Nanomaterials and nanoparticles (NPs) possess unique physico-chemical properties (size, shape, chemical composition, physiochemical stability, crystal structure, surface area, surface energy, and surface roughness), which give them beneficial characteristics. Quantitative structure-activity relationship, or QSAR, is an area of molecular modeling that studies relationships between structure and activity using mathematical statistics and machine learning methods. QSAR is efficiently used to predict toxicity of chemical substances.
- engineered nanomaterials
- safety of nanomaterials
- toxicological tests
- descriptors
- QSAR
- machine learning
- modeling
1. Introduction


2. Metal Oxides
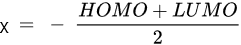
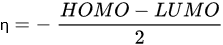
|
Source |
Dataset |
Endpoint of Cytotoxicity Measurement |
n |
R2 1 |
Software 2 |
Statistical Method |
Descriptors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Escherichia coli |
|||||||
|
[24] |
[24] |
LD50 |
7 |
0.979 |
- |
Multiple linear regression (MLR) |
Metal cation charge |
|
[20] |
[20] |
LD50 |
17 |
0.862 |
MATLAB |
MLR |
Enthalpy of formation of a gaseous cation |
|
[25] |
[20] |
LD50 |
17 |
0.741–0.838 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
SMILES-based optimal descriptor |
|
[26] |
[20] |
LD50 |
17 |
0.933 |
Minitab 16 |
MLR |
Energy gap, hardness, softness, electronegativity, and electrophilicity index |
|
[27] |
[20] |
LD50 |
17 |
0.81–0.90 |
- |
MLR |
Electronegativity, charge of the metal cation corresponding to a given oxide |
|
[28] |
[20] |
LD50 |
17 |
0.93 |
RandomForest package |
Random forest (RF) |
S1—unbonded two-atomic fragments [Me] … [Me], which were encoded based on Simplex representation of molecular structures (SiRMS)-derived descriptors [33][34], describing distance where potential reaches minimum at van der Waals interactions; rw—Wigner–Seitz radius; ρ—mass density; (CPP)—cation polarizing power; S2—SiRMS-derived electronegativity aligned descriptor of oxides molecules—in a sense of the acid-base property of oxides (this parameter increases with a number of oxygens in molecule); S3—tri-atomic fragments [Me]-[O]-[Me], which were encoded by SiRMS-derived descriptors, encoding electronegativity; and (SV)—proportion of surface molecules to molecules in volume |
|
[29] |
[20] |
LD50 |
17 |
0.955 |
Ensemble learning |
Oxygen percent, molar refractivity, and polar surface area |
|
|
[30] |
[20] |
LD50 |
17 |
- |
MATLAB |
Read-across |
Ionization enthalpy of the detached metal atoms |
|
[18] |
[20] |
LD50 |
17 |
0.889–0.982 |
CORAL |
MLR |
SMILES-based optimal descriptor |
|
[35] |
[20] |
LD50 |
16 |
0.91 |
- |
MLR |
Enthalpy of formation of a gaseous cation (ΔHMe+), charge of the metal cation (χox), and pEC50 of HaCaT |
|
[32] |
[20] |
LD50 |
16 |
0.879 |
SYBYL X1.1 and SPSS statistics v.17 |
MLR |
Enthalpy of formation of a gaseous cation (ΔHme+) and polarization force (Z/r) |
|
[36] |
[20] |
LD50 |
16 |
0.79 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
[37] |
[20] |
LD50 |
17 |
0.92 |
- |
Counter propagation artificial neural network |
Metal electronegativity by Pauling scale, number of metal atoms in oxide, number of oxygen atoms in oxide, and charge of metal cation |
|
[38] |
[20] |
LD50 |
17 |
0.968 |
- |
RF |
Oxygen in weight percentage and enthalpy of formation of a gaseous cation |
|
[39] |
[20] |
LD50 |
17 |
0.877 and 0.903 |
- |
MLR and support vector machines (SVM) |
HOMO energy, α-LUMO and β-LUMO energy, the average of α-LUMO and β-LUMO, the energy gap between the frontier molecular orbitals ∆E, and molar heat capacity |
|
[8] |
[20] |
LD50 |
17 |
0.93 |
- |
Partial least squares (PLS) |
Charge of metal ion, metal ion charge-based SiRMS, number of oxygen atoms in brutto formula weighted by ionic potential, covalent index weighted by charge of metal ion, molecular weight of metal oxide weighed by size of nanoparticle, squared thickness of interfacial layer, van der Waals repulsion weighted by size of nanoparticle, and Wigner-Seitz radius weighted by size of nanoparticle |
|
[31] |
[31] |
LD50 |
17 |
0.87 |
Self-written program |
MLR |
Electronegativity of metal and electronegativity of metal oxide |
|
[40] |
[40] |
IC50 |
24 |
- |
R |
SVM |
Conduction band energy and hydration enthalpy (ΔHhyd) |
|
Human keratinocyte cell line (HaCaT) |
|||||||
|
[28] |
[41] |
LD50 |
18 |
0.96 |
RandomForest package |
RF |
S1, rw, ρ, (CI)—covalent index of the metal ion, S2, and (AP)—aggregation parameter |
|
[30] |
[41] |
LD50 |
18 |
- |
MATLAB |
Read-across |
Mulliken’s electronegativity |
|
[41] |
[41] |
LD50 |
18 |
0.93 |
- |
MLR |
Enthalpy of formation of metal oxide, Mulliken’s electronegativity |
|
[18] |
[41] |
LD50 |
18 |
0.961–0.999 |
CORAL |
MLR |
SMILES-based optimal descriptor |
|
[35] |
[41] |
LD50 |
16 |
0.88 |
- |
MLR |
Enthalpy of formation of metal oxide (ΔHf) nano-cluster, electronic chemical potential of the cluster, and pEC50 of E. coli |
|
[36] |
[41] |
LD50 |
16 |
0.79 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
[38] |
[41] |
LD50 |
18 |
0.918 |
- |
RF |
10-based logarithm of solubility measured in mol/L (LogS), topological polar surface area (TPSA), Mulliken’s electronegativity |
|
[8] |
[41] |
LD50 |
18 |
0.83 |
- |
PLS |
Atom charge-based SiRMS descriptor, charge of the atom weighted by the bond ionicity, charge of metal ion weighted by ionicity of bond, squared ionic potential, ion change-based SiRMS descriptor, number of oxygen atoms in brutto formula per interfacial layer, mass density weighted by ionicity of bond, Wigner-Seitz radius weighted by ionicity of bond, and ionicity of bond based SiRMS |
|
[42] |
Cell viability (%) |
21 |
- |
CORAL |
Hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) and min–max normalization |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
|
Transformed bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) |
|||||||
|
[45] |
[45] |
% of membrane-damaged cells |
9 |
- |
Weka |
RF |
Atomization energy of the metal oxide, period of the nanoparticle metal, nanoparticle primary size, and nanoparticle volume fraction |
|
[6] |
[6] |
Cell viability (%) |
24 |
- |
- |
Regression tree |
Metal solubility and energy of conduction |
|
[46] |
[6] |
Cell viability (%) |
24 |
- |
RandomForest package |
RF |
Mass density, covalent index, cation polarizing power, Wigner–Seitz radius, surface area-to-volume ratio, aggregation parameter, and tri-atomic descriptor of atomic charges |
|
[47] |
[47] |
LD50 |
24 |
- |
RapidMiner |
SVM |
Conduction band energy and ionic index of metal cation |
|
[48] |
[49] |
% of membrane-damaged cells |
24 |
0.68 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
SMILES-based optimal descriptor, dose, and exposure time |
|
[42] |
Cell viability (%) |
21 |
0.713–0.733 |
CORAL |
HCA and min-max normalization |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
|
Murine myeloid cells (RAW 264.7) |
|||||||
|
[6] |
[6] |
Cell viability (%) |
24 |
- |
- |
Regression tree |
Metal solubility and energy of conduction |
|
[46] |
[6] |
Cell viability (%) |
24 |
- |
RandomForest package |
RF |
Mass density, molecular weight, aligned electronegativity, covalent index, surface area, surface area-to-volume ratio, two-atomic descriptor of van der Waals interactions, tetra-atomic descriptor of atomic charges, and size in DMEM |
|
[47] |
[47] |
LD50 |
24 |
- |
RapidMiner |
SVM |
Conduction band energy and ionic index of metal cation |
|
[52] |
[52] |
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release |
25 |
- |
R |
PLS |
Metal cation charge, hydration rate, radius of the metallic cation, and Pauling electronegativity |
|
Rat L2 lung epithelial cells and rat lung alveolar macrophages |
|||||||
|
[53] |
[53] |
Membrane damage (units L−1) |
42 |
- |
- |
Multivariate linear regression and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) |
Size, concentration, size in phosphate buffered saline, size in water, and zeta potential |
|
[54] |
[53] |
Membrane damage (units L−1) |
42 |
- |
- |
MLR and simple classification |
Size, concentration, size in phosphate buffered saline, and size in water |
1 Missing R2 value means that an SAR model was built instead of QSAR. 2 If software record is missing, then it was not mentioned in the original paper.
3. Other Metal-Containing Nanoparticles
|
Source |
Dataset |
Cell Type |
Endpoint of Cytotoxicity Measurement |
n |
R2 |
Software |
Statistical Method |
Descriptors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
[55] |
[56] |
Monocytes, hepatocytes, endothelial, and smooth muscle cells |
Cellular viability |
51 |
0.72 |
WinSVM, ISIDA |
SVM classification and k Nearest Neighbors (kNN) regression |
Size, zeta potential, R1 and R2 relaxivities |
|
[55] |
[57] |
PaCa2 human pancreatic cancer cells, U937 macrophage cell lines, primary human macrophages, HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
Cellular uptake |
109 |
0.65–0.80 |
WinSVM, ISIDA |
SVM classification and k Nearest Neighbors (kNN) regression |
Lipophilicity, number of double bonds |
|
[58] |
[56] |
Smooth muscle cells |
Cell apoptosis |
31 |
0.81 |
- |
MLR and Bayesian regularized artificial neural network |
IFe2O3, Idextran, and Isurf.chg |
|
[59] |
[56] |
Monocytes, hepatocytes, endothelial, and smooth muscle cells |
Cellular viability |
44 |
- |
- |
Naive Bayesian classifier |
Primary size, spin-lattice and spin-spin relaxivities, zeta potential |
|
[60] |
[60] |
Zebrafish embryo |
24 h post-fertilization mortality |
82 |
- |
ABMiner |
Numerical prediction |
Concentration, shell composition, surface functional groups, purity, core structure, and surface charge |
|
[61] |
[61] |
Mammalian cell lines |
TC50 |
1681 |
- |
STATISTICA v.6 |
LDA |
Molar volume, polarizability, and size of the particles |
|
[62] |
[62] |
Algae, bacteria, cell lines, crustaceans, plants, fish, and others |
CC50, EC50, IC50, TC50, LC50 |
36488 |
- |
STATISTICA |
LDA |
Molar volume, polarizability, size of NPs, electronegativity, hydrophobicity, and polar surface area of surface coating |
|
[63] |
[63] |
Bacteria, algae, crustaceans, fish, and others |
EC50, IC50, TC50, LC50 |
5520 |
- |
STATISTICA |
LDA |
Molar volume, electronegativity, polarizability, and nanoparticle size |
|
[64] |
[64] |
Algae, bacteria, fungi, mammal cell lines, crustaceans, plants, fishes, and others |
CC50, EC50, IC50, TC50, LC50 |
54371 |
- |
STATISTICA |
Artificial neural network |
Polar surface area, hydrophobicity, atomic weight, atomic van der Waals radius, electronegativity, and polarizability |
|
[65] |
[66] |
Danio rerio, Daphnia magna, Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata, and Staphylococcus aureus |
LC50, EC50, MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) |
400 |
- |
Weka |
Functional tree, C4.5 decision tree, random tree, and CART |
Molecular polarizability, accessible surface area, and solubility |
|
[67] |
[67] |
E. coli and Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells |
EC50, MIC |
17 |
0.94 |
R |
Nonlinear least-squaress |
Size and specific surface area (Brunauer-Emmett-Teller surface) |
4. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs)
|
Source |
Dataset |
Cell Type |
Endpoint of Cytotoxicity Measurement |
n |
R2 |
Software |
Statistical Method |
Descriptors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
[69] |
[70] |
Salmonella typhimurium TA100 |
Reverse mutation test TA100 |
24 |
0.65–0.81 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
[71] |
[72] |
Salmonella typhimurium TA100 |
Reverse mutation test TA100 |
30 |
0.53–0.64 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
[73] |
Salmonella typhimurium TA100 |
Reverse mutation test TA100 |
44 |
0.60–0.78 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
|
[75] |
[75] |
Four types of normal human lung cells (BEAS-2B, 16HBE14o-, WI-38, and HBE) |
Cell viability (%) |
276 |
0.60–0.80 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
5. Fullerenes
|
Source |
Dataset |
Cell Type |
Endpoint of Cytotoxicity Measurement |
n |
R2 |
Software |
Statistical Method |
Descriptors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
[73] |
Salmonella typhimurium TA100 |
Reverse mutation test TA100 |
44 |
0.60–0.78 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
|
[76] |
[74] |
S. typhimurium TA100 |
Reverse mutation test TA100 |
20 |
0.76 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
[77] |
[74] |
S. typhimurium TA100 |
Reverse mutation test TA100 |
20 |
0.63–0.76 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
[77] |
[74] |
E. coli WP2 uvrA/pKM101 |
Reverse mutation test WP2 uvrA/pKM101 |
20 |
0.68–0.82 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
6. Silica Nanomaterials
|
Source |
Dataset |
Cell Type |
Endpoint of Cytotoxicity Measurement |
n |
R2 |
Software |
Statistical Method |
Descriptors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
[78] |
[79] |
Human embryonic kidney cells HEK293 |
Cell viability (%) |
40 |
0.80–0.93 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
[80] |
[81] |
Human kidney cells HK-2 |
Cell viability (%) |
42 |
0.83–0.89 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
[82] |
[82] |
16HBE, A549, HaCaT, NRK-52E, and THP-1 |
EC25 |
19 |
0.83 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
|
[82] |
[82] |
16HBE, A549, HaCaT, NRK-52E, and THP-1 |
EC25 |
19 |
0.87 |
R |
RF |
Aspect ratio and zeta potential |
|
[83] |
[79] |
Human embryonic kidney cell line (HEK293) |
Cell viability (%) |
40 |
0.80–0.95 |
CORAL |
Monte Carlo |
Quasi-SMILES |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/molecules24244537
References
- Gatoo, M.A.; Naseem, S.; Arfat, M.Y.; Dar, A.M.; Qasim, K.; Zubair, S. Physicochemical properties of nanomaterials: Implication in associated toxic manifestations. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 498420.
- Buzea, C.; Pacheco, I.I.; Robbie, K. Nanomaterials and nanoparticles: Sources and toxicity. Biointerphases 2007, 2, 17–71.
- Gajewicz, A.; Rasulev, B.; Dinadayalane, T.C.; Urbaszek, P.; Puzyn, T.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J. Advancing risk assessment of engineered nanomaterials: Application of computational approaches. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1663–1693.
- Valko, M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M.T. Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1161–1208.
- Burello, E.; Worth, A.P. A theoretical framework for predicting the oxidative stress potential of oxide nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 228–235.
- Zhang, H.; Ji, Z.; Xia, T.; Meng, H.; Low-Kam, C.; Liu, R.; Pokhrel, S.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.P.; et al. Use of metal oxide nanoparticle band gap to develop a predictive paradigm for oxidative stress and acute pulmonary inflammation. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4349–4368.
- Lynch, I.; Weiss, C.; Valsami-Jones, E. A strategy for grouping of nanomaterials based on key physico-chemical descriptors as a basis for safer-by-design NMs. Nano Today 2014, 9, 266–270.
- Kuz’min, V.E.; Ognichenko, L.N.; Sizochenko, N.; Chapkin, V.A.; Stelmakh, S.I.; Shyrykalova, A.O.; Leszczynski, J. Combining features of metal oxide nanoparticles: Nano-QSAR for cytotoxicity. Int. J. Quant. Struct. Prop. Relat. 2019, 4, 28–40.
- Tang, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Hong, H. Deep learning for predicting toxicity of chemicals: A mini review. J. Environ. Sci. Health C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2018, 36, 252–271.
- Idakwo, G.; Luttrell, J.; Chen, M.; Hong, H.; Zhou, Z.; Gong, P.; Zhang, C. A review on machine learning methods for in silico toxicity prediction. J. Environ. Sci. Health C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2018, 36, 169–191.
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Ai, H.; Hu, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H. Applications of Machine Learning Methods in Drug Toxicity Prediction. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 987–997.
- Lu, J.; Lu, D.; Fu, Z.; Zheng, M.; Luo, X. Machine learning-based modeling of drug toxicity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1754, 247–264.
- Kar, S.; Leszczynski, J. Exploration of computational approaches to predict the toxicity of chemical mixtures. Toxics 2019, 7, 15.
- Hansch, C.; Streich, M.; Geiger, F.; Muir, R.M.; Maloney, P.P.; Fujita, T. Correlation of biological activity of plant growth regulators and chloromycetin derivatives with Hammett constants and partition coefficients. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 2817–2824.
- Bonchev, D.; Rouvray, D.H. Chemical Graph Theory: Introduction and Fundamentals; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1991.
- Cramer, R.D.; Patterson, D.E.; Bunce, J.D. Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 5959–5967.
- Klebe, G.; Abraham, U.; Mietzner, T. Molecular similarity indexes in a comparative-analysis (Comsia) of drug molecules to correlate and predict their biological-activity. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 4130–4146.
- Pan, Y.; Li, T.; Cheng, J.; Telesca, D.; Zink, J.I.; Jianga, J. Nano-QSAR modeling for predicting the cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles using novel descriptors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 25766–25775.
- Burello, E.; Worth, A.P. QSAR modeling of nanomaterials. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 3, 298–306.
- Puzyn, T.; Rasulev, B.; Gajewicz, A.; Hu, X.; Dasari, T.P.; Michalkova, A.; Hwang, H.M.; Toropov, A.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J. Using nano-QSAR to predict the cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 175–178.
- Tzoupis, H.; Leonis, G.; Durdagi, S.; Mouchlis, V.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Papadopoulos, M.G. Binding of novel fullerene inhibitors to HIV-1 protease: Insight through molecular dynamics and molecular mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann surface area calculations. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2011, 25, 959–976.
- Ahmed, L.; Rasulev, B.; Turabekova, M.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J. Receptor- and ligand-based study of fullerene analogues: Comprehensive computational approach including quantum-chemical, QSAR and molecular docking simulations. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 5798–5808.
- Jagiello, K.; Grzonkowska, M.; Swirog, M.; Ahmed, L.; Rasulev, B.; Avramopoulos, A.; Papadopoulos, M.G.; Leszczynski, J.; Puzyn, T. Advantages and limitations of classic and 3D QSAR approaches in nano-QSAR studies based on biological activity of fullerene derivatives. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 256.
- Hu, X.; Cook, S.; Wang, P.; Hwang, H.M. In vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity of engineered metal oxide nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3070–3072.
- Toropov, A.A.; Toropova, A.P.; Benfenati, E.; Gini, G.; Puzyn, T.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J. Novel application of the CORAL software to model cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles to bacteria Escherichia coli. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1098–1102.
- Venigalla, S.; Dhail, D.; Ranjan, P.; Jain, S.; Chakraborty, T. Computational study about cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles invoking nano-QSAR. New Front. Chem. 2013, 23, 123–130.
- Kar, S.; Gajewicz, A.; Puzyn, T.; Roy, K.; Leszczynski, J. Periodic table-based descriptors to encode cytotoxicity profile of metal oxide nanoparticles: A mechanistic QSTR approach. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2014, 107, 162–169.
- Sizochenko, N.; Rasulev, B.; Gajewicz, A.; Kuz’min, V.; Puzyn, T.; Leszczynski, J. From basic physics to mechanisms of toxicity: The “liquid drop” approach applied to develop predictive classification models for toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13986–13993.
- Singh, K.P.; Gupta, S. Nano-QSAR modeling for predicting biological activity of diverse nanomaterials. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 13215–13230.
- Gajewicz, A.; Cronin, M.; Rasulev, B.; Leszczynski, J.; Puzyn, T. Novel approach for efficient predictions properties of large pool of nanomaterials based on limited set of species: Nano-read-across. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 015701.
- Pathakoti, K.; Huang, M.-J.; Watts, J.D.; He, X.; Hwang, H.-M. Using experimental data of Escherichia coli to develop a QSAR model for predicting the photo-induced cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2014, 130, 234–240.
- Mu, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhao, Q.; Ji, R.; Qie, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Pang, C.; Hristozov, D.; Giesy, J.P.; et al. Predicting toxic potencies of metal oxide nanoparticles by means of nano-QSARs. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 1207–1214.
- Kuz’min, V.E.; Artemenko, A.G.; Polischuk, P.G.; Muratov, E.N.; Hromov, A.I.; Liahovskiy, A.V.; Andronati, S.A.; Makan, S.Y. Hierarchic system of QSAR models (1D–4D) on the base of simplex representation of molecular structure. J. Mol. Model. 2005, 11, 457–467.
- Kuz’min, V.E.; Muratov, E.N.; Artemenko, A.G.; Gorb, L.G.; Qasim, M.; Leszczynski, J. The effect of nitroaromatics composition on their toxicity in vivo. 1D QSAR research. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1373–1380.
- Kar, S.; Gajewicz, A.; Roy, K.; Leszczynski, J.; Puzyn, T. Extrapolating between toxicity endpoints of metal oxide nanoparticles: Predicting toxicity to Escherichia coli and human keratinocyte cell line (HaCaT) with Nano-QTTR. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2016, 126, 238–244.
- Toropova, A.P.; Toropov, A.A.; Manganelli, S.; Leone, C.; Baderna, D.; Benfenati, E.; Fanelli, R. Quasi-SMILES as a tool to utilize eclectic data for predicting the behavior of nanomaterials. NanoImpact 2016, 1, 60–64.
- Fjodorova, N.; Novic, M.; Gajewicz, A.; Rasulev, B. The way to cover prediction for cytotoxicity for all existing nano-sized metal oxides by using neural network method. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 475–483.
- Basant, N.; Gupta, S. Multi-target QSTR modeling for simultaneous prediction of multiple toxicity endpoints of nano-metal oxides. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 339–350.
- Zhou, Z.; Tang, X.; Dai, W.; Shi, J.; Chen, H. Nano-QSAR models for predicting cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles (MONPs) to E. coli. Can. J. Chem. 2017, 95, 863–866.
- Kaweeteerawat, C.; Ivask, A.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H.; Chang, C.H.; Low-Kam, C.; Fischer, H.; Ji, Z.; Pokhrel, S.; Cohen, Y.; et al. Toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles in Escherichia coli correlates with conduction band and hydration energies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1105–1112.
- Gajewicz, A.; Schaeublin, N.; Rasulev, B.; Hussain, S.; Leszczynska, D.; Puzyn, T.; Leszczynski, J. Towards understanding mechanisms governing cytotoxicity of metal oxides nanoparticles: Hints from nano-QSAR studies. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 313–325.
- Choi, J.S.; Trinh, T.X.; Yoon, T.H.; Kim, J.; Byun, H.G. Quasi-QSAR for predicting the cell viability of human lung and skin cells exposed to different metal oxide nanomaterials. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 243–249.
- Yang, X.; Liu, J.; He, H.; Zhou, L.; Gong, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Yuan, J.; Huang, H.; He, L. SiO2 nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity and protein expression alteration in HaCaT cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 1.
- Comfort, K.K.; Maurer, E.I.; Hussain, S.M. Slow release of ions from internalized silver nanoparticles modifies the epidermal growth factor signaling response. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 123, 136–142.
- Liu, R.; Rallo, R.; George, S.; Ji, Z.; Nair, S.; Nel, A.E.; Cohen, Y. Classification NanoSAR development for cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. Small 2011, 7, 1118–1126.
- Sizochenko, N.; Rasulev, B.; Gajewicz, A.; Mokshyna, E.; Kuz’min, V.E.; Leszczynski, J.; Puzyn, T. Causal inference methods to assist in mechanistic interpretation of classification nano-SAR models. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 77739–77745.
- Liu, R.; Zhang, H.Y.; Ji, Z.X.; Rallo, R.; Xia, T.; Chang, C.H.; Nel, A.; Cohen, Y. Development of structure-activity relationship for metal oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5644–5653.
- Toropova, A.; Toropov, A.; Benfenati, E.; Korenstein, R.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J. Optimal nano-descriptors as translators of eclectic data into prediction of the cell membrane damage by means of nano metal-oxides. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 745–757.
- Patel, T.; Telesca, D.; Low-Kam, C.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xia, T.; Zinc, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Relating nano-particle properties to biological outcomes in exposure escalation experiments. Environmetrics 2013, 25, 57–68.
- Akhtar, M.J.; Ahamed, M.; Kumar, S.; Khan, M.M.; Ahmad, J.; Alrokayan, S.A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles selectively induce apoptosis in human cancer cells through reactive oxygen species. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 845e857.
- Xiong, S.; George, S.; Yu, H.; Damoiseaux, R.; France, B.; Ng, K.W.; Loo, J.S. Size influences the cytotoxicity of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)(PLGA) and titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1075e1086.
- Forest, V.; Hochepied, J.-F.; Leclerc, L.; Trouvé, A.; Abdelkebir, K.; Sarry, G.; Augusto, V.; Pourchez, J. Towards an alternative to nano-QSAR for nanoparticle toxicity ranking in case of small datasets. J. Nanopart. Res. 2019, 21, 95.
- Sayes, C.; Ivanov, I. Comparative study of predictive computational models for nanoparticle-induced cytotoxicity. Risk Anal. 2010, 30, 1723–1734.
- Papa, E.; Doucet, J.P.; Doucet-Panaye, A. Linear and non-linear modelling of the cytotoxicity of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles by empirical descriptors. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2015, 26, 647–665.
- Fourches, D.; Pu, D.; Tassa, C.; Weissleder, R.; Shaw, S.Y.; Mumper, R.J.; Tropsha, A. Quantitative nanostructure-activity relationship modeling. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5703–5712.
- Shaw, S.Y.; Westly, E.C.; Pittet, M.J.; Subramanian, A.; Schreiber, S.L.; Weissleder, R. Perturbational profiling of nanomaterial biologic activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7387–7392.
- Weissleder, R.; Kelly, K.; Sun, E.Y.; Shtatland, T.; Josephson, L. Cell-specific targeting of nanoparticles by multivalent attachment of small molecules. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1418–1423.
- Epa, V.C.; Burden, F.R.; Tassa, C.; Weissleder, R.; Shaw, S.; Winkler, D.A. Modeling biological activities of nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5808–5812.
- Liu, R.; Rallo, R.; Weissleder, R.; Tassa, C.; Shaw, S.; Cohen, Y. Nano-SAR development for bioactivity of nanoparticles with considerations of decision boundaries. Small 2013, 9, 1842–1852.
- Liu, X.; Tang, K.; Harper, S.; Harper, B.; Steevens, J.A.; Xu, R. Predictive modeling of nanomaterial exposure effects in biological systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 31–43.
- Luan, F.; Kleandrova, V.V.; González-Díaz, H.; Ruso, J.M.; Melo, A.; Speck-Planche, A.; Cordeiro, M.N. Computer-aided nanotoxicology: Assessing cytotoxicity of nanoparticles under diverse experimental conditions by using a novel QSTR-perturbation approach. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10623–10630.
- Kleandrova, V.V.; Luan, F.; González-Díaz, H.; Ruso, J.M.; Speck-Planche, A.; Cordeiro, M.N. Computational tool for risk assessment of nanomaterials: Novel QSTR-perturbation model for simultaneous prediction of ecotoxicity and cytotoxicity of uncoated and coated nanoparticles under multiple experimental conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14686–14694.
- Kleandrova, V.V.; Luan, F.; González-Díaz, H.; Ruso, J.M.; Melo, A.; Speck-Planche, A.; Cordeiro, M.N. Computational ecotoxicology: Simultaneous prediction of ecotoxic effects of nanoparticles under different experimental conditions. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 288–294.
- Concu, R.; Kleandrova, V.V.; Speck-Planche, A.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Probing the toxicity of nanoparticles: A unified in silico machine learning model based on perturbation theory. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 891–906.
- Chen, G.; Vijver, M.G.; Peijnenburg, W.J. Summary and analysis of the currently existing literature data on metal-based nanoparticles published for selected aquatic organisms: Applicability for toxicity prediction by (Q)SARs. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2015, 43, 221–240.
- Chen, G.; Peijnenburg, W.J.; Kovalishyn, V.; Vijver, M.G. Development of nanostructure-activity relationships assisting the nanomaterial hazard categorization for risk assessment and regulatory decision-making. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 52227–52235.
- Mikolajczyk, A.; Sizochenko, N.; Mulkiewicz, E.; Malankowska, A.; Nischk, M.; Jurczak, P.; Hirano, S.; Nowaczyk, G.; Zaleska-Medynska, A.; Leszczynski, J.; et al. Evaluating the toxicity of TiO(2)-based nanoparticles to Chinese hamster ovary cells and Escherichia coli: A complementary experimental and computational approach. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2171–2180.
- Nymark, P.; Jensen, K.A.; Suhonen, S.; Kembouche, Y.; Vippola, M.; Kleinjans, J.; Catalán, J.; Norppa, H.; van Delft, J.; Briedé, J.J. Free radical scavenging and formation by multi-walled carbon nanotubes in cell free conditions and in human bronchial epithelial cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 4.
- Toropov, A.A.; Toropova, A.P. Quasi-QSAR for mutagenic potential of multi-walled carbon-nanotubes. Chemosphere 2015, 124, 40–46.
- Wirnitzer, U.; Herbold, B.; Voetz, M.; Ragot, J. Studies on the in vitro genotoxicity of baytubes, agglomerates of engineered multi-walled carbonnanotubes (MWCNT). Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 186, 160–165.
- Toropova, A.P.; Toropov, A.A.; Rallo, R.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J. Nano-QSAR: Genotoxicity of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2016, 10, 59–64.
- Ema, M.; Imamura, T.; Suzuki, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Naya, M.; Nakanishi, J. Evaluation of genotoxicity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in a battery of in vitro and in vivo assays. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 63, 188–195.
- Toropov, A.A.; Toropova, A.P. Quasi-SMILES and nano-QFAR: United model for mutagenicity of fullerene and MWCNT under different conditions. Chemosphere 2015, 139, 18–22.
- Shinohara, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Endoh, S.; Maru, J.; Nakanishi, J. In vitro and in vivo genotoxicity tests on fullerene C60 nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 191, 289–296.
- Trinh, T.X.; Choi, J.S.; Jeon, H.; Byun, H.G.; Yoon, T.H.; Kim, J. Quasi-SMILES-based nano-quantitative structure-activity relationship model to predict the cytotoxicity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes to human lung cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018, 31, 183–190.
- Toropov, A.A.; Toropova, A.P. Optimal descriptor as a translator of eclectic data into endpoint prediction: Mutagenicity of fullerene as a mathematical function of conditions. Chemosphere 2014, 104, 262–264.
- Toropova, A.P.; Toropov, A.A.; Veselinović, A.M.; Veselinović, J.B.; Benfenati, E.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J. Nano-QSAR: Model of mutagenicity of fullerene as a mathematical function of different conditions. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2016, 124, 32–36.
- Manganelli, S.; Leone, C.; Toropov, A.A.; Toropova, A.P.; Benfenati, E. QSAR model for predicting cell viability of human embryonic kidney cells exposed to SiO₂ nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 995–1001.
- Wang, F.; Gao, F.; Lan, M.; Yuan, H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J. Oxidative stress contributes to silica nanoparticle-induced cytotoxicity in human embryonic kidney cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2009, 23, 808–815.
- Toropova, A.P.; Toropov, A.A.; Benfenati, E. A quasi-QSPR modelling for the photocatalytic decolourization rate constants and cellular viability (CV%) of nanoparticles by CORAL. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2015, 26, 29–40.
- Passagne, I.; Morille, M.; Rousset, M.; Pujalté, I.L.; L’Azou, B. Implication of oxidative stress in size-dependent toxicity of silica nanoparticles in kidney cells. Toxicology 2012, 299, 112–124.
- Cassano, A.; Marchese Robinson, R.L.; Palczewska, A.; Puzyn, T.; Gajewicz, A.; Tran, L.; Manganelli, S.; Cronin, M.T. Comparing the CORAL and Random Forest approaches for modelling the in vitro cytotoxicity of silica nanomaterials. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2016, 44, 533–556.
- Manganelli, S.; Benfenati, E. Nano-QSAR model for predicting cell viability of human embryonic kidney cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1601, 275–290.
