Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) belong to the superfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The family of mAChRs is composed of five subtypes, M1, M2, M3, M4 and M5, which have distinct expression patterns and functions. In the eye and its adnexa, mAChRs are widely expressed and exert multiple functions, such as modulation of tear secretion, regulation of pupil size, modulation of intraocular pressure, participation in cell-to-cell signaling and modula-tion of vascular diameter in the retina. Due to this variety of functions, it is reasonable to assume that abnormalities in mAChR signaling may contribute to the development of various ocular diseases. On the other hand, mAChRs may offer an attractive therapeutic target to treat ocular diseases. Thus far, non-subtype-selective mAChR ligands have been used in ophthalmology to treat dry eye disease, myopia and glaucoma. However, these drugs were shown to cause various side-effects. Thus, the use of subtype-selective ligands would be useful to circumvent this problem.
1. Introduction
In 1914, Henry Dale first observed that the actions of acetylcholine (ACh) could be divided into nicotine-like and muscarine-like effects, respectively [
1]. Preganglionic parasympathetic neurons release neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, from synaptic vesicles of axon terminals into the synaptic cleft. From there, neurotransmitters can bind to receptors in postganglionic parasympathetic cell membranes [
2]. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) are widely localized on postganglionic parasympathetic neurons and are widely expressed in the central nervous system [
3]. Apart from neurons, mAChRs are expressed on many other cell types [
4]. In the eye and its adnexa, mAChRs were found to be expressed in the cornea, lens, uvea, conjunctiva, sclera, retina and the lacrimal gland [
5,
6,
7,
8]. Hence, it is not surprising that mAChRs are involved in diverse important physiological functions in the eye, such as tear fluid production, goblet cell secretion, keratocyte migration and proliferation, pupil size regulation, ocular drainage, lens cell signaling and ocular growth as well as cell-to-cell signaling and vascular reactivity in the retina [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. An increasing number of studies demonstrates that mAChRs are potential pharmacological targets for the treatment of various ocular diseases, such as glaucoma and myopia [
14,
15].
Glaucoma is a neurodegenerative disease, which is characterized by the impairment and loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and optic nerve fibers, which may lead to irreversible blindness [
16]. It has been estimated that there are around 80 million people with glaucoma worldwide [
17]. According to another estimate, the global number of people affected by glaucoma will increase to 111.8 million in 2040 [
18]. Although elevated intraocular pressure is a major risk factor for glaucoma, several population-based studies reported that intraocular pressure is within the normal range in a large portion of individuals with glaucoma [
19,
20]. In clinical practice, lowering intraocular pressure (IOP) is essential to prevent development and progression of the disease and to preserve the patients’ quality of life [
16]. However, in almost half of the patients the disease continues to progress despite normalization of IOP [
21]. Hence, novel complementary retinal neuroprotection strategies would be valuable to reduce progressive neurodegeneration in the retina [
22]. Pathologic myopia with characteristic degenerative changes in the sclera, choroid, and retinal pigment epithelium is a major cause of visual impairment and blindness worldwide by increasing the risk for ocular complications, such as macular degeneration, retinal detachment and glaucoma [
23]. The global prevalence of pathologic myopia is rising rapidly, especially in the younger Asian population [
24]. Holden et al. projected that by 2050 the number of people with myopia will increase to 4.758 billion (49.8% of the global population), and 938 million people (9.8% of the world’s population) will have high myopia [
25]. There is still no effective therapy in the clinical routine to prevent the progression of pathologic myopia, which makes the disease an increasing global health concern.
MAChRs belong to the class of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) containing seven transmembrane segments, which transfer signals into the cell via coupling with G-proteins. The G-proteins modulate the activity of a number of different effectors, such as ion channels and enzymes [
26,
27]. The mAChR family is composed of five subtypes, M
1, M
2, M
3, M
4 and M
5 with different molecular and signaling properties [
3,
28,
29]. For example, M
1, M
3 and M
5 have been reported to typically couple to G proteins of the Gq/11 family. However, M
2 and M
4 receptors have been shown to preferentially couple to G proteins of the Gi and Go family [
3,
29]. Some studies reported that mAChR agonists reduce IOP and exert neuroprotective effects in glaucoma [
30,
31,
32]. The non-subtype-selective mAChR antagonist, atropine, has been shown to inhibit scleral proliferation and matrix synthesis, and to prevent axial elongation of the eyeball providing a novel therapeutic approach for myopia control [
14,
33]. Unfortunately, non-subtype-selective mAChR agonists may exert ocular adverse effects in clinical practice, which are related to its constricting effects on the ciliary and pupillary sphincter muscle and systemic adverse effects including increased salivation and sweating, vomiting, diarrhoea and tachycardia [
34,
35]. For example, the non-subtype-selective mAChR agonist, pilocarpine, which has been used for long-term IOP control can cause blurred vision, brow ache from ciliary spasm and rarely retinal detachment [
35]. In addition, the non-specific mAChR antagonist, atropine, acutely induces cycloplegia and photophobia and on the long term might cause premature presbyopia, cataract, and light damage in the retina [
36].
To design more specific mAChR-based therapeutic approaches with less side-effects, it is crucial to identify the distribution and physiological function of individual mAChR subtypes and to test the use of highly subtype-selective ligands in laboratory and clinical studies. In this review, we summarize and discuss the localization, the functional and the pathophysiological role of individual mAChR subtypes in the retina. Additionally, we discuss potential therapeutic strategies targeting individual mAChR subtypes.
The identification of literature was carried out via a search on PubMed. The PubMed database search included the following keywords: ((“muscarinic acetylcholine receptors” OR “muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes” OR “muscarinic receptors” OR “mAChR” OR “mAChR subtypes” OR “M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor” OR “M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor” OR “M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor” OR “M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor” OR “M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor” OR “muscarinic receptor antagonist” OR “muscarinic receptor agonist”) AND (“retina” OR “ocular” OR “RGC” OR “glaucoma” OR “IOP” OR “diabetes” OR “retinal models”)). The search was conducted from 13 March to 28 March 2021 with the following inclusion criteria: all studies, muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the retina, written in English and published after 1976. In total, the study search resulted in 268 publications. Studies reporting the roles of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in other organs except for eyes were excluded.
2. Expression and Distribution of mAChRs in the Retina
Based on studies with the labeled radioligands, [
3H]propylbenzilylcholine mustard ([
3H]PrBCM), [
3H]N-methylscopolamine ([
3H]NMS) and [
3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate ([
3H]QNB), a high density of muscarinic binding sites has been demonstrated in rat, bovine and chick retinas, whereas relatively few binding sites have been detected in frog and salamander retinas [
37,
38,
39]. Autoradiographic experiments in embryo and adult chicken retinas revealed specific mAChR binding sites in the inner synaptic retinal layer [
40]. In 1985, Polans et al. found a high density of muscarinic binding sites in the inner plexiform layer (IPL) and the outer plexiform layer (OPL) of the salamander retina [
41]. In the same year, Hutchins and Hollyfield presented evidence for a population of mAChRs in the human retina, apparently expressed in the IPL, by using the irreversible ligand, [
3H]PrBCM [
42].
Based on autoradiographic experiments, it has been suggested in 1988 that mAChR subtype number and distribution change during retinal development [
43]. Later, experiments in the ferret retina suggested that the subtypes, number and distribution of mAChRs changes during retinal synaptogenesis [
44]. In the study, mAChR-like immunoreactivity was found at amacrine–amacrine cell contacts by electron microscopy and immunohistochemical techniques [
44]. Townes-Anderson and Vogt found that mAChRs in the salamander retina are located on amacrine/ganglion, bipolar, and horizontal cells [
45]. In 1988, Moroi-Fetters found that stimulation of muscarinic receptors by the subtype-preferring M
1 receptor antagonist, pirenzepine, in the rat retina causes phosphoinositide hydrolysis, which indicated that these receptors appear to be of the M
1 subtype [
46].
In 1989, all five mAChR subtypes (M
1, M
2, M
3, M
4 and M
5) were identified [
47,
48]. Molecular cloning techniques provided a new molecular basis to characterize expression, location and physiological function of all five mAChRs [
49]. In 1997, McKinnon et al. examined regulation of mAChR expression in the chicken embryonic retina by using immunoblot, immunoprecipitation and solution hybridization analyses [
50]. The authors reported that the M
4 receptor is the main subtype expressed at an early stage in embryonic development, while M
2 and M
3 receptor expression increases at a later stage [
50].
However, the precise anatomical location of mAChRs in the retina remained unknown at that time. One year later, Fischer et al. used purified and subtype-specific antibodies directed against M
2, M
3 and M
4 subtypes to detect receptor immunoreactivity in the retina. The study revealed that in the chick retina the M
2 receptor was expressed in amacrine and ganglion cells, the M
3 receptor was expressed in many bipolar cells and small subsets of amacrine cells and the M
4 receptor was found in amacrine and ganglion cells [
51]. In an in vitro and in vivo study, Belmonte et al. demonstrated that retinal Müller glial cells can secrete a factor called MARIA (muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-inducing activity) that can regulate M
2 expression in vitro and in vivo [
52]. Another in vitro study demonstrated the presence of the M
1 receptor in cultured human retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) at both the mRNA and the protein level [
53]. The expression of M
1 receptor mRNA was also observed in the guinea pig retina, and immunohistochemical findings revealed that the M
1 receptor was expressed in all layers of the retina [
54]. Strang et al. used RT-PCR, Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry to identify the expression and distribution of mAChR subtypes in the rabbit retina [
55]. The authors detected mRNA expression for all five mAChR subtypes in the whole neural retina by RT-PCR and Western blotting, and they confirmed that all five mAChR subtypes were expressed by subpopulations of bipolar, amacrine, and ganglion cells by immunohistochemical analyses [
55]. According to a study by Gericke et al. in 2011, only mRNA for the M
3 receptor was detected in murine retinal arterioles [
56]. In contrast, mRNA for all five mAChR subtypes was detected in ophthalmic arteries, but mRNA levels for the odd-numbered subtypes, M
1, M
3 and M
5, were higher than those for the even-numbered subtypes, M
2 and M
4 [
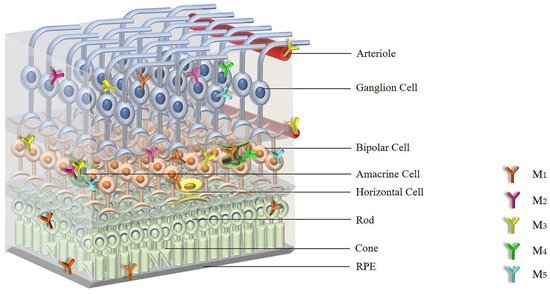
57]. shows the distribution of mAChRs within the retina.
Figure 1. The distribution of individual mAChR subtypes in the retina. Abbreviations: mAChRs: muscarinic acetylcholine receptors; RPE: retinal pigment epithelium; M1: M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor; M2: M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor; M3: M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor; M4: M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor; M5: M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor.
Based on the expression studies, all five mAChR subtypes have been detected in the retina with the individual subtypes showing an overlapping expression pattern.
3. Cellular Signaling of mAChRs
Peralta et al. and Bonner et al. first cloned and sequenced human mAChRs, which are encoded by the
CHRM1 to
CHRM5 genes [
58,
59]. The genes give rise to the five subtypes, M
1, M
2, M
3, M
4 and M
5 [
3]. The mAChR family belongs to the superfamily of seven-transmembrane receptors, which mediates cellular signal transduction pathways via G-proteins [
60]. The M
1, M
3 and M
5 subtypes, which efficiently couple to Gq/11 subtype G proteins, can mobilize phosphoinositides to generate inositol 1, 4, 5-triphosphate (IP3) and 1, 2-diacylglycerol (DAG) via activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase Cβ (PLCβ), leading to an increase in intracellular cytosolic calcium (Ca
2+) levels and protein kinase C (PKC) activity [
61]. This may help to stimulate nitric oxide (NO) production, since neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) is calcium/calmodulin-dependent [
62]. The M
2 and M
4 receptors preferentially couple to pertussis toxin-sensitive Gi and Go proteins, causing an inhibition of the cAMP-dependent pathway via suppression of adenylyl cyclase [
63]. Furthermore, both Gq/11-, Gi/o-coupled with mAChRs may exert effects through activation of small GTPases, such as Rho and Ras, and downstream effectors, such as phosphoinositide-3 kinases and mitogen-activated protein kinases [
60].
Muscarinic receptors play an important role in the development of the retina and in processing visual information [
64]. For example, mAChRs regulate the function of bipolar cells in the ON/OFF channel, and the input and output of amacrine, bipolar, ganglion and horizontal cells [
52,
64]. Additionally, Jardon et al. suggested that a cholinergic loop of amacrine cells could be involved in the inhibitory pathway from the ON channel to the OFF channel in the frog retina carrying “light on” and “light off” information from the retina to the brain [
65,
66]. Muscarinic cholinergic transmission exerts a substantial contribution in the retina [
67]. In an in vitro study, the muscarinic antagonist, QNB, enhanced the amplitude of the electroretinogram (ERG) b-wave (a measure of ON bipolar cell activation), and induced moderate vasoconstriction in the cat retina [
67].
Although mAChRs regulate many important cellular signaling pathways, it is difficult to assign specific functional roles for individual mAChR subtypes in the retina. Jositsch et al. tested the specificity of mAChRs antibodies under different conditions in immunohistochemical labelling on tissue sections by analyzing specimens from respective gene-deficient mice and wild-type mice [
68]. The data indicated that immunohistochemical detection of mAChR subtypes in tissue sections is limited to the M
2 subtype [
68]. It has been reported that cells frequently co-express more than one mAChR subtype that increases the difficulty of assigning a functional response to a single receptor subtype [
3]. The lack of highly selective pharmacological ligands and antibodies for individual mAChR subtypes has hampered conclusions regarding the physiological role of individual muscarinic receptor subtypes. The development of genetically modified mice devoid of M
1- to M
5 receptors helped to circumvent the problem of assigning a specific function to an individual mAChR subtype [
69,
70,
71,
72,
73,
74,
75]. M
1-M
5 receptor knockout mouse models (M
1-M
5R−/−) have also been used in studies of ocular tissues.
For example, Barathi et al. studied the role of each of the mAChR subtypes in the development of myopia by using M
1-M
5R−/− mice [
76]. The authors found that M
2 receptors play a crucial role in myopia development by hindering scleral fibroblast cell proliferation and further scleral remodeling [
76]. Based on studies in M
3R−/− mice, Gericke et al. showed that the M
3 receptor is responsible for mediating cholinergic responses in retinal arterioles and the ophthalmic artery [
56,
57,
77]. Laspas examined the amount of cells in the retinal ganglion cell (RGC) layer and the amount of axons in the optic nerve in 5-month-old M
1R−/− and wild-type mice and found no significant difference between both groups [
78]. More recently, the same laboratory conducted experiments in 5- and 15-month-old M
1R-M
5R−/− mice to examine whether one of the mAChRs and age have an influence on neuron survival in the retina [
30]. Based on these studies, the M
1 receptor was found to be critical for RGC survival in the aging mouse retina [
30]. These examples show how genetically modified mice may help to better understand the physiological roles of individual muscarinic receptor subtypes in the retina.
4. Functional Roles of Individual mAChR Subtypes in the Retina
According to their differential coupling to intracellular signaling cascades, the mAChR subtypes have been divided into two subfamilies, the “M
1-like” mAChR subfamily and the “M
2-like” mAChR subfamily [
79]. The odd-numbered subtypes, M
1, M
3, and M
5, belong to the “M
1-like” family, which couple to the Gq protein and activate phospholipase C (PLC)-dependent signaling pathways. In neuronal tissue, activation of this signaling cascade increases neuronal excitability through activation of nonspecific cation channels, release of Ca
2+ from intracellular stores, or inhibition of Ca
2+-activated K
+ channels [
80]. On the contrary, members of the “M
2-like” family, the even-numbered M
2 and M
4 receptor subtypes, are generally linked to inhibition of adenylyl cyclase activity [
79]. Activation of M
2 and M
4 receptors decreases neuronal activity via activation of a subset of K
+ channels, the inhibition of Ca
2+ channels, or the inhibition of the Ca
2+ priming of K
+ channels [
55,
81,
82]. This suggests that the different subtypes may subserve different functions in the retina.
A plethora of studies demonstrated that the M
1 muscarinic receptor subtype may be crucial for neuron survival in the retina [
30]. For example, M
1 receptor activation protected retinal neurons from glutamate-induced cytotoxicity [
83]. It has been proposed that activation of M
1 receptors reduces Ca
2+ influx into the cell and the expression of Bcl-2 and Caspase-3 [
62,
83,
84]. This effect can be blocked by the M
1-preferring muscarinic receptor antagonist, pirenzepine [
84]. Additionally, activation of M
1 receptors significantly increases the survival of RGCs in vitro [
85]. Pereira et al. indicated that the mechanism involved in M
1 receptor activity and the survival of RGCs is by the release of polypeptides and activation of insulin receptor kinase receptors [
85]. An in vitro study demonstrated that activation of mAChRs effectively protects against hypoxia-induced apoptosis in RGCs via modulation of the hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) pathway [
86]. Based on these in vitro data, Laspas et al. conducted a study in 5-month-old M
1R−/− mice and age-matched wild-type mice to test the neuroprotective role of the M
1 receptor in vivo. However, the authors found no differences in the number of retinal neurons and the amount of optic nerve axons between M
1R−/− and wild-type mice [
30]. In a more recent study in 2019, Laspas et al. examined the potential role of all five muscarinic receptor subtypes on neuroprotection in the RGC layer in congenic mAChR−/− mice of different age categories [
30]. Intriguingly, the authors observed that the lack of the M
1 receptor was associated with a reduced RGC density in aged mice. Aged M
1R−/− mice also displayed elevated ROS levels in the RGC layer and increased retinal mRNA expression for the prooxidative NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2) and reduced mRNA levels for the antioxidative enzymes, superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1), hemeoxygenase-1 (HO-1) and anti-glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPx1) [
30]. The findings provided the first direct evidence that the lack of the M
1 receptor leads to accelerated RGC loss in mice via changing in the oxidative/antioxidative balance in favor of oxidative in the retina [
30]. L-satropane was reported to be effective in preventing retinal neuron damage, which may be attributed to decreasing cell apoptosis and amyloid-β (Aβ) production via activation of M
1 receptor subtype [
87]. Moreover, in an in vivo study, the M
1 muscarinic receptor was reported to exert protective effects on RGCs via activation of insulin growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and insulin growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) [
88]. Additionally, activation of PKC delta was suggested to regulate neurotrophin levels by M
1 muscarinic receptor activation ultimately leading to an increase in RGCs’ survival in vitro in the retina [
89,
90]. In 2021, an in vivo study in rats showed that huperzine A lowers intraocular pressure via the M
3 receptor and exerts neuroprotective effects in the retina by increasing endogenous ACh levels and activating M
1 receptors and their downstream AKT/MAPK signaling pathways [
31].
Braga et al. first analyzed the levels of M
3 receptors in retinal cell cultures treated with 50 ng/mL phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA, a PKC activator) for 48 h. PMA induced a marked increase in M
3 receptor levels [
91]. Based on pharmacological studies employing muscarinic subtype-preferring antagonists, Borda et al. observed that carbachol can stimulate NOS activity and increase the expression of nNOS and iNOS mRNA in the rat retina via activation of M
1/M
3 receptor subtypes [
92,
93].
The expression of nicotinic AChR (nAChR: α3, α4, α6, α7, β2 and β4 nAChR subunits) and/or mAChR by amacrine and ganglion cells has been described in retinas of Rhesus monkeys and rabbits [
94,
95,
96]. Retinal nAChRs mediate visual processing and may have effects on refractive development and ocular neovascularization [
94]. In the retina, there was an overlap in the expression patterns of M
1, M
4 and M
5 muscarinic receptors with those of non-α7 and α7 nAChRs in presumptive amacrine and ganglion cells [
97]. Strang et al. suggest that the determining the role of mAChRs in retinal processing is complicated by the concomitant expression of nAChRs by the same cells [
55]. A study in α7 nAChR−/− mice demonstrated that M
2 and M
4 mAChR subtype transcripts were significantly upregulated in the RGC layer [
98].
There are not many studies on the functional role of M
2 receptors in the retina. Several pieces of evidence suggest that activation of M
2 and M
4 receptors is involved in visual processing [
55]. The M
2 receptor has been reported to increase Ca
2+ influx, exclusively due to Ca
2+ mobilization from intracellular stores [
99]. The M
2 muscarinic receptor was shown to inhibit adenylyl cyclase activity and to activate inwardly rectifying potassium (K
+) channels [
100]. However, these responses can be rapidly attenuated by receptor desensitization [
100,
101]. Antal et al. found that activation of M
2 receptors regulates feedforward inhibition following activation of RGC synapses in a manner that is strongly dependent on the number of activated RGCs [
102]. Cimini et al. indicated that the production of NO in response to M
2 muscarinic receptor activation may lead to an increase in cGMP, which can modulate the mutual interactions of acetylcholine-glycine-gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the inner retina [
103].
The M
4 receptor exerts a direct inhibitory control on dopamine D
1-like receptor signaling [
104]. In a rat glaucoma model, Almasieh et al. demonstrated that activation of M
1 and M
4 receptors promotes RGCs’ survival [
15]. Moreover, the partially selective M
1/M
4 muscarinic antagonist, pirenzepine, was reported to be successful in preventing myopia progression in animal models [
105]. The M
4-selective antagonist, himbacine, could also prevent myopia in chicken by daily intravitreal injections [
106].
All these studies provide evidence that individual mAChRs exert specific functional roles in the retina, which offers new therapeutic perspectives for mAChR ligands. A variety of studies reported associations of endothelial NOS (eNOS) genetic polymorphism or adrenergic receptor gene polymorphisms with retinal diseases [
107,
108]. Additionally, mAChR subtype gene polymorphisms have been reported [
109]. Unfortunately, studies on mAChR genetic polymorphisms with respect to retinal diseases have not been reported so far [
109]. Such studies would be appreciated to shed some light on the role of mAChR in the development of specific retinal diseases.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms22094989