The relationship between diet and the diversity and function of the intestinal microbiome and its importance for human health is currently the subject of many studies. The type and proportion of microorganisms found in the intestines can determine the energy balance of the host. Intestinal microorganisms perform many important functions, one of which is participation in metabolic processes, e.g., in the production of short-chain fatty acids—SCFAs (also called volatile fatty acids). These acids represent the main carbon flow from the diet to the host microbiome. Maintaining intestinal balance is necessary to maintain the host’s normal health and prevent many diseases. The results of many studies confirm the beneficial effect of probiotic microorganisms on the balance of the intestinal microbiome and produced metabolites, including SCFAs. The aim of this review is to summarize what is known on the effects of probiotics on the production of short-chain fatty acids by gut microbes. In addition, the mechanism of formation and properties of these metabolites is discussed and verified test results confirming the effectiveness of probiotics in human nutrition by modulating SCFAs production by intestinal microbiome is presented.
- SCFA
- metabolites of bacteria
- bacterial fermentation
- probiotics
Organic acids, principally the short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are formed in the GI tract in millimolar quantities and especially occur in high amounts in those areas where anaerobic microorganisms are predominant. SCFAs are volatile saturated fatty acids that have in their chain 1-6 carbon atoms in the aliphatic chain, existing in a straight or branched conformation [1]. In this review, attention has been focused on SCFAs with a simple conformation, which include formic, acetic, propionic, butyric, valerian, and caproic acids (Table 1).
Table 1. Chemical and structural formulas of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) [2].
|
Name |
Chemical Formula |
Structural Formula |
Molar Mass [g/mol] |
|
Formic acid |
HCOOH |
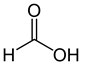 |
46.03 |
|
Acetic acid |
CH3COOH |
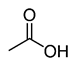 |
60.05 |
|
Propionic acid |
CH3CH2COOH |
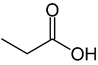 |
74.08 |
|
Butyric acid |
CH3(CH2)2COOH |
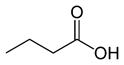 |
88.11 |
|
Valeric acid |
CH3(CH2)3COOH |
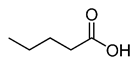 |
102.13 |
|
Caproic acid |
CH3(CH2)4COOH |
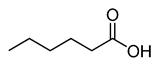 |
116.16 |
SCFAs represent the main carbon flow from the diet to the host microbiome [3]. The formation of these acids is relatively well-known and described [4][5]. The concentration and ratio of resulting SCFAs depend not only on the composition of the microbiome and the number of individual microorganisms in the colon, but also on the type of dietary fibers supplied to the microorganisms as a substrate in the fermentation process, and thus on the diet [6]. The most common are acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid (in a 3:1:1 molar ratio), which constitute 90%–95% of SCFAs present in the human colon, while a smaller proportion of these is formic acid [1].
In addition, the fermentation of selected, often rapidly fermentable non-digestible carbohydrates (NDCs) produces another organic acid-lactic acid [3]. Although it does not belong to the group of SCFAs, this acid can be produced by lactic acid bacteria, e.g., the genera Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium [5]. However, under normal conditions it is not accumulated in the colon due to the presence of some bacterial species, e.g., Eubacterium hallii, that can convert lactate into different SCFAs [5]. Metagenomic analyses have greatly facilitated the identification of the types of bacteria responsible for the production of SCFAs and lactic acid (Table 2).
Table 2. Examples of commensal and probiotic microorganisms producing SCFAs and lactic acid [7].
|
Microorganism/s |
Type |
Acid/s |
References |
|
Bifidobacterium spp., Blautia hydrogentrophica, Prevotella spp., Streptococcus spp. |
commensal |
acetic |
[8] |
|
Akkermansia muciniphilia, Bacteroides spp., |
commensal |
acetic, propionic |
|
|
Dalister succinatiphilus, Eubacterium spp. (e.g., E. halli), Megasphaera elsdenii, Phascolarctobacterium succinatutens, Roseburia spp., Salmonella spp., Veillonella spp. |
commensal |
propionic |
[9] |
|
Coprococcus spp. (e.g., Coprococcus catus), Roseburia inulinivorans |
commensal |
propionic, butyric |
|
|
Anaerostipes spp., Coprococcus comes, Coprococcus eutactus, Clostridium symbiosum, Eubacterium rectale, Eubacterium hallii, Faecalibacterium spp. (e.g., Faecalibacterium prausnitzii), Roseburia spp. (e.g., Roseburia intestinalis) |
commensal |
butyric |
|
|
Clostridium spp., Ruminococcus spp. |
commensal |
acetic, propionic, butyric |
|
|
Bifidobacterium spp. |
probiotic |
acetic, lactic |
[13] |
|
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG), Lactobacillus gasseri PA 16/8 |
probiotic |
propionic, lactic |
[7] |
|
Bifidobacterium longum SP 07/3, Bifidobacterium bifidum MF 20/5 |
probiotic |
acetic, propionic, lactic |
|
|
Lactobacillus salivarius spp salcinius JCM 1230, Lactobacillus agilis JCM 1048 |
probiotic |
propionic, butyric, lactic |
[14] |
|
Lactobacillus acidophilus CRL 1014 |
probiotic |
acetic, propionic, butyric, lactic |
1. Bacterial Fermentation Involved into Production of SCFAs
Endogenous short-chain fatty acids are formed by bacterial fermentation of food fiber and NDCs, which become available to intestinal microorganisms in the large intestine. In addition to resistant starch (RS), plant-derived NDCs include non-starch polysaccharides (NSP), oligosaccharides (prebiotics), oligofructose, disaccharides (lactose, stachyose, raffinose) and monosaccharides e.g., alcohols (sorbitol, mannitol) [19]. There are four types of resistant starch (RS1–RS4) present in the human diet that are resistant to degradation in the small intestine [20][21]. The type of RS has a significant effect on the composition of the intestinal microbiome [22]. In the case of oligosaccharides, particularly important are prebiotics defined as a nonviable food component that confers a health benefit on the host associated with modulation of the microbiota [23]. However, endogenous indigestible carbohydrates include mucin and milk oligosaccharides [19].
Fermentation is an anaerobic redox process in the cytoplasm in which organic compounds are both electron donors and acceptors. In the fermentation process, electrons detached from the oxidized substrate are transferred by NADH directly to the endogenous acceptor. ATP is formed as a result of substrate phosphorylation, with the participation of the corresponding phosphoglycerate, pyruvate, acetate or butyrate kinases. During carbohydrate fermentation, the final electron acceptor is pyruvate or the compounds that are produced from it. The end products of fermentation are various short chain carboxylic acids (e.g., formic, acetic, lactic, butyric, propionic), CO2, H2, ethanol, glycerol, acetoin, 2,3-butanediol. Importantly, bacterial growth in populations mixed with other microorganisms can affect the type and amount of products produced during fermentation. The substrates most commonly used by microorganisms in the fermentation process are hexoses and pentoses [24].
Bacteria have a variety of pathways to transform sugars. These sugars are first phosphorylated and then in glycolysis (Embden–Meyerhof–Parnassian pathway), in the Entner–Doudoroff pathway or in the Bifidobacterium pathway are transformed into pyruvate or into pyruvate and additional acetyl-phosphate. The Embden–Meyerhof–Parnassian pathway, the major colonic pathway for the catabolism of hexoses, occurs in enterobacteria, clostridia, homofermentative lactic acid bacteria, and propionibacteria, and produces only pyruvate as a partial oxidation product) [25]. The Entner–Doudoroff pathway is used in the fermentation metabolism by e.g., Zymomonas (alcoholic fermentation), as well as Escherichia coli in gluconate fermentation. The Bifidobacterium pathway is active in bacteria of the genus Bifidobacterium, inhabiting, among others, the human digestive system. Two acetate molecules and one lactate are formed in this pathway. In the phosphoketolase pathway that occurs in heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria or the Bifidobacterium pathway, an additional molecule of acetyl-phosphate is generated (Figure 1) [26].
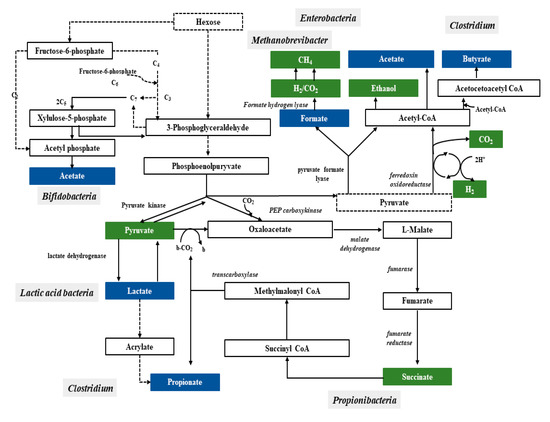
Figure 1. Pathways leading to SCFAs and lactic acid production by intestinal bacteria [25].
In a mixed population such as the intestinal microbiome, carbohydrate breakdown into a mixture of acids involves more than one species. This type of fermentation is called mixed acid fermentation or Enterobacteriaceae fermentation and is carried out by some bacteria belonging to this family, including Escherichia, Proteus, Salmonella, and Shigella [24]. The fermentation products of some species are substrates for fermentation or incorporated as intermediate metabolites into the metabolic pathways of other species, resulting in substrates being sequentially fermented. Lactate, ethanol, and pyruvate are diminished by subsequent bacterial utilization and SCFAs production. Accordingly, the main final products of sugar catabolism are SCFAs, acetate, propionate and butyrate that account for 85%–95% of total SCFAs in all regions of the colon. Other fermentation end products, such as caproate and valerate, occur in lower amounts [25].
Acetic acid is the most abundant SCFAs in the colon, accounting for more than half of the total SCFAs found in feces [26]. Intestinal microorganisms can produce acetic acid through two major metabolic processes. Most often it is fermentation of indigestible carbohydrates, while about 1/3 of acetic acid is formed as a result of synthesis from hydrogen and carbon dioxide or formic acid by acetogenic bacteria through the Wood–Ljungdahl pathway [4][10].
Some types of Clostridium (C. acetobutylicum, C. butyricum, C. pasteurianum, C. perfringens) participate in butyric fermentation, as well as e.g., Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens and Fusobacterium nucleatum. The end products are butyric acid, a small amount of acetic acid and CO2 and H2. Some species may also form lactic acid and/or ethanol as well.
For propionic fermentation, the main substrates are glucose and lactate. Its course varies depending on the bacteria; it can occur that it forms succinate or acrylate [24].
Bacteria are capable of fermenting sugar degradation products (glycerol, citrate, malate, succinate, pyruvate, lactate, ethanol, acetate), and a small share of dietary protein fermentation processes in the production of SCFAs has been shown, mainly in the form of acetic and propionic acid [27]. Bacteria of the genus Clostridium are capable of fermenting amino acids. In this process, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, acetate, as well as ammonia and butyrate may form, which have an unpleasant odor. In addition, amino acids such as valine, leucine and isoleucine resulting from the anaerobic breakdown of proteins can be converted into compounds with strong odor, such as isobutyric, isovaleric and hexanoic acids, as well as cadaverine, putrescine, other amines, and hydrogen sulfide and methylmercaptan [24]. Excessive accumulation of isobutyric acid and isovaleric acid indicates a malfunctioning fermentation and digestion processes. These are putrefactive acids, the increased production of which may be associated with an excess of unabsorbed amino acids or proteins reaching the intestines. The possibility of blood in the intestinal contents and the overly intensive development of pathogenic microbiota in the small intestine should also be taken into account, where access to protein compounds is facilitated [28].
2. Functions of Short-Chain Fatty Acids
SCFAs have been shown to have a very positive effect on the energy metabolism of mammals that use them together with glucose as a metabolic fuel [29]. It has been estimated that the use of SCFAs as an energy source can provide up to 10% of the host’s daily calories [30]. The presence of these acids in the human body, mainly acetic, butyric and propionic acids in sufficient quantities is essential for the health and well-being of the host [7]. However, the production of these acids requires the presence of appropriate substrates (dietary fiber and prebiotics) needed for the proper course of the fermentation processes.
SCFAs play a very important role in maintaining intestinal and immune homeostasis in the human body (Figure 2).
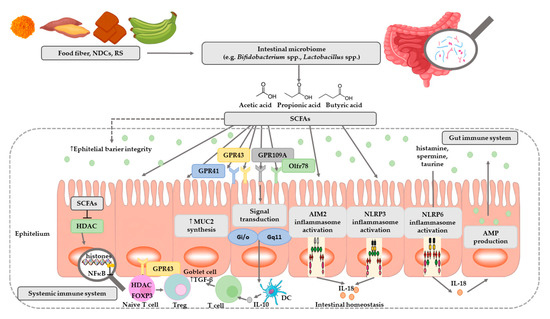
Figure 2. The role of SCFAs in regulation of intestinal homeostasis. SCFAs (acetic, propionic, and butyric acid) are produced by intestinal microbiome in fermentation of undigested food fiber, non-digestible carbohydrates (NDCs) or resistant starch (RS). SCFAs are as energy substrates for colonocytes and regulate intestinal barrier function (synthesis of mucin-MUC2) and immune system through G-protein-coupled receptors (GPR41, GPR43, GPR109A) and Olfr78 receptor signaling. SCFAs regulate the histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity which affects inhibition of nuclear factors (nuclear factor-κB; NF-κB). SCFAs affect the differentiation of regulatory T (Treg) cells and the production of interleukin-10 (IL-10) with the participation of GPR43. SCFAs also regulate dendritic cell (DC) function. In addition, SCFAs influence AIM2 and NLRP3 inflammasomes activation which then affects production of interleukin-18 (IL-18) and enhanced epithelial barrier function. Moreover, NLRP6 inflammasome activation and secretion of IL-18 regulate the production of intestinal antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) [31][32]. Abbreviations: FOXP3-forkhead box P3; TGF-β-transforming growth factor β.
SCFAs are speculated to have a mediational role in the microbiota–gut–brain axis crosstalk [33]. Two major SCFAs signaling mechanisms have been identified, namely inhibition of HDACs and activation of GPCRs—The binding partners of GPR41 and GPR43 (Table 3) [34][35].
Table 3. The characteristics of SCFAs and lactic acid receptors [8][36][37][38].
|
Receptor |
Ligand |
Protein G |
Exspression |
Physiological Function |
|
FFAR2—Free fatty acid receptor 2 (GPR43) |
Acetate, propionate, butyrate |
Gi/o, Gq11 |
Small intestinal epithelium, colonic, colonic LP cells, leukocytes in small intestinal LP, adipocytes, polymorphonuclear cells, skeltal muscle, spleen and heart etc. |
Apetite control, anti-lipolysis, increased insulin sensitivity, preadipocyte differentiation, expansion and differentiation of Tregs, protection against IBD, apoptosis of human colon cancer cel line etc. |
|
FFAR3—Free fatty acid receptor 3 (GPR41) |
Acetate, propionate, butyrate |
Gi/o |
Small intestinal epithelium, colonic, colonic LP cells (mast cells), peripheral nervous system, peripheral mononuclear cells, bone marrow spleen, adipocytes, lymph nodes, etc. |
Leptin expression, oxygen consumption rate, increased energy expenditure, decreased food intake, hematopoiesis of DCs from bone marrow, increased DC precursors alleviating asthma and Treg cells etc. |
|
HCA1—Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 1 (GPR81) |
lactate |
(Gi) |
Predominantly in adipose tissue, minor in kidney, skeletal muscle, liver, intestinal tissue, rat and human brain, mouse primary cortical neuronal cells, macrophages, etc. |
Modulation of cortical neuron activity, and enterocyte turnover in response to starvation-refeeding, anti-lipolysis, anti-inflammatory on macrophages, reduced symptom of cancer and IBD in mouse models of hepatitis and pancreatitis, etc. |
|
HCA2—Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (GPR109A) |
Niacin, ketone bodies, β-hydroxybutyric acids, butyrate |
Gi/o, Gβγ |
Apical membrane of colonic and small intestinal epithelium, monocytes, adipocytes, macrophages, DCs, neutrophils, retinal pigment epithelium, etc. |
Improved epithelial barrier function, anti-lipolysis, decrease of triglyceride, protection against CRC and colitis, increase of Treg generation and IL-10 producing T cells, etc. |
|
Olfr78 (murine) OR51E2 (human) |
Acetate, propionate |
NR |
Neurons, epithelial enteroendocrine cells of colon, enteroendocrine cells, renal afferent arteriole, smooth muscle cells, etc. |
Regulation of hormone secretion (GLP-1, PYY) and blood pressure, etc. |
|
PPARγ (Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma) |
Propionate, butyrate |
NR |
Large intestine adenocarcinoma cells, etc. |
Regulation of lipid metabolism, a joining factor between the gut microflora composition and accumulation of the adipose tissue, etc. |
Abbreviations: CRC—colorectal cancer; DC—dendritic cell; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide; GPR—G-protein coupled receptor; IBD—inflammatory bowel disease; IL-10 (interleukin-10); LP—lamina propria; NR—not reported; Olfr—olfactory receptor; PYY—peptide YY; Treg—regulatory T cell.
SCFAs play a very important role in regulating pH, increasing the absorption of calcium, iron, as well as magnesium, and are beneficial for glucose and protein metabolism in the liver. In addition, these acids affect the maintenance of the normal structure, integrity and function of the intestines [19]. They show anti-inflammatory activity, which involves inhibiting the activity of inflammatory mediators in the intestinal epithelium, and thus inhibiting the activation of NFκB macrophages, which are the main source of cytokines in the course of the inflammatory process of inflammatory bowel diseases [19]. These acids are the primary source of energy for colonocytes [39][40]. It has been shown that the source of 70% of the energy used by intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) is butyric acid produced by commensal bacteria, especially such as Ruminococcus and Faecalibacterium (Table 4) [12]. In addition, by simulating the growth of saprophytic microflora, SCFAs inhibit the development of pathogenic microorganisms such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella, or Campylobacter, competing for colonization sites [6]. Studies have shown that butyric acid stimulates the expression of the MUC2 gene in cell lines and the production of mucin, and the sticky layer it creates protects the intestinal epithelium from contact with toxins and pathogenic microorganisms [41]. In contrast, studies of programmed cell death from a tumor line have demonstrated the effectiveness of butyric acid in inhibiting their development and inducing the process of apoptosis [42][43][44]. In addition, butyric acid and propionic, acetic, and valeric acids have been shown to induce apoptosis (Table 4) [45].
SCFAs increase the amount of mucus produced and the speed of blood flow. More importantly, they provide acetyl-CoA used in the process of fat biosynthesis and cell membrane production, guaranteeing the integrity of mucous membranes [46]. There are indications that SCFAs are key mediators of the beneficial effects of intestinal microbiota. SCFAs also directly modulate host health through a number of tissue-specific mechanisms associated with intestinal barrier function, glucose homeostasis, immunomodulation, appetite regulation, obesity, and have a direct and indirect effect on cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk markers [47].
At present, relatively little is known about the function of formic acid in the intestines. There are indications that its presence is associated with methanogenesis and its concentration may be elevated during inflammation (Table 4) [48][49]. Acetic acid concentration in the colon is the highest of all SCFAs, and in cells it is a key factor in the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats [50]. In addition, acetic acid is absorbed by the liver, where it participates in the synthesis of cholesterol (Table 4) [51]. Propionic acid is produced in the human gut mainly by Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes [52]. This acid is an inhibitor of gluconeogenesis and cholesterol synthesis in the liver [53]. In addition, it has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, taking part in the protection of human intestines against pathogens [6][54]. Butyric acid exerts the strongest anti-inflammatory effect of all SCFAs [19]. The cause of the inflammatory process of the intestinal mucosa, which accompanies many pathological processes, is a lack of energy. Butyric acid is the main source of energy for intestinal epithelial cells. Butyric acid has a beneficial immunoregulatory effect on intestinal epithelial cells and other mucosal cell populations. It modulates gene expression by affecting both stimulants and inhibitors of expression. Some of these mechanisms are based on histone hyperacetylation due to inhibition of the histone deacetylase enzyme activity (Table 4) [55].
Unlike other SCFAs, the role of valeric acid in gut health is not fully understood. In a limited number of studies, it was found that valeric acid can stimulate the growth of intestinal epithelium and have a beneficial effect on the pathogenesis of diseases such as colitis, cardio-metabolic diseases and cancer (Table 4) [56][57][58].
Table 4. Examples of trials regarding the effect of SCFAs on human health.
|
Type of SCFA |
The Effect on Human Health |
References |
|
Acetate |
· Protection against E. coli O157:H7 infection |
[59] |
|
· Participates in the synthesis of cholesterol |
[51] |
|
|
Butyrate |
· Is the source of 70% of the energy used by intestinal epithelial cells |
[12] |
|
· Increases in MUC2 gene expression and the production of mucin |
[41] |
|
|
· inhibits development of tumor cells and inducing the process of their apoptosis |
||
|
· Inhibits the genotoxic activity of nitrosamides and hydrogen peroxide |
[61] |
|
|
· Has immunoregulatory effect |
[55] |
|
|
· Plays a role in the prevention and the treatment of distal ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease and cancer |
[62] |
|
|
· Improves ulcerative colitis (UC) symptoms |
[63] |
|
|
Butyrate/acetate/propionate |
· Improves the macroscopic and histological signs of inflammation |
[64] |
|
Formate |
· Presence is associated with methanogenesis and its concentration may be elevated during inflammation |
|
|
Propionate |
· Decreases cholesterol synthesis in the liver, improves lipid metabolism |
|
|
|
· Has anti-proliferative effect |
|
|
Valerate |
· Stimulates the growth of intestinal epithelium · Has a beneficial effect on the pathogenesis of diseases such as colitis, cardio-metabolic diseases and cancer |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/nu12041107
References
- David Rios-Covian; Patricia Ruas-Madiedo; Abelardo Margolles; Miguel Gueimonde; Clara G. De Los Reyes-Gavilán; Nuria Salazar; Intestinal Short Chain Fatty Acids and their Link with Diet and Human Health. Frontiers in Microbiology 2016, 7, 2030, 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00185.
- Formic acid; acetic acid; propionic acid; butyric acid; valeric acid; caproic acid . PubChem. Explore Chemistry.. Retrieved 2020-5-12
- Douglas J Morrison; Tom Preston; Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism.. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189-200, 10.1080/19490976.2015.1134082.
- T L Miller; M J Wolin; Pathways of acetate, propionate, and butyrate formation by the human fecal microbial flora.. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 1996, 62, 1589-1592, 10.1128/aem.62.5.1589-1592.1996.
- Harry J. Flint; Sylvia H. Duncan; Karen P. Scott; Petra Louis; Links between diet, gut microbiota composition and gut metabolism. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 2014, 74, 13-22, 10.1017/s0029665114001463.
- Robert Havenaar; Intestinal health functions of colonic microbial metabolites: a review. Beneficial Microbes 2011, 2, 103-114, 10.3920/bm2011.0003.
- Alejandra De Moreno De Leblanc; Florian Chain; Rebeca Martín; Luis G. Bermúdez-Humarán; Stéphanie Courau; Philippe Langella; Beneficial effects on host energy metabolism of short-chain fatty acids and vitamins produced by commensal and probiotic bacteria. Microbial Cell Factories 2017, 16, 79, 10.1186/s12934-017-0691-z.
- Ara Koh; Filipe De Vadder; Petia Kovatcheva-Datchary; Fredrik Bäckhed; From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332-1345, 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.041.
- Nicole Reichardt; Sylvia H Duncan; Pauline Young; Alvaro Belenguer; Carol Leitch; Karen P Scott; Harry J Flint; Petra Louis; Phylogenetic distribution of three pathways for propionate production within the human gut microbiota. The ISME Journal 2014, 8, 1352-1352, 10.1038/ismej.2014.48.
- Petra Louis; Georgina L. Hold; Harry J. Flint; The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2014, 12, 661-672, 10.1038/nrmicro3344.
- Marius Vital; Adina Howe; James Tiedje; Revealing the Bacterial Butyrate Synthesis Pathways by Analyzing (Meta)genomic Data. mBio 2014, 5, e00889-14-14, 10.1128/mBio.00889-14.
- Jacinta Serpa; Francisco Caiado; Tânia Carvalho; Cheila Torre; Luis Gafeira Gonçalves; Cristina Casalou; Pedro Lamosa; Margarida Rodrigues; Zhenping Zhu; Eric W-F Lam; et al. Butyrate-rich Colonic Microenvironment Is a Relevant Selection Factor for Metabolically Adapted Tumor Cells*. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2010, 285, 39211-39223, 10.1074/jbc.M110.156026.
- Enrica Pessione; Lactic acid bacteria contribution to gut microbiota complexity: lights and shadows. Frontiers in Microbiology 2012, 2, 86, 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00086.
- A. Meimandipour; M. Hair-Bejo; M. Shuhaimi; K. Azhar; A.F. Soleimani; Babak Rasti; Abdul Manap Mohd Yazid; Gastrointestinal tract morphological alteration by unpleasant physical treatment and modulating role ofLactobacillusin broilers. British Poultry Science 2010, 51, 52-59, 10.1080/00071660903394455.
- Nuria Salazar; Ana Binetti; Miguel Gueimonde; Ana Alonso; Pablo Garrido; Carmen Gonzalez Del Rey; Celestino Gonzalez-Gonzalez; Patricia Rúas-Madiedo; Clara G. De Los Reyes-Gavilán; Safety and intestinal microbiota modulation by the exopolysaccharide-producing strains Bifidobacterium animalis IPLA R1 and Bifidobacterium longum IPLA E44 orally administered to Wistar rats. International Journal of Food Microbiology 2011, 144, 342-351, 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.10.016.
- Katia Sivieri; M.L.M Villarreal; Maria A Tallarico Adorno; Isabel Kimiko Sakamoto; Susana Marta Isay Saad; Elizeu Antonio Rossi; Lactobacillus acidophilus CRL 1014 improved “gut health” in the SHIME® reactor. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13, 100-100, 10.1186/1471-230X-13-100.
- Alberto Amaretti; Tatiana Bernardi; Elena Tamburini; Simona Zanoni; Mariella Lomma; Diego Matteuzzi; Maddalena Rossi; Kinetics and Metabolism of Bifidobacterium adolescentis MB 239 Growing on Glucose, Galactose, Lactose, and Galactooligosaccharides. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2007, 73, 3637-3644, 10.1128/aem.02914-06.
- Amany A. Abdin; Eman M. Saeid; An experimental study on ulcerative colitis as a potential target for probiotic therapy by Lactobacillus acidophilus with or without “olsalazine”. Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis 2008, 2, 296-303, 10.1016/j.crohns.2008.04.002.
- Kuczyńska, B.; Wasilewska, A.; Biczysko, M.; Banasiewicz, T.; Drews, M.; Krótkołańcuchowe kwasy tłuszczowe – mechanizm działania, potencjalne zastosowanie kliniczne oraz zalecenia dietetyczne.. Now. Lek. 2011, 80, 299-304, .
- H N Englyst; S M Kingman; John H. Cummings; Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions.. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1992, 46, S33-S50, .
- Harry J. Flint; Karen P. Scott; Sylvia H. Duncan; Petra Louis; Evelyne Forano; Microbial degradation of complex carbohydrates in the gut.. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 289-306, 10.4161/gmic.19897.
- Inés Martínez; Jaehyoung Kim; Patrick R. Duffy; Vicki L. Schlegel; Jens Walter; Resistant Starches Types 2 and 4 Have Differential Effects on the Composition of the Fecal Microbiota in Human Subjects. PLOS ONE 2010, 5, e15046, 10.1371/journal.pone.0015046.
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). FAO Technical Meeting on Prebiotics: Food Quality and Standards Service (AGNS); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2007.
- Baj, J.; Bartosik, D.; Dziewit, Ł.; Jagusztyn-Krynicka, E.K.; Markiewicz, Z.; Piekarowicz, A.; Włodarczyk, M.; Wolska, K.I.. Biologia Molekularna Bakterii, 2nd ed.; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN SA: Warszawa, Polska, 2015; pp. 133-137, 417.
- Chaia, A.; Olivier, G.. Gut Flora, Nutrition, Immunity and Health; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken: NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 77-98.
- Petra Louis; Karen P. Scott; S. H. Duncan; H.J. Flint; Understanding the effects of diet on bacterial metabolism in the large intestine. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2007, 102, 1197-1208, 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03322.x.
- David L. Topping; Peter M. Clifton; Short-chain fatty acids and human colonic function: roles of resistant starch and nonstarch polysaccharides.. Physiological Reviews 2001, 81, 1031-1064, 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.3.1031.
- Ran-Ressler, R.R.; Glahn, R.P.; Bae, S.; Brenna, J.T.; Branched Chain Fatty Acids (BCFA) in the neonatal gut, and estimeated dietary intake in infacy and adulthood.. Nestle Nutr. Inst. Work. Ser. 2013, 77, 133-143, .
- Daisuke Inoue; Gozoh Tsujimoto; Ikuo Kimura; Regulation of Energy Homeostasis by GPR41. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2014, 5, 81, 10.3389/fendo.2014.00081.
- E N Bergman; Energy contributions of volatile fatty acids from the gastrointestinal tract in various species.. Physiological Reviews 1990, 70, 567-590, 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.2.567.
- Ammar Hassanzadeh Keshteli; Karen L. Madsen; Levinus A. Dieleman; Diet in the Pathogenesis and Management of Ulcerative Colitis; A Review of Randomized Controlled Dietary Interventions.. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1498, 10.3390/nu11071498.
- Ratajczak, W.; Rył, A.; Mizerski, A.; Walczakiewicz, K.; Sipak, O.; Laszczy´ nska, M.; Immunomodulatory potential of gut microbiome-derived short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2019, 66, 1-12, 10.18388/abp.2018_2648.
- Dalile, B.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Vervliet, B.; Verbeke, K.; The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids From Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication.. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019, 16, 461-478, 10.1038/s41575-019-0157-3.
- Emmanuel Le Poul; Cécile Loison; Sofie Struyf; Jean-Yves Springael; Vincent Lannoy; Marie-Eve Decobecq; Stéphane Brézillon; Vincent Dupriez; Gilbert Vassart; Jo Van Damme; et al. Functional Characterization of Human Receptors for Short Chain Fatty Acids and Their Role in Polymorphonuclear Cell Activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2003, 278, 25481-25489, 10.1074/jbc.m301403200.
- Jian Tan; Craig McKenzie; Maria Potamitis; Alison N. Thorburn; Charles R. Mackay; Laurence Macia; The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Health and Disease. Advances in Immunology 2014, 121, 91-119, 10.1016/b978-0-12-800100-4.00003-9.
- Sheril Alex; Katja Lange; Tom Amolo; Jeffrey S. Grinstead; Anders K. Haakonsson; Ewa Szalowska; Arjen Koppen; Karin Mudde; Daniëlle Haenen; Sa'ad Al-Lahham; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Stimulate Angiopoietin-Like 4 Synthesis in Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Cells by Activating Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ. Molecular and Cellular Biology 2013, 33, 1303-1316, 10.1128/MCB.00858-12.
- Emilia Korek; Hanna Krauss; [Novel adipokines: their potential role in the pathogenesis of obesity and metabolic disorders].. Postępy Higieny i Medycyny Doświadczalnej 2015, 69, 799-810, 10.5604/17322693.1161415.
- Hideo Ohira; Wao Tsutsui; Yoshio Fujioka; Are Short Chain Fatty Acids in Gut Microbiota Defensive Players for Inflammation and Atherosclerosis?. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis 2017, 24, 660-672, 10.5551/jat.rv17006.
- M R Clausen; P B Mortensen; Kinetic studies on colonocyte metabolism of short chain fatty acids and glucose in ulcerative colitis.. Gut 1995, 37, 684-689, 10.1136/gut.37.5.684.
- Christina M Van Der Beek; Johanne G. Bloemen; Maartje A Van Den Broek; Kaatje Lenaerts; Koen Venema; Wim A. Buurman; Cornelis H DeJong; Hepatic Uptake of Rectally Administered Butyrate Prevents an Increase in Systemic Butyrate Concentrations in Humans. The Journal of Nutrition 2015, 145, 2019-2024, 10.3945/jn.115.211193.
- Henrike M. Hamer; Daisy M.A.E. Jonkers; Ingrid B. Renes; Steven A.L.W. Vanhoutvin; Andrea Kodde; Freddy J. Troost; Koen Venema; Robert Jan Brummer; Butyrate enemas do not affect human colonic MUC2 and TFF3 expression. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2010, 22, 1134-1140, 10.1097/meg.0b013e32833a6ca0.
- Angela Hague; Douglas J. E. Elder; Diane J. Hicks; Christos Paraskeva; Apoptosis in colorectal tumour cells: Induction by the short chain fatty acids butyrate, propionate and acetate and by the bile salt deoxycholate. International Journal of Cancer 1995, 60, 400-406, 10.1002/ijc.2910600322.
- Emília Hijová; A Chmelarova; Short chain fatty acids and colonic health.. Bratisl Lek Listy 2007, 108, 354-358, .
- Dallas R. Donohoe; Leonard B. Collins; Aminah Wali; Rebecca Bigler; Wei Sun; Scott J. Bultman; The Warburg effect dictates the mechanism of butyrate-mediated histone acetylation and cell proliferation.. Molecular Cell 2012, 48, 612-26, 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.08.033.
- Kotunia, A.; Pietrzak, P.; Guilloteau, P.; Zabielski, R.; Kwas masłowy w przewodzie pokarmowym.. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2010, 5, 117-122, .
- Sobotka, L.. Podstawy Żywienia Klinicznego; Wydawnictwo Lekarskie PZWL: Warszawa, Polska, 2008; pp. 1-496.
- Edward S. Chambers; Tom Preston; Gary Frost; Douglas J Morrison; Role of Gut Microbiota-Generated Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Health. Current Nutrition Reports 2018, 7, 198-206, 10.1007/s13668-018-0248-8.
- Stefan Bereswill; Andre Fischer; Rita Plickert; Lea-Maxie Haag; Bettina Otto; Anja A. Kühl; Javid I. Dashti; Andreas E. Zautner; Melba Muñoz; Christoph Loddenkemper; et al. Novel Murine Infection Models Provide Deep Insights into the “Ménage à Trois” of Campylobacter jejuni, Microbiota and Host Innate Immunity. PLOS ONE 2011, 6, e20953, 10.1371/journal.pone.0020953.
- Sonja Vanderhaeghen; Christophe Lacroix; Clarissa Schwab; Methanogen communities in stools of humans of different age and health status and co-occurrence with bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Letters 2015, 362, fnv092, 10.1093/femsle/fnv092.
- Brian T. Layden; Anthony R. Angueira; Michael Brodsky; Vivek Durai; William L. Lowe Jr; Short chain fatty acids and their receptors: new metabolic targets. Translational Research 2013, 161, 131-140, 10.1016/j.trsl.2012.10.007.
- Tulika Arora; Rajkumar Sharma; Fermentation potential of the gut microbiome: implications for energy homeostasis and weight management. Nutrition Reviews 2011, 69, 99-106, 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00365.x.
- Wendy R. Russell; Lesley Hoyles; Harry J Flint; Marc-Emmanuel Dumas; Colonic bacterial metabolites and human health. Current Opinion in Microbiology 2013, 16, 246-254, 10.1016/j.mib.2013.07.002.
- Åsa M. Henningsson; E. Margareta; G. L. Nyman; Inger M. E. Björck; Content of short-chain fatty acids in the hindgut of rats fed processed bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) flours varying in distribution and content of indigestible carbohydrates. British Journal of Nutrition 2001, 86, 379-389, 10.1079/bjn2001423.
- Sa'ad H. Al-Lahham; Maikel P. Peppelenbosch; Han Roelofsen; Roel J. Vonk; Koen Venema; Biological effects of propionic acid in humans; metabolism, potential applications and underlying mechanisms. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 2010, 1801, 1175-1183, 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.07.007.
- U. Böcker; T. Nebe; F. Herweck; L. Holt; A. Panja; C. Jobin; S. Rossol; R. B. Sartor; M. V. Singer; Butyrate modulates intestinal epithelial cell-mediated neutrophil migration. Clinical & Experimental Immunology 2003, 131, 53-60, 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02056.x.
- Yinji Liang; Shu Liang; Yupei Zhang; Yuanjun Deng; Yifang He; Yanning Chen; Chan Liu; Chenli Lin; Qinhe Yang; Oral Administration of Compound Probiotics Ameliorates HFD-Induced Gut Microbe Dysbiosis and Chronic Metabolic Inflammation via the G Protein-Coupled Receptor 43 in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Rats. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins 2018, 11, 175-185, 10.1007/s12602-017-9378-3.
- Lonneke Onrust; Karolien Van Driessche; Richard Ducatelle; Koen Schwarzer; Freddy Haesebrouck; Filip Van Immerseel; Valeric acid glyceride esters in feed promote broiler performance and reduce the incidence of necrotic enteritis. Poultry Science 2018, 97, 2303-2311, 10.3382/ps/pey085.
- Samantha Yuille; Nicole Reichardt; Suchita Panda; Hayley Dunbar; Imke Mulder; Human gut bacteria as potent class I histone deacetylase inhibitors in vitro through production of butyric acid and valeric acid. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0201073, 10.1371/journal.pone.0201073.
- Shinji Fukuda; Hidehiro Toh; Koji Hase; Kenshiro Oshima; Yumiko Nakanishi; Kazutoshi Yoshimura; Toru Tobe; Julie Clarke; David L. Topping; Tohru Suzuki; et al. Bifidobacteria can protect from enteropathogenic infection through production of acetate. Nature 2011, 469, 543-547, 10.1038/nature09646.
- Angela Hague; D J Elder; D J Hicks; C. Paraskeva; Apoptosis in colorectal tumour cells: induction by the short chain fatty acids butyrate, propionate and acetate and by the bile salt deoxycholate.. International Journal of Cancer 1995, 60, 400-406, 10.1002/ijc.2910600322.
- Ingrid Wollowski; G. Rechkemmer; Beatrice L Pool-Zobel; Protective role of probiotics and prebiotics in colon cancer.. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2001, 73, 451s-455s, 10.1093/ajcn/73.2.451s.
- Yuanyuan Wang; Yilin Guo; Hui Chen; Hua Wei; Cuixiang Wan; Potential of Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY2013 and Bifidobacterium bifidum WBIN03 in relieving colitis by gut microbiota, immune, and anti-oxidative stress. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 2018, 64, 327-337, 10.1139/cjm-2017-0716.
- H. Lührs; T. Gerke; J. G. Muller; R. Melcher; J Schauber; F. Boxberger; W. Scheppach; T Menzel; Butyrate Inhibits NF-?B Activation in Lamina Propria Macrophages of Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2002, 37, 458-466, 10.1080/003655202317316105.
- James M. Harig; Konrad H. Soergel; Richard A. Komorowski; Carol M. Wood; Treatment of Diversion Colitis with Short-Chain-Fatty Acid Irrigation. New England Journal of Medicine 1989, 320, 23-28, 10.1056/nejm198901053200105.
- Anna M. Berggren; E. Margareta G. L. Nyman; Ingmar Lundquist; Inger M. E. Björck; Influence of orally and rectally administered propionate on cholesterol and glucose metabolism in obese rats. British Journal of Nutrition 1996, 76, 287-294, 10.1079/bjn19960032.
- G Jan; A-S Belzacq; D Haouzi; A Rouault; D Métivier; G Kroemer; Catherine Brenner; Propionibacteria induce apoptosis of colorectal carcinoma cells via short-chain fatty acids acting on mitochondria. Cell Death & Differentiation 2002, 9, 179-188, 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400935.
- Cong-Jun Li; T. H. Elsasser; Butyrate-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in bovine kidney epithelial cells: involvement of caspase and proteasome pathways.. Journal of Animal Science 2005, 83, 89-97, 10.2527/2005.83189x.
