Traditional manufacturing is an industrial process that converts materials into a finished product using a labor-intensive low-end operation, low precision, average resource utilization and efficiency for economic value.
- manufacturing processes
- traditional manufacturing
- reconfigurable manufacturing systems
- flexible manufacturing systems
- smart manufacturing
- smart factory
- industrial revolution
1. Introduction
The shortcomings of traditional manufacturing are articulated and documented in [1], in comparison with more sustainable forms of manufacturing that rely on modern technologies and digital innovations. Over the last two decades, manufacturing has transformed into something complex, automated, and new, ultimately into smart manufacturing. Manufacturing systems, as they evolve, must retain the ability to respond to disruption quickly while possessing a good control structure. Response to disruption involves intuitive knowledge about what to do in a changing situation, even when something has never been implemented before. Through the manufacturing approach described in [2], flexibility and reconfigurability are introduced into traditional manufacturing systems. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) and Reconfigurable manufacturing systems (RMS) are two popular forms of transformed manufacturing. Each of these forms of manufacturing possesses features that make it unique and distinct from traditional manufacturing. The resilience of FMS permits it to adjust to changes in the environment. Strict operational standards, reduced product lifetime[3], reallocation of capacity to another manufacturing process without equipment replacement or considerable retooling, and increased range of items offered are all examples of changes. RMS, on the other hand, often addresses on-demand customized flexibility via scalability to incrementally actualize alternative capabilities and capacities. RMS [4] combines the benefits of both dedicated manufacturing lines (DML) and flexible manufacturing systems (FMS). By reacting quickly to market changes and efficiently adjusting production systems, the integration of DML and FMS[5] improves the response of the entire manufacturing system to unanticipated changes in production demand. Smart factories inherit the characteristics of FMS and RMS for their operations.
According to [6], a smart factory incorporates existing production/manufacturing into existing and future communication technologies. Furthermore, manufacturing technology [4] and cyber-physical systems [7][8][9] are used in creating more complex and detailed models by integrating the previously independent and disconnected systems commonly seen in traditional architectures. According to another description, the smart factory relies on creating connections between digital and physical environments [10] while enlarging the digital space through Internet of Things (IoT) technologies to enhance the quality and precision of manufacturing processes [11]. The smart factory [10] exhibits superior information processing support structures in data analytics [8][12], cloud systems, and machine/deep learning. Intelligent systems [13] outline a context-sensitive industrial environment where dispersed communication structures improve production processes while allowing for minimal unpredictability. A system like this may also adapt to a variety of changes and environments, mainly automatically [14]. An intelligent system enables unrestricted real-time data access, collection, and distribution of relevant manufacturing information. Hozdić in [15] describes a production solution that meets current demands while integrating industrial and non-industrial partners, resulting in the efficient construction of a compelling and virtual organization. An intelligent factory is a manufacturing solution that will solve complex manufacturing problems in smart manufacturing facilities through adjustable production processes within changeable boundary conditions.
The smart factory entails integrating smart manufacturing, digital technology, intelligent computing and Big Data with physical production processes and operations, resulting in a system with greater resources for successfully managing manufacturing and supply chain. This system consists of appropriate hardware systems, such as controllers and sensors, which provide a significant amount and variety of manufacturing data, and software systems that establish communication, transmitting, processing, and requesting information. This approach also accommodates existing and future enabling communication technologies that provide significant benefits such as ultra-low latency, high reliability of connection, spacious bandwidth, ample data storage, and advanced computational powers.
In all the descriptions of intelligent/smart manufacturing, two things are crucial: incorporating man, machine, material, method and technologies and energy to ensure a comprehensive convergence model [16], and continuous improvement of the convergence model. Figure 1 depicts a convergence model that links all contributing elements to both traditional production and enabling technologies.
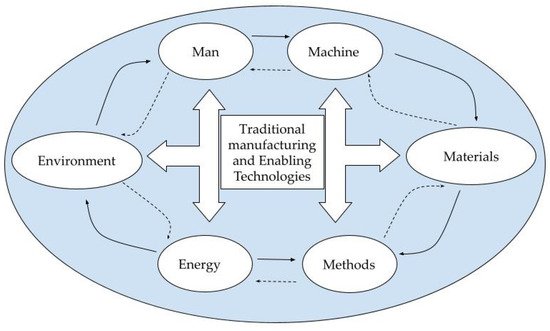
In Figure 1, traditional manufacturing and all the enabling technologies have connectivity and continuous communication with all contributing factors such as man’s knowledge, machines, materials, methods, energy and the environment. The contributing factors constantly talk and respond, establishing mutual relationships that improve smart/intelligent manufacturing. The dashed arrows symbolize the response phase, a dependent type of association, whereas the full line arrows reflect the directed association between the contributing factors. All relevant components contribute to the “left-right up” arrow.
2. Industrial Revolutions and the Enablers of Industry 4.0
The enabling technologies of Industry 4.0 have been critical to the emergence of smart manufacturing. As a result, future smart factories (FSF) will be autonomous units capable of independently planning, coordinating, and directing output. FSF can be contrasted with what existed at the commencement of the series of industrial revolutions. The increasing transformation of the economy away from the use of animal and human labor [17][18][19][ towards a large-scale mechanized, high-tech and automated system with adequate and new machines, power supply systems, and improved ways of performing work has been the hallmark of each Industrial Revolution (IR). Each IR has increased productivity and international commerce. Each nation’s achievements have been determined by the predominant energy resources available during each IR [20].
The first IR [12] is best described as an age of mechanization, steam engines, and hydraulic applications. During the second IR, there was an increase in the use of science and electricity, while mass production was in its early stages. The third IR saw the introduction of digital technology, automation in manufacturing and electronic and informatics systems into nearly all processes. 4IR is elevating the third industrial revolution and includes the Internet of Things, automation, machine learning, and cloud computing. Additionally, interconnectivity and real-time data acquisition are enabled. All previous IRs and their associated technological aspects and advancements are being seamlessly incorporated into 4IR. The fifth IR will address concerns about the dominance of the robot and may eventually take over the manufacturing process in specific sectors [21][22]. In the fifth IR, an advanced human-robot interface [23][24][25][26] will be used. Human characteristics such as creativity, craftiness, power, and imagination are being superimposed on the complex automation, consistency, productivity, and speed of the collaborating robots [27][28]. For optimal performance and efficiency, integration and interoperability are required attributes of all the parts that define each industrial revolution, especially in 4IR and 5IR. With interoperability, interconnectivity across device system sets is possible, and the required volume of data to make informed decisions is realized during the production process [29].
| IR | Energy Sources | Inventions | Final Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Coal and steam [30][31][32]. | Steam engines [33]. | Mechanization and centralized manufacturing. |
| 2nd | Electricity, natural gas, and oil [30][32][34]. | Lighting, telegraph, telephone, long-distance wireless communications, and steel production. | Industrialization [35]. |
| 3rd | Among others, a mix of energy sources: natural gas, nuclear power (energy) [32][34][36][37] coal and others. There is also a move towards renewable sources. | Solid-state electronics [38], robotics, automated process; and programmable logic control. | Factory automation and computerization [39]. |
| 4th | A mix of previous and existing energy sources and a greater focus towards sustainable sources. | Cloud computing, IoT, IIoT and blockchain. | Digitalization. |
| 5th | Most likely sustainable energy [40]. | Massive IoT, Autonomous cars, Augmented reality, and virtual reality. | Customization and personalization [41]. |
Similarly, the various accomplishments directly impacted the economy while allowing for technological advancement through the eras [42]. Presently, the fourth IR is translating and transforming manufacturing. The fourth IR's technical drivers [43][44] can be grouped into three major categories: physical, digital, and biotechnological factors [45]. Table 2 shows how each of these broad categories can be subdivided.
| Technological Drivers | Fields |
|---|---|
| Physical | Autonomous cars Additive manufacturing Advanced Robotics and Collaborating Robots |
| Digital | IoT IIoT Artificial Intelligence and machine/deep learning Big Data and (Cloud, Edge, and Fog) Computing Blockchain-powered digital platforms |
| Biotechnological | Genetic engineering Neurotechnology |
3. Traditional Manufacturing
The technology-based drivers for the fourth IR and application sectors listed in Table 2 have become the bedrock of what is known as smart manufacturing. A clear distinction between the traditional and smart manufacturing approaches utilized in various production systems can provide direction, means of improvement, or total transition for other sectors that still use traditional ways. The characteristics of traditional manufacturing are discussed in the following.
Traditional manufacturing separates automated processes from one another, necessitating numerous human interventions to handle transitions from one phase to the next. Because there is no connectivity between machines and across the business process, human workers in manufacturing must examine unrelated datasets and issue reports to identify problems and potential areas for improvement. Traditional manufacturing applications are decoupled and cannot be used to monitor and control automated processes. Traditional manufacturing lacks sufficient functionality, scalability, elaborate manufacturing, and well-organized connectivity with demand and supply diagnosability [46]. The consequences of staying with traditional manufacturing on a large scale include factory closures, short-time work, reduced production and demand, and impacted supply material chains. Reusing the same system is impossible in traditional manufacturing, and increased maintenance costs of these legacy instruments, which are prone to reoccurring breakdowns, are prevalent. In such a system, there is limited visibility [9] of operation systems and productivity data. One form of traditional manufacturing is the dedicated manufacturing system (DMS) [47], in which a rigid manufacturing structure optimized for a specific product is designed. However, DMS is not designed to meet varieties and sudden increases in demand.
In Table 3, the differences between traditional manufacturing and smart manufacturing are presented. In this perspective, traditional manufacturing refers to a production-oriented culture with a local focus and stepwise international expansion. In contrast, smart manufacturing refers to developing strategies and management processes motivated by new ideas and the concept of opportunity [48].
| Traditional Manufacturing | Smart Manufacturing |
|---|---|
| A stand-alone, manual, isolated process with separate systems that are not capable of automated monitoring and control. | A dependent, strongly related, and closely linked system that continually communicates and collaborates is backed by automation, monitoring, and control capabilities. |
| Humans are in charge of machine operation and control. | Machines and robots interact with, without or with little human intervention. |
| There is no plan to develop an action through equipment that learns from processes; therefore, gathering, evaluating, and updating information is carried out manually. | It is possible to collect, analyze, update, and develop an action that learns from data-driven processes. |
| The manufacturing line is fixed, and the system must be shut down before any reconfiguration occurs. | The production line is dynamic and can be maintained without being disconnected from the power supply. |
| The production process is centrally managed. | Decentralized production processes. |
| A less productive, flexible, sustainable system. Enterprise competitiveness suffers as a result of wasteful resource utilization. | More competitiveness is achieved by increased productivity, flexibility, sustainability, and efficient resource usage. |
| A considerable number of inexperienced operators are engaged. As a result, the factory’s production line has increased labor costs. | At a lower cost to the manufacturing, a workforce skilled in developing and operating intelligent devices is brought on board. |
| There is a lack of self-optimization and reconfiguration production systems to learn and respond to shifting demand patterns. | Self-optimisation and reconfiguration, production systems that learn and adjust to changing demand patterns, are available. |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/technologies9040077
References
- A runtime intelligent iterative manufacturing system (RIIMS) for hot stamping
- The Paradigm of Pit—Stop Manufacturing
- Flexible manufacturing systems: Industry 4.0 solution
- Xingyu Li; Aydin Nassehi; Bogdan I. Epureanu; Degradation-aware decision making in reconfigurable manufacturing systems. CIRP Annals 2019, 68, 431-434, 10.1016/j.cirp.2019.04.065.
- Mehrabi, M.G.; Ulsoy, A.G.; Koren, Y.; Reconfigurable manufacturing systems: Key to future manufacturing. J. Intell. Manuf. 2000, 11, 403–419, .
- Piotr Szulewski; The concepts and components of the smart factory. Mechanik 2017, 90, 98-102, 10.17814/mechanik.2017.2.28.
- Baotong Chen; Jiafu Wan; Lei Shu; Peng Li; Mithun Mukherjee; Boxing Yin; Smart Factory of Industry 4.0: Key Technologies, Application Case, and Challenges. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 6505-6519, 10.1109/access.2017.2783682.
- Prasanna Kumar Illa; Nikhil Padhi; Practical Guide to Smart Factory Transition Using IoT, Big Data and Edge Analytics. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 55162-55170, 10.1109/access.2018.2872799.
- Gaige Chen; Pei Wang; Bo Feng; Yihui Li; Dekun Liu; The framework design of smart factory in discrete manufacturing industry based on cyber-physical system. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing 2019, 33, 79-101, 10.1080/0951192x.2019.1699254.
- Nilufer Tuptuk; Stephen Hailes; Security of smart manufacturing systems. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 2018, 47, 93-106, 10.1016/j.jmsy.2018.04.007.
- Tahera Kalsoom; Naeem Ramzan; Shehzad Ahmed; Masood Ur-Rehman; Advances in Sensor Technologies in the Era of Smart Factory and Industry 4.0. Sensors 2020, 20, 6783, 10.3390/s20236783.
- Rabab Benotsmane; György Kovács; László Dudás; Economic, Social Impacts and Operation of Smart Factories in Industry 4.0 Focusing on Simulation and Artificial Intelligence of Collaborating Robots. Social Sciences 2019, 8, 143, 10.3390/socsci8050143.
- Lucke, D.; Constantinescu, C.; Westkämper, E. . Smart factory-a step towards the next generation of manufacturing; Mamoru, Mitsuishi;Kanji, Ueda;Fumihiko, Kimura, Eds.; Springer : London, 2008; pp. 115 -118.
- Yan Lu; Feng Ju; Smart Manufacturing Systems based on Cyber-physical Manufacturing Services (CPMS). IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 15883-15889, 10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.2349.
- Hozdić, E.; Smart factory for industry 4.0: A review. International Journal of Modern Manufacturing Technologies 2015, 7, 28 - 35, .
- Cha, S.K.; Yoon, J.Y.; Hong, J.K.; Kang, H.G.; Cho, H.C.; The system architecture and standardization of production IT convergence for Smart Factory. Journal of the Korean Society for Precision Engineering 2015, 32, 17 - 24, 10.7736/KSPE.2015.32.1.17.
- Rabeh Morrar; Husam Arman; The Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0): A Social Innovation Perspective. Technology Innovation Management Review 2017, 7, 12-20, 10.22215/timreview/1117.
- Mohajan, H. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2019, 5, 377–387; The first industrial revolution: Creation of a new global human era.. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2019, 5, 377 - 387, .
- McDonough, W.; Braungart, M. . The next industrial revolution. In Sustainable Solutions ; Charter, M.U.T., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 139–150.
- Abid Haleem; Mohd Javaid; Additive Manufacturing Applications in Industry 4.0: A Review. Journal of Industrial Integration and Management 2019, 4, 1930001, 10.1142/s2424862219300011.
- Shanlin Yang; Comments from young scholars: Can machines completely replace humans in manufacturing processes?. Frontiers of Engineering Management 2018, 5, 131 - 137, 10.15302/j-fem-2018207.
- Where Machines Could Replace Humans-And Where They Can’t (Yet)
- Kadir Alpaslan Demir; Gözde Döven; Bülent Sezen; Industry 5.0 and Human-Robot Co-working. Procedia Computer Science 2019, 158, 688-695, 10.1016/j.procs.2019.09.104.
- Industrial revolution 5.0: The transformation of the modern manufacturing process to enable man and machine to work hand in hand.
- Arash Ajoudani; Andrea Maria Zanchettin; Serena Ivaldi; Alin Albu-Schäffer; Kazuhiro Kosuge; Oussama Khatib; Progress and prospects of the human–robot collaboration. Autonomous Robots 2017, 42, 957-975, 10.1007/s10514-017-9677-2.
- Quan Liu; Zhihao Liu; Wenjun Xu; Quan Tang; Zude Zhou; Duc Truong Pham; Human-robot collaboration in disassembly for sustainable manufacturing. International Journal of Production Research 2018, 57, 4027-4044, 10.1080/00207543.2019.1578906.
- T. Arai; Ryu Kato; M. Fujita; Assessment of operator stress induced by robot collaboration in assembly. CIRP Annals 2010, 59, 5-8, 10.1016/j.cirp.2010.03.043.
- Achim Buerkle; William Eaton; Niels Lohse; Thomas Bamber; Pedro Ferreira; EEG based arm movement intention recognition towards enhanced safety in symbiotic Human-Robot Collaboration. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing 2021, 70, 102137, 10.1016/j.rcim.2021.102137.
- Thomas Burns; John Cosgrove; Frank Doyle; A Review of Interoperability Standards for Industry 4.0.. Procedia Manufacturing 2019, 38, 646-653, 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.01.083.
- Future Energy Systems: Integrating Renewable Energy Sources into the Smart Power Grid Through Industrial Electronics
- David I. Stern; Astrid Kander; The Role of Energy in the Industrial Revolution and Modern Economic Growth. SSRN Electronic Journal 2010, 33, 125 - 152, 10.2139/ssrn.1759705.
- Caineng Zou; Qun Zhao; Guosheng Zhang; Bo Xiong; Energy revolution: From a fossil energy era to a new energy era. Natural Gas Industry B 2016, 3, 1-11, 10.1016/j.ngib.2016.02.001.
- Roser, C. . Faster, Better, Cheaper in the History of Manufacturing: From the Stone Age to Lean Manufacturing and Beyond ; Productivity Press : New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 439 - 441.
- Lucreţia Dogaru; The Main Goals of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Renewable Energy Perspectives. Procedia Manufacturing 2020, 46, 397-401, 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.03.058.
- Min Xu; Jeanne M. David; Suk Hi Kim; The Fourth Industrial Revolution: Opportunities and Challenges. International Journal of Financial Research 2018, 9, 90, 10.5430/ijfr.v9n2p90.
- Skilton, M.; Hovsepian, F. . The 4th Industrial Revolution Impact:. In The 4th Industrial Revolution: Responding to the Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Business; ; Springer: Switzerland , 2018; pp. 3–28.
- Troxler, P. . Making the 3rd industrial revolution. In FabLabs: Of Machines, Makers and Inventors, Transcript; Transcript: Bielefeld, Germany, 2013; pp. 1 - 16.
- Barbara Bigliardi; Eleonora Bottani; Giorgia Casella; Enabling technologies, application areas and impact of industry 4.0: a bibliographic analysis. Procedia Manufacturing 2020, 42, 322-326, 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.02.086.
- Josef Taalbi; Origins and pathways of innovation in the third industrial revolution1. Industrial and Corporate Change 2018, 28, 1125–1148, 10.1093/icc/dty053.
- Industry 5.0 and a Critique of Industry 4.0
- Saeid Nahavandi; Industry 5.0—A Human-Centric Solution. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4371, 10.3390/su11164371.
- Challenges of the fourth industrial revolution; Prisecaru, P. . Knowl. Horiz. Econ. 2016, 8, 2016, 8, 57–62, .
- Guoping Li; Yun Hou; Aizhi Wu; Fourth Industrial Revolution: technological drivers, impacts and coping methods. Chinese Geographical Science 2017, 27, 626-637, 10.1007/s11769-017-0890-x.
- Paul Matthyssens; Reconceptualizing value innovation for Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing 2019, 34, 1203-1209, 10.1108/jbim-11-2018-0348.
- Andrija Popović; Implications of the Fourth Industrial Revolution on sustainable development. Economics of Sustainable Development 2020, 4, 45-60, 10.5937/esd2001045p.
- Sasa D. Milic; Blagoje M. Babic; Toward the Future—Upgrading Existing Remote Monitoring Concepts to IIoT Concepts. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 7, 11693-11700, 10.1109/jiot.2020.2999196.
- Ann-Louise Andersen; Thomas Ditlev Brunoe; Kjeld Nielsen; Carin Rösiö; Towards a generic design method for reconfigurable manufacturing systems. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 2017, 42, 179-195, 10.1016/j.jmsy.2016.11.006.
- Jim Bell; Dave Crick; Stephen Young; Small Firm Internationalization and Business Strategy. International Small Business Journal: Researching Entrepreneurship 2004, 22, 23-56, 10.1177/0266242604039479.
