Pathogenic bacteria interact with cells of their host via many factors. The surface components, i.e., adhesins, lipoproteins, LPS and glycoconjugates, are particularly important in the initial stages of colonization. They enable adhesion and multiplication, as well as the formation of biofilms. In contrast, virulence factors such as invasins and toxins act quickly to damage host cells, causing tissue destruction and, consequently, organ dysfunction. These proteins must be exported from the bacterium and delivered to the host cell in order to function effectively. Bacteria have developed a number of one- and two-step secretion systems to transport their proteins to target cells. Several authors have postulated the existence of another transport system (sometimes called “secretion system type zero”), which utilizes extracellular structures, namely membrane vesicles (MVs).
- membrane vesicle
- virulence factors
- secretion systems
- pathogenesis
- bacterial toxins
1. Introduction
2. Structure of Membrane Vesicles (MVs) and Mechanisms of Secretion
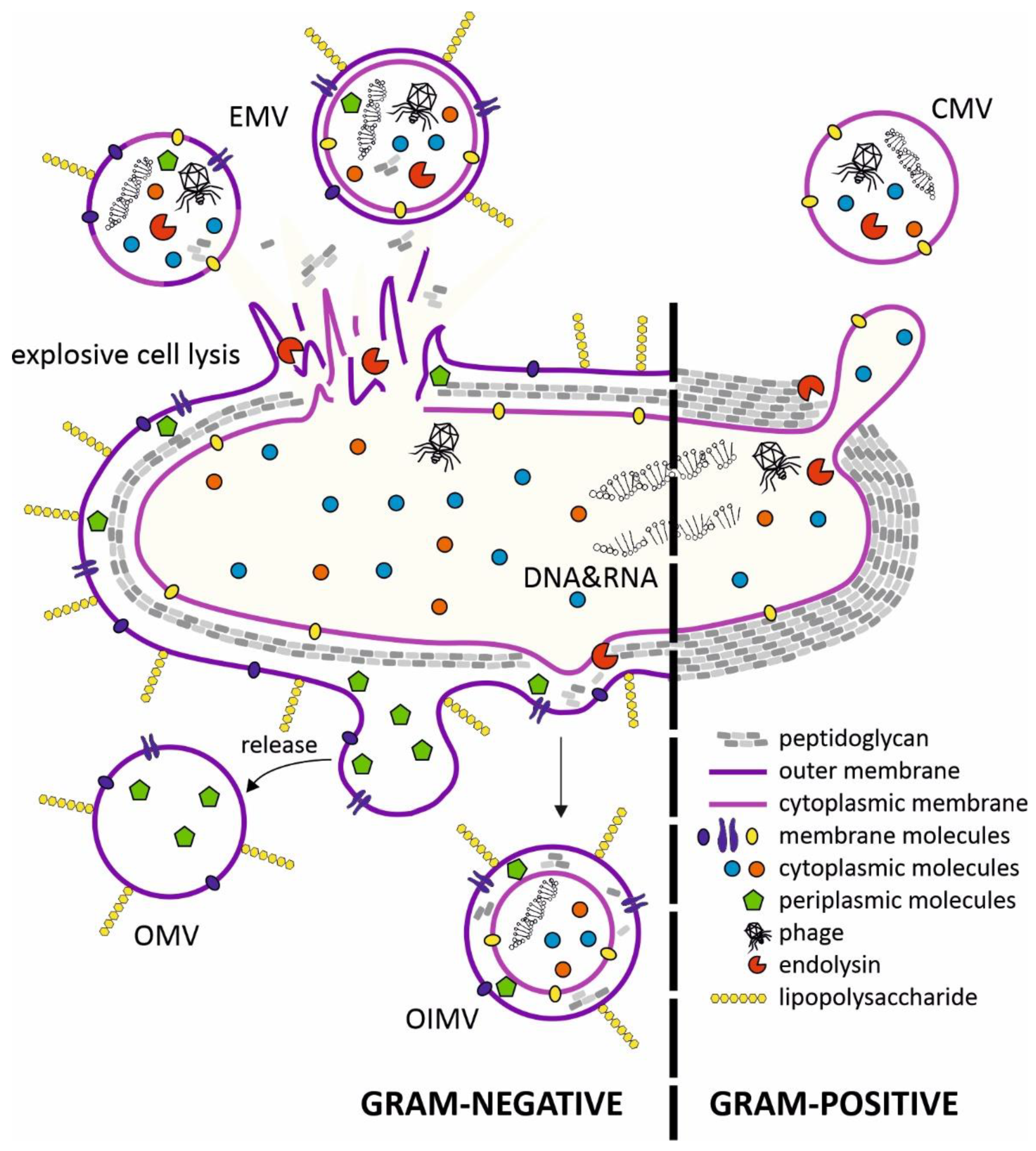
3. Conclusions
| Bacterial Species (Gram-Negative) | Active Factors | Reference |
| Acholeplasma laidlawii PG8 |
|
[18] |
| Acinetobacter baumannii |
|
[19] |
| Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae |
|
[20] |
| Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans |
|
[21] |
| Bartonella henselae |
|
[22] |
| Borrelia burgdorferi |
|
[23][24] |
| Burkholderia cepacia |
|
[25] |
| Campylobacter jejuni |
|
[26] |
| Coxiella burnetti |
|
[27] |
| Escherichia coli K1 |
|
[28] |
| Escherichia coli O157: H7 Shigella dysenteriae |
|
[29] |
| enterotoxic E. coli (ETEC) |
|
[30] |
| enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) |
|
[31] |
| extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC) |
|
[32] |
| Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib) |
|
[33] |
| Legionella pneumophila |
|
[34] |
| Moraxella catarrhalis |
|
[35] |
| Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B |
|
[36] |
| Porphyromonas gingivalis |
|
[37] |
| Salmonella enterica |
|
[38] |
| Shigella flexneri |
|
[39] |
| Treponema denticola |
|
[40] |
| Vibrio cholerae |
|
[41] |
| Yersinia pestis |
|
[42] |
| Bacterial Species (Gram-Positive) | Active Factors | Citations |
| Bacillus anthracis |
|
[ 12 ] |
| Clostridium perfringens |
|
[ 43 ] |
| Enterokok faecium |
|
[ 44 ] |
| Prątek gruźlicy |
|
[ 45 ] |
| Propionibacterium acnes |
|
[ 46 ] |
| Streptococcus mutans |
|
[ 47 ] |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae |
|
[ 48 ] |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/toxins13120845
References
- De, S.N. Enterotoxicity of bacteria-free culture-filtrate of Vibrio cholerae. Nature 1959, 183, 1533–1534.
- Chatterjee, S.N.; Das, J. Electron microscopic observations on the excretion of cell-wall material by Vibrio cholerae. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1967, 49, 1–11.
- Schwechheimer, C.; Kuehn, M.J. Outer-membrane vesicles from Gram-negative bacteria: Biogenesis and functions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 605–619.
- Caruana, J.C.; Walper, S.A. Bacterial Membrane Vesicles as Mediators of Microbe—Microbe and Microbe—Host Community Interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 432.
- Deatherage, B.L.; Cookson, B.T. Membrane vesicle release in bacteria, eukaryotes, and archaea: A conserved yet underappreciated aspect of microbial life. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 1948–1957.
- Pathirana, R.D.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M. Bacterial membrane vesicles: Biogenesis, immune regulation and pathogenesis. Cell. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1518–1524.
- Kulp, A.; Kuehn, M.J. Biological functions and biogenesis of secreted bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 163–184.
- Perez-Cruz, C.; Delgado, L.; Lopez-Iglesias, C.; Mercade, E. Outer-inner membrane vesicles naturally secreted by gram-negative pathogenic bacteria. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116896.
- Liu, Y.; Defourny, K.A.Y.; Smid, E.J.; Abee, T. Gram-Positive Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles and Their Impact on Health and Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1502.
- Brown, L.; Kessler, A.; Cabezas-Sanchez, P.; Luque-Garcia, J.L.; Casadevall, A. Extracellular vesicles produced by the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis are disrupted by the lipopeptide surfactin. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 93, 183–198.
- Bielaszewska, B.L.; Wolf, J.M.; Prados-Rosales, R.; Casadevall, A. Through the wall: Extracellular vesicles in Gram-positive bacteria, mycobacteria and fungi. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 620–630.
- Rivera, J.; Cordero, R.J.; Nakouzi, A.S.; Frases, S.; Nicola, A.; Casadevall, A. Bacillus anthracis produces membrane-derived vesicles containing biologically active toxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19002–19007.
- Nakayama, K.; Takashima, K.; Ishihara, H.; Shinomiya, T.; Kageyama, M.; Kanaya, S.; Ohnishi, M.; Murata, T.; Mori, H.; Hayashi, T. The R-type pyocin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is related to P2 phage, and the F-type is related to lambda phage. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 213–231.
- Turnbull, L.; Toyofuku, M.; Hynen, A.L.; Kurosawa, M.; Pessi, G.; Petty, N.K.; Osvath, S.R.; Carcamo-Oyarce, G.; Gloag, E.S.; Shimoni, R.; et al. Explosive cell lysis as a mechanism for the biogenesis of bacterial membrane vesicles and biofilms. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11220.
- Toyofuku, M.; Nomura, N.; Eberl, L. Types and origins of bacterial membrane vesicles. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 13–24.
- Nagakubo, T.; Nomura, N.; Toyofuku, M. Cracking Open Bacterial Membrane Vesicles. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 3026.
- Haurat, M.F.; Elhenawy, W.; Feldman, M.F. Prokaryotic membrane vesicles: New insights on biogenesis and biological roles. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 95–109.
- Chernov, V.M.; Mouzykantov, A.A.; Baranova, N.B.; Medvedeva, E.S.; Grygorieva, T.Y.; Trushin, M.V.; Vishnyakov, I.E.; Sabantsev, A.V.; Borchsenius, S.N.; Chernova, O.A. Extracellular membrane vesicles secreted by mycoplasma Acholeplasma laidlawii PG8 are enriched in virulence proteins. J. Proteom. 2014, 110, 117–128.
- Kwon, S.O.; Gho, Y.S.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, S.I. Proteome analysis of outer membrane vesicles from a clinical Acinetobacter baumannii isolate. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 297, 150–156.
- Negrete-Abascal, E.; Garcia, R.M.; Reyes, M.E.; Godinez, D.; de la Garza, M. Membrane vesicles released by Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae contain proteases and Apx toxins. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 191, 109–113.
- Thay, B.; Damm, A.; Kufer, T.A.; Wai, S.N.; Oscarsson, J. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans outer membrane vesicles are internalized in human host cells and trigger NOD1- and NOD2-dependent NF-kappaB activation. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 4034–4046.
- Roden, J.A.; Wells, D.H.; Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Koehler, J.E. Hemin binding protein C is found in outer membrane vesicles and protects Bartonella henselae against toxic concentrations of hemin. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 929–942.
- Skare, J.T.; Shang, E.S.; Foley, D.M.; Blanco, D.R.; Champion, C.I.; Mirzabekov, T.; Sokolov, Y.; Kagan, B.L.; Miller, J.N.; Lovett, M.A. Virulent strain associated outer membrane proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2380–2392.
- Toledo, A.; Coleman, J.L.; Kuhlow, C.J.; Crowley, J.T.; Benach, J.L. The enolase of Borrelia burgdorferi is a plasminogen receptor released in outer membrane vesicles. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 359–368.
- Allan, N.D.; Kooi, C.; Sokol, P.A.; Beveridge, T.J. Putative virulence factors are released in association with membrane vesicles from Burkholderia cepacia. Can. J. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 613–624.
- Elmi, A.; Watson, E.; Sandu, P.; Gundogdu, O.; Mills, D.C.; Inglis, N.F.; Manson, E.; Imrie, L.; Bajaj-Elliott, M.; Wren, B.W.; et al. Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane vesicles play an important role in bacterial interactions with human intestinal epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 4089–4098.
- Stead, C.M.; Omsland, A.; Beare, P.A.; Sandoz, K.M.; Heinzen, R.A. Sec-mediated secretion by Coxiella burnetii. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 222.
- Lee, J.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Dinh, N.T.H.; Go, G.; Tae, S.; Park, K.S.; Park, H.T.; Lee, C.; Roh, T.Y.; et al. Outer Membrane Vesicles Derived from Escherichia coli Regulate Neutrophil Migration by Induction of Endothelial IL-8. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2268.
- Dutta, S.; Iida, K.; Takade, A.; Meno, Y.; Nair, G.B.; Yoshida, S. Release of Shiga toxin by membrane vesicles in Shigella dysenteriae serotype 1 strains and in vitro effects of antimicrobials on toxin production and release. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 48, 965–969.
- Ellis, T.N.; Kuehn, M.J. Virulence and immunomodulatory roles of bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 81–94.
- Bielaszewska, M.; Ruter, C.; Kunsmann, L.; Greune, L.; Bauwens, A.; Zhang, W.; Kuczius, T.; Kim, K.S.; Mellmann, A.; Schmidt, M.A.; et al. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli hemolysin employs outer membrane vesicles to target mitochondria and cause endothelial and epithelial apoptosis. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003797.
- Berlanda, S.F.; Doro, F.; Rodriguez-Ortega, M.J.; Stella, M.; Liberatori, S.; Taddei, A.R.; Serino, L.; Gomes Moriel, D.; Nesta, B.; Fontana, M.R.; et al. Proteomics characterization of outer membrane vesicles from the extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli DeltatolR IHE3034 mutant. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 473–485.
- Winter, L.E.; Barenkamp, S.J. Immunogenicity of Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae Outer Membrane Vesicles and Protective Ability in the Chinchilla Model of Otitis Media. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2017, 24, e00138-17.
- Fernandez-Moreira, E.; Helbig, J.H.; Swanson, M.S. Membrane vesicles shed by Legionella pneumophila inhibit fusion of phagosomes with lysosomes. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3285–3295.
- Augustyniak, D.; Seredynski, R.; McClean, S.; Roszkowiak, J.; Roszniowski, B.; Smith, D.L.; Drulis-Kawa, Z.; Mackiewicz, P. Virulence factors of Moraxella catarrhalis outer membrane vesicles are major targets for cross-reactive antibodies and have adapted during evolution. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4955.
- Nagaputra, J.C.; Rollier, C.S.; Sadarangani, M.; Hoe, J.C.; Mehta, O.H.; Norheim, G.; Saleem, M.; Chan, H.; Derrick, J.P.; Feavers, I.; et al. Neisseria meningitidis native outer membrane vesicles containing different lipopolysaccharide glycoforms as adjuvants for meningococcal and nonmeningococcal antigens. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 21, 234–242.
- Grenier, D. Porphyromonas gingivalis Outer Membrane Vesicles Mediate Coaggregation and Piggybacking of Treponema denticola and Lachnoanaerobaculum saburreum. Int. J. Dent. 2013, 2013, 305476.
- Yoon, H.; Ansong, C.; Adkins, J.N.; Heffron, F. Discovery of Salmonella virulence factors translocated via outer membrane vesicles to murine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 2182–2192.
- Berlanda Scorza, F.; Colucci, A.M.; Maggiore, L.; Sanzone, S.; Rossi, O.; Ferlenghi, I.; Pesce, I.; Caboni, M.; Norais, N.; di Cioccio, V.; et al. High yield production process for Shigella outer membrane particles. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35616.
- Rosen, G.; Naor, R.; Rahamim, E.; Yishai, R.; Sela, M.N. Proteases of Treponema denticola outer sheath and extracellular vesicles. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 3973–3979.
- Cecil, J.D.; Sirisaengtaksin, N.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Krachler, A.M. Outer Membrane Vesicle-Host Cell Interactions. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7.
- Eddy, J.L.; Gielda, L.M.; Caulfield, A.J.; Rangel, S.M.; Lathem, W.W. Production of outer membrane vesicles by the plague pathogen Yersinia pestis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107002.
- Jiang, Y.; Kong, Q.; Roland, K.L.; Curtiss, R., 3rd. Membrane vesicles of Clostridium perfringens type A strains induce innate and adaptive immunity. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 431–443.
- Wagner, T.; Joshi, B.; Janice, J.; Askarian, F.; Skalko-Basnet, N.; Hagestad, O.C.; Mekhlif, A.; Wai, S.N.; Hegstad, K.; Johannessen, M. Enterococcus faecium produces membrane vesicles containing virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance related proteins. J. Proteom. 2018, 187, 28–38.
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, L.; Garcia, R.C. Extracellular Vesicles in Mycobacterial Infections: Their Potential as Molecule Transfer Vectors. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1929.
- Choi, E.J.; Lee, H.G.; Bae, I.H.; Kim, W.; Park, J.; Lee, T.R.; Cho, E.G. Propionibacterium acnes-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Acne-Like Phenotypes in Human Epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1371–1379.
- Liao, S.; Klein, M.I.; Heim, K.P.; Fan, Y.; Bitoun, J.P.; Ahn, S.J.; Burne, R.A.; Koo, H.; Brady, L.J.; Wen, Z.T. Streptococcus mutans extracellular DNA is upregulated during growth in biofilms, actively released via membrane vesicles, and influenced by components of the protein secretion machinery. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 2355–2366.
- Jhelum, H.; Sori, H.; Sehgal, D. A novel extracellular vesicle-associated endodeoxyribonuclease helps Streptococcus pneumoniae evade neutrophil extracellular traps and is required for full virulence. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7985.
