Gluten proteins, major determinants of the bread-making quality of wheat, are related to several digestive disorders. Advances in plant genetic breeding have allowed the production of wheat lines with very low gliadin content through the use of RNAi and gene editing technologies.
- gluten
- coeliac disease
- NCWS
- transgenic wheat
- RNAi
- CRISPR/Cas9
1. Wheat and Wheat Proteins
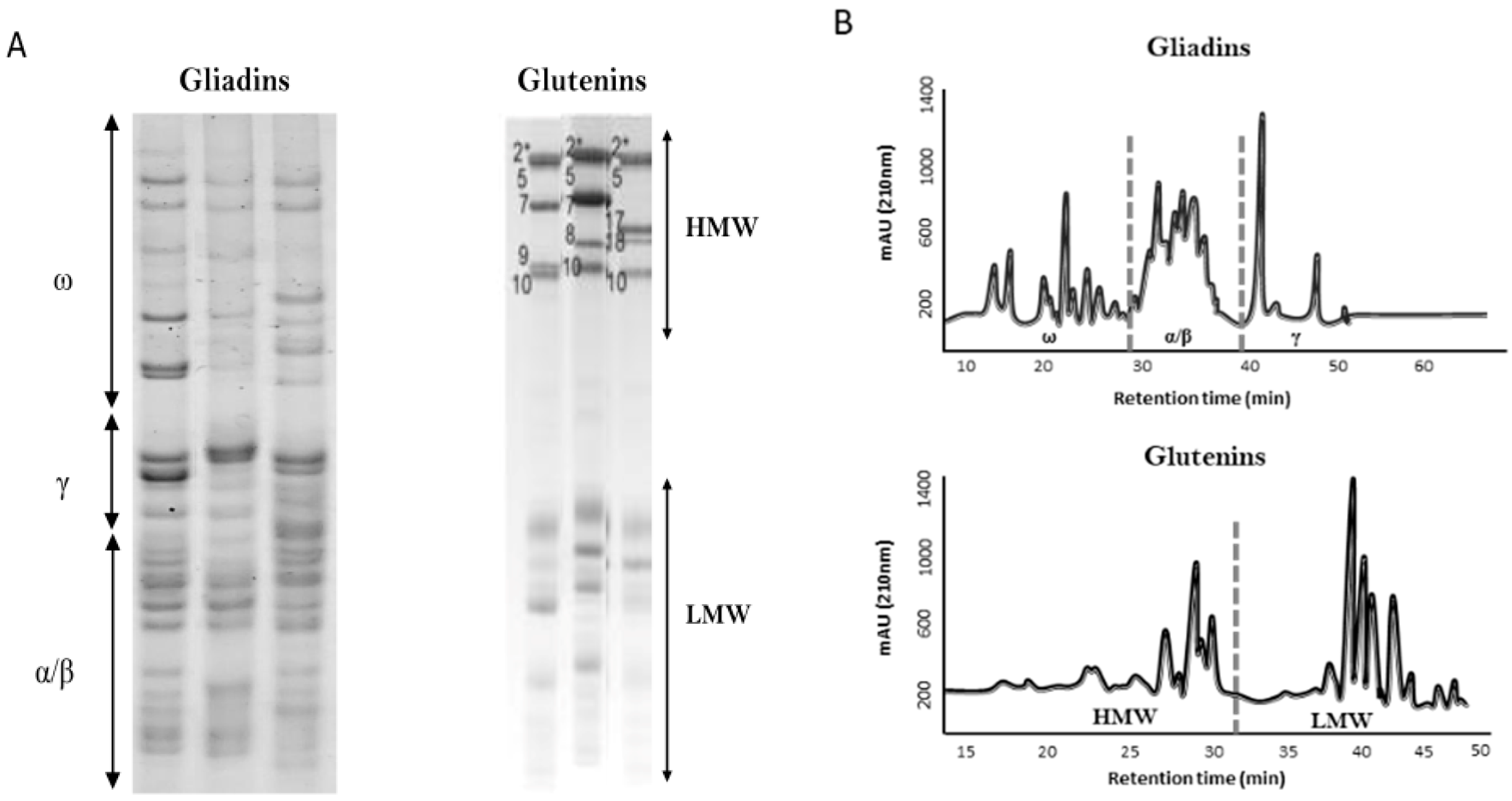
2. Wheat Pathologies and Gluten-Free Diet (GFD)
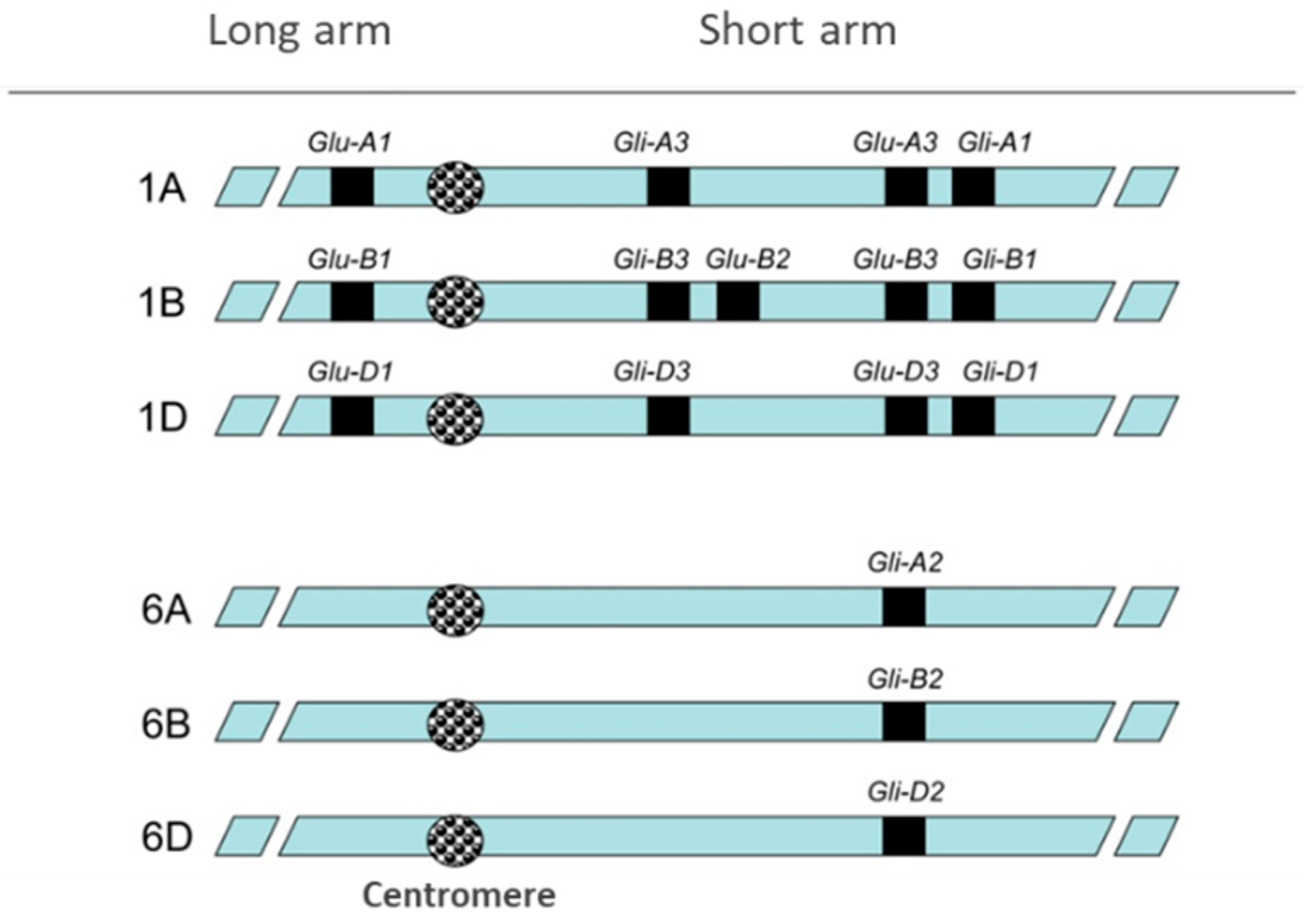
3. Towards Obtaining Wheat Lines with Low Immunogenic Peptides
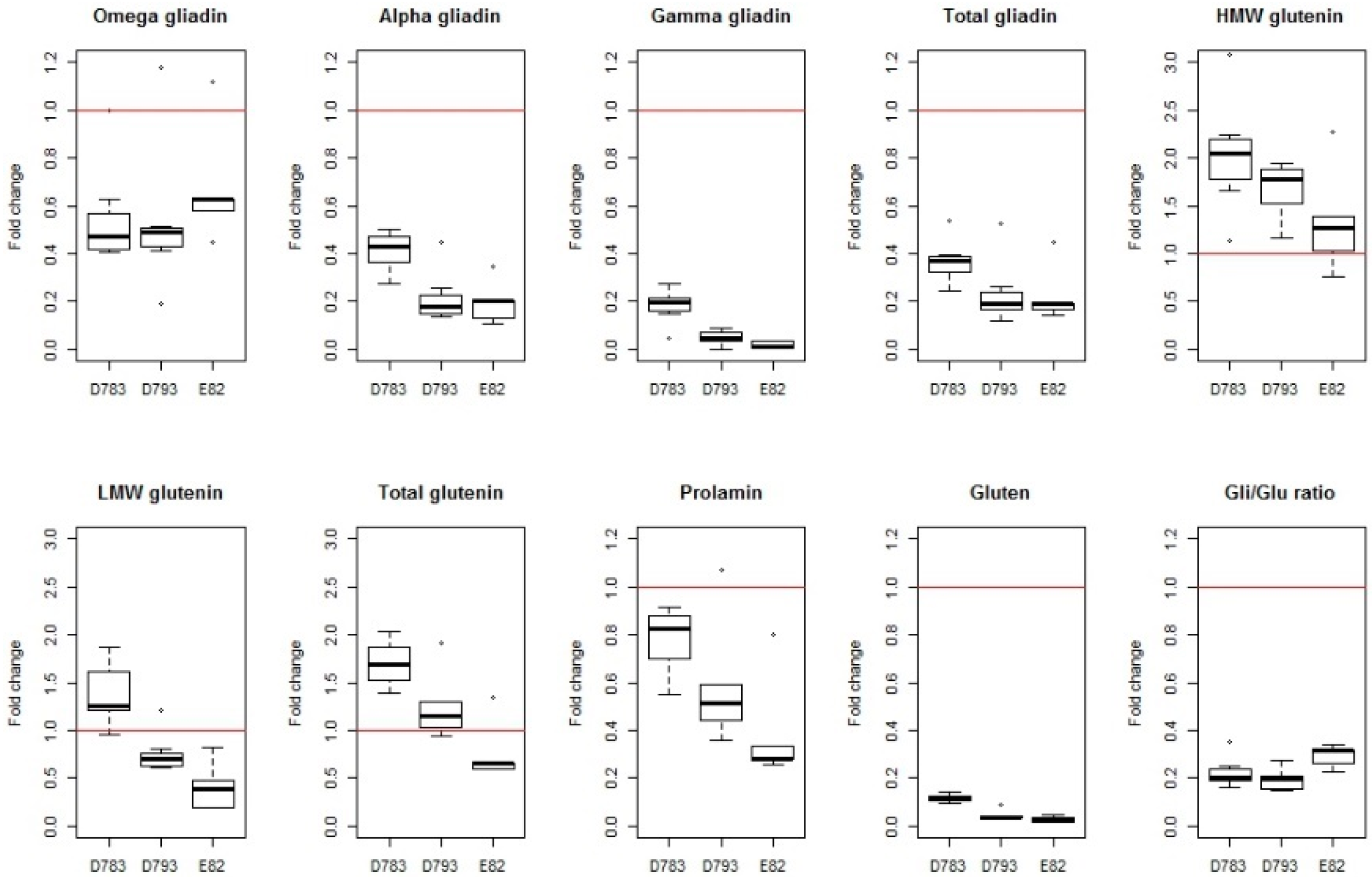
4. Stability of the Gliadin Silencing
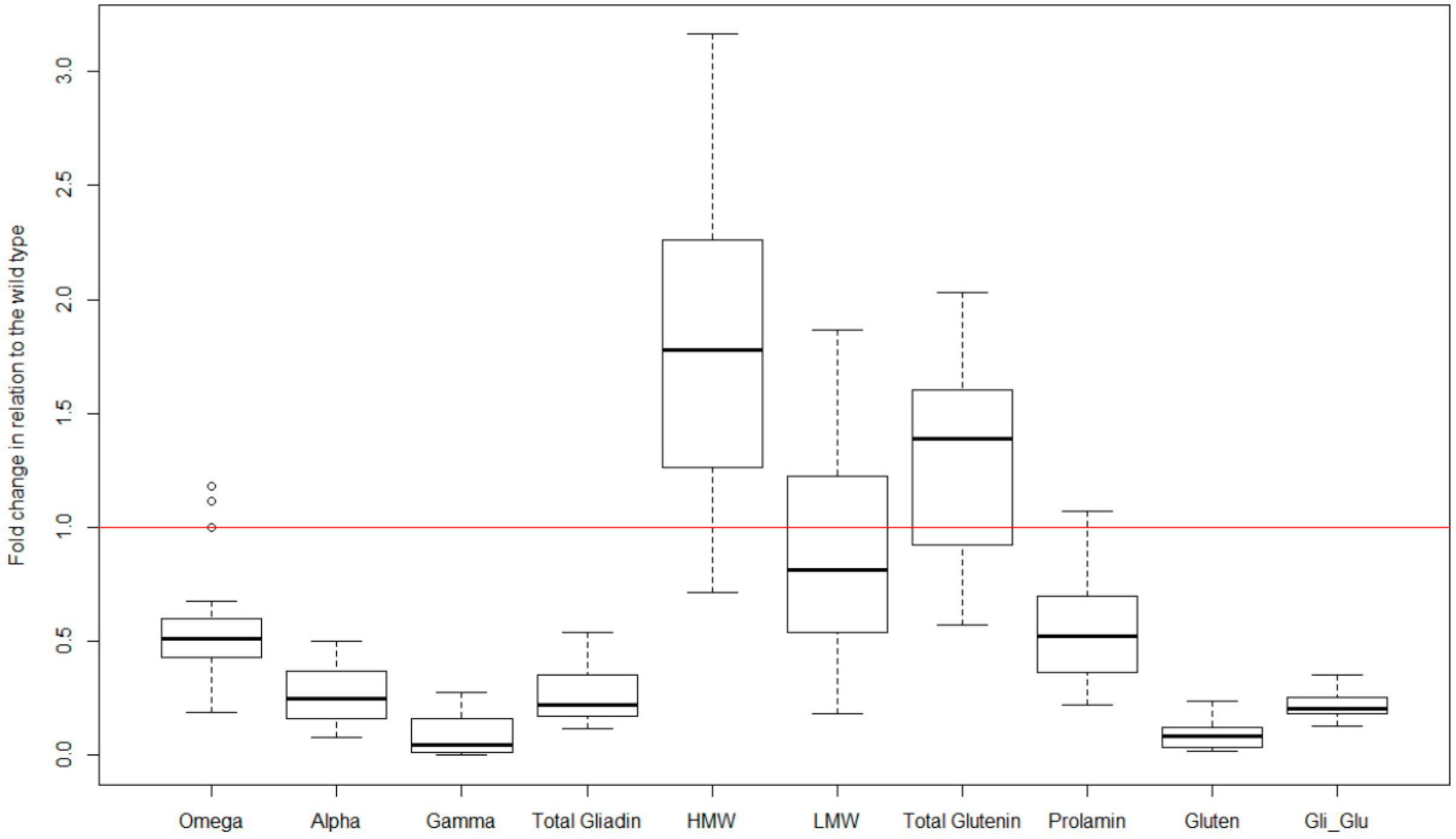
|
Variable |
Min. |
1st Qu. |
Median |
Mean |
3rd Qu. |
Max. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Omega (mg/g) |
7.7 |
10.8 |
14.1 |
14.9 |
19.5 |
21.7 |
|
Alpha (mg/g) |
14.9 |
27.5 |
37.7 |
33.3 |
39.1 |
42.6 |
|
Gamma (mg/g) |
8.9 |
25.5 |
26.7 |
24.5 |
27.8 |
28.8 |
|
Total gliadin (mg/g) |
31.5 |
65.0 |
77.8 |
72.4 |
83.5 |
93.1 |
|
HMW (mg/g) |
6.3 |
7.1 |
12.4 |
12.3 |
17.0 |
19.4 |
|
LMW (mg/g) |
12.6 |
13.0 |
18.6 |
18.5 |
21.9 |
28.1 |
|
Total glutenin (mg/g) |
18.9 |
20.0 |
30.9 |
30.8 |
38.8 |
47.5 |
|
Prolamin (mg/g) |
51.9 |
84.0 |
108.7 |
103.1 |
121.8 |
140.6 |
|
Gluten (mg/kg) |
45,266 |
67,134 |
134,673 |
111,548 |
149,843 |
166,942 |
|
Gliadin to Glutenin ratio |
1.6 |
2.0 |
2.2 |
2.5 |
3.4 |
3.5 |
HMW, high molecular weight, LMW, low molecular weight.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/nu11030487
References
- Shewry, P.R.; Napier, J.A.; Tatham, A.S. Seed storage proteins: Structures and biosynthesis. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 945–956.
- Shewry, P.R.; Halford, N.G. Cereal seed storage proteins: Structures, properties and role in grain utilization. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 947–958.
- Shewry, P.R.; Halford, N.G.; Tatham, A.S.; Popineau, Y.; Lafiandra, D.; Belton, P.S. The high molecular weight subunits of wheat glutenin and their role in determining wheat processing properties. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2003, 45, 219–302.
- Payne, P.I. Genetics of Wheat Storage Proteins and the Effect of Allelic Variation on Bread-Making Quality. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1987, 38, 141–153.
- Wrigley, C.W.; Békés, F.; Bushuk, W. Gluten: A Balance of Gliadin and Glutenin. In Gliadin and Glutenin: The Unique Balance of Wheat Quality; Wrigley, C.W., Bekes, F., Bushuk, W., Eds.; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2006; pp. 3–32.
- Mariné, M.; Farre, C.; Alsina, M.; Vilar, P.; Cortijo, M.; Salas, A.; Fernández-Bañares, F.; Rosinach, M.; Santaolalla, R.; Loras, C.; et al. The prevalence of coeliac disease is significantly higher in children compared with adults. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2011, 33, 477–486.
- Sapone, A.; Lammers, K.; Casolaro, V.; Cammarota, M.; Giuliano, M.; De Rosa, M.; Stefanile, R.; Mazzarella, G.; Tolone, C.; Russo, M.I.; et al. Divergence of gut permeability and mucosal immune gene expression in two gluten-associated conditions: Celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 23–33.
- Salcedo, G.; Sánchez-Monge, G.; García-Casado, G.; Armentia, A.; Gómez, L.; Barber, D. The cereal α-amylase/trypsin inhibitor family associated with bakers’ asthma and food allergy. In Plant Food Allergens; Mills, E., Shewry, P.R., Eds.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 70–86.
- Palosuo, K.; Varjonen, E.; Kekki, O.-M.; Klemola, T.; Kalkkinen, N.; Alenius, H.; Reunala, T. Wheat ω-5 gliadin is a major allergen in children with immediate allergy to ingested wheat. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2001, 108, 634–638.
- Tatham, A.S.; Shewry, P.R. Allergens to wheat and related cereals. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 1712–1726.
- Morita, E.; Matsuo, H.; Mihara, S.; Morimoto, K.; Savage, A.W.J.; Tatham, A.S. Fast ω-gliadin is a major allergen in wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2003, 33, 99–104.
- Palosuo, K.; Varjonen, E.; Nurkkala, J.; Kalkkinen, N.; Harvima, R.; Reunala, T.; Alenius, H. Transglutaminase-mediated cross-linking of a peptic fraction of ω-5 gliadin enhances IgE reactivity in wheat-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2003, 111, 1386–1392.
- Junker, Y.; Zeissig, S.; Kim, S.J.; Barisani, D.; Wieser, H.; Leffler, D.A.; Zevallos, V.; Libermann, T.A.; Dillon, S.; Freitag, T.L.; et al. Wheat amylase trypsin inhibitors drive intestinal inflammation via activation of toll-like receptor 4. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 2395–2408.
- Bucci, C.; Zingone, F.; Russo, I.; Morra, I.; Tortora, R.; Pogna, N.; Scalia, G.; Iovino, P.; Ciacci, C. Gliadin does not induce mucosal inflammation or basophil activation in patients with nonceliac gluten sensitivity. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 1294–1299.
- Sollid, L.M. Coeliac disease: Dissecting a complex inflammatory disorder. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 647–655.
- Shan, L.; Molberg, Ø.; Parrot, I.; Hausch, F.; Filiz, F.; Gray, G.M.; Sollid, L.M.; Khosla, C. Structural Basis for Gluten Intolerance in Celiac Sprue. Science 2002, 297, 2275–2279.
- Molberg, Ø.; McAdam, S.N.; Körner, R.; Quarsten, H.; Kristiansen, C.; Madsen, L.; Fugger, L.; Scott, H.; Norén, O.; Roepstorff, P.; et al. Tissue transglutaminase selectively modifies gliadin peptides that are recognized by gut-derived T cells in celiac disease. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 713–717.
- Karell, K.; Louka, A.S.; Moodie, S.J.; Ascher, H.; Clot, F.; Greco, L.; Ciclitira, P.J.; Sollid, L.M.; Partanen, J.; Members of the European Genetics Cluster on Celiac Disease. Hla types in celiac disease patients not carrying the DQA1*05-DQB1*02 (DQ2) heterodimer: Results from the European genetics cluster on celiac disease. Hum. Immunol. 2003, 64, 469–477.
- Tye-Din, J.A.; Stewart, J.A.; Dromey, J.A.; Beissbarth, T.; van Heel, D.A.; Tatham, A.; Henderson, K.; Mannering, S.I.; Gianfrani, C.; Jewell, D.P.; et al. Comprehensive, Quantitative Mapping of T Cell Epitopes in Gluten in Celiac Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 41–51.
- Shan, L.; Qiao, S.-W.; Arentz-Hansen, H.; Molberg, Ø.; Gray, G.M.; Sollid, L.M.; Khosla, C. Identification and Analysis of Multivalent Proteolytically Resistant Peptides from Gluten: Implications for Celiac Sprue. J. Proteome Res. 2005, 4, 1732–1741.
- Vader, W.; Kooy, Y.; van Veelen, P.; de Ru, A.; Harris, D.; Benckhuijsen, W.; Peña, S.; Mearin, L.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Koning, F. The gluten response in children with celiac disease is directed toward multiple gliadin and glutenin peptides. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1729–1737.
- Camarca, A.; Anderson, R.P.; Mamone, G.; Fierro, O.; Facchiano, A.; Costantini, S.; Zanzi, D.; Sidney, J.; Auricchio, S.; Sette, A.; et al. Intestinal T Cell responses to gluten peptides are largely hertogeneous: Implications for a peptide-based therapy in celiac disease. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4158–4166.
- Ventura, A.; Magazzù, G.; Greco, L. Duration of exposure to gluten and risk for autoimmune disorders in patients with celiac disease. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 297–303.
- Van den Broeck, H.C.; van Herpen, T.W.J.M.; Schuit, C.; Salentijn, E.M.J.; Dekking, L.; Bosch, D.; Hamer, R.J.; Smulders, M.J.M.; Gilissen, L.J.W.J.; van der Meer, I.M. Removing celiac disease-related gluten proteins from bread wheat while retaining technological properties: A study with Chinese Spring deletion lines. BMC Plant. Biol. 2009, 9, 41–52.
- Van Herpen, T.W.; Goryunova, S.V.; van der Schoot, J.; Mitreva, M.; Salentijn, E.; Vorst, O.; Schenk, M.F.; van Veelen, P.A.; Koning, F.; van Soest, L.J.M.; et al. Alpha-gliadin genes from the A, B, and D genomes of wheat contain different sets of celiac disease epitopes. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 1–13.
- Spaenij-Dekking, L.; Kooy-Winkelaar, Y.; van Veelen, P.; Wouter Drijfhout, J.; Jonker, H.; van Soest, L.; Smulders, M.J.M.; Bosch, D.; Gilissen, L.J.W.J.; Koning, F. Natural variation in toxicity of wheat: Potential for selection of nontoxic varieties for celiac disease patients. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 797–806.
- Juhász, A.; Belova, T.; Florides, C.G.; Maulis, C.; Fischer, I.; Gell, G.; Birinyi, Z.; Ong, J.; Keeble-Gagnère, G.; Maharajan, A.; et al. Genome mapping of seed-borne allergens and immunoresponsive proteins in wheat. Sci. Adv. 2018.
- Sollid, L.M.; Qiao, S.-W.; Anderson, R.P.; Gianfrani, C.; Koning, F. Nomenclature and listing of celiac disease relevant gluten T-cell epitopes restricted by HLA-DQ molecules. Immunogenetics 2012, 64, 455–460.
- Arentz-Hansen, H.; Korner, R.; Molberg, O.; Quarsten, H.; Vader, W.; Kooy, Y.M.; Lundin, K.E.A.; Koning, F.; Roepstorff, P.; Sollid, L.M.; et al. The intestinal T cell response to alpha-gliadin in adult celiac disease is focused on a single deamidated glutamine targeted by tissue transglutaminase. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 603–612.
- Altenbach, S.B.; Allen, P.V. Transformation of the US bread wheat "Butte 86" and silencing of omega-5 gliadin genes. GM Crops 2011, 2, 66–73.
- Wen, S.; Wen, N.; Pang, J.; Langen, G.; Brew-Appiah, R.A.T.; Mejias, J.H.; Osorio, C.; Yang, M.; Gemini, R.; Moehs, C.P.; et al. Structural genes of wheat and barley 5-methylcytosine DNA glycosylases and their potential applications for human health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20543–20548.
- Gil-Humanes, J.; Pistón, F.; Hernando, A.; Alvarez, J.B.; Shewry, P.R.; Barro, F. Silencing of γ-gliadins by RNA interference (RNAi) in bread wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 48, 565–568.
- Pistón, F.; León, E.; Lazzeri, P.A.; Barro, F. Isolation of two storage protein promoters from Hordeum chilense and characterization of their expression patterns in transgenic wheat. Euphytica 2008, 162, 371–379.
- Gil-Humanes, J.; Pistón, F.; Tollefsen, S.; Sollid, L.M.; Barro, F. Effective shutdown in the expression of celiac disease-related wheat gliadin T-cell epitopes by RNA interference. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17023–17028.
- Barro, F.; Iehisa, J.C.; Gimenez, M.J.; Garcia-Molina, M.D.; Ozuna, C.V.; Comino, I.; Sousa, C.; Gil-Humanes, J. Targeting of prolamins by RNAi in bread wheat: effectiveness of seven silencing-fragment combinations for obtaining lines devoid of coeliac disease epitopes from highly immunogenic gliadins. Plant. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 986–996.
- Piston, F.; Gil-Humanes, J.; Barro, F. Integration of promoters, inverted repeat sequences and proteomic data into a model for high silencing efficiency of coeliac disease related gliadins in bread wheat. BMC Plant. Biol. 2013, 13, 136–149.
- García-Molina, M.D.; Barro, F. Characterization of Changes in Gluten Proteins in Low-Gliadin Transgenic Wheat Lines in Response to Application of Different Nitrogen Regimes. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 257–269.
- Ozuna, C.V.; Barro, F. Safety evaluation of transgenic low-gliadin wheat in Sprague Dawley rats: An alternative to the gluten free diet with no subchronic adverse effects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107, 176–185.
