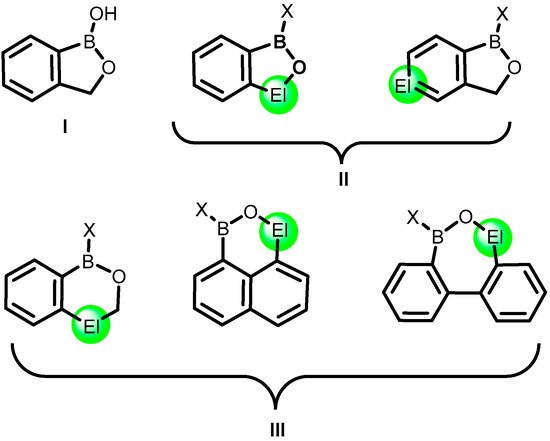
2. Benzoxadiboroles and Related Ring-Expanded Systems Comprising B-O-B Linkage
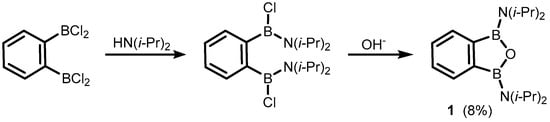
The formal substitution of the C3 carbon atom in benzoxaborole results in a benzoxadiborole framework featuring a B-O-B linkage within the five-membered ring. An example of such a well-defined boracyclic system (
1) was reported by Kaufmann et al. in 1994 [
5]. It was isolated in a low yield by aminolysis of 1,2-bis(dichloroboryl)benzene [
6] followed by ring closure with hydroxide anion (
Scheme 2).
Scheme 2. Synthesis of 1,3-bis(diisopropylamino)-1,3-dihydro-2,1,3-benzooxadiborole.
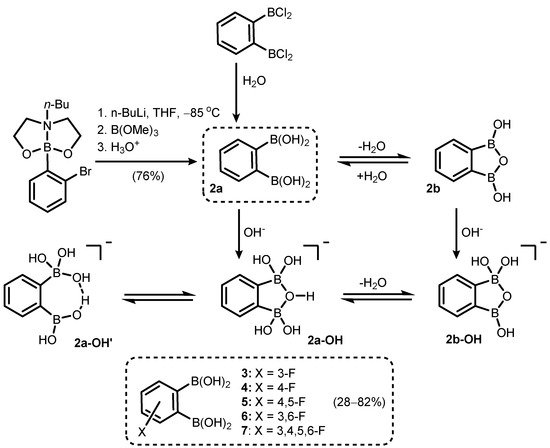
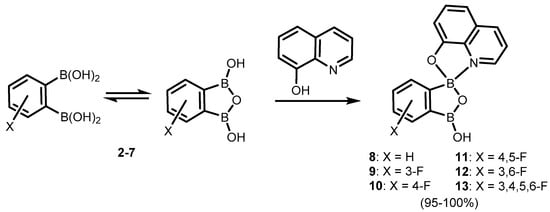
Phenylene-1,2-diboronic acid (
2a) was found to be a useful precursor of benzooxadiborole derivatives (
Scheme 3). It can be readily obtained by careful hydrolysis of 1,2-bis(dichloroboryl)benzene [
6] or a Br/Li exchange reaction of 2-(2-bromophenyl)butyl[1,3,6,2]dioxazaborocan, followed by quenching the aryllithium intermediate with B(OMe)
3 (
Scheme 3) [
7]. Subsequent studies on the structural behaviour of
2 and its fluorinated derivatives (
3–
7) revealed that those compounds tend to equilibrate in solution with respective cyclic semi-anhydrides, i.e., 1,3-dihydroxy-1,3-dihydro-2,1,3-benzoxadiboroles (
Scheme 3).
1H and
13C NMR analyses in various dry deuterated solvents (acetone, THF, DMSO) revealed that cyclization (
2a→
2b) occurs to a significant extent. Moreover, the
11B NMR spectrum showed that boron atoms (
2) are slightly deshielded (by ca. 4 ppm) with respect to free acid. However, the B-O-B linkage is readily cleaved upon the addition of water (or D
2O), shifting the equilibrium towards free acid (
2b).
Scheme 3. Synthesis of phenylene-1,2-diboronic acid (2a). Cyclization and acid-base equilibria involving 2a and 1,3-dihydroxybenzoxadiborole (2b).
The formation of 1,3-dihydroxybenzoxadiborole scaffold (
2b) (
Scheme 3) clearly accounts for the apparent stronger acidity (p
Ka = 6.0) of the entire equilibrium system compared to related acyclic meta- and para-substituted phenylenediboronic acids [
8,
9]. Theoretical (DFT B3LYP) studies indicate that the relative stabilization the anionic form (
2b-OH) is important in this respect, although the persistence of its hydrated forms, i.e., a cyclic species (
2a-OH) with a bridging hydroxyl anion bound simultaneously by two boronic groups in a bidentate fashion and an unsymmetrical form (
2a-OH′), stabilized by charge-assisted intramolecular H-bond, should also be taken into account.
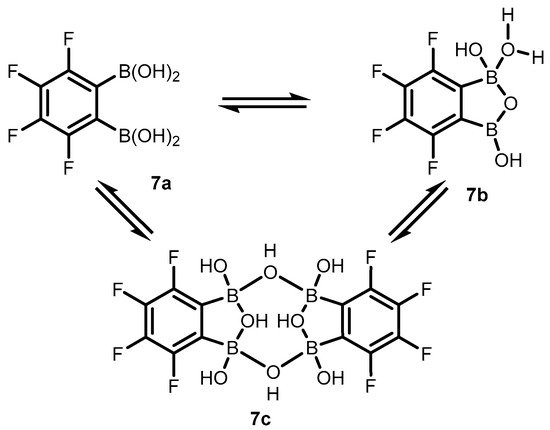
Subsequent studies revealed that 3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophenylene-1,2-diboronic acid
7 shows a stronger tendency to intramolecular cyclization. X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed the formation of perfluorinated benzoxadiborole (
7b), complexed with water molecules (
Scheme 4) [
8]. Interestingly, a unique dimeric form of
7c was also obtained by crystallization in toluene. The molecule consists of two benzoxadiborole frameworks fused by means of two B-OH-B bridges and additionally stabilized by π-π interactions of aromatic rings, resulting in a general chair-type conformation. Overall, the impact of perfluorination results in the strong acidity enhancement of
7 compared to
2, leading to an apparent p
Ka of 3.0, which is among the lowest figures for boronic acids and related species.
Scheme 4. Structural diversity of 3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophenylene-1,2-diboronic acid (7) involving the standard open form (7a), the benzoxadiborole tautomer (7b) and the cyclic dimer (7c).
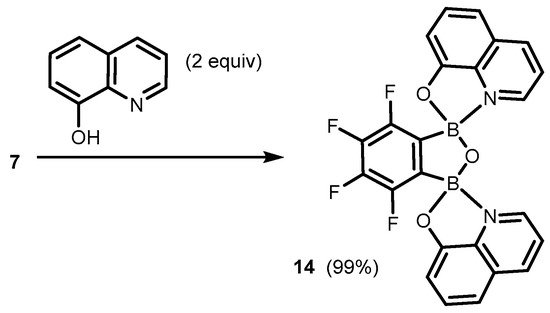
It was found that the benzoxadiborole scaffold is strongly stabilized upon treatment with -8-hydroxyquinoline (
Scheme 5) [
10]. The reactions of
2a/2b and its fluorinated derivatives
3–
7 afforded respective chelate complexes
8–
13, both in solution and under mechanochemical conditions. The most Lewis acidic
7 also bound readily two 8-oxyquinolinato ligands, yielding bis(chelate) (
14) (
Scheme 6) [
10]. All of the obtained complexes exhibit green luminescence in acetonitrile solution (λ
em = ca. 525 nm, Φ = 13–15%), resembling other organoboron 8-oxyquinolinato complexes. Interestingly, it is blue-shifted in solid state (λ
em = ca. 500 nm), which was ascribed to the effect of H-bonding and other polar interactions of discrete molecules in the crystal lattice. Importantly, the electroluminescence properties of complexes
8 and
14 was proved by testing OLEDs containing those compounds as emitters [
10]. Later on, complex
8 became the subject of in-depth structural characterization, which included interesting solvatomorphic behaviour [
11] as well as high resolution single-crystal X-ray diffraction electron density studies performed for the first time in the case of a luminescent oxyquinolinato organoboron complex [
12]. Furthermore,
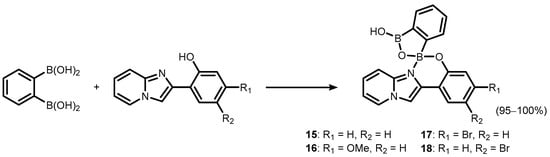
2 was also employed for the synthesis of a series of luminescent (
O,
N)-chelate complexes (
15–
18) with 2-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-2-yl)phenol ligands (
Scheme 7) [
13]. The products were also characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction, which revealed formation of H-bonded dimers in the solid state.
Scheme 5. Synthesis of benzoxadiborole 8-oxyquinolinato complexes 8–13.
Scheme 6. Synthesis of benzoxadiborole bis(8-oxyquinolinato) complex 14.
Scheme 7. Synthesis of benzoxadiborole (O,N)-chelate complexes 15–18 with 2-(imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-2-yl)phenol.
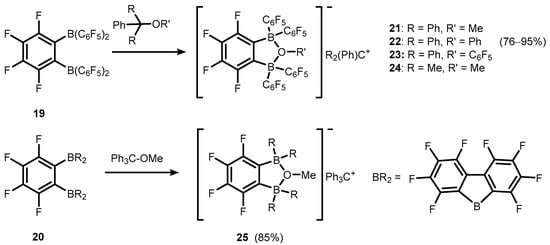
Transformations of strong bidentate Lewis acids of a general formula
o-C6F4(BR2)2, R = C
6F
5 (
19), and BR
2 = BC
12F
8 (
20) gave rise to various anionic or neutral boracyclic species structurally closely related to
7b/
7c (
Scheme 8) [
14,
15,
16,
17]. However, it should be noted that most of them are formed, at least in a formal sense, by means of dative O→B interactions. Specifically, weakly-coordinating borate anions
o-C6F4[B(C
6F
5)2]2(
μ-OR), R = Me, Ph, C
6F
5, and C6F4[BC
12F
8]2(
μ-OMe) were employed for stabilization of selected tertiary carbocations in respective ion-pair compounds (
21–
24 and
25, respectively) (
Scheme 8) [
15,
16,
17,
18]. It was found that trityl salts (
21–
23) are effective co-catalysts of ethylene polymerization due to activation of dimethyl zirconocene (Cp
2ZrMe
2), resulting in corresponding products with Cp
2ZrMe
+ cation [
15,
18]. Compound
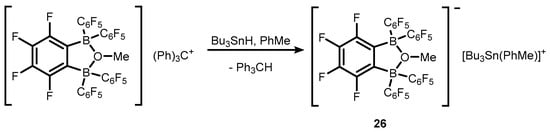
21 was also used for generation of stannylium cationic species
26 (
Scheme 9) [
19].
Scheme 8. Synthesis of ion-pair compounds 21–25, comprising tertiary carbocations and weakly-coordinating anions based on perfluorinated benzoxadiborole backbones.
Scheme 9. Synthesis of stannylium cationic species 26.
The analogous oxonium salt with (Et
2O)
2H
+ counterion was also obtained [
19]. Similarly, related Bronsted acids based on solvated protons were generated from reactions of
19–
20 with an excess of protic reagents (MeOH, H
2O) (
Scheme 10) [
20]. It should be noted that such species are generally prone to protolytic cleavage of B-C, which results in fragmentation of a boracyclic anions derived from
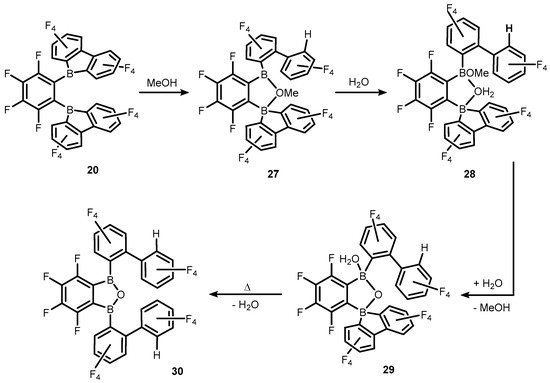
19. On the other hand, controlled treatment of
20 with MeOH/H
2O gives rise to various neutral species such as cyclic borinic ester (
27) obtained upon protonolysis of one B-C bond in the borafluorene ligand, the unique system (
28) with water molecule bridging two boron centres, water-coordinated borinic acid (
29) as well as the benzoxadiborole (
30) arising from the cleavage of another B-C bond. The molecular structures of compounds
27–
30 were determined by X-ray diffraction. The studies on the reactivity of
19–
20 towards water were directly connected to their use as potent initiators of isobutene polymerization. They were aimed at shedding light on the plausible role of dissolved water as a chain transfer agent in polymerizations involving
19–
20 that give rise to weakly-coordinating counteranions. It was suggested that species featuring bridging water molecule such as compound
28 are active as a strong Brønsted acid that is able to protonate isobutene which initiates the polymer chain growth [
20].
Scheme 10. Transformations of 20 to various boracyclic systems (27–30) upon interactions with MeOH and H2O.
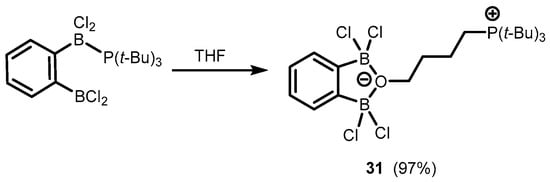
In addition, one can also mention herein the synthesis of a zwitterionic system (
31) based on an anionic benzoxadiborole framework with a C
4-chain attached to an oxygen atom and decorated with a cationic phosphonium end group. This was obtained by the ring opening of the THF molecule due to interaction with a Frustrated Lewis Pair system composed of 1,2-bis(dichloroboryl)benzene and tris(
tert-butyl)phosphine (
Scheme 11) [
21].
Scheme 11. Synthesis of a zwitterionic system 31 based on an anionic benzoxadiborole framework.
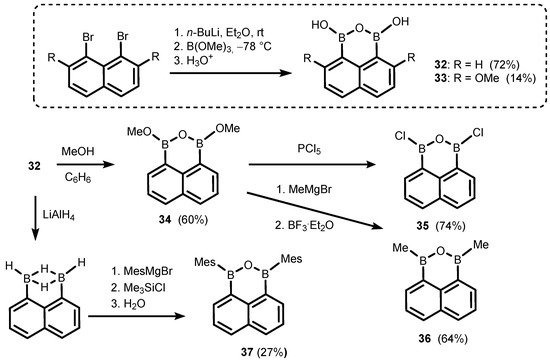
The ring-expanded benzoxadiborole analogues are based on naphthalene and biphenyl scaffolds. Thus, 1,3-dihydroxy-1
H,3
H-naphth[l,8-
cd][l,2,6]oxadiborin (
32) (
Scheme 12) is easily accessible by diboronation of 1,8-dilithionaphthalene with B(OMe)
3 [
22,
23,
24]; 4,9-Dimethoxy derivative (
33) was obtained analogously and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction [
25]. Compound
32 was successfully used as a coupling partner in selected Suzuki–Miayura cross-coupling reactions, resulting in the formation of new aryl-aryl bonds [
26,
27,
28]. Thus, its behaviour seems to be rather typical of arylboronic acids and their derivatives. However, unlike benzoxadiboroles, the B-O-B linkage in
32 seems to be rather stable as there are no data which might indicate that a reversible hydrolysis to naphthalene-1,8-diboronic acid occurs to any appreciable extent. Compound
32 was used as a starting material for synthesis of a few 1
H,3
H-naphth[l,8-
cd][l,2,6]oxadiborin derivatives (
34–
37) where hydroxyl groups were replaced with OMe, Cl, Me [
23], or mesityl (Mes) substituents [
24], respectively.
Scheme 12. Synthesis of 1,3-dihydroxy-1H,3H-naphth[l,8-cd][l,2,6]oxadiborins (32–33) and conversion of 32 to 34–37.
Very recently, a structurally extended analogue of
32 based on bicyclohexene-
peri-naphthalene framework
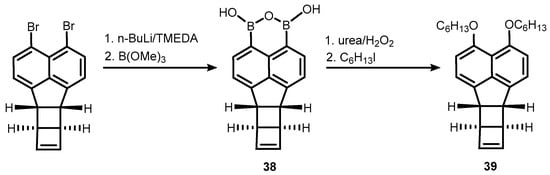
38 was obtained using an analogous protocol involving bromine-lithium exchange in an appropriate dibromide, followed by boronation. It should be stressed that the system features a significant ring strain arising from the presence of two C4 and one C5-ring fused with the naphthalene core. Nevertheless,
38 was used successfully for the synthesis of peri-substituted bis(hexyl ether) (
39)via oxidation of B-C bonds followed by alkylation (
Scheme 13) [
29].
Scheme 13. Synthesis and transformation of a boracyclic system (38) featuring B-O-B linkage attached to bicyclohexene-peri-naphthalene scaffold.
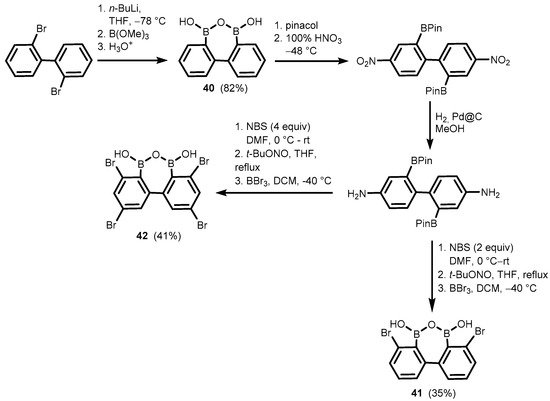
Related oxadiborepins, i.e., 7-membered boracyclic systems comprising B-O-B linkage and 2,2′-biphenyl core, were also obtained [
30,
31,
32]. It should be noted that the plausible equilibrium between biphenyl-2,2′-diboronic acid and its cyclic semi-anhydride (
40) has not been studied to date, although its synthesis was reported already in 2002 [
30], followed by crystallographic determination of
38 in 2011 [
31]. Compounds
41–
42 were obtained in a multistep protocol starting with 2,2′-dibromobiphenyl (
Scheme 14). Remarkably,
41–
42 were reported as efficient catalysts of dehydrative amidation of carboxylic acids with amine substrates. Initially, they were employed for efficient preparation of various α- and β-hydroxy substituted amides [
32] but thereafter also proved effective in catalyzing the formation of Weinreb amides [
33,
34] as well as various oligopeptides [
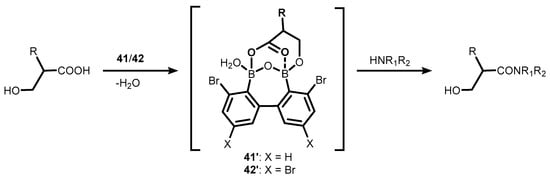
35]. In the former case, the proposed mechanism of the catalytic process involves the cooperation of the two boron atoms in
41–
42, which enables the formation of a cyclic mixed anhydride with carboxylic acid molecule, as evidenced by the ESI MS spectrum; this is followed by an attack of amine on the activated carbonyl group (
Scheme 15) [
32]. It should be noted that the performance of
42 is impressive, as evidenced by low catalyst loading (even a 0.01 mol% turnover number (TON) parameter up to 7500).
Scheme 14. Synthesis of oxadiborepins 40–42.
Scheme 15. Direct amidation of β-hydroxy substituted carboxylic acids with amines in the presence of bromo-substituted oxadiborepins 41–42.
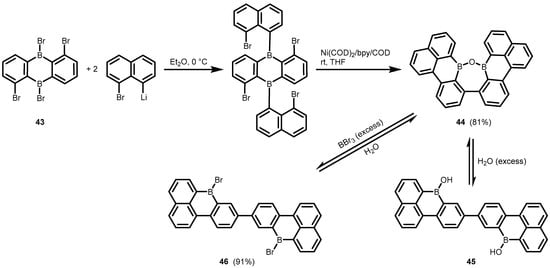
One can also mention the unexpected synthesis of the fused polycyclic oxadiborepin (
44) from the diboraanthracene precusor (
43) which involved double arylation with 8-bromo-1-naphthyllithium followed by successful debromination/C–C coupling using Ni(COD)
2/bpycatalyst (
Scheme 16) [
36]. The formation of a third C–C bond and the cleavage of two B–C bonds was observed when THF was used as the solvent. The
1H NMR studies on the structural behaviour of
44 revealed that it exists in equilibrium with the respective diborinic acid (
45) upon the addition of water, whereas complete conversion to the dibromo derivative (
46) occurs upon heating with an excess of BBr
3. Compound
46 is readily reconverted back to
44 upon the addition of water.
Scheme 16. Synthesis and cleavage of the fused polycyclic oxadiborepin 44.