Over the last two decades, oxide nanostructures have been continuously evaluated and used in many technological applications. The advancement of the controlled synthesis approach to design desired morphology is a fundamental key to the discipline of material science and nanotechnology. These nanostructures can be prepared via different physical and chemical methods; however, a green synthesis approach is a promising way to produce these nanostructures with desired properties with time and energy savings and/or less use of hazardous chemicals. In this regard, ZnO and TiO2 nanostructures are prominent candidates for various applications given their thermal stability, non-toxicity and cost-effective.
Note: The following contents are extract from your paper. The entry will be online only after author check and submit it.
1. Introduction
Green technologies have gained enormous attention over the last decade. Natural resources are being depleted daily, and the green approach appears to be a prominent solution without destroying natural resources. This technology deals with the fabrication of nanomaterials and their applications in the medical, sensor, optoelectronics, energy, food industries, etc. [1]. There are many physical and chemical methods of preparing metal nanoparticles (NPs) and metal oxide nanostructures such as sputtering, lithography, and electrospinning. However, they are quite expensive, and involvement with toxic chemicals results in health risks. In this regard, the green synthesis approach does not require any harmful chemicals, high-pressure reactors, or high temperatures. Most importantly, it results in degradable waste with less risk of contamination at the end [2,3]. Over the past few years, researchers have shown interest in green chemistry to synthesize NPs using environmentally benign agents such as plants, fruits, flowers, algae, yeasts, bacteria, fungi. Additionally, extensive research has been carried out using plant extracts for the synthesis of NPs, and it was observed that compared to other means, plants are more suitable for the production of NPs, even at the pilot scale [4,5,6,7,8,9].
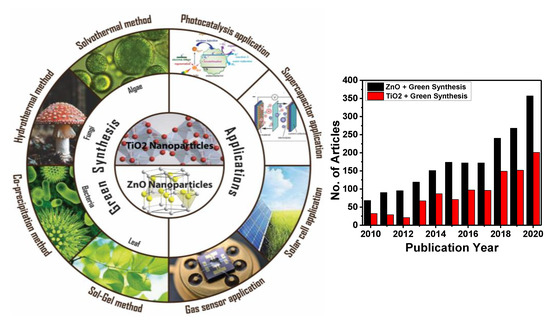
Nanostructured semiconductor metal oxides are a class of materials that play an important role in the development of most electronic devices such as solar cells, transistors, diodes, and sensors [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Among various metal oxides, ZnO and TiO2 NPs are of much interest in the scientific community due to the fact of their unique electronic, chemical, and physical properties, their high surface-to-volume ratio, and availability of more surface atoms for an immediate chemical reaction [11,14,27,28]. Zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are n-type wide bandgap semiconductors (Eg = 3.37 and 3.6 eV, at 300 K, respectively) [9,29]. These compounds have drawn the interest of many researchers due to the wide range of their application. They are highly acceptable for commercialization due to the fact of their shape, size, conductivity, etc. Meanwhile, depending on their morphology, these materials can be prepared via various top-down and bottom-up methods. However, the green synthesis approach has motivated researchers to achieve the desired properties, size, and shape because of their facile one-step approach and environmentally friendly protocol. Nevertheless, some factors are always kept in mind while performing green synthesis, such as pH, reaction temperature and time, stability, risk assessment, and regulatory challenges [30,31]. shows the schematic illustration of green synthesis approaches and applications that we explore in the following section, along with the progress in the scientific articles on green synthesis to synthesize ZnO and TiO2 nanostructures in recent years.
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of green synthesis approach of ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) and their application. The number of publications on green synthesis of ZnO and TiO2 NPs from 2010 to 2020 (internet search of Scopus on 10 March 2021). Keywords searched: ZnO + Green Synthesis and TiO2 + Green Synthesis.
2. Green Synthesis Methods of TiO2 and ZnO Nanostructures
This review summarizes the most widely used green synthesis methods in the fabrication of TiO2 and ZnO nanostructures for technological applications such as photocatalytic, supercapacitor, solar cell, and gas sensors. Our main objective was to shed light on the scope of solvothermal, hydrothermal, co-precipitation, and sol-gel methods and their advantages, drawbacks, and research advancements.
2.1. Sol-Gel Synthesis
Sol-gel is a widely used method of synthesizing ceramic oxide nanostructures from solution by transforming liquid precursors to “sol” and ultimately to a network structure called “gel” in wet chemical phases [
32]. The composition of the sol is usually achieved by hydrolysis and condensation of metal alkoxide precursors. Still, a sol may generally be called a colloidal suspension involving a more comprehensive range of systems. There are also several different ways to form a gel, which Flory described in 1974. He divided gel into four groups: lamellar gel, ordered gel, disordered particulate gels, and physically aggregated polymers [
33]. Later in 1996, Kakihana demonstrated more classifications of different gels [
34]. outlines the five major categories of gel types used in sol-gel chemistry. Since there are many articles on the sol-gel synthesis approach used to fabricate various nanostructures, our goal was to show the green approach using sol-gel chemistry.
Table 1. Classification of five different types of “gels” essential to a material’s sol-gel synthesis [
35].
Recently, researchers have demonstrated a high interest in the development of metal oxide NPs through a greener approach because they are eco-friendly, less toxic, and generate less hazardous waste. In this context, nanostructured oxide semiconductors have generated considerable interest due to the fact of their fundamental importance in addressing some of the main issues in fundamental physics and their possible applications as advanced materials. These nanostructures have been prepared by a variety of different fabrication methods. However, the reproducible and scalable synthesis of these nanostructures is the major difficulty for technological applications. Furthermore, many of these methods require expensive equipment and have little control over the scale, shape, and composition of NPs. In this way, the green approach of sol-gel processes can overcome some of the major limitations.
2.1.1. Green Sol-Gel Synthesis Approach for ZnO Nanostructures
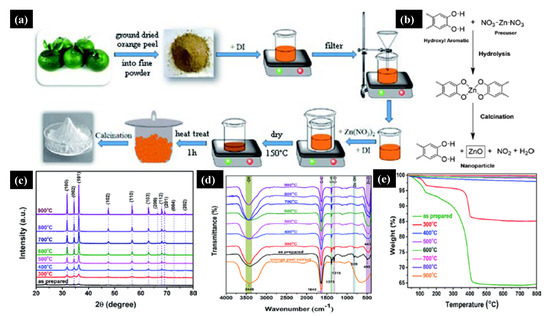
Tu Uyen Doan Thi et al. [
36] utilized the green sol-gel method to produce ZnO NPs by orange fruit peel extracts and studied the impact of pH and temperature on the morphology and antibacterial activities. a shows a schematic of the ZnO NPs’ synthesis in which zinc nitrate and orange extract powder were mixed, followed by annealing at 400 °C for one hour. b shows the reaction mechanism between the orange peel extract and zinc precursor, where the orange peel extract acts as a ligand agent. They analyzed the morphology and antibacterial properties by annealing the ZnO NPs at different temperatures ranging from 300–900 °C. c shows the X-ray diffraction pattern (XRD) of the ZnO NPs annealed at a different temperature; it can be seen that compared to high-temperature samples, the crystal structure and diffraction peaks were poor at a lower temperature. By increasing the annealing temperature, the crystalline size increased, and NPs became reoriented and reduced the number of defects in grain boundaries. d shows the Fourier transform infrared spectra (FTIR) of ZnO NPs under different annealing temperatures; a vibration bonding Zn–O and orange peel extract at 450 and 1640 cm
−1 were observed, respectively.
Figure 2. (
a) Schematic of the green sol-gel synthesis of ZnO NPs. (
b) Chemical mechanism of the ZnO NPs’ formation. As synthesized and annealed ZnO samples at temperatures of 300–900 °C. (
c) X-ray diffraction pattern. (
d) FTIR Plot. (
e) Thermogravimetric spectra. Figure adapted with permission from Reference [
36]. Copyright 2020 RSC.
Moreover, at low annealing temperatures, residual organic extract vibrations in the NPs were present, which gradually disappeared at higher annealing temperatures. Thermal stability and weight loss of the ZnO samples were evaluated by thermogravimetry Analysis (TGA). Significant weight loss was observed at a lower annealing temperature due to the loss of moisture and organic substances. In contrast, no weight loss was observed at higher annealing temperatures (e).
Similarly, Sasirekha et al. [
37] fabricated the ZnO/C nanocomposite via a cost-effective sol-gel method via a green approach in which they used sucrose as a capping agent. They studied the structural and electrochemical behavior of the prepared ZnO/C. Moreover, they performed electrochemical measurements which revealed a maximum specific capacitance of 820 F g
−1 with a current density of 1 A g
−1. Moreover, when they performed charge–discharge up to 400 cycles, a power retention of 92% was observed. In another work by Silva and co-workers [
38], it was reported for the first time the facile green sol-gel synthesis of ZnO NPs using whey as a chelating agent, characterizing the samples using different analytical techniques.
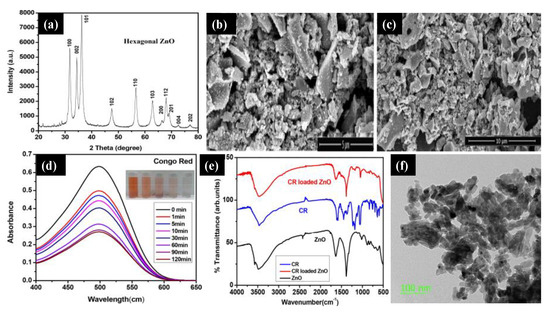
Sahoo and co-workers [
39] reported ZnO NPs using acacia concinna fruit extract as a surfactant. They used the
acacia concinna powder to prepare the Zinc precursor solution, followed by a mixing and calcination process to achieve pure ZnO NPs. a shows the XRD pattern of pure ZnO NPs, which reveals the hexagonal wurtzite phase. The ZnO sample’s sharp peak indicates the crystalline nature of the materials, and the Debye–Scherer equation measured the crystalline size (26 nm). Structural analysis of the ZnO sample was confirmed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and it can be seen that all the NPs were agglomerated (b,c). The UV-Vis spectra of the ZnO NPs were analyzed at 498 nm at different time intervals, and it was found that there was a steady decrease in the intensity of the Congo red (CR) dye over time (d). The FTIR analysis was carried out for the ZnO NPs, CR dye, and CR-loaded ZnO NPs (e). The peaks observed at 1386 cm
−1 and 1681 cm
−1 indicate the C=O group’s asymmetric stretching vibration. In addition, the peak at 1057 cm
−1 was due to the occurrence of m (C–N), and the peaks at 1235 and 1178 cm
−1 were due to the aromatic C–N stretching and absorption of CR. Even after loading the CR with ZnO NPs, there were no changes in peak positions and bands. f displays the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of ZnO NPs. It appears that the particles were irregular with an average particle size of approximately 30 to 50 nm. Similarly, the research group of Guy Van Assche [
40] reported the cost-effective green synthetic route “sol-gel injection” to incorporate ZnO NPs onto porous silica matrix. They also confirmed that by enclosing ZnO NPs in the silica matrix, there is a way to monitor the size of the particles, the size distribution, and the NPs’ ability to aggregate and open up a new possibility to explore the application for catalysis and optical detection.
Figure 3. (
a) X-ray diffraction pattern of the ZnO NPs. (
b,
c) Scanning electron microscopy images of agglomerated ZnO NPs. (
d) UV–Vis spectra of the Congo red (CR) dye versus time. (
e) The FTIR spectra of the ZnO NPs, CR dye, and CR–loaded ZnO NPs. (
f) Transmission electron microscopy of the ZnO NPs at a 100 nm scale. Figure adapted with permission from Reference [
39]. Copyright 2020 Elsevier.
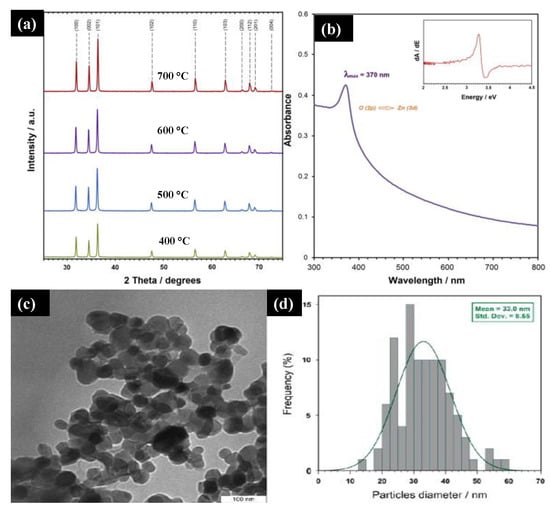
Majid Darroudi et al. [
41] studied the temperature effect of zinc oxide NPs prepared using gum tragacanth (GT)—a green, economical, and readily available polysaccharide component. They mixed zinc nitrate as a zinc source and GT in the water and fixed it at 80 °C in an oil bath. The final product was washed, cleaned, and calcined at different temperatures (400–700 °C). a displays the powder XRD of the ZnO NPs at different calcination temperatures. It can be seen that all the diffraction peaks with miller indices were indexed to a pure ZnO wurtzite structure with a crystalline size below 50 nm. The UV-Vis spectra of the ZnO NPs showed a 3.3 eV bandgap, and a sharp absorption peak at 370 nm was observed, which can be assigned to the absorption of the intrinsic bandgap because of the transition from the valence band to the conduction band (b). The TEM images (c,d) indicate the narrow size distribution of the ZnO NPs in GT media with a mean size of approximately 33 nm confirmed with Image J software. These NPs are expected to find potential applications in various fields such as cosmetics, paints and coatings, sensors, and medicines.
Figure 4. (
a) XRD plot of synthesized ZnO NPs at different calcinations at 600 °C. (
b) The UV-Vis spectra of the ZnO NPs synthesized at 600 °C. (
c,
d) TEM image and particle size distribution of ZnO NPs in gum tragacanth (GT) media synthesized at 600 °C. Figure adapted with permission from Reference [
41] Copyright 2013 Elsevier.
Similarly, Araujo et al. [
42] reported a novel approach to preparing ZnO NPs using karaya gum—a polysaccharide extracted from low-cost
Sterculia species. The prepared ZnO NPs were characterized by analytical techniques and their photocatalytic performance was studied. Moreover, some biosynthesis approaches for the synthesis of ZnO nanostructures were reported using plant extracts, fruit, and leaves ().
Table 2. Biosynthesis approaches to synthesize ZnO NPs from different plant sources.
2.1.2. Green Sol-Gel Synthesis Approach for TiO2 Nanostructures
Several synthetic approaches to the preparation of TiO
2 nanostructures have been developed to date. The sol-gel method’s green approach is widely used because of the eco-friendly and cost-effective concept for obtaining TiO
2 nanostructures. Li Yang et al. [
89] reported the sol-gel route to synthesize TiO
2 microtubes using
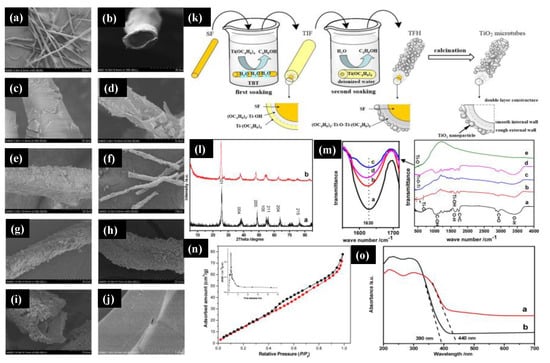
Platanus acerifolia seed fibers (SFs). a,b show SEM images of the natural seed fibers that display the hollow tubular structures with a diameter of 25–30 μm and a wall thickness of 3–5 μm. c,d show the titanium sol-impregnated fibers (TIFs), and e shows the titanium fiber hybrid (TFH). The TiO
2 microtubes were obtained with further calcination of the TFH at 500 °C for two hours with an average diameter of 24 μm and a wall thickness of 2 μm (f–h). With the high magnification of the image with the TiO
2 microtubes, it can be seen that the wall of the microtubes consisted of two layers, where NPs covered the outer wall with a rough surface, and the inner wall was very smooth and compact (i).
Figure 5. (
a,
b) Scanning electron microscopy images of the
Platanus acerifolia seed fibers, (
c,
d) titanium sol-impregnated fibers (TIF), (
e) titanium fiber hybrid (TFH), (
f–
i) hollow tubular TiO
2 microtubes, and (
j) an inner wall of the TiO
2 microtubes. (
k) Schematic of the double soaking sol-gel route for the preparation of TiO
2 microtubes. (
l) The XRD pattern of the TiO
2 microtubes (
a,
b) their inner wall. (
m) The FTIR spectra of the natural SFs (
a) and TIF (
b), TFH (
c), and TiO
2 microtubes (
d) prepared from the natural SFs. (
n) The BET surface is a pore-size distribution of the TiO
2 microtubes. (
o) UV-Vis spectra of the commercially available TiO
2 (
a) and synthesized TiO
2 microtubes (
b). Figure adapted with permission from Reference [
89]. Copyright 2017 Elsevier.
Furthermore, j shows the enlarged view of the TiO2 microtubes’ inner wall that was composed of a dense structure of TiO2 nanospheres of a diameter of 25 ± 5 nm. We can further understand the double soaking sol-gel route of the synthesized TiO2 microtubes based on the morphological changes. k shows a schematic of the fabrication process of the TiO2 microtubes, and the first soaking step was to hydrolyze natural seed fibers with titanium sol to generate the metal alkoxide layer on the fibers’ surface. Once the Titanium sol was completely hydrolyzed on the deionized water, they formed the rough external wall that was the second soaking step. The final product was obtained with the calcination step to obtained anatase TiO2 microtubes. The XRD pattern of the TiO2 microcubes and the microtubes’ internal wall (l) were analyzed and confirmed that all the peaks were indexed to the pure anatase TiO2 phase. There was a slight shift towards a lower degree in the XRD pattern of the internal wall (TiO2 microcubes) because of fine TiO2 NPs, which we had seen in the SEM image. m shows the FTIR spectra of the natural SFs and TiO2 microtubes, TIF, and TFH prepared from natural SFs. The major characteristics peaks of C=O, C=C, and C–OH at 2937, 1735, and 1033 cm−1 from cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin, while the enlarged view of flexural vibration of O–H at 1630 cm−1 was attributed due to the existence of the moisture in the Platanus acerifolia seed fibers. n shows the surface area obtained by the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method and pore distribution of the TiO2 microtubes. A mesoporous size distribution was observed with a surface area of 128.2 m2/g with a pore diameter of 3.553 nm, which is higher than that reported for the commercial P25 TiO2. The UV-Vis spectra of synthesized TiO2 microtubes and commercial P25 TiO2 were analyzed (o). The sharp absorption edge for TiO2 microtubes and commercial P25 TiO2 microtubes were observed at 400 and 390 nm. The bandgaps were measured and were 2.81 eV and 3.17 eV for TiO2 microtubes and commercial P25 TiO2, respectively; this difference was observed due to the carbon in the densely packed TiO2 NPs. This research demonstrated the use of a novel double soaking sol-gel route to synthesize TiO2 microtubes that have two advantages: they are environmentally friendly and green and they have excellent properties.
In another work, Muhammad Atif Irshad and co-workers reported a novel sol-gel approach using plant extracts (Trianthema portulacastrum (T2) and Chenopodium quinoa (T3)) to synthesize TiO2 NPs. They also compared this green method with a chemical process to analyze the antifungal activity and observed that TiO2 prepared via the green approach showed a better antifungal response against wheat rust. The various green sources have been used for TiO2–NPs synthesis via the sol-gel route, as reported in , which gives a broader view of the sol-gel method’s green approach.
Table 3. Green sol-gel synthesis approach for the preparation of TiO2 nanostructures.
Despite the beneficial aspects of TiO
2 NPs, a few minor drawbacks limit the practicality of its application. The bandgap of anatase TiO
2 is 3.23 eV, which can hamper the photocatalyst’s efficiency due to the fast recombination rate of the generated charge carriers, combined with a slow transfer rate of electrons to oxygen. Therefore, doping or modification of TiO
2 NPs with noble metals, such as gold, silver, platinum, and palladium, is an alternative way to lower the bandgap and to promote and enhance visible light absorption. Hariharan et al. [
90] reported the fabrication of Pd@TiO
2 NPs using
Aloe vera gel, which acts as a capping and reducing agent during fabrication. In another work, Rostami-Vartooni et al. [
91] reported a novel sol-gel approach to fabricating Ag–TiO
2 nanocomposites using
C. acinaciformis leaf and flower extracts to achieve the desired photocatalytic properties. They confirmed that silver-doped-TiO
2 nanocomposites showed faster photocatalytic degradation than pure TiO
2 NPs.
2.2. Co-Precipitation Method
Metal oxides can be synthesized using the co-precipitation method through a two-step process: first, the precipitation of metal hydroxides and, second, a heat treatment to crystallize the oxide. In the homogeneous liquid phase, the nucleation and growth kinetics of the particles are determined by the controlled release of anions and cations in the solution, and the shape and size distribution can be adjusted by controlling parameters such as pH and concentration of reagents/ions [
99]. The co-precipitation method has some advantages over other chemical routes such as low cost, low energy and time consumption, and the possibility of large-scale production [
100,
101]. In addition, green synthesis can be easily adapted to this method including TiO
2 and ZnO nanostructures.
Mainly, green co-precipitation synthesis involves the use of plant extracts (leaf, root, fruit, bark). The biocomponents present in the extract can act as a stabilizing, reducing, capping, or chelating agent, changing both the morphology and the properties of the nanostructures, improving their performance in applications. Other strategies for obtaining nanostructures through green routes include the use of less aggressive solvents, fewer reagents, less energy consumption, the use of renewable feedstocks, reduced derivatives, and production of self-degrading products [
102]. In general, the green syntheses of TiO
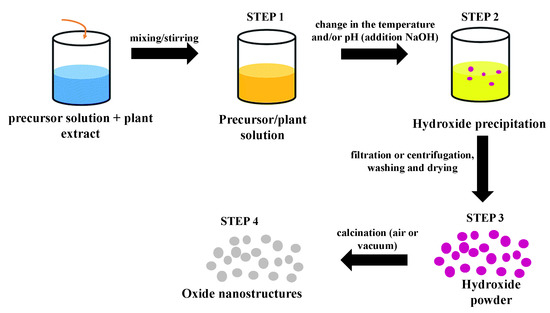
2/ZnO nanostructures produced by the plant extract-mediated co-precipitation method follows an approximately similar route: First, a precursor solution is mixed with a solution of the plant extract under agitation. Then, changes in the temperature and/or pH of the mixture (addition of NaOH) initiates the precipitation process and hydroxide formation. The third step consists of the separation (simple or by centrifugation) of the precipitate, washing with deionized water and/or ethanol accompanied or not by a drying process at low temperatures. The last step consists of thermal treatment (calcination) at higher temperatures to crystallize the oxide. The final product can also be ground in a crystal mortar pestle. depicts a schematic diagram containing all these steps for a generic green synthesis using the co-precipitation method.
Figure 6. Schematic diagram showing all steps involved in a generic green synthesis mediated by plant extract using the co-precipitation method.
2.2.1. Green Co-Precipitation Synthesis Approach for TiO2 Nanostructures
In general, reports of the green syntheses of TiO
2 nanostructures using the co-precipitation method in the literature are still modest but have shown notable growth in recent years due to the method’s ease of use and timesaving qualities. Next, we report on some works in this area. In recent years, Rawat and collaborators have produced different TiO
2 nanostructures using a green co-precipitation method. They synthesized spherical TiO
2 NPs (20–30 nm) using
Phyllanthus emblica (Amla) leaf extract and TTIP as a titanium source [
103]. In a typical process, the TiO
2 precursor and the leaf extract (1:1 ratio by volume) were mixed and stirred at room temperature for 20 min until the color of the solution changed from transparent to whitish brown. Then, ammonia was added drop by drop to the solution, initiating the formation of the precipitate. Anatase NPs were obtained after filtering the solution and rinsing the precipitate with alcohol, calcining in a muffle furnace (400 °C, 3 h), and grinding in a crystal mortar pestle. This same method was previously used to obtain anatase nanocubes using
Tinospora cordifolia leaf extract [
104]. In this, it was observed that the control of the morphology provided by the extract’s biomolecules proved to be fundamental in the performance of the nanostructures for degradation of the neutral red (NR) dye: cubic TiO
2 was more efficient for dye photodegradation than non-cubic NPs, reaching a percentage of 93.4% against 65.3% after 120 min under UV illumination.
Many other works have reported using plant extract mediating the synthesis of anatase TiO
2 NPs using the co-precipitation method [
105,
106,
107,
108]. However, as with traditional syntheses, green syntheses of the rutile phase are scarcer. One of the disadvantages of the co-precipitation method is the rapid nucleation and growth of the nanostructures; the accelerated growth can result in a strong agglomeration of the final product. However, many green syntheses have shown that using plant extracts can improve the dispersion of the synthesized NPs using this method. Goutam et al. [
95], for example, synthesized TiO
2 NPs using
Jatropha curcas L. leaf extract and showed that the low formation of NP agglomerates was related to the performance of phytochemicals present in the extract as capping agents. A similar effect was observed by Subhapriya and Gomathipriya [
109] and by Kaur et al. [
94] in the green synthesis of polydisperse TiO
2 NPs from
Trigonella foenum leaf extract and
Lagenaria siceraria leaf extract, respectively.
In this scenario, we highlight the green co-precipitation synthesis in which no plant extract was used, as reported by Muniandy et al. [
110], for the production of mesoporous anatase NPs using TTIP as a titanium source, water as a solvent, and starch as a template. According to the authors, starch plays a key role in the formation of mesoporous structures: the nucleation and initial crystal growth occur when the precursor diffuses and forms complexes with amylose molecules close to the interspaces between the swollen starch microspheres. With the calcination process, these starch granule templates are removed, giving rise to mesoporous structures. The morphology of the synthesized structures in this work was analyzed by Field Emission scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) and High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM) and can be seen in . The influence of the amount of Ti precursor and the pH of the solution on the morphology and photocatalytic activity of the material was also evaluated in this work.
Figure 7. FESEM micrographs of TiO
2 NPs synthesized using (
a) uncalcined TiO
2; (
b) 0.01 mol titanium tetraisopropoxide (TTIP), pH 5; (
c) 0.01 mol TTIP, pH 7; (
d) 0.01 mol TTIP, pH 9, insert: HRTEM image; (
e) 0.07 mol of TTIP in pH 9; (
f) pore channels of TiO
2 NPs. Figure adapted with permission from Reference [
110]. Copyright 2017 RSC.
2.2.2. Green Co-Precipitation Synthesis Approach for ZnO Nanostructures
As for the production of ZnO nanostructures, there is a more abundant number of papers using the co-precipitation method, especially when this process is mediated by plant extract. This is largely due to the work of Singh et al. [
56], who reported a simple and efficient method for green synthesis of ZnO NPs using this method. In the mentioned work, zinc oxide NPs were produced using latex from
Calotropis procera as an alternative to chemical syntheses. For the synthesis, 0.02 M of aqueous zinc acetate dihydrate solution was mixed with 50 mL of distilled water with vigorous stirring. After 10 min, 0.25, 0.5, and 1.0 mL of latex were added, one part at a time, to the acetate solution. Then, NaOH (2.0 M) was added to the solution until it reached pH 12, then the obtained mixture was placed on a magnetic stirrer for 2 h. The precipitate was collected, rinsed repeatedly with distilled water and ethanol to remove impurities, and left to dry overnight in a vacuum at 60 °C. The final product was spherical NPs (5–40 nm) and granular nanosized with little agglomeration; it remained stable and without visible changes even one month after synthesis. These characteristics were attributed to the effective role of latex as a stabilizing and reducing agent. From this pioneering work, many other green syntheses mediated by plant extracts have been reported for the production of zinc oxide NPs using the co-precipitation method. presents works in the literature reporting the use of this type of green synthesis to produce ZnO nanostructures and the functionality of each of the biocomponents used in its preparation.
Table 4. Green co-precipitation syntheses of ZnO nanostructures mediated by plant extract.
Regarding the syntheses that do not use plant extract for the synthesis of ZnO nanostructures, we can highlight the work of Akir et al. [
125] in which structures with different morphologies were produced from three different protocols for the addition of basic solution in the zinc aqueous solution: spherical NPs, nanosheets, and hexagonal prismatic NPs, indicating that the speed of addition of the basic solution to the zinc precursor is a key factor for the morphology of the structures. Charoenthai and Yomma [
126] synthesized ZnO NPs with a hexagonal wurtzite structure using a process similar to that adopted by Akir et al. [
125]. In this case, the authors showed that the use of water as a solvent, in comparison with ethanol, methanol, propanol, and butanol solvents, results in the formation of smaller NPs with greater surface area and greater pore volume that caused an increased photodegradation for methylene blue (MB) and methyl orange (MO) dyes.
2.3. Hydrothermal Method
Nanoparticle synthesis is widely studied today, and many processing methods have been developed to produce homogeneous structures with high crystalline quality. Among all methods used to synthesize nanostructures, hydrothermal synthesis has been considered one of the most promising methods in this regard. In this method, the stability provided by using a closed system, where temperature and pressure are controlled, allows greater control over the size, nucleation, and degree of crystallinity of the NPs [
127,
128]. Thus, the hydrothermal method has been used to synthesize several nanostructures, including TiO
2 and ZnO nanostructures (mono-dispersed and highly homogeneous NPs, nano-hybrid materials, and nanocomposites), as part of the framework of green synthesis [
99]. In general, green hydrothermal syntheses are synthesized by non-toxic solvents and non-corrosive solutions in their process, which minimizes damage to the environment and reduces the consumption of raw materials. There are still few reports on green synthesized TiO
2 and ZnO nanostructures compared to other methods such as co-precipitation and sol-gel. However, promising results have been presented in the literature and are summarized as follows.
2.3.1. Green Hydrothermal Synthesis for ZnO Nanostructures
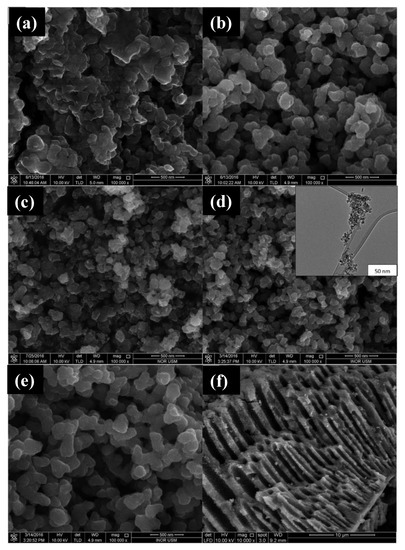
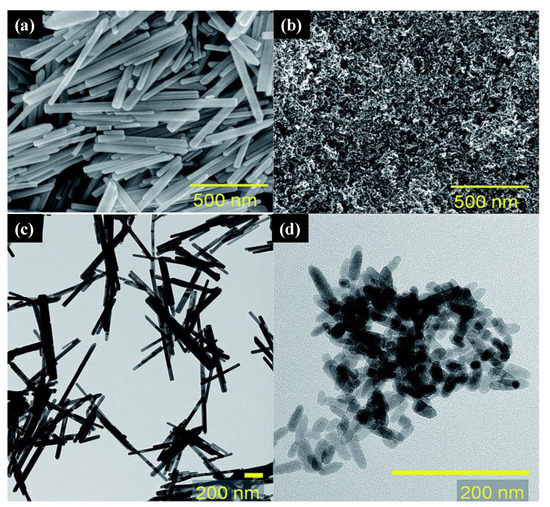
Recently, Chang et al. [
129] used a green hydrothermal route for the synthesis of versatile nanostructured zinc oxide particles (nZnOs) from zinc acetate precursors (a). The morphological characterization showed that the NPs were shaped like nanorods (b), nanoplatelets (c), and multibranched flower-like particles (d) for growth times of 6, 12, and 24 h, respectively. e shows the nZnO nanostructure used in antimicrobial activity testing. The multibranched flower-type ZnO presented more remarkable, reliable, and stable antifungal activity than the other nZnOs, probably because it has a larger surface area.
Figure 8. (
a) Precursors (zinc acetate, hexamethylenetetramine (HMT), and sodium hydroxide) used in the synthesis of different nZnO morphologies; auto-clave treatment at 90 °C was maintained for (
b) 6 h to get nanoplatelets, (
c) 12 h to achieve multibranched flower-like particles, and (
d) 24 h to obtain nanorods. (
e) Diagram of the antimicrobial activity test for the ZnO multibranched flower-like particles. Figure adapted with permission from Reference [
129]. Copyright 2020 Elsevier.
Guo et al. [
130] showed that the reaction temperature and time in the hydrothermal method were also fundamental to defining the crystalline phase of the material and the morphology. Changing the autoclave treatments at 100–120 °C for 6 h (or 170 °C for 0 h) to treatment at 170 °C for 3–6 h, the obtained product changed from cubic ZnO
2 nanocrystals to hexagonal ZnO nanorods. The UV-Vis absorption spectra showed the synthesized ZnO
2 nanocrystals had optical bandgaps around 4.1 eV, and the ZnO nanorods presented at 3.3 eV, which makes both structures good candidates for applications in photocatalysis and optoelectronic devices with a short wavelength. In another work, Lam et al. [
77] proposed a green hydrothermal approach for the large-scale synthesis of ZnO nanotubes (NTs) using powder ZnO and aqueous H
2O
2 solution (volume 30%) as starting materials and performing an autoclave treatment at 130 °C for one day. The ZnO NTs with an average diameter of 10 nm and a wall thickness of 3–5 nm (rolling the nanosheet layer) were applied as photocatalysts for degradation of endocrine chemical disruptor methylparaben under UV irradiation. The degradation of methylparaben has been associated with the unique tubular structure and the large surface area of the NTs of ZnO that give rise to increased separation of electrons and holes and the formation of a large number of reactive radicals in the photocatalytic process. Liu et al. [
131] also used the same method with an aqueous solution of H
2O
2 as a solvent for the production of hollow ZnO NTs and nanospheres (treatment in an autoclave at 120 °C for 6 h). An interesting study was also presented by Patrinoiu et al. [
111] regarding control over ZnO nanostructures’ morphology; different nanostructures were produced by the variation in concentrations of zinc acetate precursor and starch reagent in the hydrothermal synthesis (autoclave treatment at 180 °C for 24 h). The authors claimed that the key parameter for the morphological alterations was the gelation capacity of amylose released by the starch. The study also showed that all the ZnO nanostructures exhibited antibacterial activity and antibiofilm potential.
2.3.2. Green Hydrothermal Synthesis for TiO2 Nanostructures
Wang et al. [
132] successfully synthesized TiO
2 NPs with different morphologies (i.e., nanorods, nanospheres, and microspheres) and crystalline phases by variating oxalic acid (OA) and TTIP precursor concentrations in a surfactant-free green hydrothermal approach. At first, OA was dissolved into H
2O and magnetically stirred until a transparent solution was obtained. The TTIP was dropped until a colorless solution was reached. The solution was hydrothermally treated at 180 °C for 12 h. Deposits were collected by vacuum filtration, washed in deionized water and anhydrous ethanol, and calcinated at 80 °C for 12 h in a vacuum box. To reach different TiO
2 phases (i.e., anatase and rutile), several TTIP/OA molar ratios were used, from 2:1 to 1:1, 1:3, 1:6, and 1:9 with the same initial route. Their work also showed that the microspheres with mixed anatase and rutile phases presented better photocatalytic performance.
Similarly, Spada et al. [
133] used annealing temperature variations of 400–1000 °C (4 h) to control the crystalline phase and the particle size of TiO
2 NPs. The XRD data show that at temperatures above 600 °C, the anatase phase started a transition to the rutile phase, and at temperatures above 1000 °C pure rutile was found. The size of the crystals increased proportionally with the increase in temperature, ranging from 17 to 57 nm; on the other hand, the bandgap decreased from 3.21 to 2.93 eV. Degeneration tests of the rhodamine B (RhB) dye showed that the NPs obtained at 600 °C, with small fractions of the rutile phase, presented improved photocatalytic performance. Green hydrothermal synthesis mediated by plant extracts were also used for the production of TiO
2 NPs. Recently, Hariharan et al. [
134] synthesized TiO
2 NPs using
Aloe vera gel and deionized water as starting materials (autoclave treatment at 180 °C for 4 h). Sample characterization showed TiO
2 anatase NPs with good crystalline quality and sizes ranging from 6 to 13 nm. In addition, the use of plant extract resulted in a better performance of NPs for picric acid photodegradation than NPs synthesized by the chemical hydrothermal route. Subsequently, Hariharan et al. [
135] used the same method for producing Ag-doped TiO
2 NPs. The Ag–TiO
2 NPs were found to have an improved activity for photodegradation of picric acid under visible light and also showed anticancer activity, decreasing the growth of cancer cells and increasing the reactive oxygen species.
2.4. Solvothermal Method
Solvothermal synthesis is a widely used process to synthesize several technological materials such as ferrite [
136,
137,
138], Sn: In
2O
3 [
139,
140], CeO
2 [
141,
142], ZnO [
143,
144,
145,
146,
147], Metal Organic Frameworks (MOFs) [
148,
149,
150,
151,
152], TiO
2 [
153,
154,
155,
156,
157,
158]. In this approach, an organic solvent (non-aqueous) is used as reactional media in which a solute is dissolved and, subsequently, crystallized under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions. These conditions are achieved by confining the solution to a special sealed system such as an autoclave. There are several advantages associated with using the solvothermal approach instead of other inorganic synthesis, but by far the most attractive one is the simplicity of the approach. Other significant advantages are the control over shape, size distribution, and crystalline phases. Despite the tremendous success of the solvothermal approach for synthesizing TiO
2 and ZnO nanostructures [
143,
144,
145,
146,
147,
153,
154,
155,
156,
157,
158], it is still an approach that uses highly corrosive and toxic chemical precursors for human beings. For this reason, it is essential to seek greener approaches to synthesize these metal oxide nanostructures, since they are of high technological interest. In this context, our goal was to present the most recent bibliography on the green solvothermal approach to synthesize TiO
2 and ZnO NPs.
2.4.1. Green Solvothermal Synthesis Approach for ZnO Nanostructures
In this section, the green solvothermal approach is presented in a slightly broader concept by considering papers that use plant extracts and natural templates and references in which authors tried to simplify their methodologies, reducing the quantity of precursors, or substituting hazards solvents or not using surfactants. In general, there are still few reports on the green synthesis of ZnO and TiO
2 nanostructures in which the solvothermal approach was employed. Despite this fact, Zhang et al. [
159] successfully synthesized Er–Al co-doped ZnO NPs by using a one-pot and surfactant-free, non-toxic solvothermal approach. The authors characterized the samples’ structural features and photocatalytic activity by degrading methyl orange (MO) in water under visible light irradiation. The XRD, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements revealed that Er and Al ions doped the ZnO’s pristine structure. The UV-Vis measurements revealed that the co-doping caused a widening in the ZnO bandgap from 3.14 eV (i.e., pristine structure) to 2.95 (Er–Al co-doped sample) and, consequently, an increase in the visible light absorption of ZnO. The authors also showed that Er–Al co-doped ZnO presented an enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light illumination with 98.9% MO degradation efficiency. Šutka et al. [
160] showed a straightforward and ethanol-based solvothermal synthesis of plasmonic Al-doped ZnO (AZO) NPs using Al and Zn salts as starting materials.
The control of ZnO samples was synthesized by mixing zinc acetate dehydrate (Zn(CH3CO2)2∙2H2O) in ethanol, resulting in a 0.1 M solution be mixed with a second solution prepared with NaOH in ethanol. Previously to their mixing, both solutions were vigorously stirred and heated to 80 °C. After this, the two solutions were mixed and left under stirring at 80 °C for 10 h. The final mixture was then transferred into a 50 mL Teflon-lined, stainless-steel autoclave, sealed, and heated at 150 °C for 24 h. The resulting material was filtered and washed with methanol and dried in air at 60 °C for 5 h. Doped samples were synthesized by substituting an amount of Zn(CH3CO2)2∙2H2O in ethanol by Al(NO3)3∙9H2O. Structural characterization showed that the Al atoms effectively substituted Zn in the zincite structure. Morphological features of the undoped and doped ZnO samples were studied by SEM and TEM measurements as presented in .
Figure 9. SEM images for ZnO (
a) and Zn
0.85Al
0.15O (
b) and TEM for ZnO (
c) and Zn
0.85Al
0.15O (
d). Figure adapted with permission from Reference [
160]. Copyright 2020 RSC.
a,c show that the ZnO samples have a nanowire morphology with diameters ranging from 20 to 70 nm, lengths ranging from 0.2 μm to 1 μm, and aspect ratios up to 50. The increase of the Al dopant in the ZnO structure (b,d) causes the aspect ratio to decrease, leading the final products to be NPs and nanorods (lengths below 50 nm and diameters around 10 nm). The authors showed via diffuse reflectance measurements the presence of localized surface plasmon absorption in the NIR region for all doped samples. They demonstrated the doped samples could be used for technological applications such as a hyper-realistic piezoresistive sensor based on a composite material formed by mixing Zn
0.925Al
0.075O nanocrystals into polydimethylsiloxane. In another work, Liu and co-workers [
161] reported the synthesis of an octahedral ZnO/ZnFe
2O
4 heterostructure through a surfactant-free solvothermal method followed by thermal treatment. At the first step, the precursor to the ZnO/ZnFe
2O
4 final product was synthesized using the solvothermal method in which ZnCl
2 and FeCl
3·6H
2O were dissolved in ethylene glycol (EG), and to this mixture, it was added CH
3COONa. This mixture was then stirred for 30 min and then sealed into a Teflon-lined, stainless-steel autoclave (200 °C for 12 h). The final octahedral ZnO/ZnFe
2O
4 was achieved after the precursor was annealed in air at 500 °C. The authors showed the water treatment promising character of octahedral ZnO/ZnFe
2O
4 samples because of their excellent adsorption capacity of malachite green (MG) and selectivity in mixtures of dyes such as in MG/MO and MG/RhB. Mahlaule-Glory et al. [
162] synthesized ZnO NPs using an eco-friendly approach to the traditional solvothermal method in which
Sutherlandia frutescens extract was used as a reducing and capping agent for the synthesis of ZnO NPs. The plant composite formed by the
Sutherlandia frutescens and ZnO NPs showed bactericidal effects against Gram-positive and -negative strains and antiproliferative effects against the A549 human alveolar lung cancer cell line. Although the authors claim that they used the solvothermal approach to synthesize the ZnO nanostructures, the parameters used in the synthesis were not described in the text.
2.4.2. Green Solvothermal Synthesis Approach for TiO2 Nanostructures
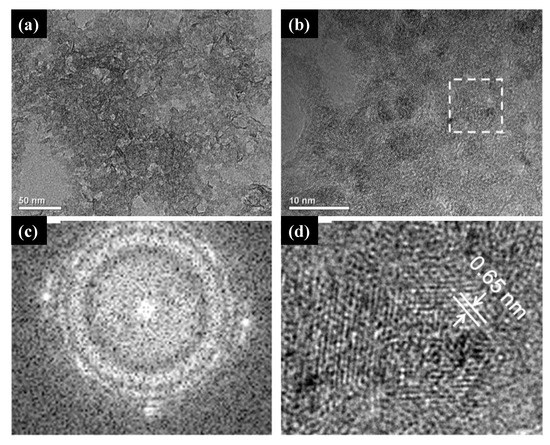
Several authors reported the use of titanium alkoxide as the metal precursor of solvothermal green synthesis of titanium oxide nano- and microstructures [
163,
164,
165,
166]. Wang and co-workers [
164] reported a successful, single-step, green synthesis of the monoclinic metastable phase of TiO
2 known as TiO
2 (B). The samples’ structural characterizations confirmed the crystalline phase, and their composition was mainly formed by titanium and oxide atoms. The HRTEM measurements revealed that the as-synthesized TiO
2 (B) comprised tiny crystallites and nanoporous structures (a,b). In c,d, the fast Fourier transition (FFT) image revealed the crystalline character of the sample, and the inverse fast Fourier transition (IFFT) image showed the (0 0 1) plane of TiO
2 (B), respectively. Wang et al. [
164] also found that green synthesized TiO
2 (B) was highly efficient and stable for the decomposition of MO dye in agreement with previously reported studies in which non-green synthesized TiO
2 (B) was found to be a highly efficient phase for the degradation of this dye.
Figure 10. (
a) TEM and (
b) HRTEM image of the as-synthesized catalysts. (
c) the fast Fourier transition (FFT) image of the selected area, and (
d) inverse fast Fourier transition (IFFT) image obtained from (
c). Figure adapted with permission from Reference [
164]. Copyright 2010 Elsevier.
Additionally, TiO
2 core–shell microspheres were synthesized by a template-free and hydrofluoric acid-free solvothermal synthesis starting from TTIP, isopropyl alcohol, and organic amine [
166]. The photocatalytic activity was also studied under visible irradiation and UV-Vis irradiation. Structural characterization data showed that the TiO
2 core–shell was mainly composed of NPs aggregates covered by perpendicular assembled nanosheets with high-energy {116} facets exposed. The XPS measurements revealed that in situ doping with nitrogen at the interstitial sites of TiO
2 shells occurred and induced local states above the valence band edge, leading to the narrowing of the bandgap and resulting in a visible light response of the material. Zhao et al. [
167] reported the synthesis of spinous hollow pure anatase TiO
2 and ZrO
2-doped TiO
2 microspheres using a solvothermal green approach in which sunflower pollen acted as bio templates. Shortly, the methodology used for the TiO
2 pure phase was based on the dispersion of sunflower pollen template in absolute ethanol and then the addition of titanium butoxide under continuous magnetic stirring. After 2 h, water was added, and the mixture was submitted to the solvothermal conditions. A calcination process was also conducted after the solvothermal synthesis to ensure the samples’ crystalline and stoichiometry. Doped samples were synthesized in a very similar way by mixing titanium butoxide and zirconium
n-butoxide instead of titanium butoxide.
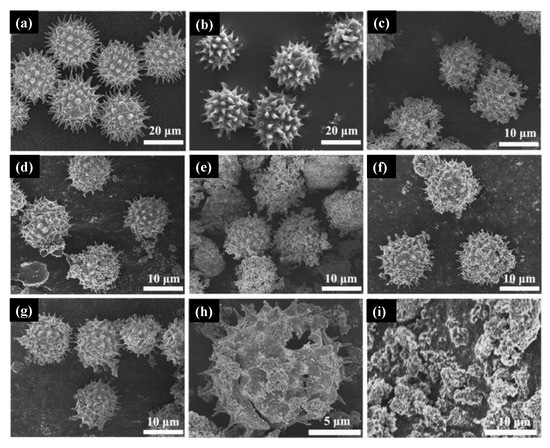
In a, the sunflower pollen morphology was close to a sphere covered with spines at the surface. Without calcination, ZrO
2-doped TiO
2 spinous hollow microspheres presented a very similar morphology as depicted in b. The micrographs obtained for pure TiO
2 and doped samples synthesized with 4.6%, 8.8%, 12.6%, and 18.2% molar ratio of zirconium
n-butoxide in mixed esters can be seen in c–f, respectively. These results indicated that all samples retain the spherical shape of the pollen templated besides the different amounts of ZrO
2 introduced in the synthesis. Calcined samples presented smaller diameters due to the removal of the pollen templates (g), and the hollow structure is presented in h by observation of a broken microsphere in the micrograph. The authors claim that the samples’ hollow features probably be originated from the release of CO
2 during the carbonization process of organic matter in pollen. i depicts the samples synthesized without templates. Zhou and collaborators [
168] reported the synthesis of anatase TiO
2 mesocrystals using a green solvothermal method based on a halide precursor TiCl
3. The authors showed that the as-synthesized samples were mainly composed of anatase mesocrystals with the Wulff construction in which the facet exposed was {101}.
Figure 11. Micrograph of sunflower pollen (
a), ZrO
2-doped TiO
2 spinous hollow sample before calcination (
b), 4.6% doped TiO
2 sample (
c), 8.8% doped TiO
2 sample (
d), 12.6% doped TiO
2 sample (
e), 18.2% doped TiO
2 sample (
f), calcinated sample presented in a smaller size due to the removal of the pollen template (
g), hollow microsphere (
h), and TiO
2 samples synthesized without templates (
i). Figure adapted with permission from [
167] Copyright 2018 Elsevier.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/molecules26082236