Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Urology & Nephrology
Chronic kidney disease (CKD), defined as the presence of irreversible structural or functional kidney damages, increases the risk of poor outcomes due to its association with multiple complications, including altered mineral metabolism, anemia, metabolic acidosis, and increased cardiovascular events. The mainstay of treatments for CKD lies in the prevention of the development and progression of CKD as well as its complications.
- acute kidney injury
- chronic kidney disease
- renal progression
- therapy for renal failure
1. Introduction
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is defined as a progressive and irreversible loss of renal function evidenced by an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of <60 mL/min per 1.73m2, the persistent presence of manifestations that are suggestive of kidney damage (proteinuria, active urine sediments, histological damages, structural abnormalities or a history of kidney transplantation), or both, lasting for more than 3 months [1]. CKD has long been a worldwide public health concern and constitutes a heavy healthcare and economic burden, as a reduced GFR is widely known to increase the risk of cardiovascular events, hospitalization, cognitive dysfunction, and overall mortality [2]. The prevalence of CKD varies according to geographic areas, mostly ranging from 10 to 20%, but rises gradually, particularly in developed countries [3,4,5]. This trend can be partially attributed to the expanding aging population globally [6]. In addition, the increased prevalence of risk factors such as diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension, and obesity in patients with CKD is also notable [7,8].
Having a diagnosis of CKD means that an individual’s renal function has entered into a “point of no return,” indicating that the deterioration of renal function over time is inevitable and frequently irreversible. However, there can still be different patterns of renal function decline in patients with CKD. These patterns can be classified intuitively into very fast, fast, moderate, or slow, depending on the threshold required for defining the renal function decline rate, using mL/min/year or mL/min/month (Figure 1A). These differences in patterns largely reflect the heterogeneity of CKD origins and the subsequent pathologies, adjunct comorbidities, interventions that patients receive, and other harsh environmental exposures [9]. From this perspective, finding how to retard renal progression in patients with CKD is still fraught with challenges.
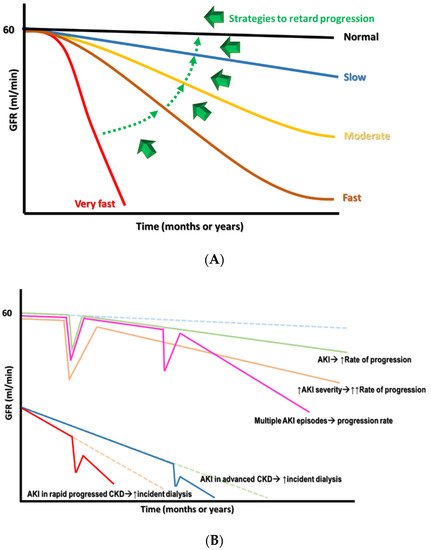
Figure 1. (A) The different declined rates of renal function in CKD with the target switch from superfast to slow rate. (B) The consequence of AKI on CKD progression, depending on the severity and frequency of episodes.
2. Risks of CKD Progression
Estimated GFR trajectories are highly variable in CKD. This phenomenon implies that a wide array of heterogeneous risk factors may contribute to CKD progression and that these risk factors may be potential therapeutic targets if we wish to achieve renoprotection. Socioeconomic factors and lifestyle factors (e.g., diet, sleep deprivation, smoking, and lack of exercise) are well-known risk factors that are associated with CKD progression. Systemic and metabolic disorders, including DM, hypertension, gout, and cardiovascular diseases, can also precipitate the development of CKD and aggravate eGFR decline (Figure 2) [10]. Recently, atrial fibrillation (AF) has also been shown to be a contributor to rapid eGFR decline, and the CHA2DS2-VASc score, a stroke-risk stratification model for patients with AF, can predict renal progression [11].
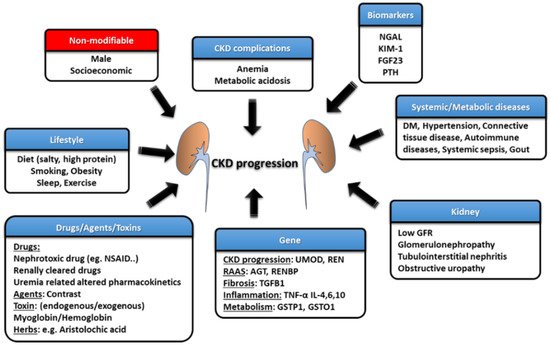
Figure 2. The risk factors and management strategies of CKD development and progression.
The intrinsic factors that are related to kidneys per se also play an important role in influencing renal function decline, such as GFR, proteinuria, glomerulopathy, interstitial lesions, and renal outlet obstruction (obstructive nephropathy). Each glomerulopathy distinctly influences the pace of renal function deterioration; for example, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is more likely to result in a faster GFR decline, while the rate is lower for patients with IgA nephropathy (IgAN), membranous nephropathy (MN), and diabetic kidney disease (DKD) [12]. Polymorphisms in the genes involved in pathways such as those associated with inflammatory reactions (e.g., tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-4), fibrosis (e.g., TGFB1), phase-II metabolism (e.g., GSTP1 and GSTO1), CKD worsening (e.g., UMOD) and the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) (e.g., AGT and RENBP) have been suggested to affect the progression rate of patients with CKD [13].
3. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)
Renal fibrosis, including nephrosclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis, constitutes the final common pathway of renal injuries, regardless of etiologies. EMT is the major mechanism promoting renal fibrosis, and myofibroblasts are the main cell type that produces the extracellular matrix [14]. The origin of myofibroblasts in the kidney remains uncertain, but several candidates have been suggested, including resident fibroblasts, bone marrow-derived fibroblasts, or transition from pericytes or endothelial cells [15]. Recent research has revealed that EMT is fairly uncommon, as fibroblasts derived from EMT are rarely found in renal interstitium. A novel concept of partial EMT, indicating that tubular epithelial cells gain mesenchymal characteristics but retain their attachment to the basement membrane, may explain the pathogenic role of renal tubular epithelia in renal fibrosis [16].
After acute kidney injury (AKI) attacks, the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) signal is activated in tubular epithelial cells to enhance the expression of typical mesenchymal markers (e.g., e-cadherin, α-smooth muscle actin) and to upregulate profibrogenic factors (mainly transforming growth factor (TGF)-β and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF)) [17]. The persistent activation of the TGF-β pathway leading to an increased expression of SNAI1 and TWIST1 further promotes G2/M arrest. Cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase in injured tubular cells, through JNK activation, amplifies the profibrogenic factors, such as TGF-β and CTGF, constituting a vicious cycle culminating in the fibrosis progression [18]. Fatty acid oxidation (FAO) is the main energy source of the proximal tubule (PCT). SMAD3 activated by TGF-β will suppress PPARGC1a expression to cause dysregulated FAO with lipid accumulation in the PCT, one of the characteristic features of EMT [19]. The PCT cells with lipid accumulation will enhance inflammation, innate immunity, and apoptosis to worsen renal fibrosis. Tubular cells with partial EMT can also activate fibroblasts and recruit inflammatory cells via the secretome composed of growth factors, chemokines, and cytokines, subsequently aggravating fibrosis [20]. Blocking EMT with approaches targeting the cell cycle or the inhibition of SNAI1 or TWIST1 expressions has been found to repress inflammation and fibrosis, pointing to the fact that EMT may be a good target mechanism to reverse renal fibrosis [15,18]. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 (BMP-7) can reverse EMT by counteracting the TGF-β/SMAD2/3 pathway and serves as another potential therapeutic target for improving renal injury [21]. However, the results in clinical studies of BMP-7 analogs involving patients with CKD are heterogeneous, suggesting a complex interaction between BMP-7 and other EMT-related pathways, as well as the necessity of determining the optimal serum BMP-7 concentration [22].
Epigenetic modifications, including DNA methylation and histone modification, also participate heavily in the regulation of partial EMT. The inhibition of DNA methylation was reported to ameliorate renal fibrosis. For example, low-dose hydralazine causing the de-methylation of the NASAL1 promotor and 5′-azacytidine, resulting in an inhibition of DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) [23,24,25]. Furthermore, agents targeting histone modification also confer renal benefits in CKD or AKI-to-CKD transition through the inhibition of histone methyltransferase (e.g., enhancer of zeste homolog 2) or the inhibition of histone deacetylases by directly inhibiting deacetylase (e.g., valproic acid) or indirectly interfering with histone modification readers (e.g., bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) protein inhibitors) [26,27,28]. Epigenetics may be a novel therapeutic target for renal diseases.
4. Avoidance of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) in Patients with CKD
AKI is associated with significant morbidity and mortality, including an increase in adverse renal outcomes. Cumulative evidence suggests that AKI is never self-limited, as it serves as a gateway to subsequent AKI episodes and, potentially, incident CKD, regardless of whether patients show recovery from AKI episodes or not [29]. Moreover, a single episode of severe AKI superimposed on patients with pre-existing CKD can cause further renal deterioration to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) rapidly at a non-linear pace (Figure 1B). The risk factors associated with the AKI-related acceleration of renal progression were identified previously, and include older age, delayed renal function recovery from AKI, severe AKI episodes, the presence of proteinuria, and comorbidities such as DM, hypertension, and heart failure [30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132]. Long-term renal sequelae become very serious if patients have acute tubular necrosis (ATN) or ischemic AKI compared with those who have other forms of AKI, suggesting that the etiology of the AKI may also be a very important risk factor [33].
Biomarkers such as kidney injury molecule (KIM)-1 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) are able to detect AKI earlier than conventional indicators [34,35]. Moreover, a combination of biomarkers such as insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) was shown to successfully predict the development of AKI during the 12 h following blood tests and can guide the selection of interventions to prevent AKI [36,37].
The mechanisms that are responsible for the transition from AKI to CKD remain under active investigation, and a maladaptive repair response with partial epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), especially at the proximal tubule (PCT), has an important role. Cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase, the dysregulated regeneration of injured PCT due to mitochondrial dysfunction, and the aberrant activation of developmental pathways (such as the Wnt, Hedgehog, and Notch pathways) also contribute to AKI-to-CKD transition. Phenotypic changes of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts or the formation of tertiary lymphoid tissue, as well as defective switches of recruited T cells and M1 macrophages to regulatory T cells and M2 macrophages, respectively, will perpetuate inflammation and fibrosis, leading to capillary rarefaction, hypoxia, and tubule cell damage, constituting a vicious cycle [38,39,40]. Furthermore, the persistent expression of either transforming growth factor (TGF)-β or kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) has also been held responsible [41,42]. Notably, several pathogenic processes contributing to AKI-to-CKD transition are also physiological repair processes within kidneys. Additional insults, including high salt and high protein intake and nephrotoxic agents, during or after AKI episodes, as well as the underlying diseased kidney (e.g., diabetic nephropathy), may turn physiological renal responses into disordered regeneration.
Identification of Factors Causing AKI
The fundamental management of AKI in patients with CKD involves preventing the occurrence of AKI, and the success of this approach largely depends on the identification of the etiologies contributing to AKI (Table 1). Furthermore, treating the underlying etiologies of AKI, the optimization of volume and hemodynamic status, the withdrawal of nephrotoxic agents, the adjustment of medication doses according to renal function, adopting a conservative (<180 mg/dL), rather than an intensive glycemic control goal, and maintaining higher mean arterial pressure in patients with underlying hypertension can be crucial strategies for AKI management [43,44]. Drug regimens should be reviewed carefully to prevent drug–drug interactions. For example, adding piperacillin/tazobactam should be avoided, as it potentiates the nephrotoxicity of vancomycin. Several agents and strategies have been tested for treating AKI, including recombinant alkaline phosphatase and L-carnitine for sepsis-related AKI, as well as p53-targeted small interfering RNA (siRNA) and remote ischemic preconditioning for surgery-associated AKI [45,46].
Table 1. Common etiologies of acute kidney injury.
| Categories | Mechanism | Examples | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prerenal | Cardiac output↓ | Acute myocardial infarction, valve rupture, acute pericarditis, acute myocarditis Drugs exacerbate heart failure (COX inhibitors, CCB, TZD, DPP-4i) Drugs cause direct heart injury (rheumatologic agents (e.g., TNF-α inhibitors), anthracyclines, taxanes, targeted therapy (e.g., bevacizumab, sorafenib), anti-Parkinson (Pergolide, Pramipexole) |
History: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, chest pain, orthopnea, palpitation, urine output↓, liver/CV diseases Drug: diuretics, NSAID Physical exam: BP↓/HR↑, skin turgor/mucosa, edema |
| True hypovolemia | Renal loss (diuretics, osmotic diuresis); Extrarenal loss (diarrhea, hemorrhage, burn, third spacing) | ||
| Effective volume↓ | Sepsis, neurogenic shock, anaphylaxis | ||
| Intrarenal vasoconstriction | Hypercalcemia, hepatorenal syndrome, drugs (CNIs, NSAID, vasoconstrictors.) | ||
| Intrinsic | Glomerular injury | Nephrotic (MCD, MPGN, drugs (NSAID, gold, penicillamine))213607Nephritic (IRGN, lupus nephritis, AAV, anti-GBM disease, IgAN, drugs (e.g., hydralazine)) | History: Fever, cellulitis, URI, flank pain, foamy urine, urine output↓, myalgia, hemoptysis Drug: antibiotics, NSAID, statin, contrast Physical exam: BP, Skin rash, arthritis |
| Tubular injury | Severe prerenal causes, toxins (endogenous: hemolysis, rhabdomyolysis, tumor lysis syndrome) or exogenous (aminoglycoside, contrast, CNIs, acyclovir, lithium, vancomycin)) | ||
| Interstitial injury | Allergy (drug: cephalosporin, penicillin, PPI, NSAID, herbs); Infection (bacteria, fungus, virus, leptospirosis); Autoimmune (Lupus, anti-TBM disease, AAV) | ||
| Vascular injury | Small caliber (TMA (malignant hypertension, HUS/TTP, DIC), scleroderma renal crisis) Large caliber (renal infarction, renal vein thrombosis) |
||
| Postrenal | Urinary tract | Benign prostatic hyperplasia; neurogenic bladder; Intra-ureter (stones, tumors); Extraureter (retroperitoneal fibrosis, intra-abdominal tumors) lesions | History: low urinary tract symptoms, gross hematuria Physical exam: suprapubic tenderness, abdomen mass Image: e.g., ultrasound |
| Intrarenal | Crystals (acyclovir, indinavir), stones, tumors, paraproteins (myeloma) |
Denote: AAV: ANCA associated vasculitis, COX: cyclooxygenase, CNIs: calcineurin inhibitors, DPP-4i: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors, DIC: disseminated intravascular coagulation, HUS: hemolytic uremic syndrome, IgAN: IgA nephropathy, MCD: minimal change disease, MPGN: membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, NSAID: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, PPI: proton pump inhibitor, TBM: tubule basement membrane, TMA:thrombotic micrangiopathy, TNF: tumor necrosis factor, TTP: thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, TZD: Thiazolidinedione.
5. An Etiology-Based Treatment Strategy for CKD
As mentioned above, the different etiologies of CKD themselves have various impacts on renal progression. As an etiology-based treatment strategy for CKD has not been well addressed, we touch on this management issue for both the common and less-appreciated causes of CKD.
5.1. Glomerulopathy
Glomerulopathy is a heterogeneous group of diseases and accounts for a significant number of CKDs. It occurs more commonly in young people with non-specific presentations. Although novel diagnostic tools are under investigation, renal biopsy is still the gold standard for achieving a definite diagnosis. A slow deterioration of renal function occurs in a proportion of patients. The risk factors for a faster GFR reduction include obesity, smoking, hypertension, significant proteinuria (usually >1 g/day), CKD at the diagnosis of glomerulopathy, and pathologically chronic renal lesions (glomerulosclerosis, tubular atrophy, and interstitial fibrosis) [47]. Genetic factors contribute to a rapid GFR loss, such as APOL1 in those with FSGS [48]. Fabry disease is a frequently ignored X-link inherited disease caused by a pathogenic mutation involving GLA-encoding lysosome enzyme α-galactosidase A [49]. The deficient enzyme function results in the intracellular accumulation of globotriaosylceramide, which impairs cell metabolism. Apart from neurological and cardiovascular associations, the kidneys may also be affected by presentations of proteinuria and renal failure. Enzyme replacement therapy is the cornerstone of renal progression reduction or prevention. A brief summary of the preferred treatment for different underlying glomerulonephritis is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. The therapy of glomerulopathy and the common side effects of the pharmacotherapy.
| Non-Immune Therapy | Immunosuppressant Therapy | Denote | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↓Dietary salt/protein SGLT2 inhibitors RAAS blockades Blood pressure Infection prophylaxis (vaccine, antibioticsantiviral agents) Vitamin D + calcium |
Diuretics ↑Oncotic pressure (albumin infusion) Lipid lowering Anticoagulation (prevent or treat thromboembolism) |
Steroids | Calcineurin inhibitors | Antimetabolite | Alkalizing agents | Anti-CD20 | PP | ||
| Prednisolone ACTH |
Cyclosporine Tacrolimus |
Mycophenolate Azathioprine |
CYC Chlorambucil |
Rituximab | |||||
| MCD | ν | ν | ν | ν | ν | ν | ν | ||
| FSGS | ν | ν | ν | ν | ν | Genetic test: Congenital/infantile type, APOL1 (adult) | |||
| MN | ν | ν | ν | ν | ν | ν | ν | Serum anti-PLA2R: diagnosis, follow-up and outcomes | |
| MPGN | ν | ν | ν | ν | Treat underlying diseases (e.g., MM, lymphoma or HCV) | ||||
| IgAN | ν | ν (IgAN+MCD) | ν | ν (some RTCs) | Adjuvant antimalarial Ongoing trial: Fostamatinib, Atacicept, Bortezomib |
||||
| LN | ν | ν (class V) | ν | ν | ν | ν | Antimalarial agents AZA for maintenance |
||
| AAV | ν | ν | ν | ν | ν severe AKI PH |
Disease activity: chemokine C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 13, matrix metalloproteinase-3, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 | |||
| Ani-GBM | ν | ν | ν | ν till anti-GBM (-) | Overlap syndrome (ANA, ANCA) | ||||
| Common S/E | Rare | Rare | ↑Glucose Cushing ↑BP |
Nephrotoxic | GI upset Leukopenia | Bone marrow suppression Infertility |
Infusion reaction, Infection Cytopenia |
Fever Urticaria | |
Denote: AAV: ANCA associated vasculitis, BP: blood pressure, CYC: cyclophosphamide, FSGS: focal segmental glomerulonephropathy, GI: gastrointestinal, GBM: glomerular basement membrane, IgAN: IgA nephropathy, LN: lupus nephritis, MCD: minimal change disease, MM: multiple myeloma, MN: membranous nephropathy, MPGN: membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, PH: pulmonary hemorrhage, PP: plasmapheresis, RAAS: renin-agiotensin-aldosterone system, SGLT2: sodium glucose cotransporter 2, S/E: side effect.
5.2. DM-Related CKD
DM is the most common etiology of CKD and ESKD worldwide [50]. DKD usually occurs in patients with poor glycemic control, but also arises in 30–40% of patients with intensive glycemic control, suggesting a complex and multifactorial pathogenesis of DKD [51,52,53]. Clinical manifestations of DKD include impaired renal function with proteinuria. Several risk factors have been discovered, including early onset of DM, hypertension, ethnicity, obesity, the severity of proteinuria, and smoking [54,55,56,57]. In addition to adequate glycemic control, RAAS blockade is the centerpiece of DKD management. Pentoxiphylline can delay the initiation of dialysis and exert a significant antiproteinuric effect in DM patients already receiving RAAS blockades [57]. Although most statins exhibit minimal renoprotective effects [58,59,60], fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) α-agonist, has been shown to have an antiproteinuric effect in DKD [61]. Thiazolidinediones, a PPARγ agonist, can be beneficial for DKD, with salt and fluid retention side effects [62,63] that should be considered.
Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are the latest anti-hyperglycemic agent capable of decreasing blood glucose effectively by blocking glucose reabsorption in the PCT. In addition to cardiovascular benefits, SGLT2 inhibitors also postpone renal deterioration and reduce the severity of proteinuria in patients with DM (Figure 3) [64,65,66]. It is proposed that SGLT2 inhibitors protect the kidney by enhancing glycemic control, improving cardiovascular function, and decreasing body weight, as well as restoring intra and extrarenal hemodynamics, including lowering blood pressure (BP), promoting natriuresis, and re-activating tubuloglomerular feedback [67]. Structurally, SGLT2 inhibitors also are known to reverse PCT hypertrophy, which is induced by insulin resistance and hyperglycemia-related increasing sodium and glucose reabsorption through SGLT2 [68]. With the reversal of PCT hypertrophy and decreased Na+-glucose reabsorption, the kidney will be protected due to reduced energy demand and subsequently less oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis, and growth factor expression. Furthermore, AMPK/SIRT1 signaling, which is suppressed by hyperglycemia, could be re-activated by SGLT2 inhibitors to promote anti-inflammatory hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-2α and to suppress the expression of pro-inflammatory HIF-1α [69,70,71]. Hyperglycemia increases the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), diacylglycerol (DAG), and advanced glycation end products (AGEs), all contributing to the impaired autophagic clearance of SNAI1 and activated p21 and p27. Accumulated SNAI1 and the activation of p21 and p27 result in G2/M cell cycle arrest, the hallmark of EMT, and maladaptive renal tubular regeneration. The use of SGLT2 inhibitors can restore normal autophagic clearance and inhibit pathways due to the products of hyperglycemia, attenuating cell cycle arrest-related kidney damage. Notably, it is found that the renoprotective effect may be extended to non-diabetic patients with kidney diseases [72].
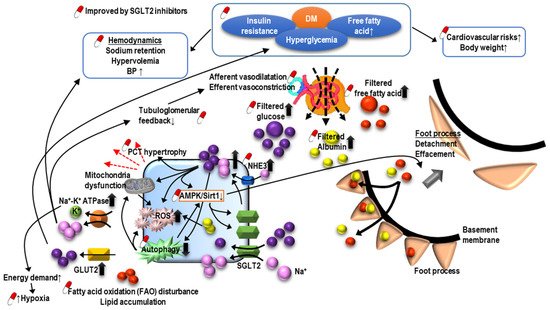
Figure 3. The pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy and mechanism of sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitors-associated renoprotection.
O-GlcNAcylation is a post-translational modification of proteins and can regulate various physiological or pathological processes. In DM, O-GlcNAcylation has a role in insulin resistance and can mediate glucose toxicity, and subsequently, DM complications, including DKD. Recent research has demonstrated that the O-GlcNAcylation of cellular proteins such as ICln impairs cell volume regulation in diverse cell types, a common phenomenon in DM [73]. A hypertrophic PCT is a typical feature of DKD as increased filtrated glucose promotes the reabsorption of glucose and sodium in PCT. O-GlcNAcylation may result in the cell death of PCT and contribute to the development or progression of DKD by impairing the volume regulation, which could be reversed by reducing the O-GlcNAcylation of ICln [74]. Moreover, O-GlcNAcylation in PCT was found to correlate with fatty acid oxidation [75]. These findings suggest that the manipulation of O-GlcNAcylation may be a potential target for the treatment DKD [76].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms221810084
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
