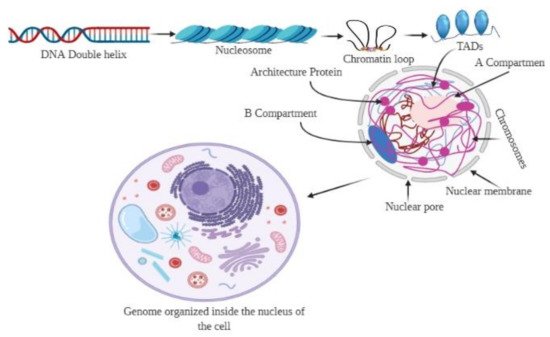
The genome is the most functional part of a cell, and genomic contents are organized in a compact three-dimensional (3D) structure. The genome contains millions of nucleotide bases organized in its proper frame. Rapid development in genome sequencing and advanced microscopy techniques have enabled us to understand the 3D spatial organization of the genome. Chromosome capture methods using a ligation approach and the visualization tool of a 3D genome browser have facilitated detailed exploration of the genome.
- 3D
- genome
- topologically associated domain
- cohesin
- lamin
- chromosome capture
- hi-C
- capture C
- DNase
- circular chromosome conformation capture
- chromosome conformation capture carbon copy
1. Introduction
|
Method |
Assay Type |
Ligation Procedure |
Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
|
snHi-C |
Whole genome to whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
3C variant used to map chromatin interaction |
|
scHi-C |
Whole genome to whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
Hi-C variant enable to map chromatin interaction at single cell |
|
sciHi-C |
Whole genome to whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
Enable mapping of chromatin interactions using combinatorial barcoding |
|
3C |
One locus to one locus |
Proximity ligation |
Founding method of 3C |
|
4C |
One locus to the genome |
Proximity ligation |
Method to detect chromatin interaction between a specific locus and rest of the genome |
|
Enhanced ChIP-4C |
One to one gene |
Proximity ligation |
A variant of 4C. It improves the sensitivity through replacement of inverse PCR with primer extension |
|
Unique molecular identifier-4C |
Detect chromosomal interaction between loci and conditions |
Proximity ligation |
Improved 4C variant for improved sensitivity and specificity. It uses molecular identifier to derive high-complexity quantitative chromatin contact profiles |
|
5C |
Proximity ligation |
Method used to probe chromatin interaction of multiple loci |
|
|
CAPTURE |
One to one in the region of interest |
Proximity ligation & biotinylation |
Uses biotinylated dCas9-mediated locus specific chromatin interaction |
|
Capture-3C |
Whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
High throughput 4C that combines with 3C with DNA capture technology |
|
Capture Hi-C |
Whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
High throughput 4C that combines with Hi-C with DNA capture technology |
|
Dilution Hi-C |
Whole genome to whole genome |
Biotinylated proximity ligation |
Maps topological domains whose boarders are occupied by CTCF binding sites |
|
RNA-TRAP |
Locus to locus |
Proximity biotinylation |
Combination of RNA-FISH with ChIP to probe chromatin interaction associated with transcriptional active genes |
|
Targeted DNAse Hi-C |
Whole genome to whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
Combines DNase Hi-C with DNA capture technology |
|
Associated chromosome trap |
Long range allele specific/interchromosomal |
Proximity ligation |
Used to identify distant DNA region that interact with defined DNA target |
|
ChIA-PET |
Whole genome to whole genome mediated by protein of interest |
Proximity ligation |
Combines ChIP with proximity ligation to detect genome-wide chromatin interaction mediated by specific proteins |
|
PLAC-Seq |
Whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
Proximity ligation conducted in nuclei prior to chromatin shearing |
|
HiChIP |
Whole genome/Multi-scale |
Proximity ligation |
Combines 3C with ChIP to ascertain genome-wide chromatin interaction intervene by specific protein |
|
Hi-C |
Whole genome to whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
Used to map all chromatin interaction in a cell population |
|
DNase Hi-C |
Whole genome to whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
Is variant of Hi-C that uses DNase I to break the chromatin |
|
In Situ Hi-C |
Whole genome to whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
Is an in-situ version of Hi-C that uses chromatin digestion and proximity ligation of intact nuclei |
|
Tethered chromosome conformation capture |
Whole genome to whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
Similar to Hi-C, but ligation performed in solid substrate rather than solution |
|
In Situ DNase Hi-C |
Whole genome to whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
Hi-C variant that uses DNase to break the chromatin |
|
Micro-C |
Whole genome to whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
Is a variant of Hi-C that uses micrococcal nuclease to digest the chromatin |
|
Bridge linker Hi-C |
Whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
Used to capture structural and regulatory chromatin interaction by restriction enzymes |
|
Chromosome walks |
Whole genome |
Proximity ligation |
Links multiple genomic loci together into the proximity |
|
Genome architecture mapping (GAM) |
Whole genome |
Co-localization |
Enables identification of the interactions of enhancer and active genes across large genomic distance |
|
Split pool recognition of interaction by tag extension (SPRITE) |
Whole genome/interchromosomal |
Co-association |
Enables understanding of genome-wide detection of higher-order interactions within the nucleus |
|
Multi-ChIA |
Locus to locus |
Co-localization |
Mapping of multiplex chromatin interactions with single molecule precision. Allow mapping of chromatin interaction mediated by protein of interest |
|
Tethered conformation capture |
Chromosome scale assembly |
Proximity biotinylation |
Allows mapping of inter and intrachromosomal contacts |
2. Techniques to Study 3D Genome Organization
2.1. Microscopy-Based Visualization of the 3D Genome
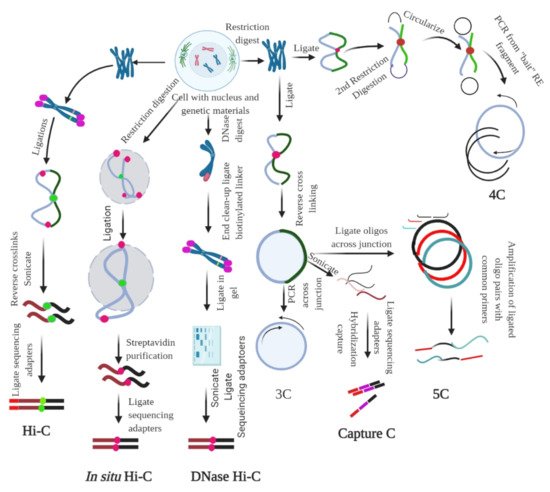
2.2. Ligation-Based Detection of Contacts
2.3. Non-Ligation-Based Detection
2.4. Cell Imaging of the Nuclear Structure
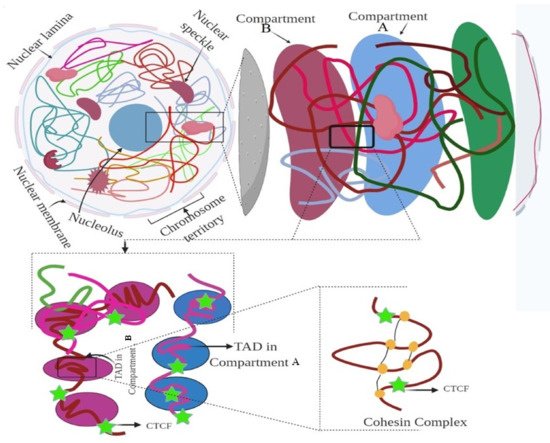
3. Hierarchy of the 3D Genome
4. 3D Genome and Gene Expression
5. Data Structure of the 3D Genome
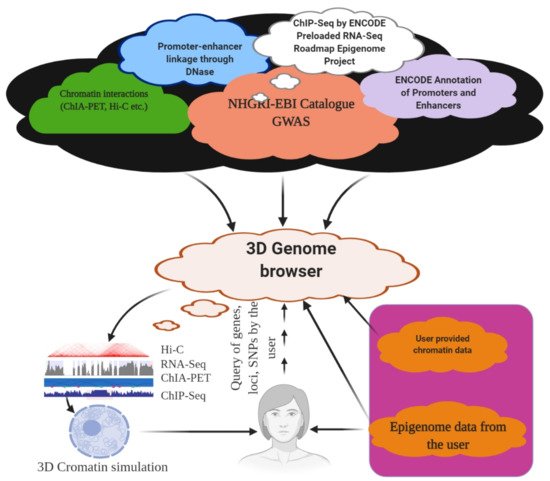
6. 3D Genome Browser
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms222111585
