The digital revolution is transforming education by using information and communication technologies (ICTs) to improve student's learning outcomes. In the last 50 years, changes can be seen in every area of society, such as culture, entertainment, and social interaction. However, the current educational model is very similar to how it was back then. Due to the characteristics of mobile devices, and the inexperience of teachers and educational institutions, students may experience distractions in their learning and may be involved in inefficient educational methodologies. Digital revolution is transforming these educational models, involving students, teachers, and educational institutions in this process[3]. The appropriate use of digital technologies and a pedagogical approach in the design of learning models could generate an improvement in the learning results of the students. Today’s world demands more efficient learning models that allow students to play a more active role in their education. Technology is having an impact on how instruction is delivered and how information is found and share. Until very recently, the educational models encouraged memorization as an essential learning skill. These days, technologies have changed the educational model and access to information. Knowledge is available online, mostly free, and easily accessible. Reading, sharing, listening and, doing are currently necessary skills for education. The study of innovation in education systems has increasingly attracted the attention of academics around the world. Educational innovation refers to new ways of delivering education in a way that impacts new generations of students. The educational model in higher education institutions (HEIs) was not designed for this generation of "digital natives". Therefore, HEIs face the challenge of improving their teaching strategies and making them attractive to students and their needs. Mobile devices have become a complete set of applications, support, and help for educational organizations. By conducting an analysis of the behavior and use of mobile devices on current students, efficient educational applications can be developed. Although there are several initiatives for the use of mobile learning in education, there are also issues linked to this technology that must be addressed.
- mobile learning
- learning
- education
- mobile education
- technologies
1. Introduction
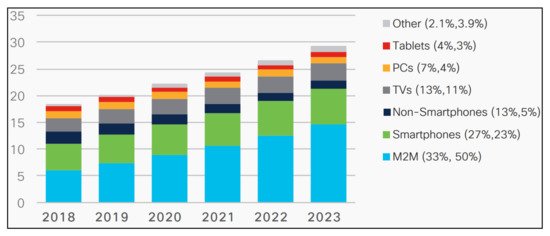
2. Use of Mobile Devices in Education
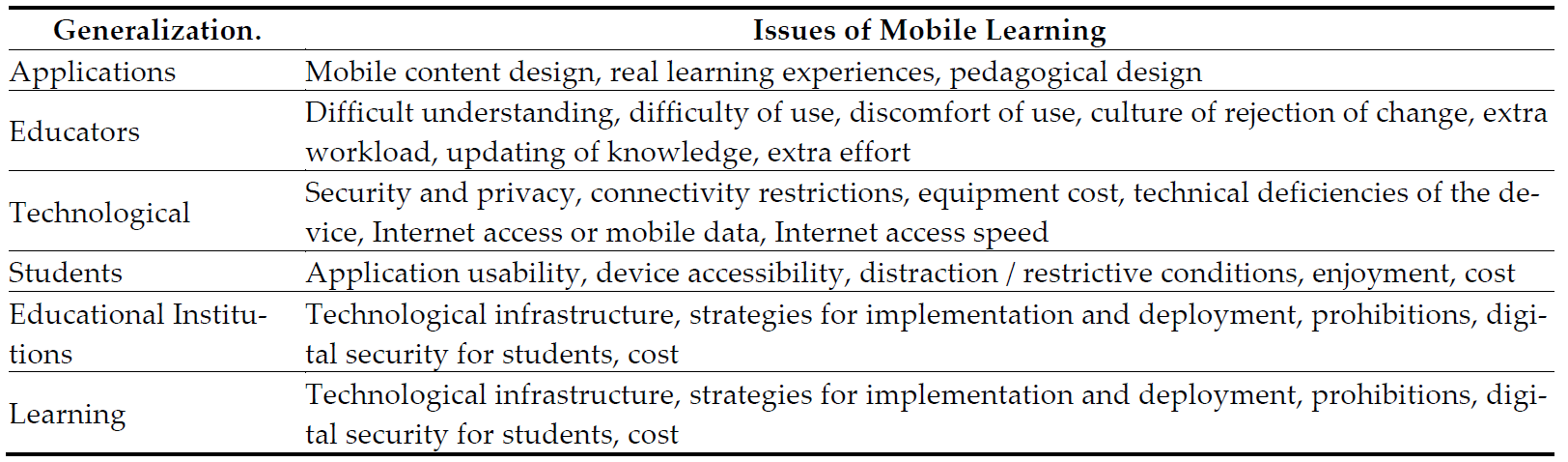
3. Issues of using mobile learning in education
4. Benefits of using mobile learning in education

5. Conclusions
The general analysis of the research indicates students are predisposed to use their mobile devices in the teaching-learning process because they are familiar with their utilization. Moreover, the success of m-learning is highly dependent on the educational institution, the teachers involved, and the students. Due to the physical characteristics of mobile devices, technological limitations are one of the main issues this technology has for its use in the educational area.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/app11094111
References
- Fombona, J; Pascual, M. A.; Ferra, M. P.; Analysis of the educational impact of M-learning and related scientific research. J. New Approaches Educ. Res 2020, 9, 167 - 180, 10.7821/naer.2020.7.470.
- Alhumaid, K; Four Ways Technology Has Negatively Changed Education. J. Educ. Soc. Res 2019, 9, 10-20, 10.2478/jesr-2019-0049.
- Krull, G.; Duart, J. M.; Research trends in mobile learning in higher education: A systematic review of articles (2011 - 2015). nt. Rev. Res. Open Distance Learn 2017, 18, 1-23, .
- Criollo-C, Santiago; Luján-Mora, Sergio; Jaramillo-Alcázar, Ángel; Advantages and disadvantages of m-learning in current education. Proceedings Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, x FOR PEER REVIEW 16 of 19 IEEE World Engineering Education Conference 2018, 0, 0, 10.1109/EDUNINE.2018.8450979.
- Annual Internet Report (2018 - 2023) . Cisco: Annual Internet Report. Retrieved 2021-5-7
- Kukulska-Hulme, A.; Pettit, J.; Bradley, L.; Carvalho, A.A.; Herrington, A.; Kennedy, D.M.; Walker, A. Mature Students Using Mobile Devices in Life and Learning. Int. J. Mob. Blended Learn. 2011, 3, 18–52.
- Sobral, S R; Mobile learning in higher education: A bibliometric review. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies 2020, 14, 153-170, 10.3991/ijim.v14i11.13973.
- Sattler, B; Spyridakis, N; Ramey,J; The learning experience: A literature review of the role of mobile technology. IEEE Int. Prof. Commun 2010, 0, 38-45, 10.1109/IPCC.2010.5529811.
- Bucea-Manea-Tonis, R; Bucea-Manea-Tonis, R; Simion, V.E.; Ilic, D.; Braicu, C.; Manea, N; Sustainability in higher education: The relationship between work-life balance and XR e-learning facilities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5872, 10.3390/su12145872.
- Sattler, B; Spyridakis, N; Ramey,J; The learning experience: A literature review of the role of mobile technology. IEEE Int. Prof. Commun 2010, 0, 38-45, 10.1109/IPCC.2010.5529811.
