Brain injuries are devastating conditions, representing a global cause of mortality and morbidity, with no effective treatment to date. Increased evidence supports the role of neuroinflammation in driving several forms of brain injuries. High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein is a pro-inflammatory-like cytokine with an initiator role in neuroinflammation that has been implicated in Traumatic brain injury (TBI) as well as in early brain injury (EBI) after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). Herein, we discuss the implication of HMGB1-induced neuroinflammatory responses in these brain injuries, mediated through binding to the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE), toll-like receptor4 (TLR4) and other inflammatory mediators. Moreover, we provide evidence on the biomarker potential of HMGB1 and the significance of its nucleocytoplasmic translocation during brain injuries along with the promising neuroprotective effects observed upon HMGB1 inhibition/neutralization in TBI and EBI induced by SAH. Overall, this review addresses the current advances on neuroinflammation driven by HMGB1 in brain injuries indicating a future treatment opportunity that may overcome current therapeutic gaps.
- high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1)
- traumatic brain injury (TBI)
- subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)
- neuroinflammation
- biomarker
Introduction
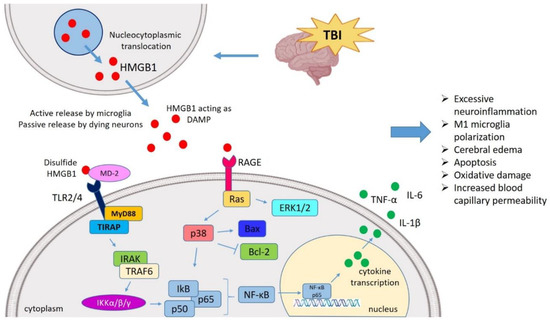
Insights into the HMGB1 Biology
HMGB1 Targeted Therapies against Brain Injuries
HMGB1 Neutralization against TBI
| S.N. | Study Model | Intervention and Dosing Schedule | Observations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FPI-induced TBI in adult male Wistar rats | Anti-HMGB1 mAb (1 mg/kg, I.V.) was administered at 5 min and 6 h after TBI |
|
[102] |
| 2 | ICH-induced brain injury in male Wistar rats | Anti-HMGB1 mAb (1 mg/kg, I.V.) was administered immediately and 6 h after ICH. |
|
[103] |
| 3 | FPI-induced TBI in adult male Wistar rats | Anti-HMGB1 mAb (1 mg/kg, I.V.) was administered at 5 min and 6 h after TBI |
|
[12] |
| 4 | CCI-induced TBI in male C57Bl/6 mice | GL (for acute recovery study) (50 mg/kg, I.P.) was administered 1 h, 6 h, 1 d and 2 d post-injury, plus 1 h pre-injury. GL (for chronic recovery study) was administered 1 h pre-injury, at 1 h, 6 h post-injury, plus once daily for 7 added days for 1 week. |
|
[21] |
| 5 | TBI induced by modified Feeney’s free weight drop method in male SD rats | GL (10 mg/kg, I.V.) administered 30 min after TBI |
|
[64] |
| 6 | FPI-induced TBI in adult male Wistar rats | GL (0.25, 1.0 or 4.0 mg/kg, I.V.) was administered 5 min after injury |
|
[59] |
| 7 | ICH-induced injury in male SD rats | GL (50 mg/kg) was administered 20 min post-ICH, and then once daily for 3 days. |
|
[113] |
| 8 | DAI-induced brain injury in adult SD rats | Glycyrrhizic acid (GA) (10 mg/kg, I.V.) administered 30 min before DAI |
|
[114] |
| 9 | Weight-dropping TBI model in male adult SD rats | Ethyl pyruvate (EP) (75 mg/kg, I.P.) prepared at 30 min, 1.5 h, and 6 h |
|
[60] |
| 10 | Feeney’s weight drop model in male SD rats | EP (75 mg/kg, I.P.) administered 5 min, 1 h, and 6 h post-TBI |
|
[108] |
| 11 | CCI-induced TBI in male SD rats | Minocycline (90 mg/kg, I.P.) was administered 10 min and 20 h after injury |
|
[65] |
| 12 | Feeney DM TBI model in adult male SD rats | ω-3 PUFA (2 mL/kg, I.P.) was administered 30 min after TBI, each day for 1 week. |
|
[44] |
| 13 | Feeney DM TBI model in adult male SD rats | ω-3 PUFA (2 mL/kg, I.P.) was administered 30 min post-TBI, each day for 1 week. |
|
[111] |
HMGB1-Targeted Therapy Attenuates EBI Post-SAH
| S.N. | Study Model | Intervention and Dosing Schedule | Observations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Endovascular puncture model of SAH adult male Wistar rats | Anti-HMGB1 mAb (1 mg/kg, I.V.) was administered post-SAH, twice at an interval of 24 h. |
|
[13] |
| 2 | Endovascular perforation model of SAH adult male SD rats | Anti-HMGB1 mAb (1 mg/kg, I.V.) was administered post-SAH, twice at an interval of 24 h. |
|
[81] |
| 3 | Prechiasmatic cistern SAH model in male SD rats | Glycyrrhizin (GL) (15 mg/kg, I.P.) was administered immediately and then 6, 12 and 18 h post-SAH. |
|
[85] |
| 4 | SAH in male SD rats | GL (5 mg/kg/day) was administered 24 h prior (precondition) and 1 h post-SAH (treatment). |
|
[120] |
| 5 | Modified double-hemorrhage SAH model in male SD rats | Glycyrrhizic acid (GA) (10 mg/kg, I.P.) was administered immediately after SAH and was continued for three consecutive days. |
|
[87] |
| 6 | Endovascular perforation induced SAH in male SD rats | AG490 (inhibitor of JAK2/STAT3) (2 mL, I.V.) was administered 30 min before SAH |
|
[76] |
| 7 | Prechiasmatic cistern SAH model in male SD rats | Resveratrol (60 mg/kg, I.P.) was administered at 2 and 12 h post-SAH. |
|
[116] |
| 8 | Double-hemorrhage SAH model in male SD rats | Purpurogallin (100, 200 and 600 mg/kg/day) was administered 1 h after SAH. |
|
[117] |
| 9 | Prechiasmatic cistern SAH model in SD rats | Melatonin (150 mg/kg, I.P.) was administered 2 and 24 h after SAH. |
|
[119] |
| 10 | Rodents SAH model in male SD rats | Rhinacanthin-C (RCT-C) (100, 200, and 400 µmol/kg/day) was administered orally 1 h after SAH and every 12 h. |
|
[118] |
| 11 | Double-hemorrhage SAH model in male SD rats | 4OGOMV (100, 200 and 400 µg/kg/day) was administered 1 h post-SAH. |
|
[121] |
Discussion and Future Suggestions
Conclusions
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms21134609
