymal-epithelial transition and circulating tumor cells in small cell lung cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 994, 229–245.
- Loh, C.-Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-cadherin and N-cadherin switch in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: Signaling, therapeutic implications, and challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118.
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196.
- Zanetti, A.; Affatato, R.; Centritto, F.; Fratelli, M.; Kurosaki, M.; Barzago, M.M.; Bolis, M.; Terao, M.; Garattini, E.; Paroni, G. All-trans-retinoic acid modulates the plasticity and inhibits the motility of breast cancer cells role of Notch1 and Transforming Growth Factor (Tgf). J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 17690–17709.
- Doi, A.; Ishikawa, K.; Shibata, N.; Ito, E.; Fujimoto, J.; Yamamoto, M.; Shiga, H.; Mochizuki, H.; Kawamura, Y.; Goshima, N.; et al. Enhanced expression of retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA) induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and disruption of mammary acinar structures. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 355–364.
- Fisher, K.R.; Durrans, A.; Lee, S.; Sheng, J.; Li, F.; Wong, S.T.C.; Choi, H.; El Rayes, T.; Ryu, S.; Troeger, J.; et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature 2015, 527, 472–476.
- Zheng, X.; Carstens, J.L.; Kim, J.; Scheible, M.; Kaye, J.; Sugimoto, H.; Wu, C.-C.; LeBleu, V.S.; Kalluri, R. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 527, 525–530.
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
