For small structures on the scale of nanometers, the intermolecular van der Waals (vdW) interaction can play a leading role in some cases. Since their discovery, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have shown great application prospects in various fields with their excellent physical and mechanical properties.
- vdW interaction
- cohesive energy
- vibration
1. Introduction
2. Quantification of the vdW Interaction between Carbon Atoms
The vdW energy variation with the distance between two carbon atoms is shown in Figure 1. For r < r0, the repulsive force is dominant, defining the repulsive domain, whereas the attractive force is dominant for r > r0, forming the attractive domain. The blue dash, red dot and black solid lines in Figure 1b represent the repulsive, attractive and resultant forces between the two interacting atoms, respectively.

3. Cohesive Energy between Two Finite-Length Parallel CNTs

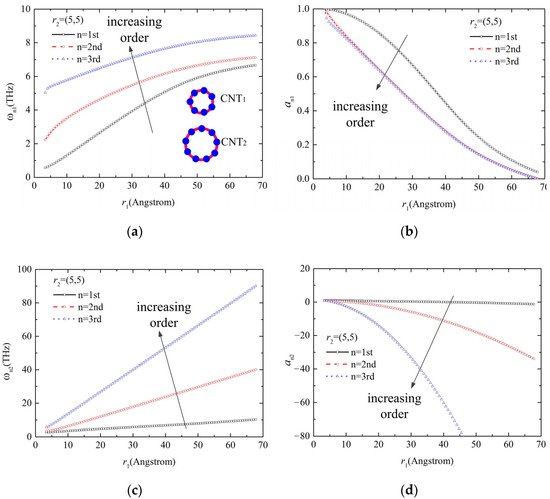
4. Research on the Vibration Modes for Nano Tubes


This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/molecules26247470
References
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19.
- Alian, A.R.; Meguid, S.A.; Kundalwal, S.I. Unraveling the influence of grain boundaries on the mechanical properties of poly-crystalline carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2017, 125, 180–188.
- Kothari, R.; Kundalwal, S.I.; Sahu, S.K. Transversely isotropic thermal properties of carbon nanotubes containing vacancies. Acta Mech. 2018, 229, 2787–2800.
- Kundalwal, S.I.; Choyal, V. Transversely isotropic elastic properties of carbon nanotubes containing vacancy defects using MD. Acta Mech. 2018, 229, 2571–2584.
- Carrella, A.; Brennan, M.J.; Waters, T.P. Static analysis of a passive vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness characteristic. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 301, 678–689.
- Ru, C.Q. Effect of van der Waals forces on axial buckling of a double-walled carbon nanotube. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 7227–7231.
- Ru, C.Q. Axially compressed buckling of a doublewalled carbon nanotube embedded in an elastic medium. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2001, 49, 1265–1279.
- He, X.Q.; Kitipornchai, S.; Liew, K.M. Buckling analysis of multi-walled carbon nanotubes: A continuum model accounting for van der Waals interaction. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2005, 53, 303–326.
- Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, C.M.; Tan, V.B.C. Buckling of carbon nanotubes: A literature survey. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 4221–4247.
- Lu, W.B.; Wu, J.; Song, J.; Hwang, K.C.; Jiang, L.Y.; Huang, Y. A cohesive law for interfaces between multi-wall carbon nanotubes and polymers due to the van der Waals interactions. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2008, 197, 3261–3267.
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, J.-W.; Jia, Y.; Guo, W.; Rabczuk, T. A theoretical analysis of cohesive energy between carbon nanotubes, graphene and substrates. Carbon 2013, 57, 108–119.
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Nshimiyimana, J.P.; Deng, Y.; Hou, G.; Chi, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, P.; Wang, G.; et al. Wafer-Scale fabrication of suspended single-walled carbon nanotube arrays by silver liquid dynamics. Small 2017, 13, 1701218.
- Chang, T. A molecular based anisotropic shell model for single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2010, 58, 1422–1433.
- Ghabussi, A.; Ashrafi, N.; Shavalipour, A.; Hosseinpour, A.; Habibi, M.; Moayedi, H.; Babaei, B.; Safarpour, H. Free vibration analysis of an electro-elastic GPLRC cylindrical shell surrounded by viscoelastic foundation using modified length-couple stress parameter. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2021, 49, 738–762.
- Ghabussi, A.; Habibi, M.; NoormohammadiArani, O.; Shavalipour, A.; Moayedi, H.; Safarpour, H. Frequency characteristics of a viscoelastic graphene nanoplatelet–reinforced composite circular microplate. J. Vib. Control. 2021, 27, 101–118.
- Safarpour, M.; Ghabussi, A.; Ebrahimi, F.; Habibi, M.; Safarpour, H. Frequency characteristics of FG-GPLRC viscoelastic thick annular plate with the aid of GDQM. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 150, 106683.
- Habibi, M.; Darabi, R.; de Sa, J.C.; Reis, A. An innovation in finite element simulation via crystal plasticity assessment of grain morphology effect on sheet metal formability. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2021, 235, 1937–1951.
- Peng, D.; Chen, S.; Darabi, R.; Ghabussi, A.; Habibi, M. Prediction of the bending and out-of-plane loading effects on formability response of the steel sheets. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2021, 21, 1–13.
- Shariati, A.; Jung, D.W.; Mohammad-Sedighi, H.; Żur, K.K.; Habibi, M.; Safa, M. Stability and Dynamics of Viscoelastic Moving Rayleigh Beams with an Asymmetrical Distribution of Material Parameters. Symmetry 2020, 12, 586.
- Ebrahimi, F.; Hashemabadi, D.; Habibi, M.; Safarpour, H. Thermal buckling and forced vibration characteristics of a porous GNP reinforced nanocomposite cylindrical shell. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 26, 461–473.
- Rueckes, T.; Kim, K.; Joselevich, E.; Tseng, G.Y.; Cheung, C.-L.; Lieber, C.M. Carbon nanotube-based nonvolatile random access memory for molecular computing. Science 2000, 289, 94–97.
- Wang, L.; Hu, H. Thermal vibration of a rectangular single-layered graphene sheet with quantum effects. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 233515.
- Al-Furjan, M.S.H.; Dehini, R.; Khorami, M.; Habibi, M.; Jung, D.W. On the dynamics of the ultra-fast rotating cantilever orthotropic piezoelectric nanodisk based on nonlocal strain gradient theory. Compos. Struct. 2021, 255, 112990.
- Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Yu, T. Quasi-static compression and hygrothermal stability of BMI/CE co-cured composite lattice cylindrical shell. Compos. Struct. 2021, 257, 113130.
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, P.; Guan, C.; Liu, T.; Kang, W.-H.; Feng, P.; Gao, S. An ultra-lightweight CFRP beam-string structure. Compos. Struct. 2021, 257, 113149.
- Dai, Z.; Zhang, L.; Bolandi, S.Y.; Habibi, M. On the vibrations of the non-polynomial viscoelastic composite open-type shell under residual stresses. Compos. Struct. 2021, 263, 113599.
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Habibi, M.; Ghabussi, A.; Alyousef, R. Low-velocity impact, resonance, and frequency responses of FG-GPLRC viscoelastic doubly curved panel. Compos. Struct. 2021, 269, 114000.
- Brenner, D.W.; Shenderova, O.A.; Harrison, J.A.; Stuart, S.J.; Ni, B.; Sinnott, S.B. A second-generation reactive empirical bond order (REBO) potential energy expression for hydrocarbons. Mater. Sci. 2002, 14, 783–802.
- González Noya, E.; Srivastava, D.; Chernozatonskii, L.A.; Menon, M. Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube peapods. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 115416.
- Xu, Z.; Buehler, M.J. Geometry controls conformation of graphene sheets: Membranes, ribbons, and scrolls. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3869–3876.
- Wei, N.; Fan, Z.; Xu, L.-Q.; Zheng, Y.-P.; Wang, H.-Q.; Zheng, J.-C. Knitted graphene-nanoribbon sheet: A mechanically robust structure. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 785–791.
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, K.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, J.-C.; Zhao, J.; Wei, N. Interfacial thermal conductance in graphene/black phosphorus heterogeneous structures. Carbon 2017, 117, 399–410.
- Polak, E. Optimization: Algorithms and Consistent Approximations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997.
- Nosé, S. A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 511–519.
- Hoover, W.G. Canonical dynamics: Equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 31, 1695.
- Yoon, J.; Ru, C.Q.; Mioduchowski, A. Vibration of an embedded multiwall carbon nanotube. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1533–1542.
