Tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP) is an ectoenzyme bound to the plasma membranes of numerous cells via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) moiety. TNAP is one of many proteins localized to Brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs), and is highly abundant in human and rodent cerebral microvessels [33]. There are four alkaline phosphatase (AP) isoenzymes in humans and they include: TNAP, germ cell alkaline phosphatase (GCAP), intestinal alkaline phosphatase (IAP), and placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP). Although TNAP is ubiquitous in many tissue, it is most highly expressed in bone, liver, intestine, kidney, and brain, while the three other AP isoenzymes are expressed in the tissues for which they are named. TNAP is also highly expressed in cerebral microvessels.
- brain microvascular endothelial cells
- cerebral microvessels
- tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase
- Alpl
- TNAP
- cerebrovascular
1. TNAP Biology
1.1. Cell Biology
1.2. Global Gene Expression and Enzyme Activity
1.3. Gene Expression and Enzyme Activity in BMECs
| Animal Models | TNAP Activity in Cerebral Microvessels | Gene Name | Time Period When First Detected in CNS | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zebrafish | Activity is present in the brain parenchyma and vessels | alpl | 11 h post-fertiilzation (hpf) | [78] |
| Mouse | Strong activity in vessels and weaker activity in the brain parenchyma | Alpl or Akp2 | Embryonic day 7–14 | [59,64] |
| Rat | Strong activity in vessels and weaker activity in the brain parenchyma | Alpl or Akp2 | Embryonic day 15 | [54,64] |
| Guinea Pig | Strong activity in vessels and weaker activity in the brain parenchyma | Alpl | - | [64] |
| Frog | Activity is absent on vessels but present on inner arachnoid and perineurium | alpl | - | [68] |
| Chicken | Weak activity in vessels and strong activity in the brain parenchyma | ALPL | Day 2 of the incubation period | [64,79] |
| Rabbit | Activity is absent in vessels but strong in brain parenchyma | ALPL | - | [64] |
| Cat | Strong activity in vessels and weaker activity in the brain parenchyma | ALPL | - | [64] |
| Rhesus Monkey | Strong activity in vessels and laminar activity pattern in the brain parenchyma (i.e., some areas/layers have higher activity than others) | ALPL | - | [80] |
| Human | Strong activity in vessels and laminar activity pattern in the brain parenchyma (i.e., some areas/layers have higher activity than others) | ALPL | 28 weeks of gestation | [63,81] |
2. Models and Tools to Study TNAP
2.1. Mouse Models
| Mouse Model Type | Cre-Mediated Target Cell | Preclinical Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNAP OE | Vascular smooth muscle cells (Tagln-Cre or SM22-Cre) | Mice had increased AP enzyme activity, increased systolic blood pressure, and increased vascular calcification. Male TNAP-OE mice lifespan was shorter than WT controls, as all died by 5 months of age. | [90] |
| TNAP OE | Endothelial cells (Tie2-Cre) | Increased AP activity was localized to the luminal side of the aorta and vascular networks of heart, lung, kidney, liver, small intestine, and pancreas. No skeletal abnormalities were detected; however, in the heart, kidney, mesentery, pancreas, spleen, and lung parenchyma there were calcified lesions in adult mice. | [91] |
| TNAP OE with “wicked high cholesterol” (C57BL/6J-LdlrHlb301/J) | Endothelial cells (Tie2-Cre) | Mice displayed increased AP activity in endothelial cells and increased sub-endothelial calcification nodules in their coronary arteries, which recapitulates murine atherosclerosis. | [92,93] |
| TNAP OE | Endothelial cells (Cdh5-Cre) | Over-expression of TNAP on endothelial cells resulted in increased survival and decreased clinical severity post-sepsis compared to controls. Locomotor activity in the last 5 min of open field testing was also increased in VE-cOE mice compared to controls. | [35] |
| TNAP KO | Osteoblasts and odontoblasts (Col1a1-Cre); Early limb bud mesenchyme and a subset of craniofacial mesenchyme (Prx1-Cre) |
While both Cre recombinase drivers result in similar phenotypes with regards to skeletal defects in cortical and trabecular bone, Prx1-cKO mouse long bones appeared more severely affected. Both models resulted in increased osteoclast numbers on alveolar bone surfaces and reduced alveolar bone height. Both models resulted in cementum and periodontal ligament defects, consistent with periodontal disease. | [94] |
| TNAP KO | Endothelial cells (Cdh5-Cre) | Primary BMECs revealed decreased barrier integrity compared to controls, which was mitigated after treatment with fasudil. | [37] (results reported in a preprint) |
2.2. TNAP Pharmacological Tools and Pharmaceuticals
3. TNAP in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Health and Function
3.1. TNAP and the Heterogeneity of the Brain’s Vasculature
3.2. Potential Mechanism(s) of Action for TNAP in the Brain’s Vasculature
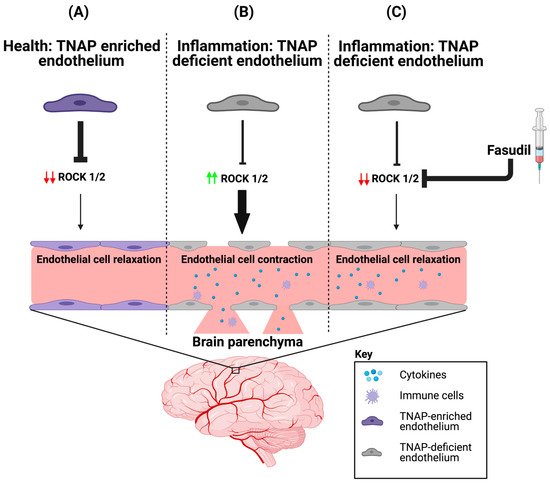
4. A Role for Endothelial TNAP in the Brain’s Microvasculature in Aging and Disease
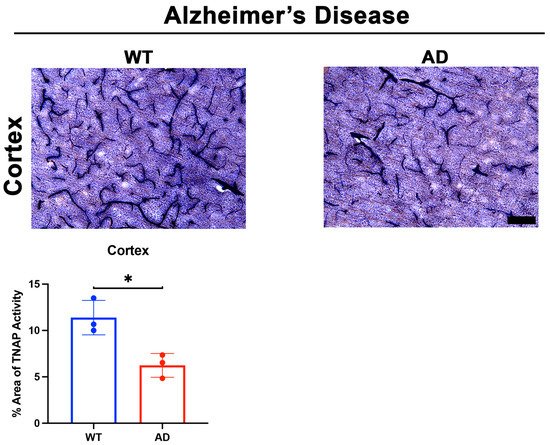
4.1. Brain Microvascular TNAP in Disease
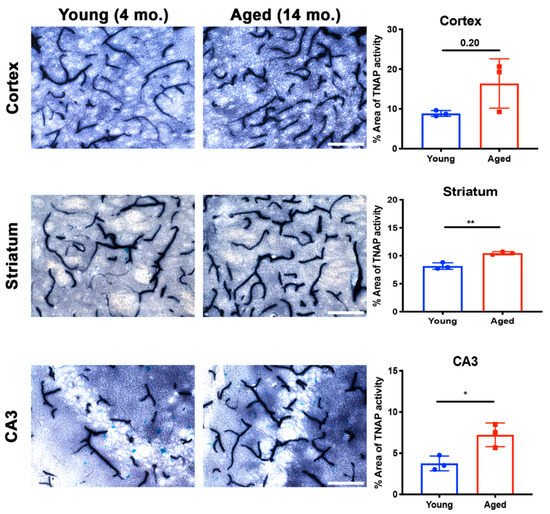
4.2. Brain Microvascular TNAP in Aging
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms22105257
